AP Psych Unit 1 Structures of the Brain
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
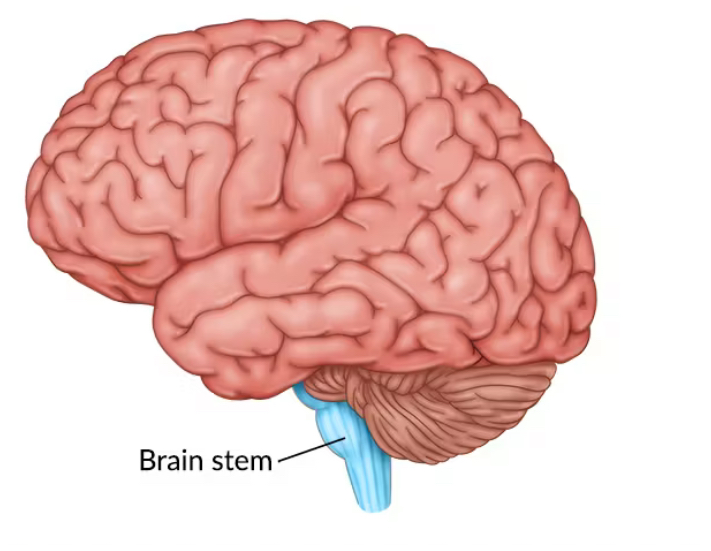
Brain Stem
Controls basic life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. Includes the medulla (controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate). Located at the base of the brain, connecting to the spinal cord.
Midbrain
Plays a role in sensory and motor pathways. Helps with visual and auditory reflexes. Coordinates some automatic movements, such as reflexive turning of the head. Located above the pons, part of the brainstem.
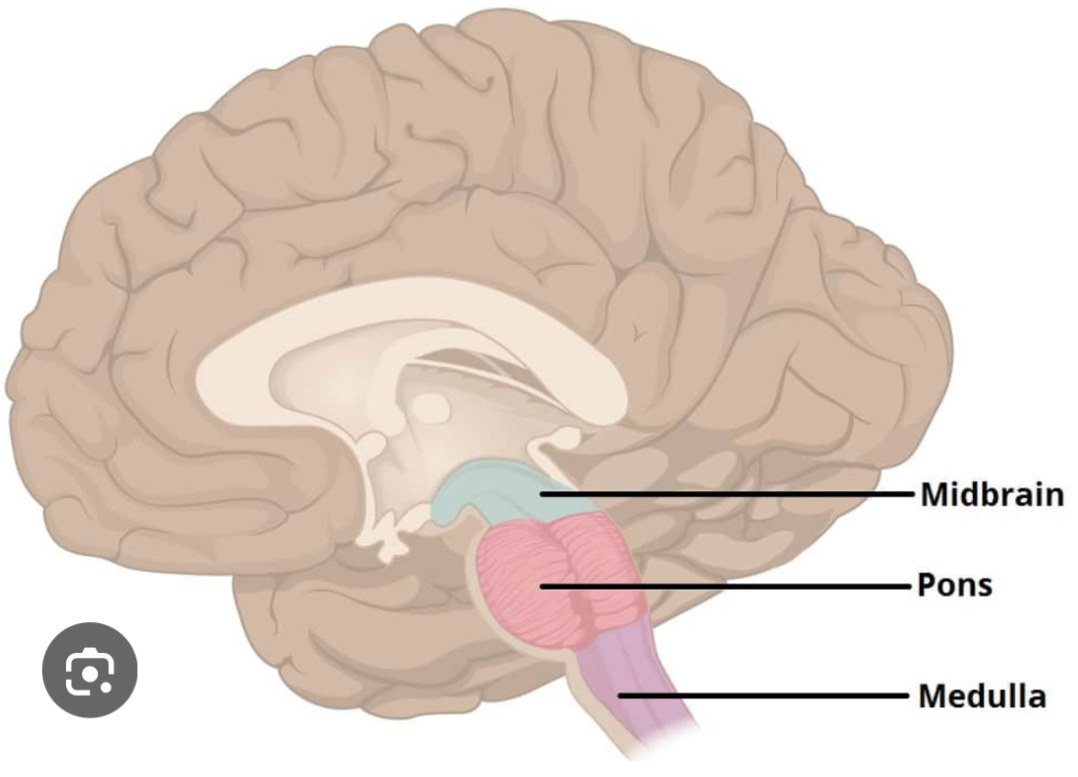
Medulla Oblongata
Controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. Located in the lower part of the brainstem.
