NS 1150 Exam 2
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cornell University NS1150 Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy can change forms but is neither created nor destroyed
Catabolic
Breaking down larger molecules into smaller one
Anabolic
Synthesis of smaller molecules into larger ones
Glycolysis
Breaking down of glucose into 2 pyruvate
Beta Oxidation
Breaking down of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA. remove 2 carbon units and generate electron carriers
Lipolysis
Breakdown of triglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol
Proteolysis
Breakdown of protein to amino acids
Gluconeogenesis
Glucose synthesis from noncarbohydrate sources
Glycogenesis
Formation of glucose
Lipogenesis
Synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides. Excess glucose are converted to fatty acids and then are combined with glycerol to form TGs and stored in fat cells
Catabolic & Anabolic reactions…
Can be coupled in a complex metabolic pathway to be able to do work
Adenosine Triphosphate
The energy that is released from the body during catabolic breakdown. Energy is stored between phosphate bonds.
Energy from ATP is used for…
Powering anabolic reactions
Acetyl CoA Routes
Synthesis of fats for storage (lipogenesis, anabolic pathway) or oxidative phosphorylation (generates ATP)
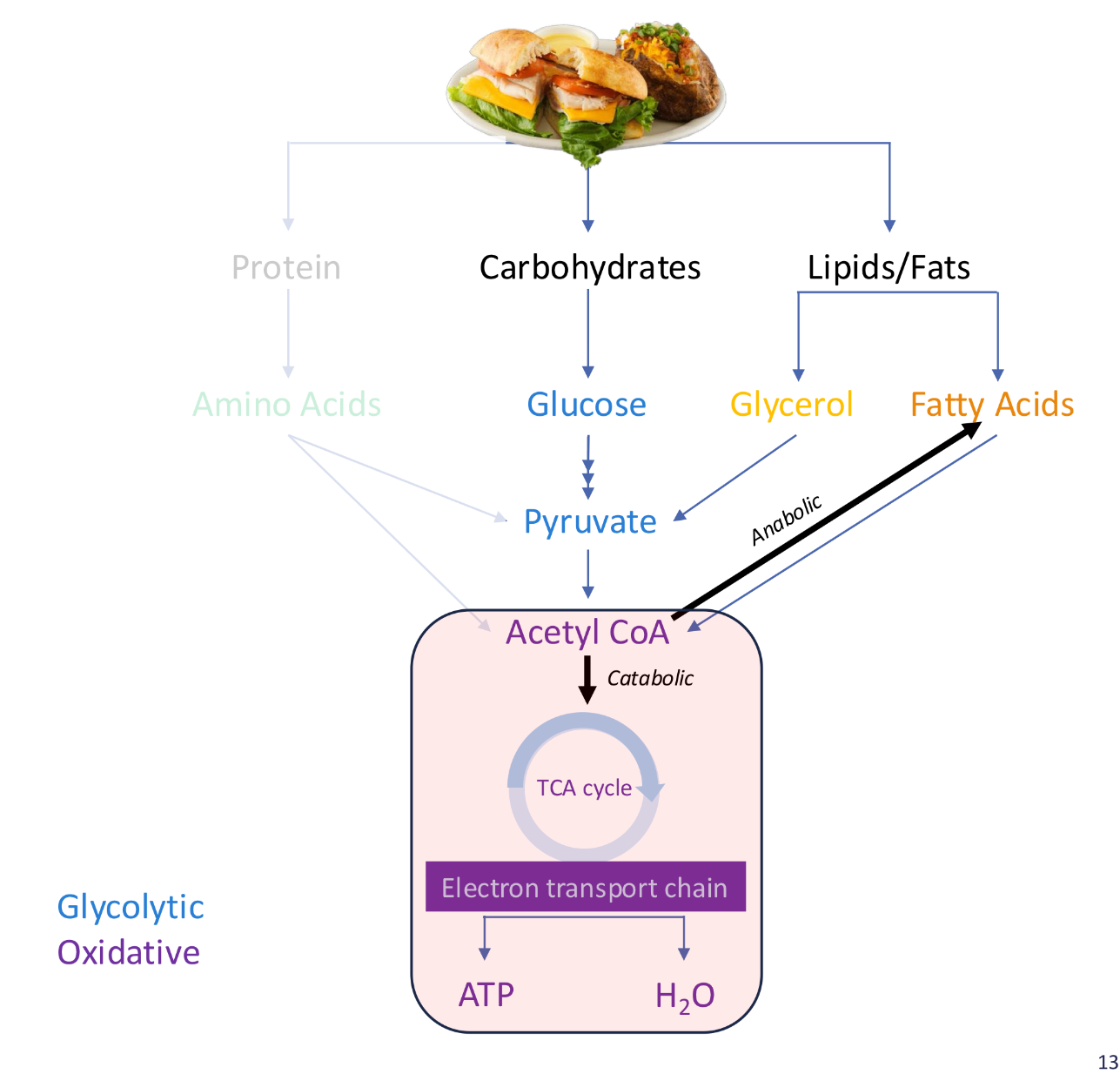
Glucose storage form
Stored as glycogen in the liver and muscle
Lipids/fats (free-fatty acids) storage
Stored as Triglycerides in the adipose tissue, muscle, and serum
Protein storage
Simple form is amino acids used in the muscles. Does NOT get stored for later use
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The primary source of ATP at rest and during steady exercise. Uses carbs and fats as substrates. In Mitochondria.
Mitochondria
TCA cycle and ETC. Inner compartment: pyruvate to acetyl CoA, fatty acid oxidation, TCA cycle. Inner membrane: site of ETC reaction
Aerobic glycolysis
CHO —> Glucose —> Pyruvate —> Acetyl CoA
Glycolysis (cytosol), Tricarboxylic acid cycle, ETC (mitochondria)
Aerobic Lipolysis
Fatty acids —> Acetyl CoA
TCA Cycle
Produces high-energy electron carriers (NADH, FADH2)
Oxidative System
