23 - Vertebrates - Mammals
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are synapsids?
Amniotes that include mammals, characterized by a new jaw joint formed between the dentary and squamosal bones.
What are some derived characters of mammals?
Mammary glands, hair, fat layer for insulation, kidneys, endothermy, high metabolic rate, large brain-to-body-size ratio, and extensive parental care.
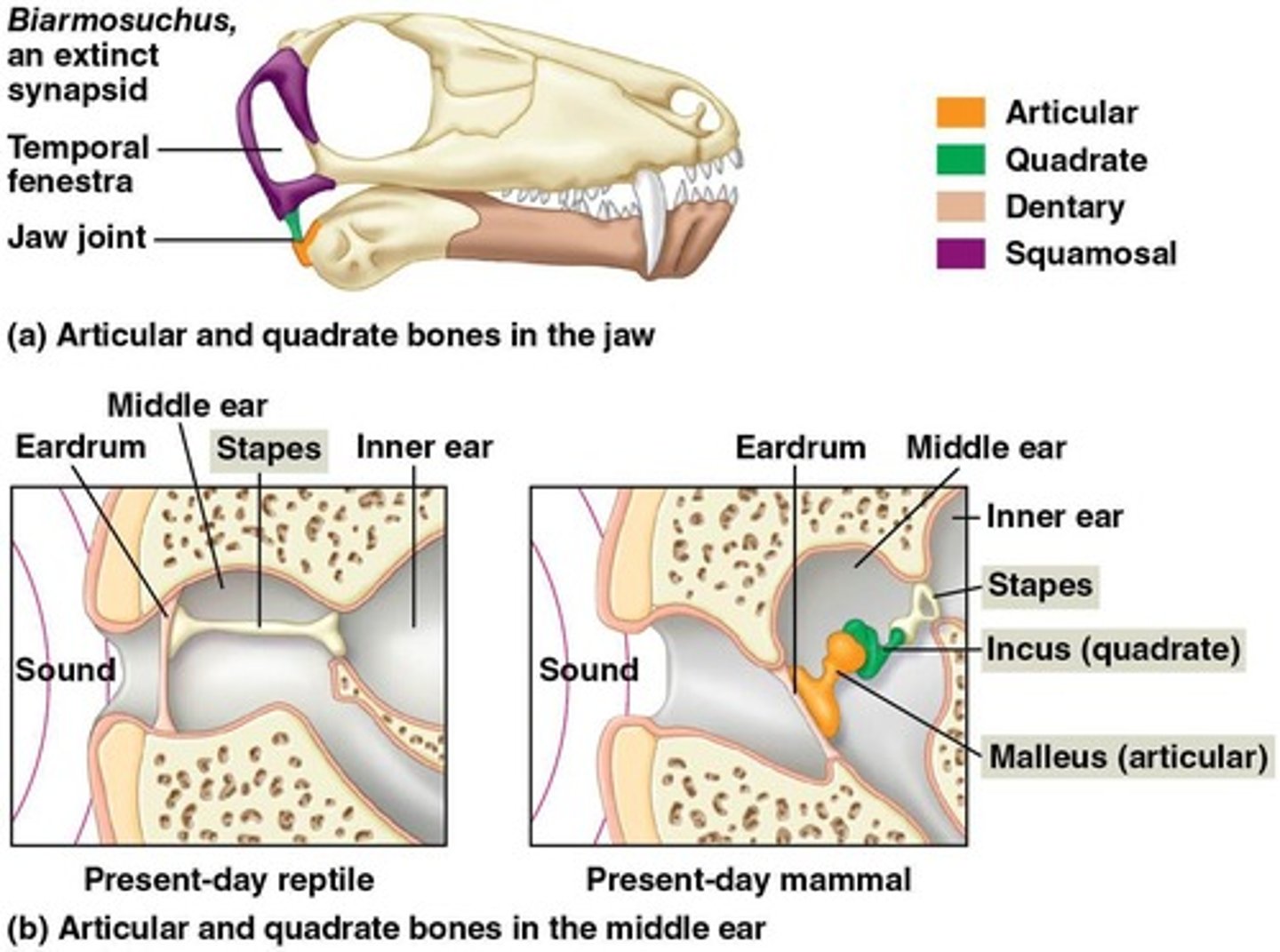
What is the significance of the mammalian jaw joint?
