Pulmonary Infectious Disease
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is pneumonia?
inflammation of the lungs where the air sacs are filled with pus and may become solid
What are the types of pneumonia?
community acquired, hospital acquired, ventilator associated
What is community acquired pneumonia?
acquired outside the hospital setting or develops in the hospital within 48 hours of admission
What is Nosocomial pneumonia?
Development of pneumonia > 48 hours after admission
What are the most common pathogens in nosocomial pneumonia?
Pseudomonas or MRSA
What is ventilator acquired pneumonia?
Pneumonia that develops more than 48 hours after endotracheal intubation (ET tube)
What pathogens are responsible for bacterial pneumonia?
Strep pneumonia, H.flu, Klebsiella, and Staph aureus
Pulmonary exam findings of typical bacterial pneumonia
Dullness to percussion, increased tactile remits, ego phony, and crackles.
Workup of pneumonia
CBC w/diff, CMP, Sputum gram stain, sepsis workup, possibly bronchoscopy
What is the GOLD standard for diagnosing pneumonia?
Infiltrates on CXR
Klebsiella pneumonia is most common in
alcoholics and patients with chronic disease (DM)
what will the sputum in Klebsiella pneumonia look like?
purple colored
What is the CURB-65 score?
estimates mortality of CAP to determine appropriate disposition (discharge or admit)
0-1 CURB-65 score OR 0-2 expanded CURB-65
Outpatient
2 CURB-65 score OR 3-4 expanded CURB-65
Inpatient
3+ CURB-65 score OR 5-8 expanded CURB-65
ICU
Aspiration pneumonia is most common in the
right lower lobe
Which type of pneumonia has foul smelling sputum?
aspiration pneumonia
Wheezing heard in the lungs is described as
whistling
Rhonchi heard in the lungs is described as
rattling typically deeper than wheezing
Crackles heard in the lungs is described as
bubbly, caused by fluid buildup
who has a high risk for viral pneumonia
pregnant women, elderly, young children, and immunocompromised
What is the most common cause of viral pneumonia?
influenza virus
What is the most common cause of viral pneumonia in infants and children?
RSV
Physical exam findings of viral pneumonia?
Tachypnea, crackles, intercostal retractions, dullness to percussion, and pleural friction rub.
workup for viral pneumonia
CBC, CMP, PCR viral panel, cytology, respiratory bio fire panel
what is the most common type of atypical pneumonia
mycoplasma pneumonia "walking pneumonia"
Mycoplasma pneumonia most often affects
young, healthy people
Physical exam findings of Mycoplasma pneumonia
Conjunctivitis, oropharyngeal inflammation, and bulbous myringitis (in the eardrum but rare)
What is the most common CXR finding in mycoplasma pneumonia
reticulonodular patterns
What causes Legionella pneumonia?
contaminated water or air conditioner units.
Who is at the greatest risk for Legionella pneumonia?
immunocompromised, smokers, elderly, and chronic lung disease
Physical exam findings of Legionella pneumonia
AMS, fever >102, water non-bloody diarrhea, localized crackles.
Nosocomial legionella has up to ___% mortality
50%
What causes histoplasmosis pneumonia?
contamination from soil containing bird or bat droppings
Physical exam findings of histoplasmosis pneumonia
blood diarrhea, fever, ulcers, adrenal insufficiency
What is influenza?
Flu
This is a virus that invades the airway and respiratory tract
what is acute bronchitis
inflammation of bronchi due to upper airway infection
"common cold"
what is the most common cause of acute bronchitis?
Influenza A/B and rhinovirus
A patient comes in with a cough that has lasted more than 5 days. Chest wall tenderness. Sore throat. Congestion. What do you suspect the patient has?
Acute bronchitis
True or false?
Fever is an unusual sign in acute bronchitis.
True
What would be the significance of order a CXR when you suspect acute bronchitis
Used to exclude pneumonia
What are the types of acute respiratory failure (ARF)
hypoxemic, hypercapnic, and mixed
What is acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Acute, diffuse inflammatory form of lung injury and respiratory failure. Onset within hrs to a few days
ARDS is most common in
critically ill patients
What is the most common causes of ARDS
sepsis*, pneumonia, and aspiration of gastric contents.
