FBLA Economics Study Guide: Key Concepts and Definitions
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
absolute advantage
the producer can produce the most output/requires the least amount of inputs
tons of trade
how many units of one product would they benefit from another product
private sector
part of the economy that is run by individuals and businesses
public sector
the part of an economy that is controlled by the government.
factor payments
payments for the factors of production, namely rent, wages, interest, and profit
transfer payments
When the government redistributes income (ex: welfare, social security)
subsidies
government payments to businesses
Law of Demand
there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
substitution effect
customers switching to cheaper products as prices increases
income effect
the change in consumption resulting from a change in real income
law of diminishing marginal utility
the principle that consumers experience diminishing additional satisfaction as they consume more of a good or service during a given period of time
substitute
increase in price of one good, increases demand for another good
complements
increase in price of one good, decreases demand for other
normal goods
as income increases, demand decreases
inferior goods
as income increases, demand decreases
total revenue test
Total revenue rises with a price increase if demand is price inelastic and falls with a price increase if demand is price elastic
price ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold
trade
- if we can buy something at a cheaper world price, that means that price will fall, producer surplus will get smaller, but consumer surplus will get bigger
consumer surplus
the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it
producer surplus
the amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller's cost of providing it
Utility Maximization
The proposal that people make decisions by selecting the option that has the greatest utility.
law of diminishing marginal resources
as variable resources are added to fixed resources the additional output produced by each additional worker will eventually fall
fixed costs
Costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produced Ex: rent, insurance, Managers Salaries
variable costs
costs that vary with the quantity of output produced ex: raw materials, electricity, labor
total costs
fixed costs + variable costs
marginal cost
the cost of producing one more unit of a good
average total costs
total cost divided by the quantity of output
average variable cost
variable cost divided by the quantity of output
economies of scale
factors that cause a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises
Characteristics of Perfect Competition
- many small firms
- identitcal products
- low barriers: easy to enter and exit
- seller has no need to advertise
- Firms are "price takers": got to take price that is set by market
- seller has NO control of price
horizontal demand curve
perfectly elastic demand