Series of electron carriers mounted in the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane to the outer compartment of the mitochondrion
Oxidation of Fats: Aerobic Lipolysis
Fat is stored as triglycerides inside muscle fibers and in adipocytes within adipose tissue. Broken down into 1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids. Fatty acids must be converted to acetyl CoA to be used for energy.
Takes place in mitochondria matrix. Beta oxidation occurs.
Basal metabolic rate
energy needed to perform normal bodily functions (respiration, circulation, digestion). Can be increased with more muscle.
Thermogenesis
The energy cost of food processing (ingestion, digestion, absorption, transport, storage)
Physical activity
Body movement determining activity-induced
Direct Calorimetry
A bomb calorimeter is used to determine the E content of nutrients
Respiratory exchange ratio
CO2 made / O2 used
Simple sugars
Mono & Di Saccharides
Complex Carbohydrates
Oligo & Poly Saccharides
Monosaccharides
Single unit sugars that differ in their arrangement of atoms. Glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharides
Pairs of monosaccharides. Put together via condensation reactions and taken apart by hydrolysis
Oligosaccharides
3-10 monosaccharides. We cannot digest some but the gut bacteria can
Polysaccharides
Chains of monosaccharides, including glycogen, starches, and fiber. Made almost exclusively by glucose
What food sources are NOT a good source of carbs (CHO)?
Fats and animals
Glucose
Consumed as a component of disaccharides and polysaccharides. Is used as fuel, stored as glycogen, or converted to fatty acids and stored in adipose tissue
Galactose
found mostly in milk as part of lactose
Fructose
Occurs naturally in fruits and honey
Disaccharides
Sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), maltose (glucose + glucose)
Complex Carbohydrates
Starch, glycogen, fiber
Starch
Varying levels of amylose and amylopectin
Rich in plant products including gains, root crops and tubers, and legumes
Glycogen
Main storage of glucose for animals. Found in a limited extend in meats, not a significant source of CHO
Fiber
Structural components of plants that are indigestible by humans
Complex CHO
Grains, legumes, root vegetables.
