economics edexcel a level (a)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Treasury
The funds of a state or institution or a place where treasure is stored
Chancellor of the exchequer
A member if parliament who manages the countries national budget and the allocation of funds nationwide as well as monitoring the amount of money the government has
George osborn
Chancellor from 2010 - 2016
Phillip Hammond
Chancellor from 2016 - 2019
Sajid Javid
Chancellor from 2019 - 2020
Base rate
The minimum interest rate set by the central bank for lending to other banks or institutions which serves as a benchmark for loaning to individuals
Interest rate
The rate of money growth in relation to the initial amount deposited or loaned which is set by the commercial bank
Inflation
an increase in the cost of living as the price of goods and services rise
Economics goods
Rescources
Scarcity
Means that the economic agents such as individuals, firms, governments and international agencies can only obtain a limited amount of rescources
Free goods
Goods that are not scarce
Capital
A good used to produce another good (e.g tools machines and equipment)
Enterprise or Entrepreneurship
The seeking out of profitable opportunities and ideas and tak8ng the risks to support this
Land
The Land itself and all natural rescources in the area
Labour
The workforce of that economy and their vaoue (human captial) this is increased by education and training
Opportunity cost
The cost of the next best alternative that you leave behind when you make a decision
Positive statements
A statement that can be proven with a true or false and is objective
Normative statements
Opinion statements that cannot be proved true or false
Hidden economy
Parts of the economy that are not accounted for in the national gdp
Capital goods
Goods that are made to be made into other products
Consumer goods
Goods used by the people
Production possibility front
An economic model that considers the maximum possible production a country can produce using all its factors of production efficiently to make 2 goods
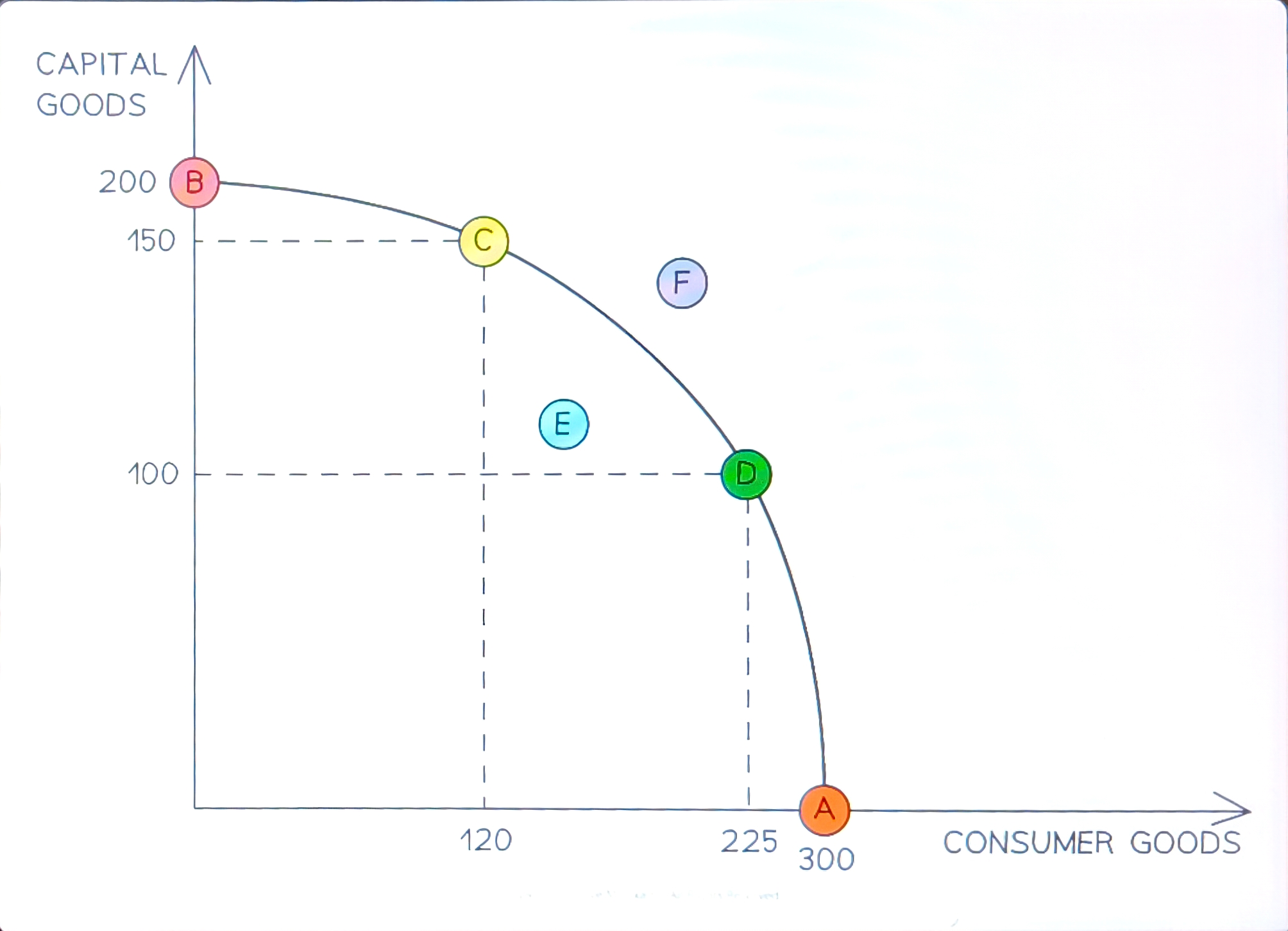
Law of diminishing returns
The marginal output of consumer goods diminishes as more factor rescources are allocated to it
Factor mobility
Occurs when factors of production can easily be moved from one use to another
Geographical mobility
Rescources can move easily between areas/regions/countries
Occupational mobility
Rescources can move easily between different types of work
Specialisation
The concentration of individuals/firms/countries on producing a limited amount of rescources
Division of labour
