3.6 Human Impact on the Environment
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
State the reasons for extinction
-Natural selection
Habitat destruction
Pollution
Hunting and collecting
Competition from domestic animals
Define biodiversity
A measure of the number of different species and number of individuals in the species, living in a specified area
Define an Endangered species
A species at risk of becoming extinct because there are few breeding pairs left
Define extinction
The total loss of a species
What does IUCN stand for
International Union for Conservation of Nature
What does IUCN do
makes assessments of plants and animals, grading them to their vulnerability to extinction
State the gradings given by the IUCN
EX - extinct
EW - extinct in the wild
CR - critically endangered
EN - endangered
VU - vulnerable
NT - near threatened
LC - least concern
State the 3 aspects of biodiversity
Genetic diversity
Species diversity
Ecosystem diversity
Define conservation
The planned management of ecosystems to enhance biodiversity and protect gene pools
State the main reasons for conservation
Ethical
Economic
Cultural and aesthetic
State the ethical reason for conservation
It is unethical to drive species to extinction and reduce biodiversity
Other species have occupied earth far longer than we have and should be allowed to coexist with us
State the economic reason for conservation
Living organisms contain a gigantic pool of genes with the capacity to make millions of substances such as medicines
State the cultural and aesthetic reason for conservation
Habitats and organisms enrich our lives.
State ways in which conservation may be achieved
Habitat protection by nature reserves and SSSI
International cooperation between governments and organisations
Restricting activities that threaten an endangered species
Legislation to prevent overfishing and poaching
Breeding programmes
Sperm banks and seed stores
Reintroduction programmes
Pollution control
With good forestry practice. How can efficiency be increased
Planting trees the optimum distance apart - planting trees together will result in intraspecific competition
Controlling pests and disease
What is selective logging
Involves felling only some of the largest trees.
Pros of selective logging
valuable on steep slopes where the total removal of trees would leave the soil very vulnerable to erosion
maintains nutrients in the forest soil
Cons of selective cutting
Uses large machinery which causes disturbance to the area
How is deforestation causing soil erosion
Removal of vegetation leads to a reduction in rainfall accelerating desertification
Removal of vegetation on the higher slopes of valleys results in heavy rain sweeping exposed soil to the flood plains below
On the lower slope the absence of plants results in only evaporation occurring which is generally slower than transpiration in returning water vapour to the atmosphere so soil conditions become wetter
How is deforestation causing climate change
Cutting down forest reduces the rate of removal or carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by photosynthesis
How can the different stages of coppicing help increase biodiversity
-More varied habitats/creates more niches
-Secondary succession occurs
-More types of food
Changing light level resulting in flowers thriving in open areas
What is coppicing
A system based on the fact that most deciduous trees grow from the base when their trunks are cut down. The trees are cut down close to the ground and then left for several years to regrow
Consequences of deforestation
Climate change
Destruction of natural habitats leading to loss of biodiversity
Soil erosion caused by loosening of topsoil through digging and ploughing
What is long rotation time
Involves leaving each part of the forest for many years before re-harvesting it
Reasons for deforestation
World demand for timber as a building material
Wood is used as a fuel
land is cleared for agriculture by subsistence farmers and cash crops
New roads are built to provide a transport infra structure
There is a demand for paper and packaging
What is the effect of monocultures
Decrease hybrid vigour
increase in homozygosity
What happens if the same crop is grown on the same plot year after year
Yield progressively decline because…
The roots are always the same length so they extract the same minerals from the same depth in the soil.
This has increased the use of fertilisers
Same crop is always susceptible to the same pests which increase in number
suggest how the conflicts of interest between food production and conservation can be resolved.
▪ Sustainable farming techniques / or description/ less (nitrate) fertiliser (close to water courses)/ owtte
▪ Regeneration of forests / planting endemic species.
