2.1.1 Eye and visual pathways
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
List the 2 parts of the retina, which fields of view they can see and which sides of the optic tracts they are innervated by. (3)
Temporal and nasal
Temporal- medial view, nasal- lateral view
Temporal retina- contralateral decussating fibres, nasal retina- ipsilateral non decussating fibres
Describe what happens to vision when the pituitary gland swells. (2)
Pressure on caudal optic chiasma —> pressurises the decussating tracts
Tunnel vision as nasal retinas are obstructed and cannot see temporal view
What advantage does having partial decussation of the optic tract have?
Images from one eye are shared at both hemispheres (each eye has medial vision linking to other side and lateral vision linking to decussation from same side)
Which structure in the thalamus do sight signals go through?
Lateral geniculate nucleus
Describe the movement of the ventral oblique muscle.
Right eye clockwise, left eye anticlockwise
Describe the actions and corresponding muscles and nerves of the menace response (2).
CNVII- orbicularis oris shuts eye
Tectospinal tract turns neck away
Where in the midbrain do signals from the eye pass through and what 3 responses is it responsible for triggering? (4)
Pretectal nuclei of rostral colliculi
Reducing pupil size (parasympathetic response) via CNIII Edinger Westphal nucleus
Increasing pupil size (sympathetic response) via T1-T3 cranial cervical ganglia
Turning head via vestibular tectospinal tract
Where in the hypothalamus do signals from the eye pass through and what response is it responsible for?
Suprachiasmtic nucleus
Circadian rhythm from light stimuli
Describe the pupillary light reflex. (3)
CNII senses too much light
Signal travels to pretectal nuclei in rostral colliculi
CNIII reduces pupil size via constricting circular iris muscles via Edinger Westphal nucleus (GVM)
Describe the pupil dilation reflex. (3)
CNII senses too little light
Signal travels to pretectal nuclei in rostral colliculi
T1-T3 sympathetic fibres increase size of pupil via contraction of radial muscles
Describe the fixating response. (6)
CNII senses stimulus
Signal travels through lateral geniculate nucleus in thalamus to occipital lobe
CNIII actions on ventral/medial/dorsal rectus + ventral oblique (GSM)
CNIV action on dorsal oblique (GSM)
CNVI action on lateral rectus (GSM)
Tectospinal tract turns neck towards target
Describe the corneal reflex. (3)
Touch detected on cornea by long ciliary branch of nasociliary branch of ophthalmic trigeminal (V1)
CNVI signals retractor bulbi to retract eye (GSM)
CNVII closes eye via orbicularis oculi (GSM)
Describe the nictitating reflex. (3)
Touch detected on cornea (when eyelid held open) by long ciliary branch of nasociliary branch of ophthalmic trigeminal
CNVI signals retractor bulbi to retract eye (GSM)
Retraction of eye enables protrusion of third eyelid
Describe the palpebral reflex. (2)
Touch on eyelid/palpebra detected by ophthalmic trigeminal (V1, maybe V2 if lateral palpebra)
CNVII signals orbicularis oculi to close eyelids
Describe the oculocardiac reflex. (3)
Pressure on eyeballs detected by ophthalmic trigeminal (V1)
Input sent to cardiac center in medulla
CNX slows down heart rate (GVM)
List 5 signs of Horner’s syndrome.
Miosis (constricted pupils due to decreased sympathetic flow)
Ptosis (drooping of upper eyelid due to smooth muscle relaxation)
Intraocular pressure reduction (due to conjunctival vascular engorgement)
Enophthalmia (smaller, more retracted eye due to reduction in pressure and periorbital muscle relaxation)
Nictitating membrane protrusion (due to enophthalmia)
List 5 potential lesions causing Horner’s and whether this would cause unilateral or bilateral lesions.
Brainstem- bilateral
Spinal cord- bilateral
Vagosympathetic trunk- bilateral
Cranial cervical ganglia- bilateral
Postganglionic sympathetic fibres- unilateral
List 3 causes of unilateral ptosis.
CNIII lesion (compromised levator palpebrae superioris)
Horner’s
CNVII lesion (compromised face muscle tone)
What salivary gland swelling could cause facial paralysis?
Parotid gland- sits next to CNVII
What is the most common cause for bilateral ptosis?
CNVII lesion
What clinical sign is often seen in uveitis?
(Unilateral) miosis- inflammed choroid/ciliary body and iris constricts pupils
What is the most common cause of bilateral miosis?
Tectal lesion- upper motor neurons no longer inhibiting Edinger Westphal nucleus (causing excessive parasympathetic response)
Which drug is commonly used in surgery and causes mydriasis?
Atropine (sympathomimetic)
What is the most common cause of bilateral mydriasis?