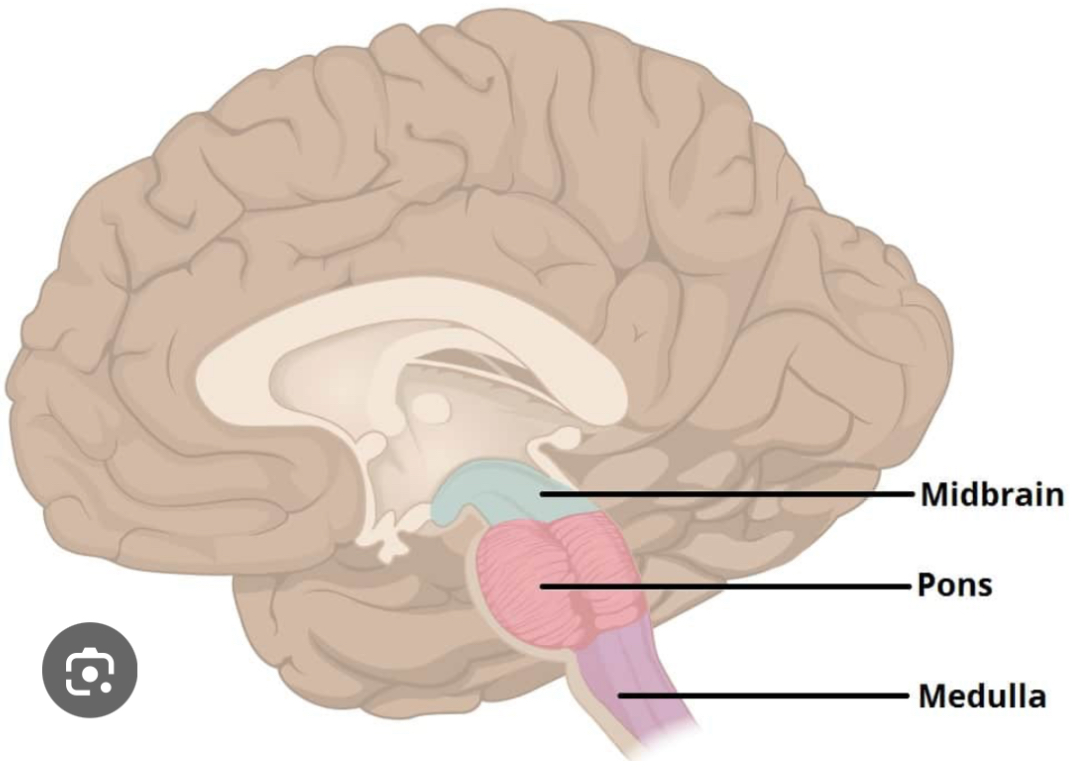
Pons
Regulates sleep and arousal. Helps with breathing regulation. Connects the cerebellum to the cerebral cortex, playing a role in coordination and communication between different brain regions. Located above the medulla, part of the brainstem.