▪ Change to lifestyle e.g. encourage eating less meat/ Alternatives to palm oil
▪ National parks / SSSIs / encourage ecotourism as alternative source of income/ seed banks
▪ Change in government policy / public awareness/ education
Schemes and legislation that aims to reverse the effect of agricultural exploitation
Organic farming
Set aside schemes
Legislation
Define monoculture
The growth of a large number of genetically identical plants in a defined area
How are hedges valuable to wildlife
They provide wildlife corridors
Habitats
How are agriculturists meeting the growing demand
Creating larger fields by removing hedges
Cultivated monoculture
Increased their use of fertilisers and pesticides
What do ecotourism do
Minimise the negative impacts of tourism
Contributes to conservation efforts
Employ local people and give money back to the community
Educate visitors about the local environment and culture
Cooperate with local people to manage natural areas
Define overfishing
The rate at which fish are harvested exceeds the rate at which they reproduce
Describe drift netting
Involves suspending a net from floats stretched between two boats so that fish swim into it
Describe trawling
Involves dragging a large net through the water,
Issue of trawling
Damages the ocean bed, destroying the habitats
Issue of drift netting
Non target species become caught
State the ways to reduce the impact of overfishing
Fishing quotas
Reducing size of fishing fleets
Restricting seasons for fishing
Restricting mesh sizes for fishing nets
Banning fishing from some zones
Fish farming
Benefit of restricting mesh sizes
By having a minimum mesh size, larger fish will be caught but smaller fish who are often juvenile will be able to escape from the nets and go on to breed
State the problems around fish farming
Fish are very densely stocked so disease can be spread easily which can spread to wild fish
Huge amount of antibiotics are used to keep the fish healthy
Pesticides used to control fish parasites are known to harm marine invertebrates
When fish escape the farmed fish interbreed with wild fish and potentially weaken wild stocks as they have a selective advantage over wild fish
Eutrophication
Define planetary boundary
Limits between which global systems must operate to prevent abrupt and irreversible environmental change
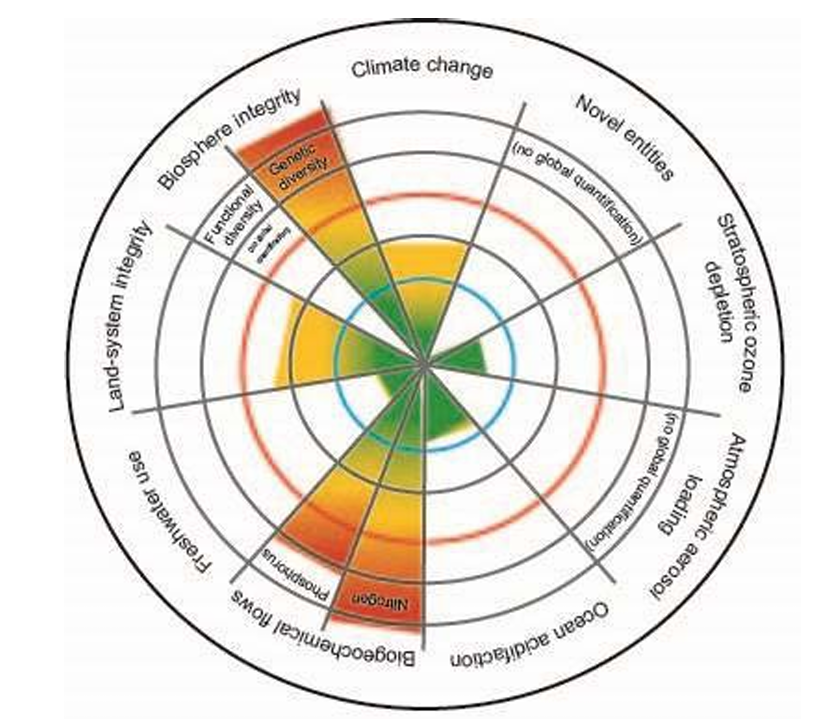
Describe a safe operating space for humanity
Where planetary systems are stable
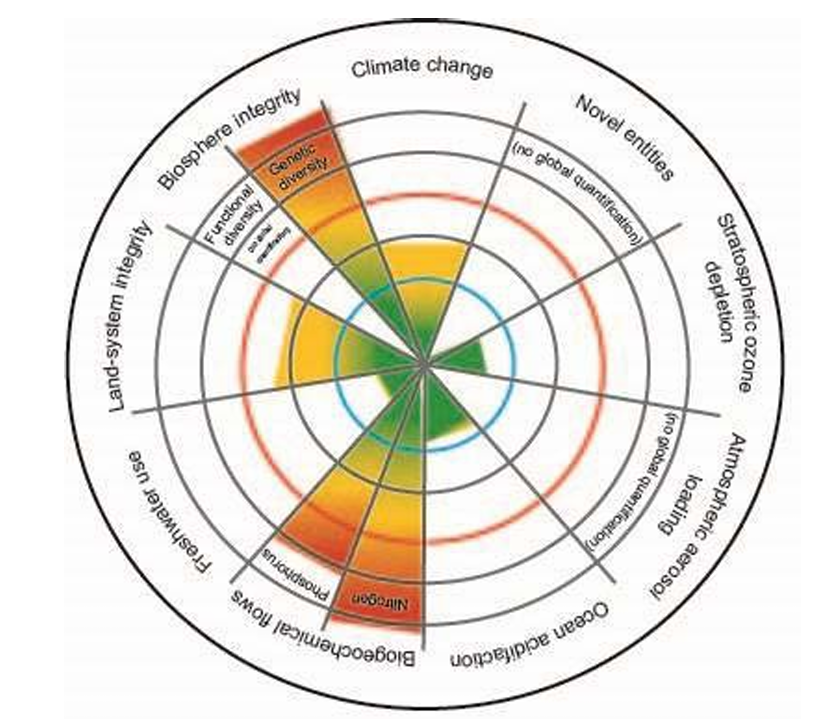
Name the planetary boundaries
Biosphere integrity
Climate change
Chemical pollution and novel entities
Ozone depletion
Aerosol loading
Ocean acidification
Biochemical flows
Freshwater consumption and the water cycle
Land system change
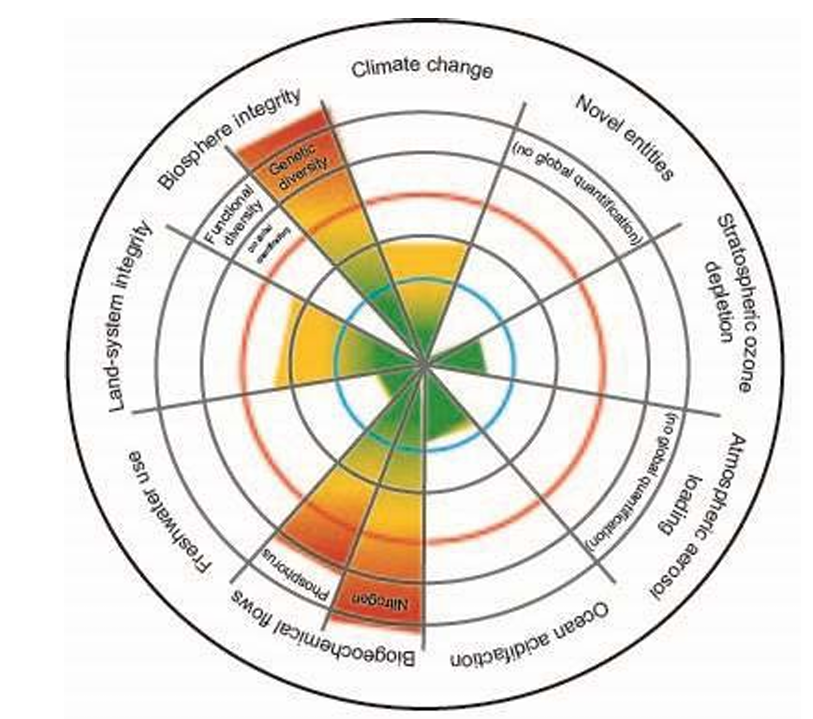
Genetic diversity
Variety of alleles within a species
Species diversity
Variety of species within a habitat
Ecosystem diversity
Variety of habitats within a ecosystem