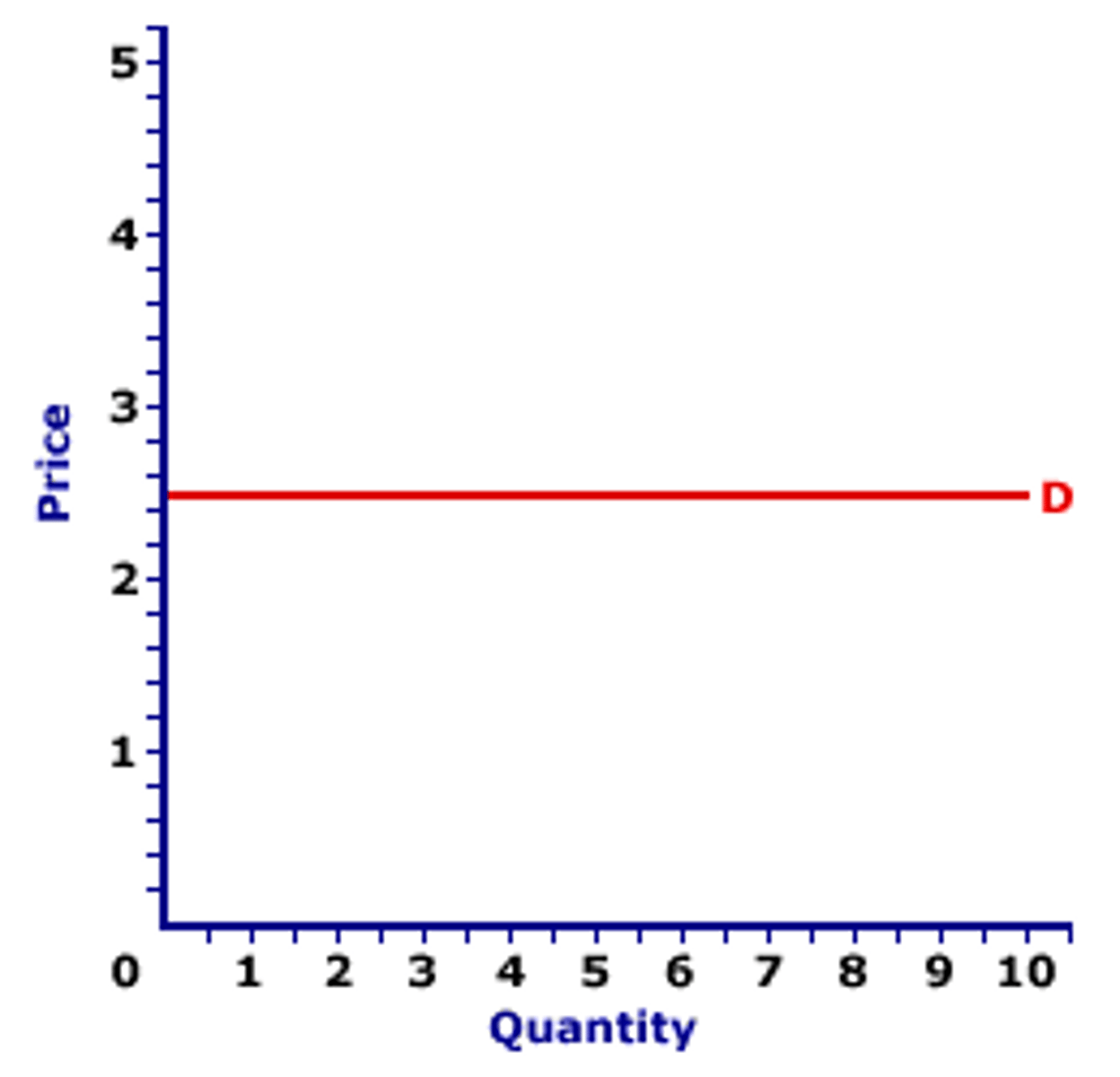
Profit Maximizing Rule
MR=MC
shut down rule
a firm should shut down if the price falls below the minimum AVC
Accounting v Economic Profit
- accountants look at only explicit costs
- economists examine both explicit, and implicit costs
Perfect Competitive Firms earn zero Economic Profit and positive Accounting profit , supply shifts to right
productive efficiency
where price=min ATC, producing at lowest possible cost
allocative efficiency
producing at the amount most desired for society
price=mariginal cost
Monopoly
- one large firm
-unique product
- high barriers: firms cannot enter the industry
- price makers
- require some advertising
Natural Monopoly
a market that runs most efficiently when one large firm supplies all of the output
price discrimination
the business practice of selling the same good at different prices to different customers
Oligopoly
-A market structure in which a few large firms dominate a market
- identical or differentiated products
- high barriers to entry
- control over price(price maker)
- mutual interdependence
dominant strategy
a strategy that is best for a player in a game regardless of the strategies chosen by the other players
Nash Equilibrium
a situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the other actors have chosen
monopolistic competition
- relatively large number of sellers
- differentiated products
- same control over price
- easy entry and exit
- a lot of advertising
derived demand
Business demand that ultimately comes from (derives from) the demand for consumer goods.
if the demand goes up for pizza, demand for pizza drivers will go up
minimum wage
- quantity demanded falls
- quantity supplied increases
Marginal Revenue Product
The additional revenue generated by an additional worker
MRC
the additional cost of an additional worker
Least Cost Rule
The combination of labor and capital that minimizes total costs for a given production rate. Hire L and K so that MPL / PL = MPK / PK or MPL/MPK = PL/PK
Market Failure
a situation in which the market does not distribute resources efficiently
public goods
Goods, such as clean air and clean water, that everyone must share.
shared consumption
A good or service where more than one person can simultaneously enjoy it.
non exclusion
the idea that you cannot exclude people that don't pay
negative externalities
by-products of production or consumption that impose costs on third parties
positive externalities
benefits created by a public good that are shared by the primary consumer of the good and by society more generally
dead weight loss
the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium
the lorenz curve
the curve that illustrates income distribution
progressive taxes
-takes more from rich ppl (current federal income tax system)
proportional (flat)
- takes the same amount of taxes from rich and poor (20% of income)
regressive tax
A tax for which the percentage of income paid in taxes decreases as income increases (sales tax, consumption tax)