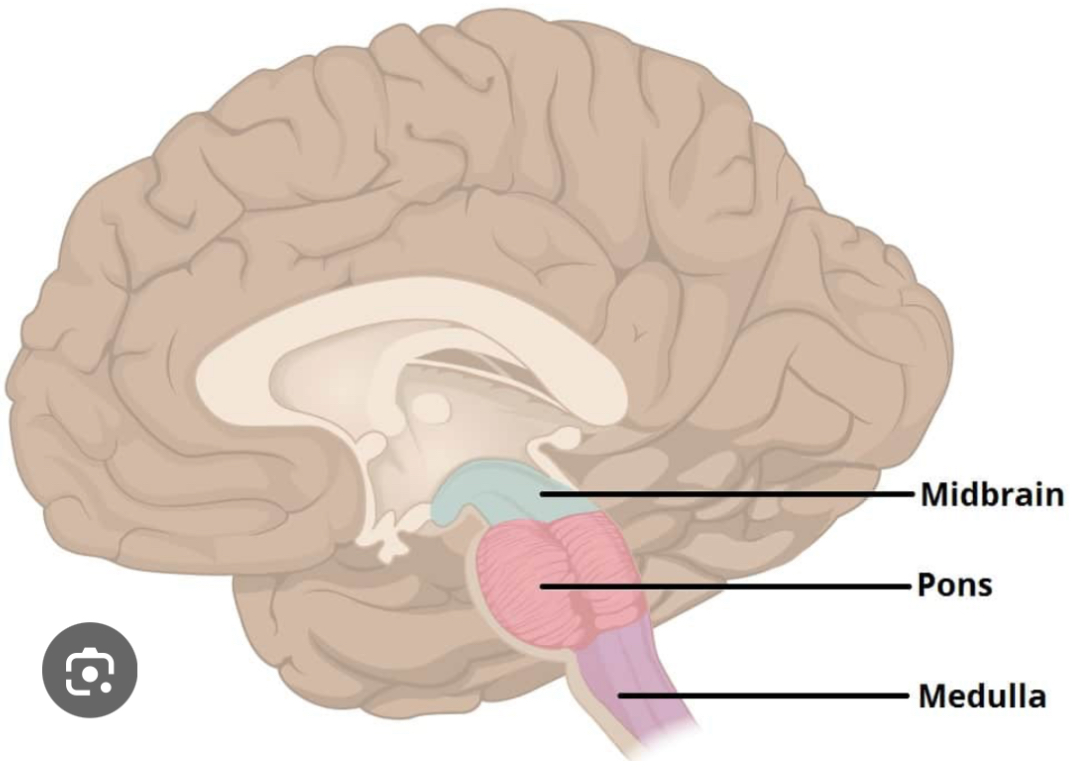
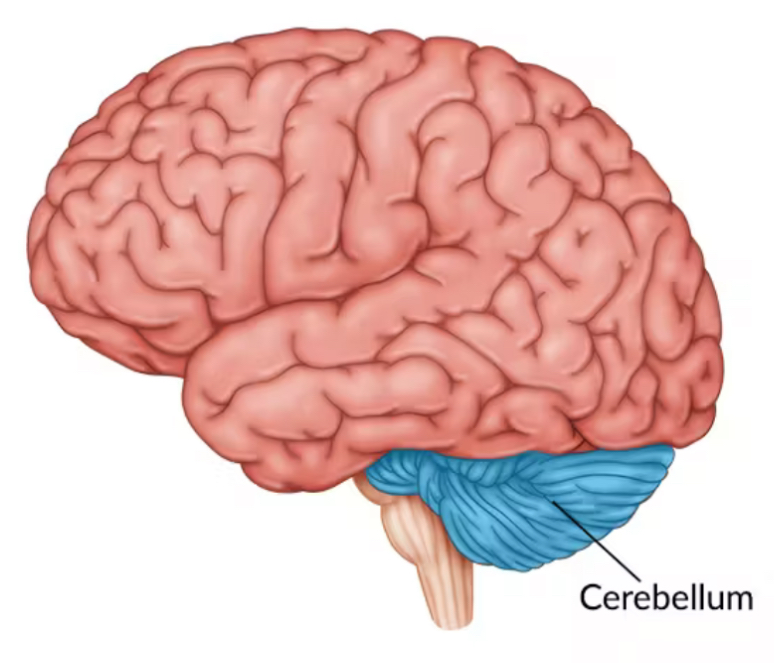
Cerebellum
Coordinates muscle and balance. Involved in procedural learning (learning tasks that become automatic like riding a bicycle). Located beneath the occipital lobe at the back of the brain.
