Functions
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
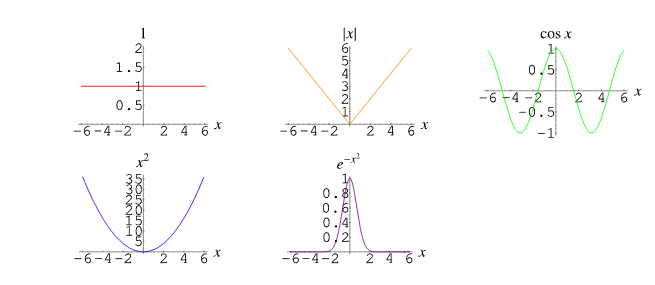
Even Functions
f(-x) = f(x)
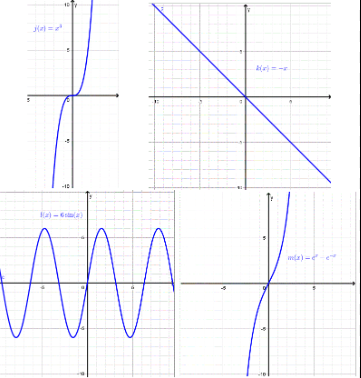
Odd Functions
f(-x) equals -x
Piecewise Function
A function made up of multiple functions on domains so that each input has exactly 1 output
y = f(x) +/- k
shifts y up/down
y = a * f(x)
stretches y by a; if >1, will stretch, if <1, will compress, if <0, inverts over x axis
y = f(x + h)
Shifts y left/right
y = f(b * x)
Dilates the x-values; 3x divides all values by 3, 1/5x multiplies all values by 5
AROC
f(b) - f(a) / b - a
Negative Leading Coefficient
Even function’s ends point down; odd function begins in upper left square rather than lower left square
Point of Inflection
The point of transition between concave up and concave down
Concave Up
The ends of a graph point down, with the middle bowed up
Concave Down
The ends of a graph point up, with the middle bowed down
Secant Line
A line passing through two points of the curve of a function (slope equivalent to AROC)
y = mx + b
slope-intercept form
y = m(x - x1) + y1
point-slope form
Quadratic Functions
Classic curve function; AROCs of AROC are constant
The Greatest Integer Function
Function that chops off decimals and only considers sig figs at the ones place or above
Degree
greatest exponent of a polynomial
Leading Coefficient
the coefficient of the variable with the highest exponent
Multiplicity of One
Graph passes linearly through the x-axis at that point
Even Multiplicity
Graph bounces at the x-axis at that point
Odd Multiplicity
Graph is locally cubic (curves weird) at the x-axis at that point
Successive Differences
taking the AROC of the AROC until you get a constant number; the amount of AROCs will be equal to the degree of the polynomial
Pascal’s Triangle
Pyramid of multiplicities which displays the patterns of coefficients in binomials
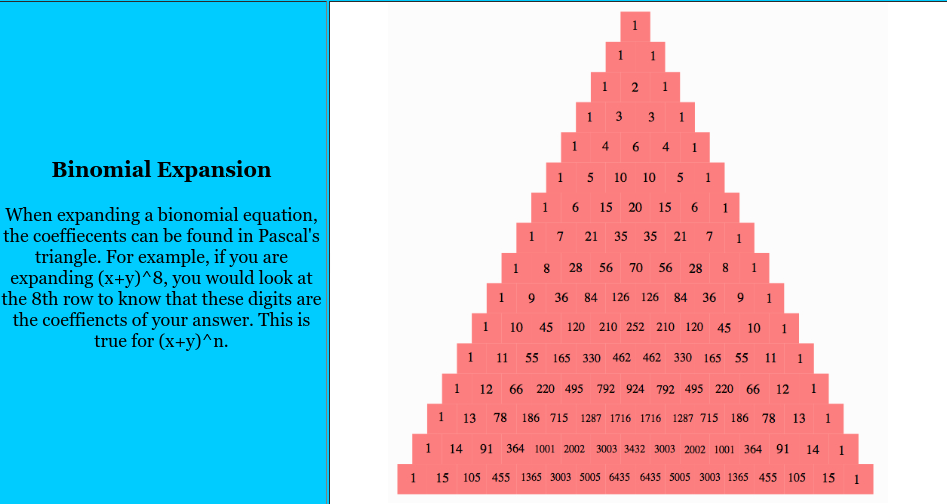
Countdown Pattern in Expanded Binomials
As you go from left to right or right to left, the exponents of either x or y (depending on direction) will count down from the original exponent to 0
First Coefficient Rule
The first and last non-one coefficients in an expanded binomial will always be equal to the exponent of the original binomial
AROC
Average Rate of Change