Unit 4 Vocabulary
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sensation and Perception, Thinking and Intelligence, Memory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
sensation
process of detecting, converting, and transmitting raw sensory information from the external and internal environments to the brain
perception
process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensory info
bottom-up processing
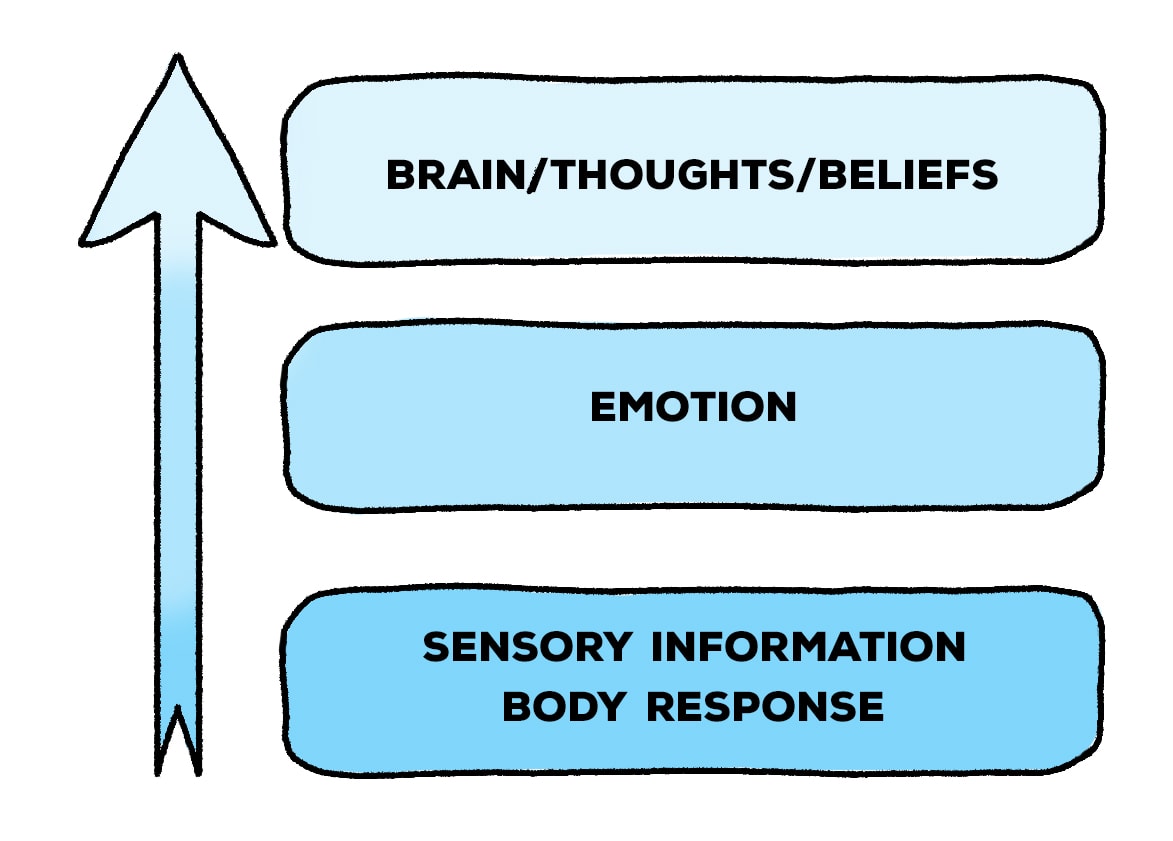
top-down processing
usually when there is not enough info, need to make a quick decision, based on experience and expectation
selective attention
paying attention to a certain thing
inattentional blindness
failure to notice
cocktail party effect
ability to focus listening attention on a single talker among background noise
change blindness
failure to notice obvious change
transduction
conversion from sensory stimulus energy to action potential
absolute threshold
minimum amount of stimulus energy that must be present for stimulus to be detected 50% of the time
just noticeable difference
how much difference in stimuli is required to detect a difference between them
sensory adaptation
senses become less responsive to a constant stimulus over time
signal detection theory
ability to identify a stimulus when it is embedded in a distracting background
depth perception
ability to perceive the relative distance of objects in one’s visual field
retinal disparity
the slightly different images received by each eye
convergence
rotation of the eyes inward towards a light source so the image falls on corresponding points on the foveas
relative clarity
depends on atmospheric conditions
nearer objects are more clear
distant objects are less distinct (appear bluer)
relative size
separate objects seem to be the same size
BUT! larger ones seen as closer
texture gradient
progressive decline in resolution of textures as viewer moves away from them
linear perspective
principle that size of object’s image is a function of its distance from the eye
this makes 2 objects appear closer together as the distance from them increases and appear to converge on the horizon
interposition
2 objects are in the same line of vision
closer object, which is fully in view, partly covers the farther object
proximity
when objects placed together, the eye perceives them as a group
similarity
when objects look similar to one another, the eye perceives them as a group or pattern
closure
when an object is incomplete or not completely enclosed
levels of processing
theory emphasizes the new degree to which new material is analyzed
prototype
first concept of something that comes along
assimilation
having the same schema
accommodation
does not fit into the schema anymore
amplitude
distance from center line to the top or bottom point
wavelength
length of a wave from one peak to the next
frequency
number of waves that pass a given point in a given time period, expressed in hertz (Hz)
cornea
transparent covering over the eye, involved in focusing light waves that enter the eye
pupil
small opening at that allows light to pass
iris
control/connected to muscles that control pupils size, colored part of the eye
lens
curved, transparent, helps provide extra focus
fovea
where the lens focuses images onto small indentation in the back of the eye
retina
light-sensitive lining of the eye
cones
special type of photoreceptors that work best in bright light conditions
rods
special photoreceptors that work well in low light conditions
algorithm
