Bio FINAL MCQ PRACTICER
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Where on a hemoglobin does the O2 attach?
Heme group
C
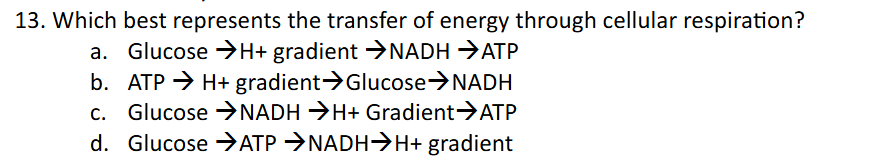
In what processes of cellular respiration is NADH produced?
Glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle

D

B
What types of amino acid sequence changes can mutations cause?
Redundant codon (no change), amino acid substitution, truncated protein (early stop), or frameshift from INDEL.
How can a mutation in a regulatory sequence affect gene expression?
It can alter transcription factor binding or the timing of polymerase action.
How can a mutation in the OCA gene's amino acid sequence affect the phenotype?
It can reduce the efficiency of the protein transporter, affecting melanin transport.
How can a mutation in a regulatory sequence affect P protein production?
A mutation in a transcription factor binding site can reduce P protein production.
What mutation causes reduced P protein in blue-eyed individuals?
A mutation in the HERC2 gene reduces the binding of a transcription factor, which lowers OCA2 expression.
In a heterozygote for the HERC2 mutation, how much P protein is expressed?
One copy produces a lot; the mutated copy produces a small amount of P protein.
Why is brown eye color dominant over blue?
One functional HERC2 allele produces enough P protein to allow melanin transport and brown eye color.
What pigments are present in green eyes?
Pheomelanin and possibly some eumelanin.
How did average human height change from 1810 to 1980?
It increased.
What are possible reasons for increased height from 1810 to 1980?
Various factors such as improved nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions.
Why might a multicellular organism need a cell to divide?
To grow, replace cells, or heal wounds.
Why might a cell be stopped from dividing?
If growth/healing is not needed or if DNA is damaged.
What proteins are needed for DNA replication?
DNA polymerase, topoisomerase, helicase, single-stranded binding protein, primase, DNA clamp.
How are replication proteins made?
Transcription factors recruit RNA polymerase to transcribe genes → mRNA is translated by ribosomes into proteins.
How does gamma radiation affect cell division?
It decreases the frequency of cell division.
Why is it beneficial to stop cell division after radiation exposure?
To prevent the spread of DNA damage by avoiding division of damaged cells.
How do P53 and P21 respond to radiation?
Their levels increase in response to radiation.
What type of protein is P53?
A transcription factor.
What type of proteins are E2F and RB?
E2F is a transcription factor; RB is a co-repressor.
What happens if P53 is mutated and can't bind DNA?
It won’t promote P21 transcription → P21 won’t dephosphorylate RB → RB won’t repress E2F → unchecked division.
In the gas/brake analogy of the cell cycle, what roles do P53, P21, and RB play?
They act as brake pedals.
What is the relationship between Myc and wounding?
Myc increases in response to wounding.
Does cell division increase or decrease after wounding?
It increases to help with wound healing.
How does Myc promote cell division after wounding?
By increasing cyclin and E2F expression.
In the gas/brake analogy of the cell cycle, what role does Myc play?
Myc is the gas pedal.
What happens if Myc is overactive due to mutation?
Cell division may occur even without signals, potentially leading to uncontrolled growth.