Central brainstem lesion affecting GVM output of both EW nuclei
Describe the consequence a swollen pituitary gland has on vision. (2)
Medial decussating fibres compressed (lateral nondecussating fibres are fine)
Medial decussating fibres innervate nasal retinae- lack of lateral vision (tunnel vision)
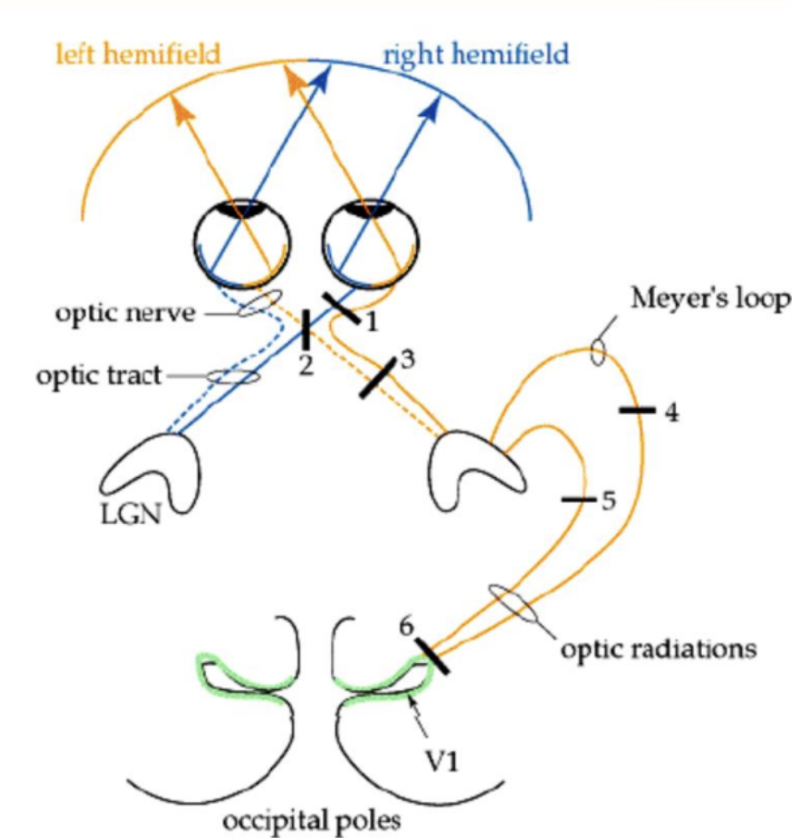