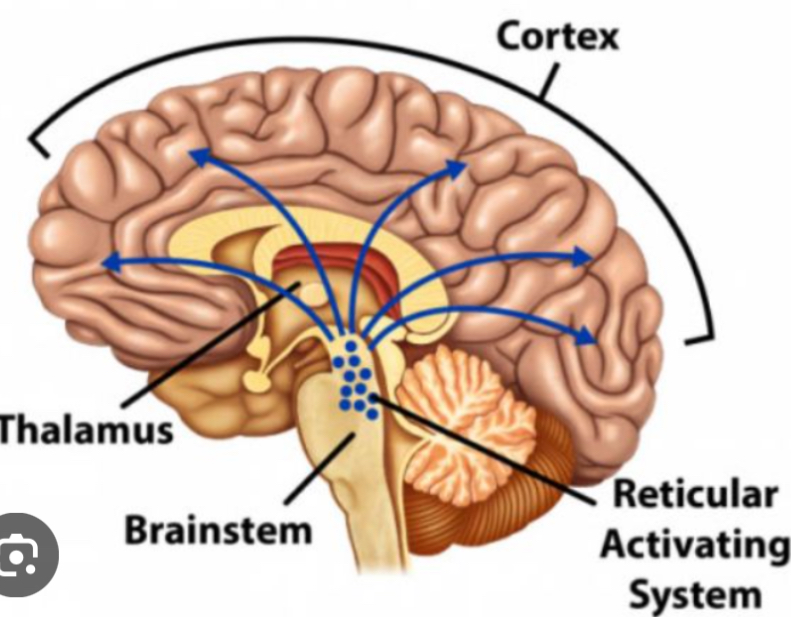
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
Controls arousal, wakefulness, and attention. Plays a role in voluntary movement and some types of learning and attention. Runs through the brainstem.
Limbic System
Responsible for emotion, motivation, and memory. (Made up of multiple structures). Located deep within the brain, under the cerebral cortex.
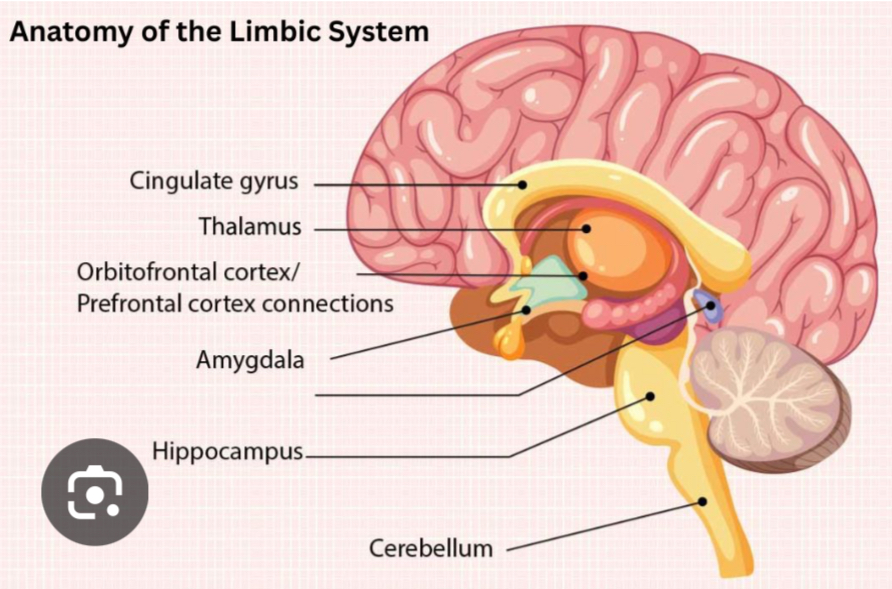
Amygdala
Plays a key role in processing emotions, particularly fear and aggression. Helps form emotional memories. Part of the Limbic System, deep within the temporal lobe.