A patient has new onset respiratory failure, new radiographic pulmonary opacities, and impaired oxygenation (PaO2 >80mmHg). What do you suspect the patient has?
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Symptoms of ARDS
Acute dyspnea, hypoxemia, and multiorgan failure
Workup of ARDS
CXR or CT, CBC, CMP, BNP, EKG, ABG
(Patient is very sick, so lots for labs will need to be done).
Diagnostic criteria for ARDS
- hypoxemia that does not improve with supplemental O2
- infiltrates on CXR
- PF ratio <300
What is prone position
lying on stomach
what are the most specific labs/tests for Histoplasmosis?
Sputum or blood cultures
Who has an increased risk for severe cases of Influenza virus?
Pregnant women in 2nd and 3rd trimester
Clinical history of influenza
Abrupt onset of nausea, high fever/chills, body aches, HA, and worsening cough
Why do we avoid the use of aspirin to treat symptoms in children?
Reye syndrome, which can lead to hepatorenal failure and brain swelling
Rales indicate disease beyond
bronchi
What are potential cough suppressants that can be used in the treatment of acute bronchitis?
- Dextromethorphan (Robitussin)
- Guaifenesin (Mucinex)
True or False?
Patients with acute bronchitis do not experience benefit from ABX treatment
True
What is hypoxemia respiratory failure
Failure of the lungs and heart to provide adequate O2 to meet metabolic needs
what is hypercapnia respiratory failure
failure of the lungs to eliminate adequate CO2
Describe the process of ARDS
Damage to alveoli and their capillaries, leading to impaired O2 and CO2 exchange
What would you find on a CXR that will differentiate ARDS from heart failure?
In ARDS, the costophrenic angles are spared from the collecting edema.
The lower the PF ratio in ARDS, the _____ the mortality rate
higher
What intervention should be used in patients with ARDS to prevent atelectasis?
Prone position
When is it appropriate to use ECMO in a patient with ARDS?
This is saved for the most severe patients who do not improve with traditional ventilation.
"salvage option"
What does SARS-CoV-2 stand for?
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
What are risk factors of SARS-CoV-2?
- close contact with confirmed cases
- traveling in ares with incidence
- comorbidities
- immunocompromised
Incubation period of SARS-CoV-2
2-14 days
What are the variants of SARS-CoV-2
alpha, delta, omicron
How would you describe a mild case of COVID-19?
no dyspnea, sore throat, fatigue
How would you describe a severe case of COVID-19?
dyspnea, RR >30/min, hypoxia
How would you describe a critical case of COVID-19?
respiratory failure, shock, and multiorgan dysfunction
What is Long COVID?
Sx persisting > 4 weeks PLUS evolving sx
What are COVID toes?
