Glycogen Synthesis
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What does glycgoen degradation yeild?
Glucose 1-phosphate
What does glycogen synthesis require?
UDP-glucose
what is the glucose synthesis equation?
Glucogenn + UDP-glucose → glucogenn+1 + glucose 1-phosphate
What is the glucose degridation equation?
Glycogenn+1+ Pi → glycogenn + glucose 1-phosphate
What is UDP-glucose?
An activated form of glucose
What is UDP-glucose in glycogen synthesis?
Glucose donor
What is the equation that synthesizes UDP-glucose?
Glucose 1-phosphate + UTP
What enzyme sythesizes UDP-glucose?
UDP-glucose phyrophosphorylase
What does glycogen synthase catalyze?
The transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to a growing chain
What unit of UDP-glucose is attached to glycogen?
The activated glucosyl unit
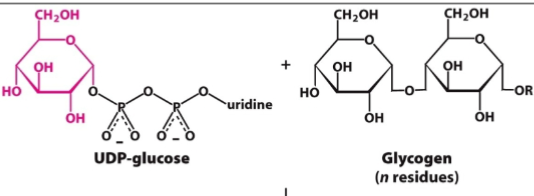
How is the activated unit of UDP-glucose attached?
VIa an a-1,4-glycoside bond
What enzyme catalyzes the addition of an activated glucosyl unit of UDP-glucose to glycogen?
Glycogen synthase
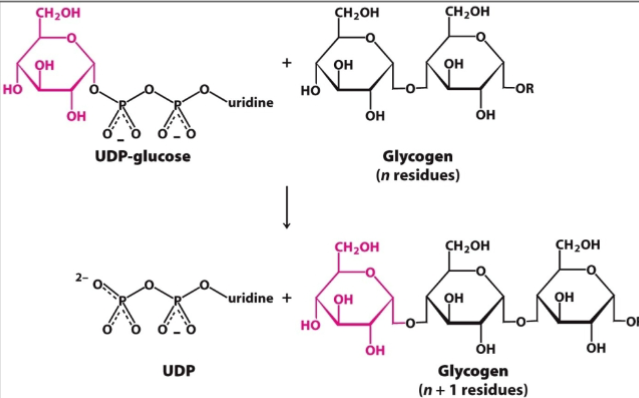
What does glycogen synthase require to attach the activated glucose from UDP-glucose to glycogen?
An oligosaccharide of glucose residue as a primer
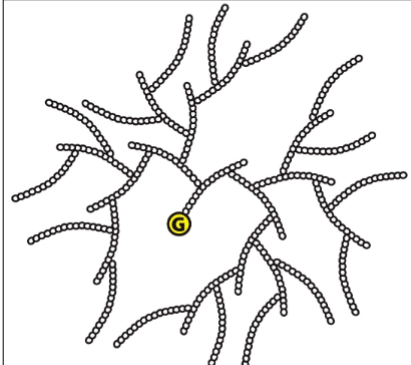
What is the glucose oligosaccharide primer synthezied by?
Glycogenin
What does glycogenin do?
Generate an oligosaccharied of 10-20 glucose residues to be a primer for glycogen synthase
What does glycogen synthase do after getting the oligosaccharide primer?
Extend it
What can glycogen synthase ONLY synthesize?
a-1,4 linkages
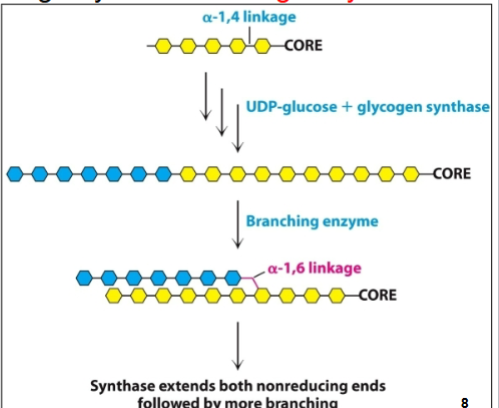
How is a branch greated?
VIa breaking an a-1,4 linkage and taking a block of about seven glucose residues and synthesizing an 1,6 linkage.
How is the 1,6 linkage synthesized?
The branching enzyme
What does branching do?
Incraeses the solubility and rate of the synthesis and degradation of glycogen
What end does synthase extend glycogen?
Both nonreducing ends, followed by more branching
What is glycogen synthesis inhibited by?
Glucagon and epinephrine signalling, the same that STIMULATE glycogen breakdown
What stimulates glycogen breakdown?
Protein kinase A
How does protein kinase A stimulate glycogen breakdown?
Phosphorylating and activating phosphorylase kinase
What inhibits glycogen synthesis?
Protien kinase A via phoshoyrlation
Glycogen synthase kinase
Phosphorylates and inhibits glycogen synthase
What is glycogen degradion activated by?
phosphorylation
What is glycogen synthesis inhibited by?
phosphorylation
When glycogen degradation is activated, what happens with phosphorylase b?
Phosphorylase b (less active) → phosphorylase a (active)
When glycogen synthesis is inhibited by phosphorylation what happens to synthase a and b?
synthase a (active) → synthase b (less active)
What does proteins phosphatase 1 (PP1) reverse?
Regulatory effects of kinases of glycogen metabolism
What does PP1 shift?
Glycogen metabolism from degradation to synthesis
PP1 does what to glycogen synthase b?
dephosphorylates glycogen synthase b, converting it to the more active form, stimulating synthesis
What does PP1 dephosphorylate?
Phosphrylase kinase and glycogen phosphorylase, inhibting glycogen degradation
What does PP1 inhibit?
Glycogen degradation, switching on phosphorylase b
What does PP1 stimulate?
Glycogen synthase, turning on syntahse a
After a meal, what is switched on?
Glycogen synthesis
During fasting or exercise, what is activated?
Glycogen breakdown
What does insulin do?
Stimulate glycogen synthesis by inactivating glycogen synthase kinase
What does glucagon and epinephrine simtulate?
Glycogen degradation
What does glucagon and epinephrine inhibit?
Glycogen synthesis
What does insuline stimulate?
Glycogen synthesis
What does insulin inhibit?
Glycogen degradation
Type 1 diabetes
autoimmune destruction of insuline producing cells
glucagon excess
in fasting mode
a shift in fuels usage from carbohydrates to fat
an accumulation of ketone bodies (diabetic ketosis)
Type 2 diabetes
Insuline resistance
Cori disease (III)
defective enzyme: a-1,6-glucosidase (debranching enzyme)
effects muscle and liver
Structure of liver and muscle glycogen is abnormal and glycogen amount is increased and mild hypoglycemia
Von gierke disease (type1)
Massive enlargement of the liver and severe hypoglycemia due to the lack of glucose 6-phosphatase in the liver
What is von gierke disease also caused by?
mutations in gene encoding the glucose 6-phosphate transporter
McArdle disease (Type V)
Defective muscle glycogen phosphorylase
Painful cramps when exercising