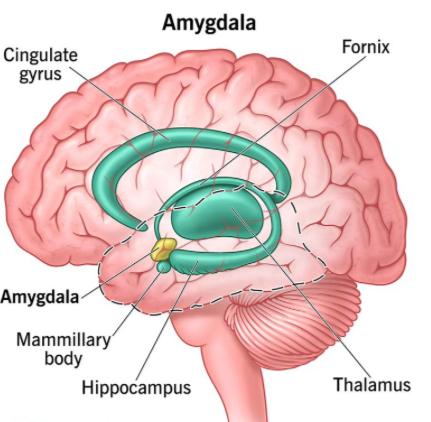
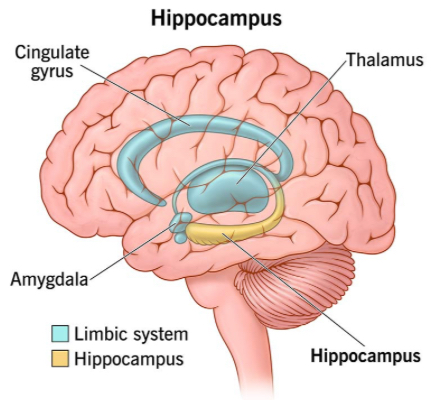
Hippocampus
Essential for the formation of new memories and converting short-term memory into long-term memory. Involved in spatial navigation. In the Limbic System, adjacent to the amygdala.
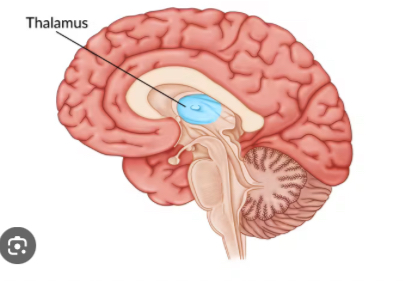
Thalamus
Acts as the brain’s sensory relay station, directing incoming sensory information (except smell) to appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex. Above the brainstem, in the center of the brain.
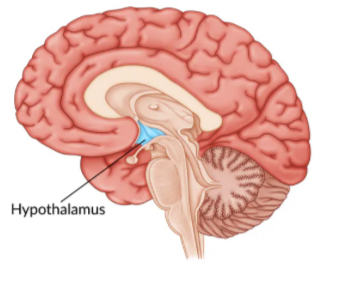
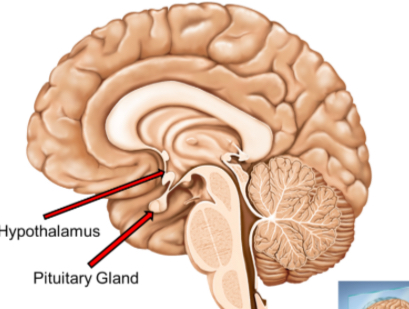
Hypothalamus
Maintains homeostasis by regulating hunger, thirst, temperature, and circadian rhythms. Controls the pituitary gland, influencing hormone release and linking the nervous system to the endocrine system. Located below the thalamus, part of the Limbic System.
Pituitary Gland
Known as the “master gland” because it controls the function of other endocrine glands. It regulates growth, metabolism, and stress response by releasing various hormones. Located below the Hypothalamus.
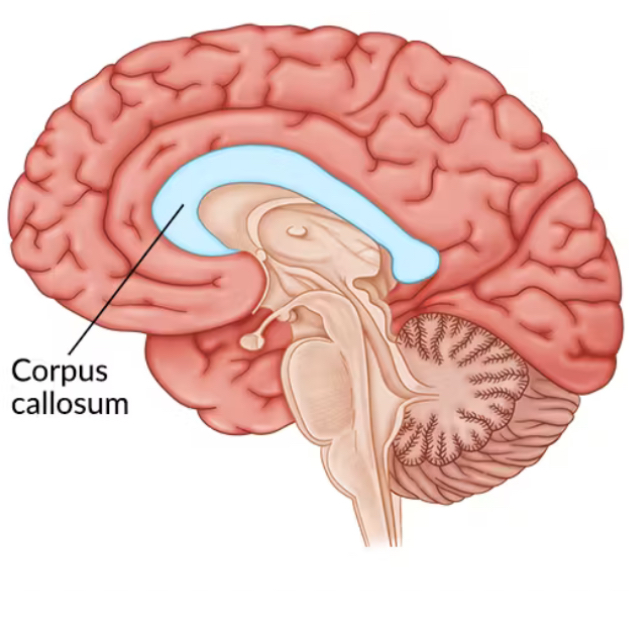
Corpus Callosum
Connects the left and right hemispheres, allowing them to communicate with each other. Located between the two hemispheres of the brain.