Refined grains
Endosperm: starchy portion
Bran
fiber-filled outer layer
Germ
nutrient-packed core with vitamins and healthy fats
Endosperm
Starchy carb middle layer with some proteins and vitamins
High fructose corn syrup
Made from corn. Part fructose and glucose
Once consumed, fructose is…
Converted into glucose, glycogen, and/or fatty acids and is stored in the liver. Excess fructose can lead to health concerns
Salivary amylase
breaks down starch in the mouth
pancreatic amylase
breaks down starch in the small intestine
Maltase
breaks down maltose to the monosaccharide glucose
Sucrase
breaks down sucrose to the monosaccharide glucose and fructose
Lactase
Breaks down lactose to glucose and galactose
Enterocytes
Absorptive cells where monosaccharide absorption across intestinal wall occurs
Functions of carbohydrates
use excess glucose to make glycogen when blood glucose is high
decreases gluconeogenesis
prevents protein catabolism
Recommended dietary intake for CHO
45-65% DRI
130g/day. Added sugar should be no more than 25% of total kcals
Fiber DRI
Not set due to insufficient data
AI: 21-25 female, 30-38 male
Dental cavities
sugar can contribute to dental decay. Also drinks with sugar and low pH
Nutrient deficiencies
Added sugars contribute to nutrient deficiencies by displacing nutrients
Obesity
Syndromic Forms
Non-syndromic Forms
biological and social factors.
Syndromic: chromosomal rearrangements, pleiotropic
Non-syndromic: polygenetic, monogenetic
GLUT
14 in the body
Primarily facilitate glucose transport via facilitated diffusion
GLUT4 receptors are the most abundant of the GLUT receptors
Pancreas
primary player in glucose homeostasis
produces key hormones
Acinar cells, pancreatic juice 95%
Islet of Langerhans: hormone producing cell 2.5%
liver
stores and releases energy
Insulin/Beta cells
promotes energy storage
serves as a signal for rapid transfer of GLUT4
Glucagon/Alpha cells
promotes mobilization of stored energy
Glucose homeostasis after a meal
blood glucose levels increase, releasing insulin
insulin enables glucose transporters to take up glucose from the blood into cells
insulin promotes the formation of glycogen in the liver and the conversion of excess glucose into fat for storage
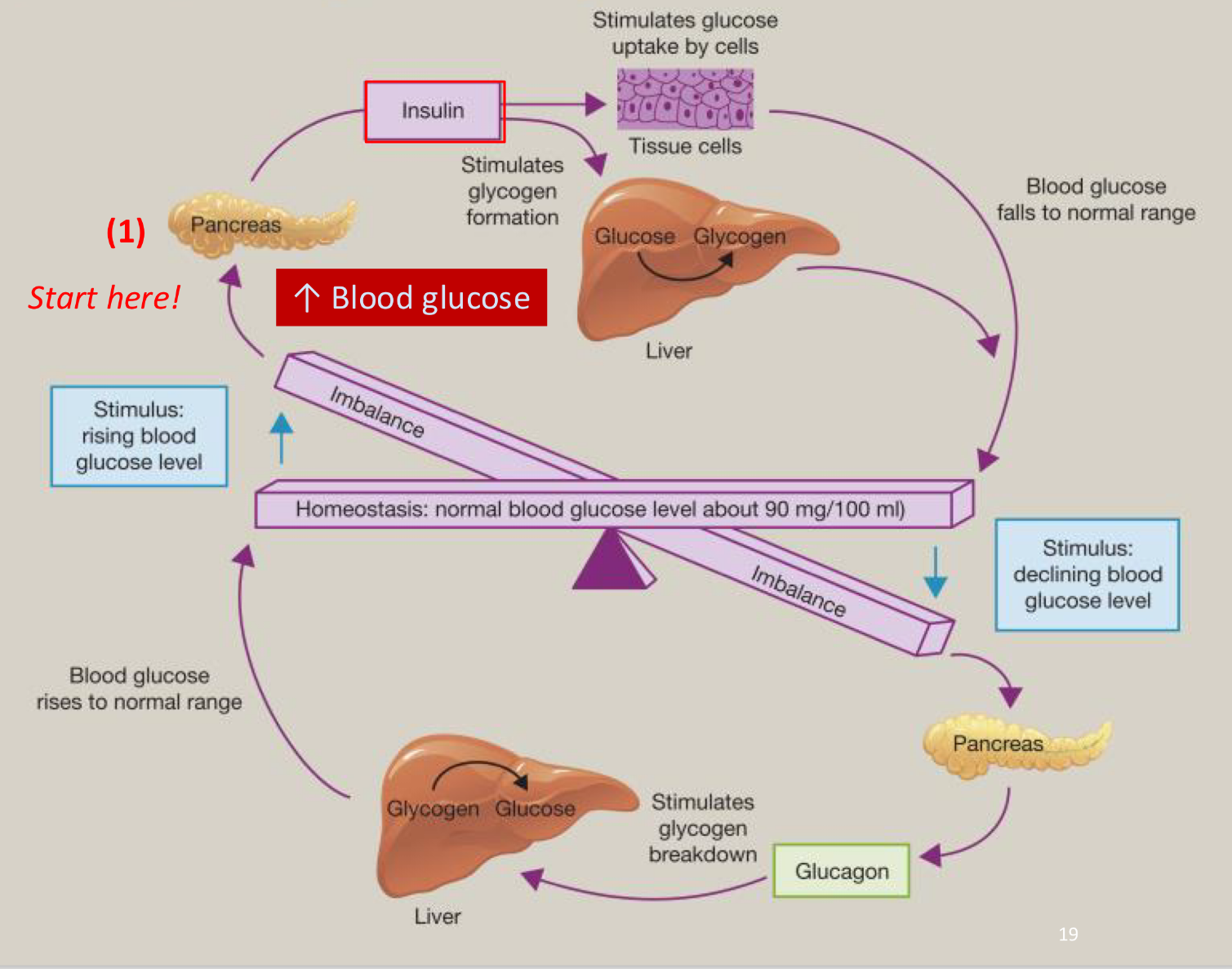
Glucose homeostasis in between meals
low blood glucose stimulates the release of the hormone glucagon from the pancreas