It formed between the dentary and squamosal bones and became incorporated into the middle ear to transmit sound.
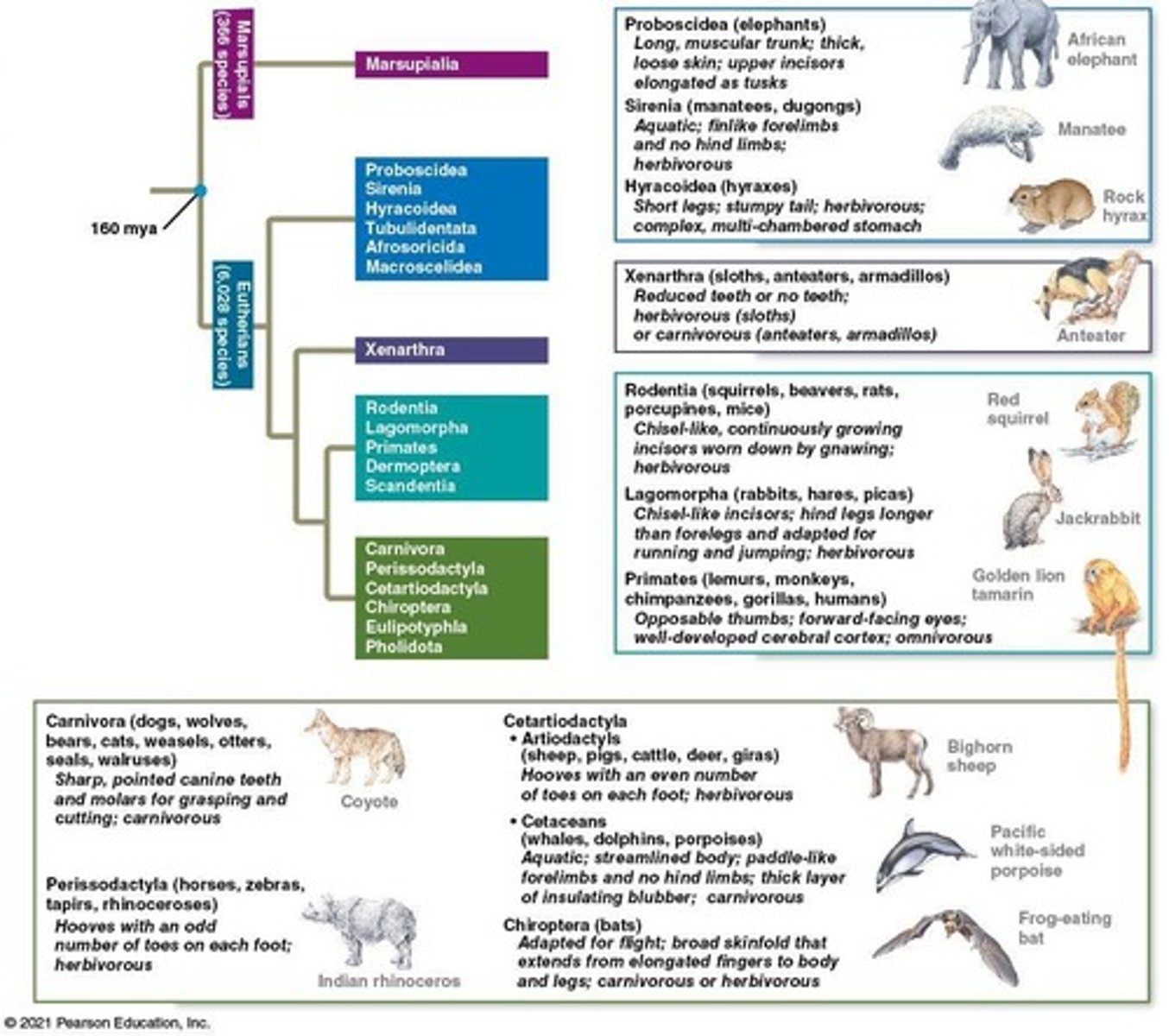
What are the three major lineages of mammals?