thought to be an immune response to COVID, where the toes swell, become red, and the skin blisters possibly turning purple
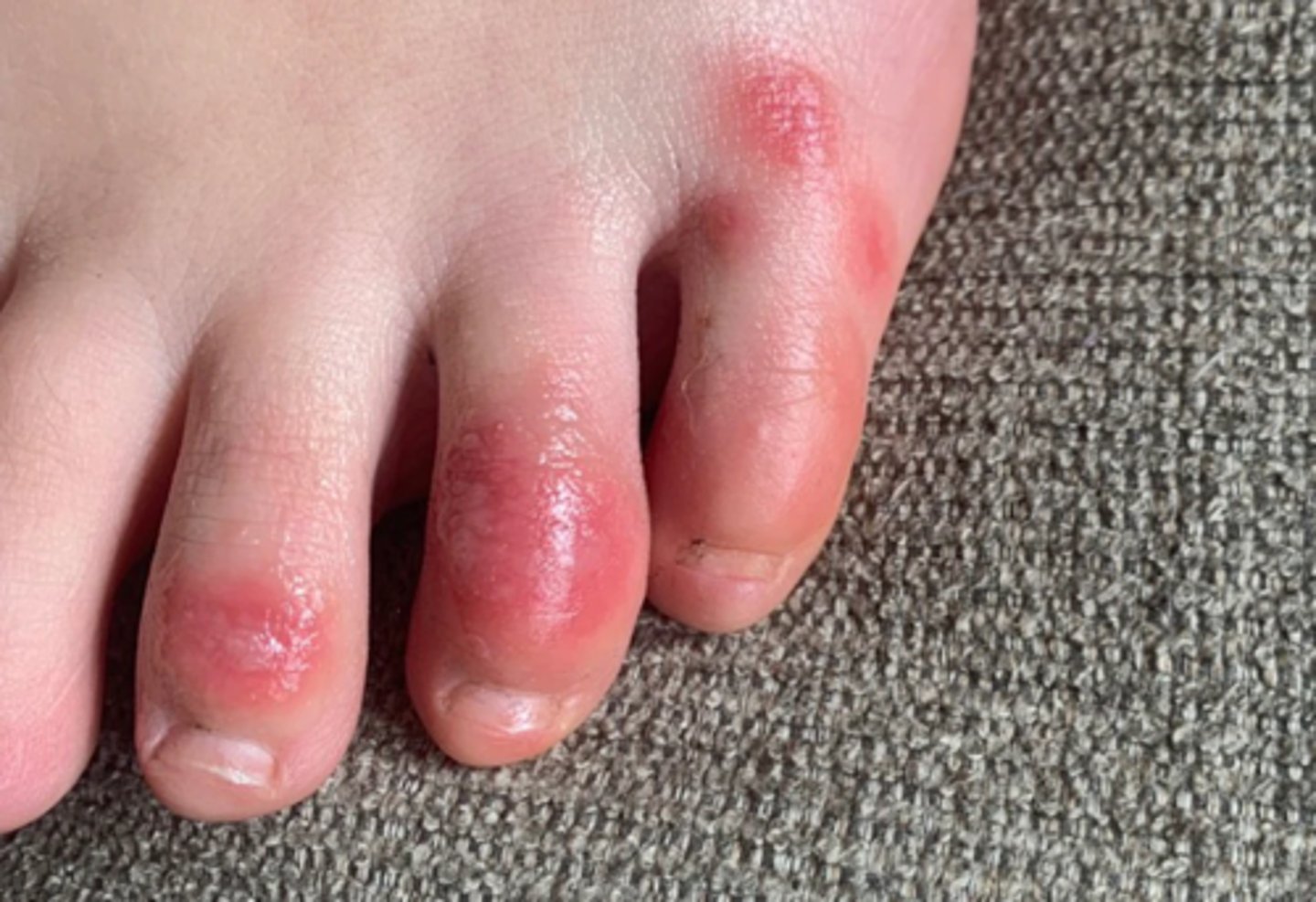
When would it be indicated for a patient with COVID to be admitted to the hospital?
- Hypoxia, SaO2 <94%
- If they need O2 ventilatory support.
Which variant of SARS-CoV-2 has the highest mortality rate?
Alpha variant
What is Tuberculosis?
Pulmonary infection caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis
If a patient has tuberculosis, who do you report that information to?
The health department
What is a characteristic finding of TB on imaging?
tiny tubercles/nodules
What is latent TB?
The patient is asx, cannot spread TB, and if it is not treated it can turn into active TB.
What is active TB?
The patient can spread the disease, they feel very ill, and can be treated.
What are symptoms of tuberculosis?
Unexplained weight loss, night sweats, and hemoptysis.
Why is it important to obtain a pregnancy test in female patients you suspect have TB?
B/c the drugs used to treat TB are NOT safe for fetus
What is the workup for tuberculosis?
Sputum AFB culture
What reading of a PPD/TB skin test is suggestive that the patient may be positive for TB?
10-14mm
What reading of a PPD/TB skin test is a for sure positive TB?
>15mm
What do you need to monitor during tuberculosis treatment?
Renal function, liver enzymes, vision changes, hearing changes.