glucagon stimulates the breakdown of glycogen in the liver and the release of glucose into the blood
Diabetes
Elevated levels of glucose in blood, hyperglycemia
Causes of T1D
autoimmune disease
destruction of pancreatic beta cells leading to failure to produce and secrete insulin
Causes of T2D
chronically elevated levels of blood glucose can lead to increased insulin production but receptors are not responsive. insulin resistance
Complications of Diabetes
cells produce sugar alcohols and glycoproteins
Structure of blood vessels and nerves becomes damaged, loss of circulation and blood flow
Diagnosing diabetes
Hemoglobin A1C: avg blood sugar levels over past months
GTT: blood sugar before and after glucose drink
Recommendations for preventing diabetes
whole foods, fiber rich, non-starchy vegetables, minimize added sugars, lose weight, limit saturated fat, 2 or more servings of fish per week, limit alcohol intake
Fatty acids
Most abundant lipid
composed of CHO
Omega CH3 end *left
Alpha COOH end *right
Short chain fatty acid
2-5 carbons, predominant
Medium chain fatty acid
6-12 carbons
Long-chain fatty acid
more than 12 carbons
Saturated fatty acid
SOLID at room temp
ALL single bonds
Unsaturated fatty acid
LIQUID
monounsaturated: One DB
Polyunsaturated: many double bonds
Cis Unsaturated fatty acid
H atoms are positioned on the same side of the double bond
LIQUID at room temp
Trans Unsaturated fatty acid
H atoms on opposite sides of DB
SOLID at room temp
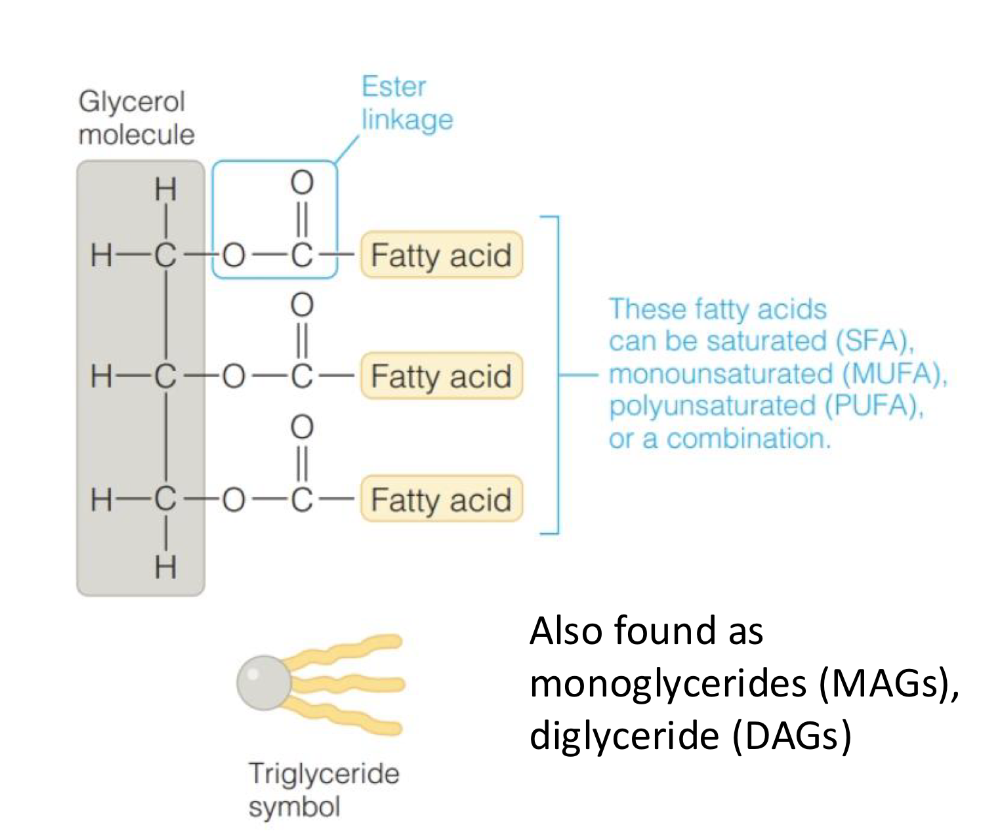
Triglycerides
Primary dietary lipid and a major source of energy
composed on 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids bound together via ester linkages
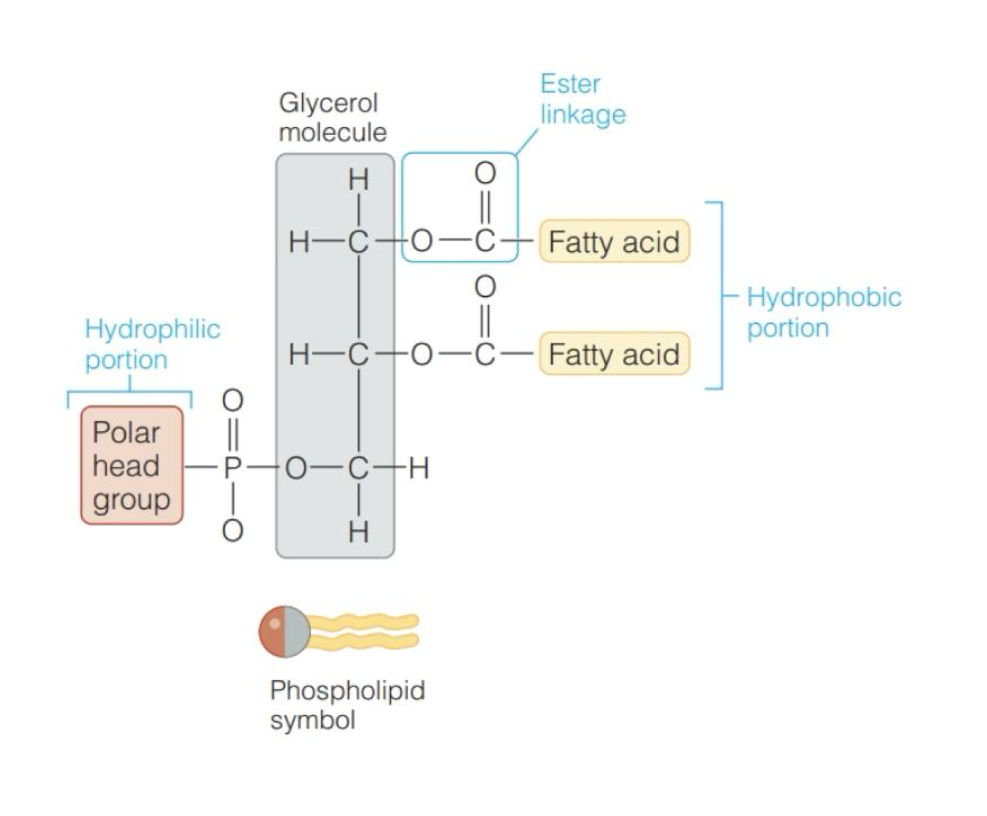
Phospholipids
Found naturally in most foods
Composed of 1 glycerol + 2 FA bound via ester linkages
Phosphate-containing a polar head group
Amphipathic molecules
Sterols
Lipids with multi-ring structures
Cholesteroyl ester
Can be synthesized endogenously
Needed to synthesize bile acids and steroid hormones
Digestion and absorption of lipids
TGs are broken down into monoglycerides
Form micelles
Absorb to enterocytes
MAGs back into TAGs then packed to chylomicrons

Lipoproteins
Chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL
Transport lipids
Apoproteins
Proteins associated with lipoproteins, play a key role in the transport of lipids
Lipid absorption