Consequence of lesion at 1
Complete blindness in right eye
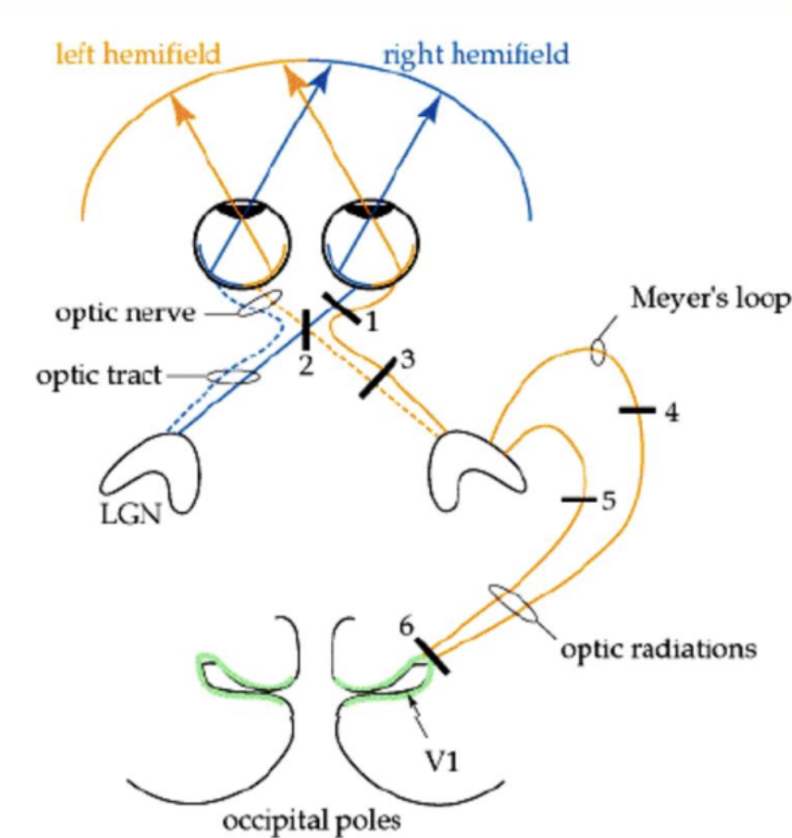
Consequence for lesion at 2
Tunnel vision (usually due to enlarged pituitary)
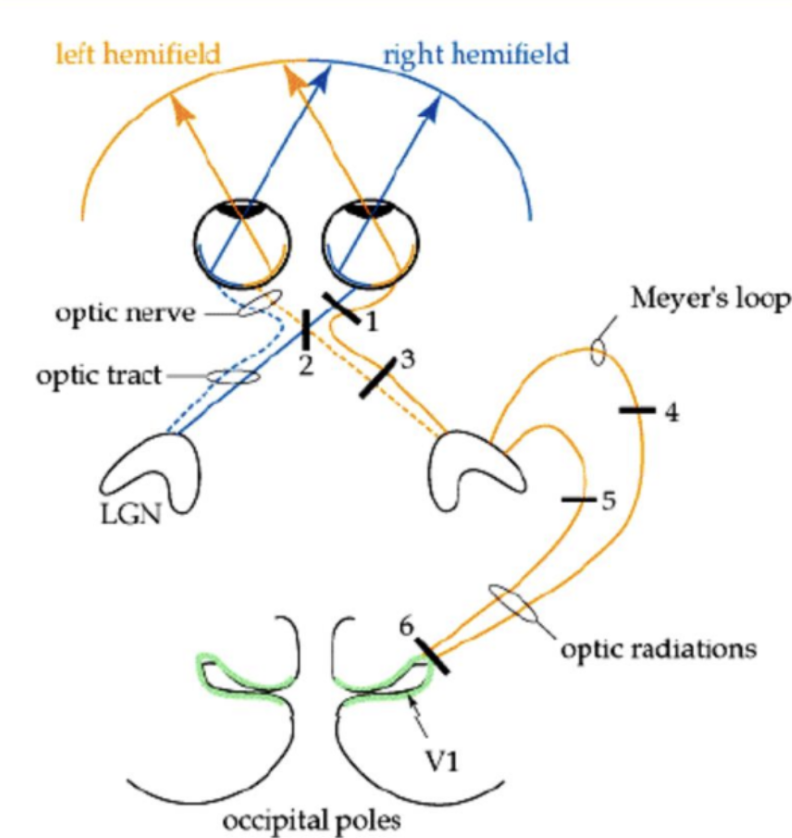
Consequence for lesion at 3
Blindness in nasal view in right eye and temporal view in left eye
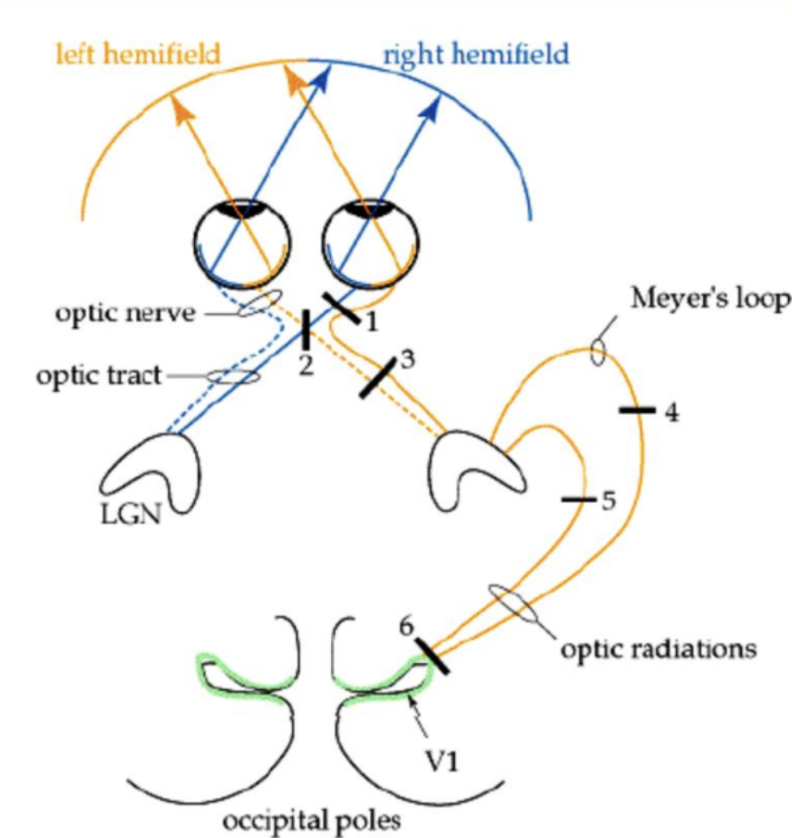