A form of specialisation in which the tasks needed to make something are split up among the workers
GDP
measures the value of real output of the economy over a period of time
nominal gdp
The monetary value of all goods and services produced in the economy (GDP at current prices)
Real GDP
the nominal value of GDP adjusted for inflation
Real GDP per capita
national income per person often used as a proxy measure for the standard of living
value v volume
the value of goods and services shows what they are worth; the volume shows the number that are produced
GNI
GDP + net income from abroad compensation of employees and property income
Purchasing power parities
used to assess the relative living standards between countries, PPP compares the price of a basket of comparable goods between countries.
standard of living
a measure of economic welfare and well-being. Income typically increases the standard of living; the relationship is not exact
subjective happiness
‘self reported’ levels of happiness with ones life
Easterlin paradox
life satisfa; satisfaction raises with average incomes but only to the point that the marginal gain in happiness declines
inflation
a sustained increase in the general price level
deflation
a sustained decrease in the general price level
disinflation
a reduction in the rate of inflation
Cost-of-living
a measure of changes in the average cost for a household of buying a basket of different goods and services
inflation target
a target set by the government which the central bank should aim to achieve (in the UK it is CPI inflation = 2% ± 1% point)
CPI
tracks changes in the prices of a basket of goods and services purchased by an average family
formula for calculating CPI
CPI inflation rate = [(current CPI - previous CPI)]* 100
CPIH
similar to cpi but also monitors owner occupier housing costs in its basket (costs around owning maintaining and living in ones home)
RPI
the basket of goods/ services includes some items not in the cpi such as council tac & mortgage interest payments and is used to calculate increases in welfare benefits, pensions etc
‘core’ inflation
sustained increase in prices of goods in the basket excluding goods such as energy food alcohol and tobacco which can have volatile prices
demand - pull inflation
inflation caused by excess aggregate demand in the economy
cost - push inflation
inflation caused by increases in the costs of production in the economy
stagflation
when the economy stagnates as the price level rises
deflation caused by fall in aggregate demand
inflation caused by a lack of AD in the economy, producers have to reduce their prices and their profits fall