every possible option, solution guaranteed, step-by-step plan, takes time
heuristic
shortcut, solution not guaranteed
representative heuristic
mental shortcut that involves judging whether something belongs to a given class on the basis of its similarity to other members of that class (stereotypical)
availability heuristic
mental shortcut in which judgments are based on information that is most easily brought to mind (immediately)
optic nerve
carries visual info from the retina to the brain
blind spot
even when light is focused on it, it is not seen
trichromatic theory
all colors in the spectrum can be produced by mixing red, blue, and green
opponent process theory
color is coded in opponent pairs (black-white, yellow-blue, green-red)
afterimage
continuation of a visual sensation after removal of stimulus
depth perception
ability to perceive spatial relationships in 3D space
binocular cues
relying on the use of both eyes
binocular/retinal disparity
difference between images seen by left and right eye
monocular cues
only need one eye to see something
mental set
temporary readiness to perform certain functions that influences the response to a situation/stimulus
fixation
preoccupation with a single idea
cognitive dissonance
the stress that results when a person holds 2 or more conflicting values
priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of particular associations in memory
framing
process of defining the context surrounding a problem, question, or event, in a way that serves to influence how the context or issues are perceived/evaluated
gambler’s fallacy
mistaken belief held by some people that independent events are interrelated
sunk-cost fallacy
tendency to continue a course of action in which one has already invested money, time, or effort
divergent thinking
creative thinking where one solves a problem or reaches a decision using strategies that come from commonly used or previously taught strategies
convergent thinking
critical thinking where one uses logical steps to analyze a number of already formulated solutions to a problem to determine the correct one
functional fixedness
inability to consider a new function for an item
cognition
thinking, and it encompasses processes associated with knowledge and perception
concepts
categories/groupings of linguistic information and ideas
natural concepts
created naturally through experience, can be developed from direct or indirect experiences
artificial concept
defined by a specific set of characteristics
schema
mental construct consisting of a cluster or collection of related concepts
role schema
makes assumptions about how an individual in certain roles will behave
event schema
set of behaviors that can feel like a routine
trial and error
continue trying different solutions until problem is solved
anchoring bias
tendency to focus on one particular piece of info when making decisions or problem solving
confirmation bias
focuses on info that confirms existing beliefs
hindsight bias
belief that the event just experienced was predictable
representative bias
making a decision based on perceived similarity to existing stereotypes or prior beliefs
encoding
translating sensory stimuli into neural coding that can be stored
storage
retaining neutral coded info over time
retrieval
recovering info from memory storage
automatic processing
big event happens and is just stored immediately
effortful processing
learn and thinking, connecting to what you already know
self-reference effect
tendency for one to have