Chylomicrons transport diet-derived lipids from the small intestine via the lymph system
Lipid transport
As chylomicrons circulate the blood, they encounter Lipoprotein Lipase which is found within capillaries of adipose, liver, and muscle tissue. LPL stimulates TG into FA to enter the cells
Low Density Lipoproteins LDL
BAD
transports cholesterol
deposit cholesterol into the blood vessels
High Density Lipoproteins HDL
GOOD
Removes cholesterol
Main functions of lipids
Energy reservoirs, prevent protein catabolism, insulation and protection, structural components, hormones
Lipid metabolism after a meal
Increase insulin, decrease glucagon
Insulin stimulates lipogenesis
Lipid metabolism in between meals
Decrease insulin, increase glucagon
Glucagon stimulates lipolysis
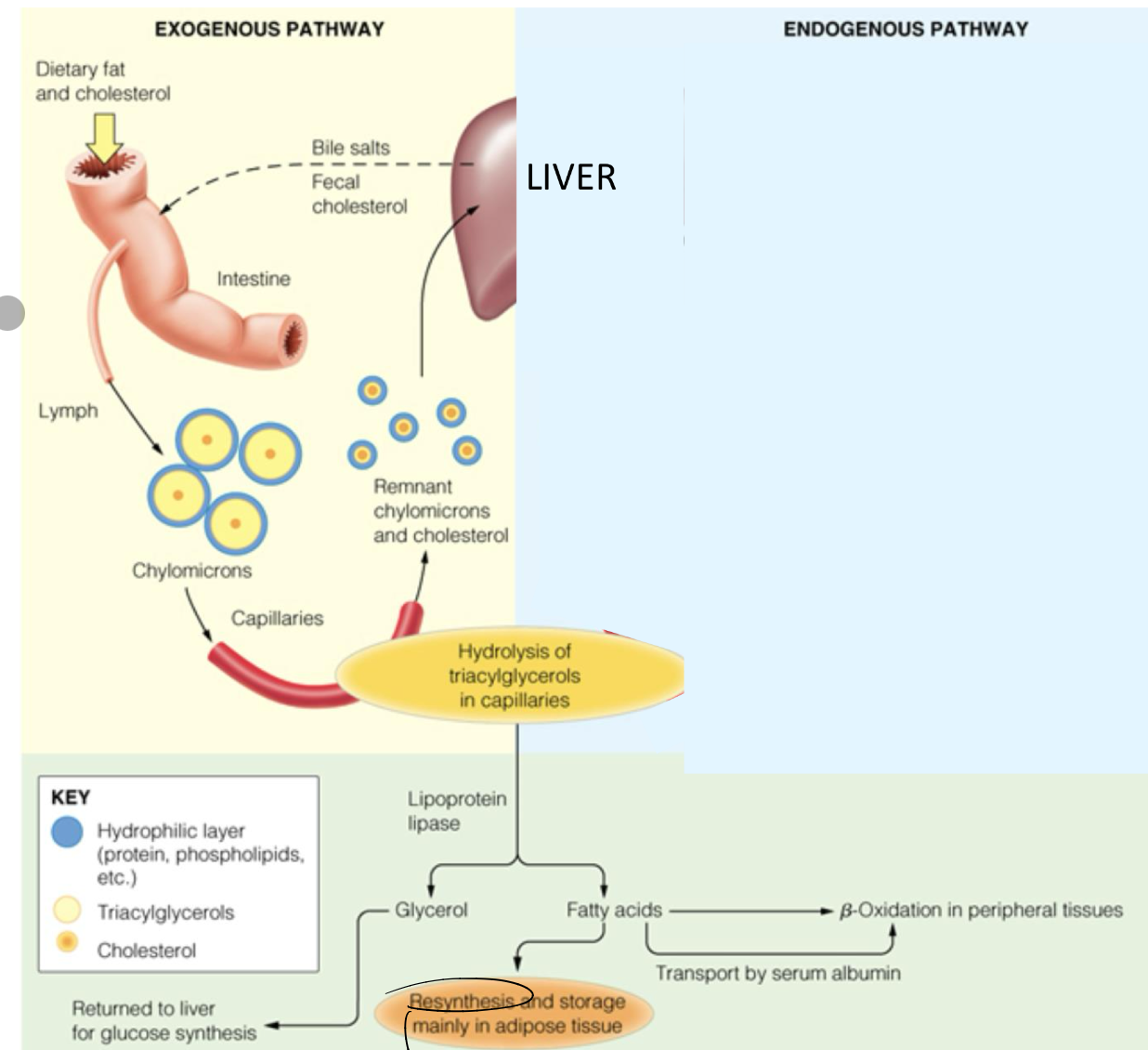
Exogenous pathway lipids after a meal
The exogenous pathway refers to the process by which dietary lipids are absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, incorporated into chylomicrons, and transported to tissues for utilization or storage.
Digestion occurs in SI, aided by bile salts and pancreatic lipases, which emulsify fats and break them down into fatty acids and monoglycerides.