Monotremes (egg-laying), marsupials (pouch), and eutherians (placental).
Where are monotremes found?
Only in Australia and New Guinea.
How do marsupials differ from eutherians?
Marsupials have a shorter gestation period, give birth to less developed young, and have a pouch for nursing.
What evolutionary event allowed mammals to radiate?
The mass extinction of dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous period.
What are some characteristics of eutherians?
More complex placenta, longer pregnancies, and complete embryonic development within the uterus.
What adaptations do primates have for living in trees?
Big toes and moveable thumbs for grasping branches, enhanced depth perception, and eye-hand coordination.
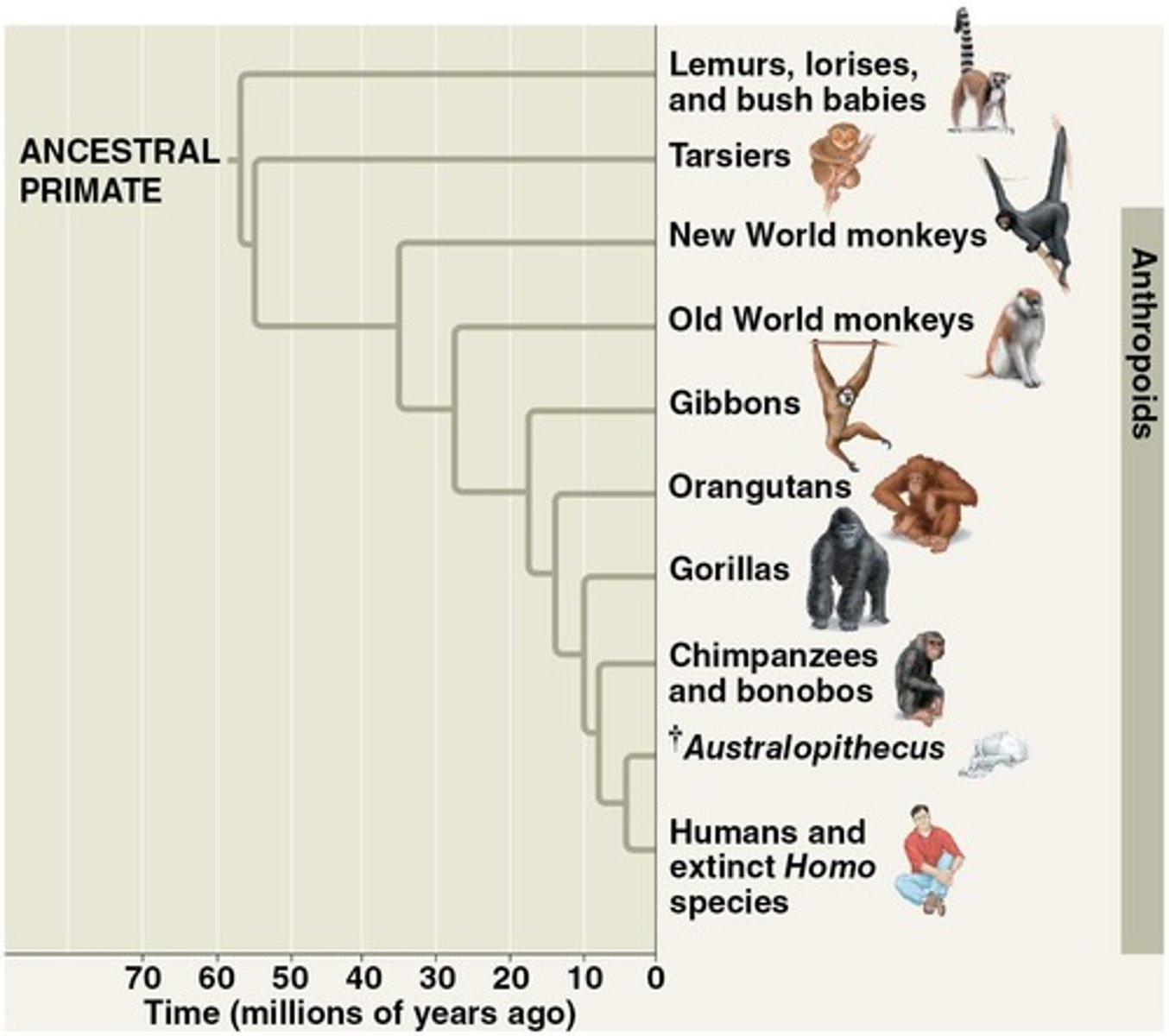
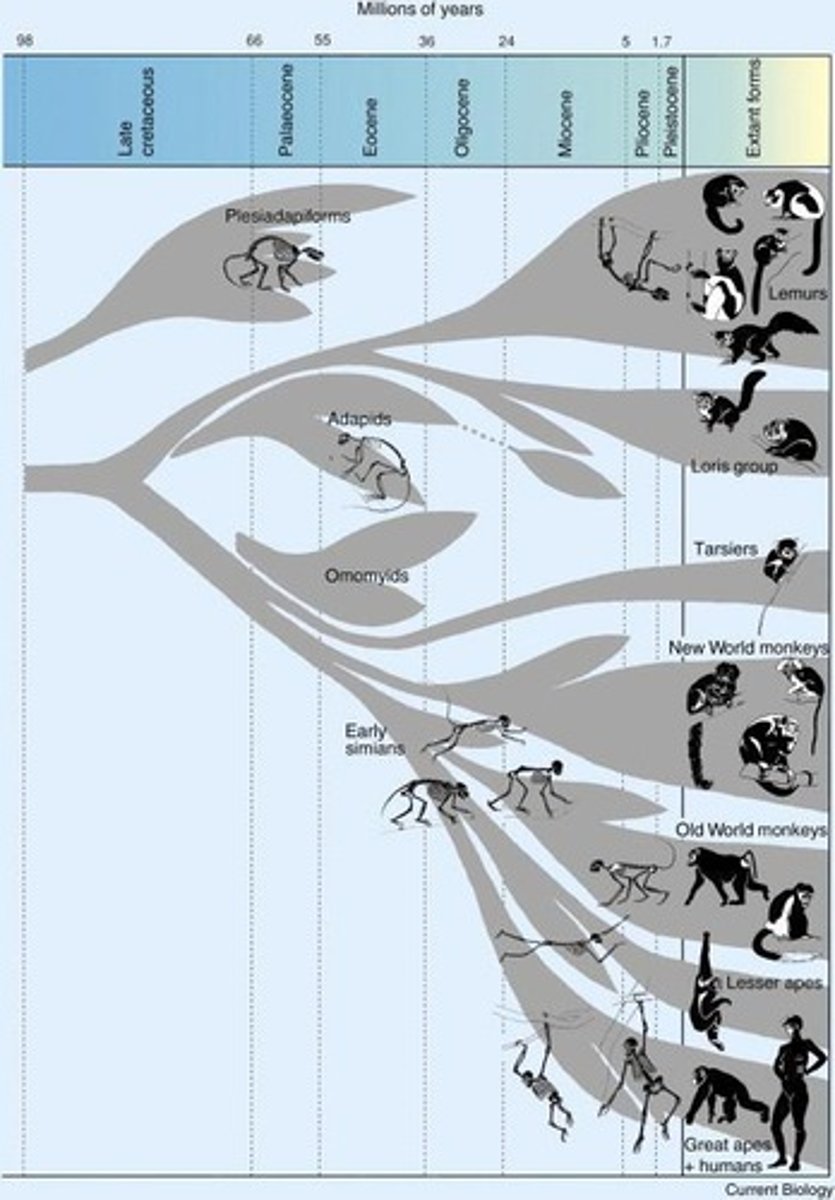
What are the three main groups of living primates?