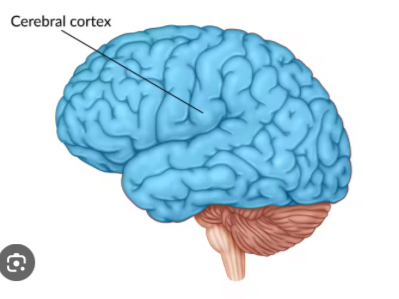
Cerebral Cortex
Involved in higher-order thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making. Responsible for processing complex sensory information. Divided into four lobes (Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, and Temporal Lobe) Located on the outer layer of the brain, covering both hemispheres.
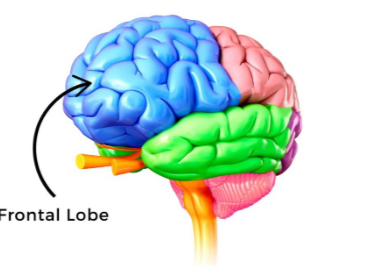
Frontal Lobe
Controls decision-making, problem-solving, planning, language production (Broca’s area), and voluntary movement (motor cortex). Located behind the forehead.
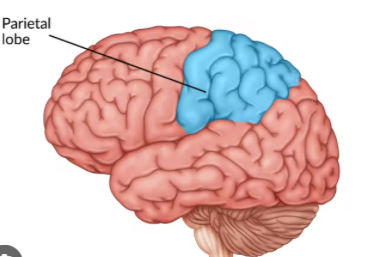
Parietal Lobe
Processes touch, pain, temperature, and includes the somatosensory cortex. Located at the top and rear of the brain.
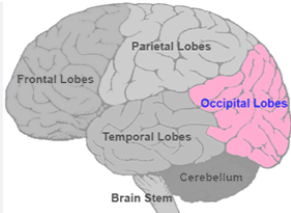
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for visual processing. Located at the back of the brain.
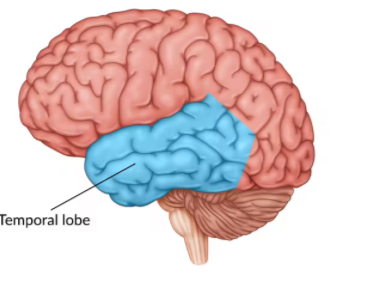
Temporal Lobe
Handles auditory processing and language comprehension (Wernicke’s area). Located on the sides of the brain.
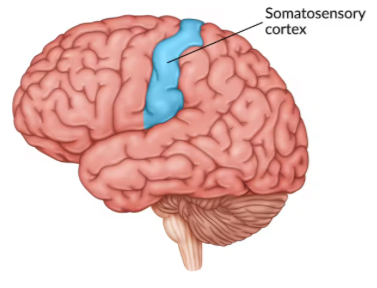
Somatosensory Cortex
Processes sensory input from the body, including touch, pressure, and temperature. Located at the front of the parietal lobe.
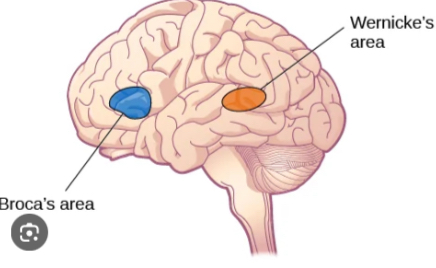
Broca’s Area
Responsible for speech production. Damage to this area can result in Broca’s Aphasia, which impairs speaking ability. Located in the left frontal lobe.
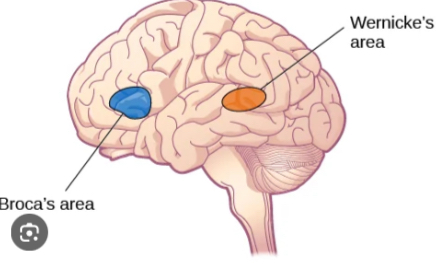
Wernicke’s Area
Responsible for language comprehension. Damage here can lead to Wernicke’s Aphasia, affecting the ability to understand language. Located in the left temporal lobe.