Consequence for lesion at 4
Quadrantopia in superior FoV (pie in the sky)
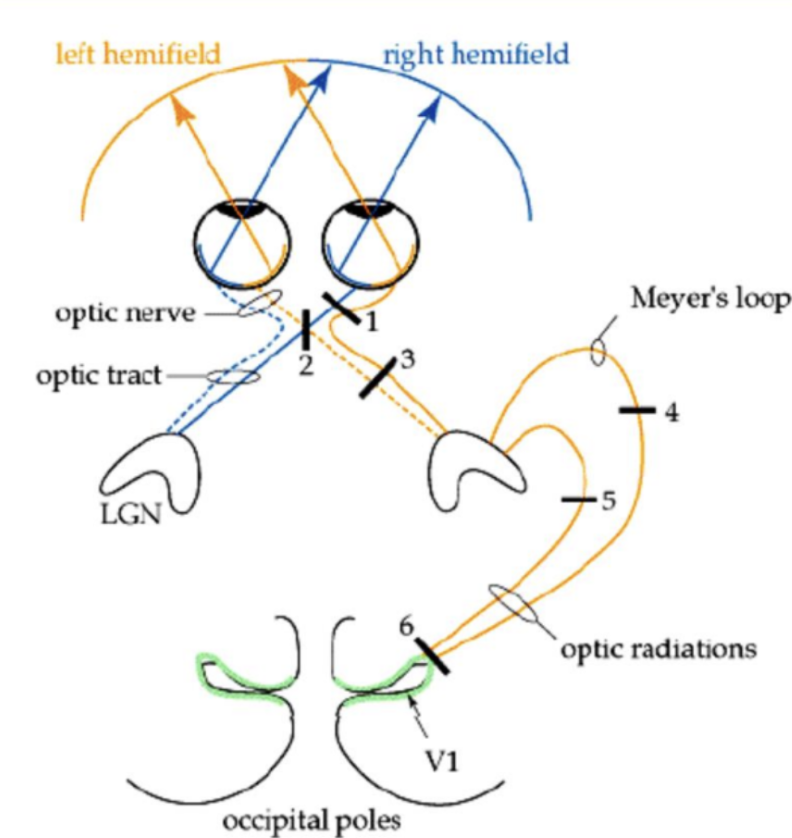
Consequence for lesion at 5
Quadrantopia in ventral FoV (pie on the floor)
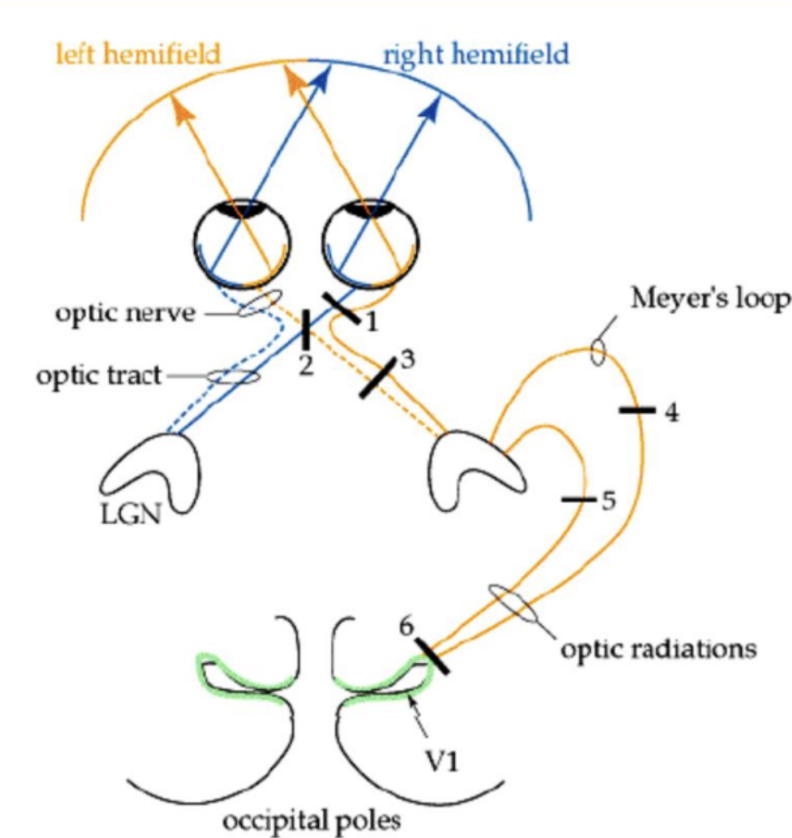
Consequence for lesion at 6
Blindness in nasal view in right eye and temporal view in left eye