Lemurs, tarsiers, and anthropoids (monkeys and apes).
What distinguishes humans from other apes?
Upright posture, bipedal locomotion, larger brains, tool use, and reduced jawbones.
What is bipedalism?
The ability to walk upright on two legs, supported by specific adaptations in the human skeleton.
What are some derived characters of humans?
Larger brains capable of language, symbolic thought, artistic expression, and a shorter digestive tract.
What is the relationship between chimpanzees and humans?
Chimpanzees and bonobos are the closest living relatives to humans, with a divergence occurring around 7 million years ago.
What is convergent evolution in marsupials and eutherians?
Geographically isolated marsupials and eutherians can look similar due to similar adaptations to their environments.
What are the evolutionary links between apes and Homo sapiens?
Hominins diverged from chimpanzees, with shared characteristics such as tool use and social behavior.
What evolutionary adaptations are seen in the skeletons of bipedal organisms?
Changes in pelvis and lumbar region shape to support upright posture.
What is the significance of mammary glands in mammals?
They produce milk to feed young, a key characteristic of mammals.
What are the ecological roles of mammals after the extinction of dinosaurs?
Mammals became the dominant vertebrates in terrestrial ecosystems, evolving into large predators, herbivores, and various other forms.
What adaptations do monotremes have for reproduction?
Females lack nipples and secrete milk from glands on their bellies; babies suck milk from their fur.
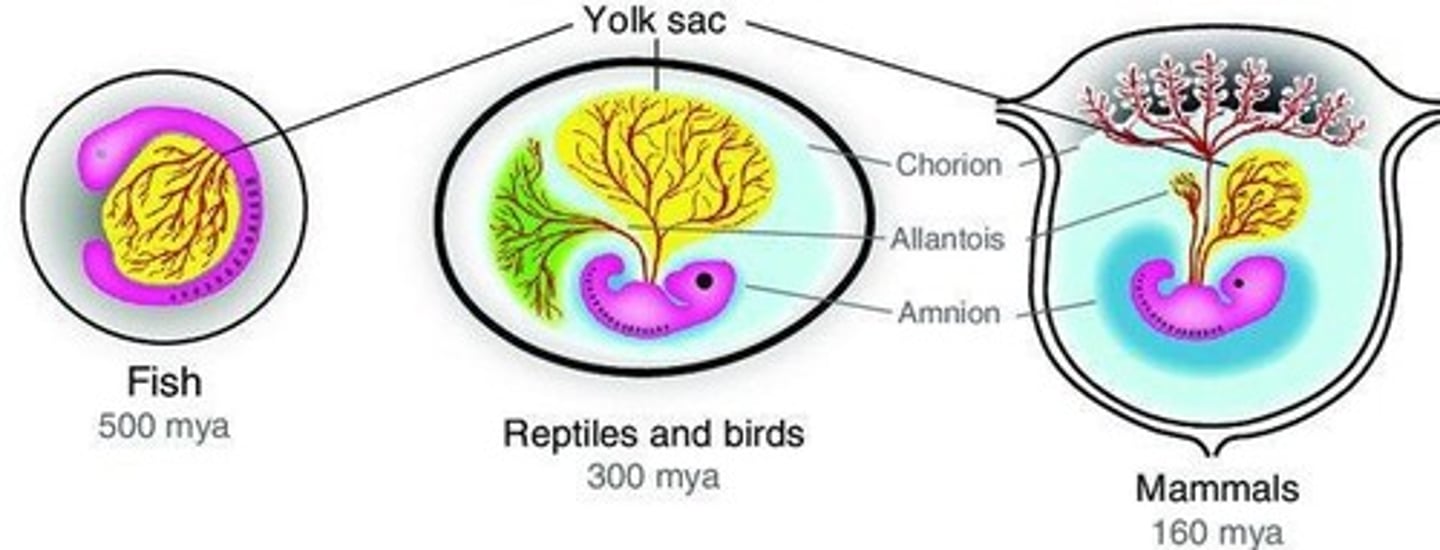
What are the extraembryonic membranes in mammals?