FFA are absorbed by enterocytes and re-esterified and packed into CM
CM released into lymph capillaries and eventually into the blood stream
Endogenous pathway in a post-absorptive state
Start at the liver
Newly synthesized FA arrive from extrahepathic tissues
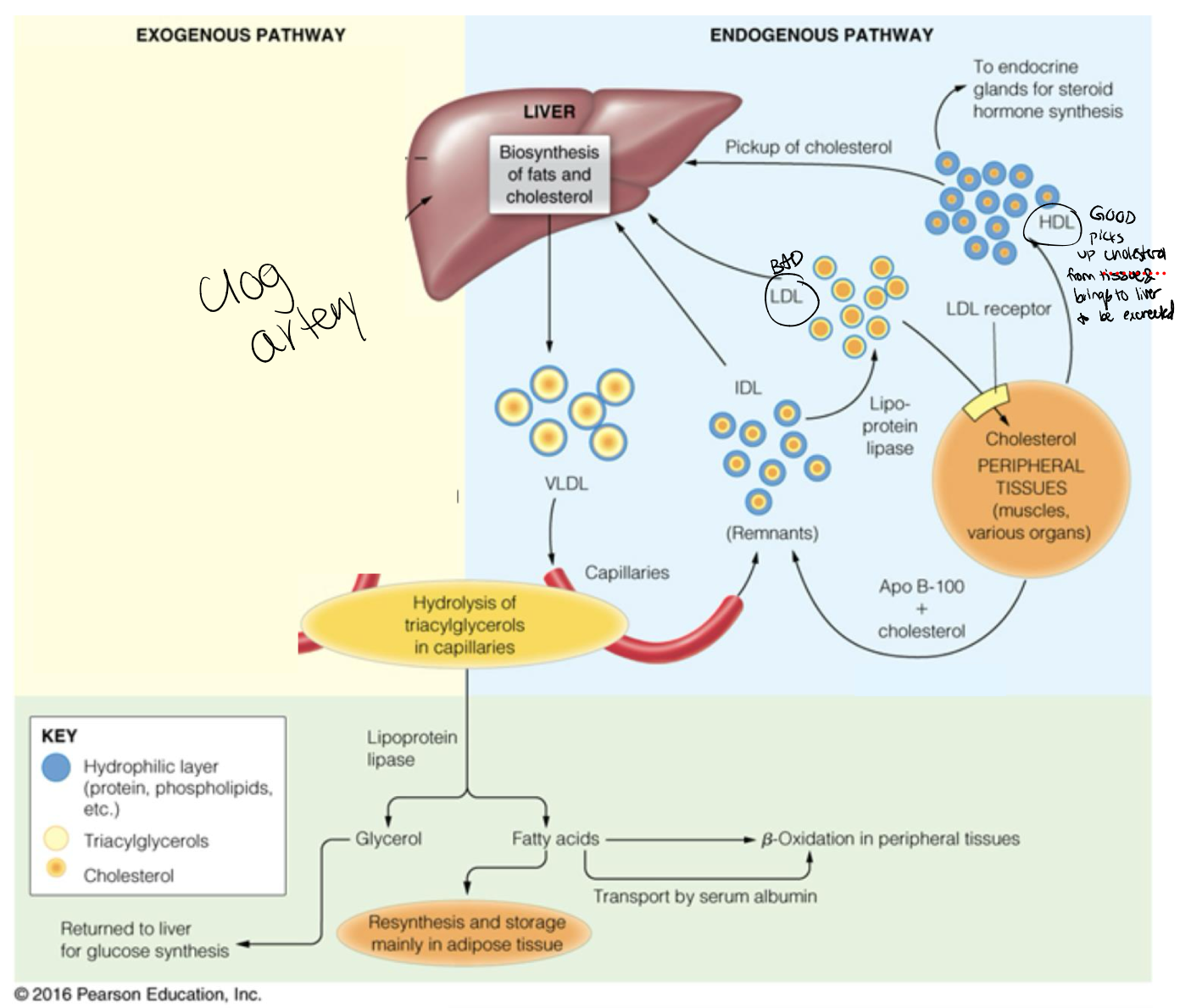
Reverse Cholesterol pathway/HDL purpose
Lipoprotein form in both the liver and small intestines
Transports cholesterol esters from peripheral tissues to the liver, converted to bile