Yolk sac, amnion, chorion, and allantois, which support embryonic development.
What is the evolutionary history of marsupials?
Marsupials existed worldwide in the Mesozoic era but are now primarily found in Australia and the Americas.
What are the derived characters of marsupials?
Higher metabolic rates, nipples for milk, live young, and embryonic development in the uterus.
What is the significance of the mammalian skull remodeling?
It allowed for the development of a new jaw joint and adaptations for hearing.
What are the implications of having a high metabolic rate in mammals?
It supports endothermy and the ability to maintain body temperature in varying environments.
What role does parental care play in mammalian evolution?
Extensive parental care increases the survival rate of young, contributing to reproductive success.
How did mammals adapt after the extinction of dinosaurs?
They radiated into diverse forms, including large predators and various ecological niches.
What is the significance of the foramen magnum's position in human evolution?
The foramen magnum shifted forward, indicating bipedality.
How did the African climate influence early hominins?
Natural selection favored bipedality as the climate became drier and hominins inhabited open woodlands.
What are some derived characters of early hominins?
Shorter fingers, straighter phalanges, longer opposable thumbs, smaller teeth, and a flatter face.
How does human brain size compare to other primates?
The human brain is three times the size of other primate brains and five times the relative size of most mammalian brains.
When did Homo sapiens first arise?
Homo sapiens arose about 200,000 years ago.
What is the earliest known hominin species?
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, dating back to 6.5 million years ago.
What are the key traits shared by early hominins and modern humans?
Reduced canine teeth, relatively flat faces, and bipedalism.
What defines Australopiths?
A paraphyletic assemblage of hominins that lived between 4 to 2 million years ago.
Which Australopith is considered the earliest known?
Australopithecus anamensis, which lived 4.2 to 3.9 million years ago.
What are the characteristics of Homo habilis?
Known as 'handy man', they had shorter jaws and larger brains than Australopiths.
What adaptations did Homo ergaster have?
Fully bipedal, large-brained, with long slender legs adapted for long-distance walking.
What is notable about Neanderthals?
Homo neanderthalensis lived in Europe and the Near East and had a larger brain than modern humans.
What was the first hominin to migrate out of Africa?
Homo erectus, migrating out at least 1.8 million years ago.
What is the relationship between humans and Neanderthals?
Humans did not descend directly from Neanderthals; they share a common ancestor from about 600,000 years ago.
What evidence supports the recent African origin of Homo sapiens?
Paleontological and genetic evidence indicates anatomically modern humans arose in Africa around 200,000 years ago.
How did modern humans migrate out of Africa?
They migrated from East Africa roughly 70-50,000 years ago, spreading to Asia and Oceania.
What is a common misconception about human evolution?
That early hominins were chimpanzees; in reality, they share a common ancestor.
What does the evolutionary tree of humans indicate?
It is non-linear with many branches, not a direct ladder from ancestral apes to Homo sapiens.
What evolutionary traits link mammals to humans?
Inheritance based on nucleic acids, genetic code, and key traits accumulated through evolutionary time.
What adaptations do primates share that link them to humans?
Grasping hands/feet, opposable thumbs, improved depth perception, and large brains.
What is the significance of mitochondrial DNA in human evolution?
It indicates that humans are closely related to extinct Neanderthals and traces back to African populations.
What does hybridization evidence suggest about modern humans and Neanderthals?
There was extensive interbreeding, altering perceptions of Neanderthals and modern humans as distinct populations.
What does the term 'anatomically modern humans' refer to?
Homo sapiens that appeared between 150,000 and 250,000 years ago, very similar in appearance to modern humans.
What evolutionary changes have continued in Homo sapiens?
Changes in teeth, face, pelvis, hands, and brain size relative to ancestral hominins.