2.3.1 & 2.3.2 Short Run Supply
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Define aggregate supply
The total volume of goods and services that producers are willing and able to supply at a given price and a given price level.
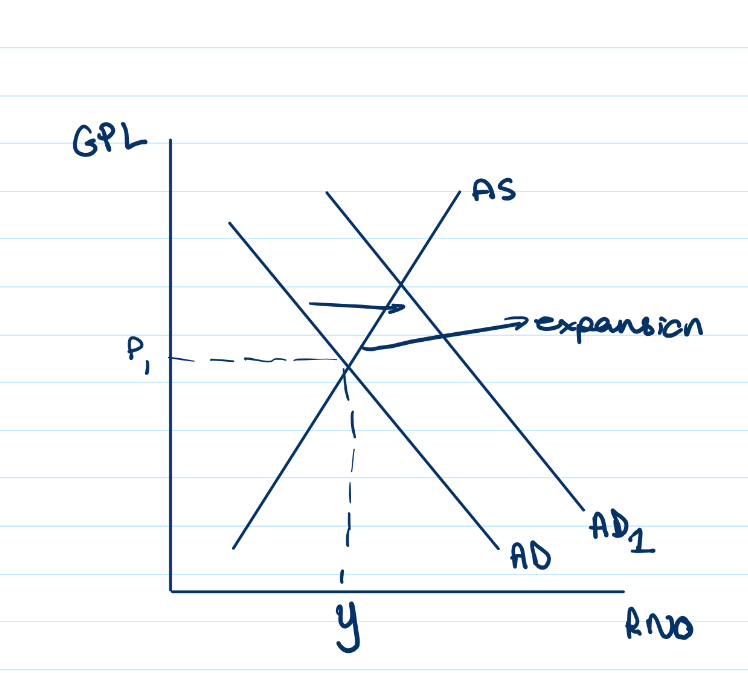
Draw what an aggregate supply curve would look like following an increase in aggregate demand
An increase in aggregate demand means outward shift in the AD curve
Leading to an expansion along the supply curve
Because the price of the product increase - so supply expands
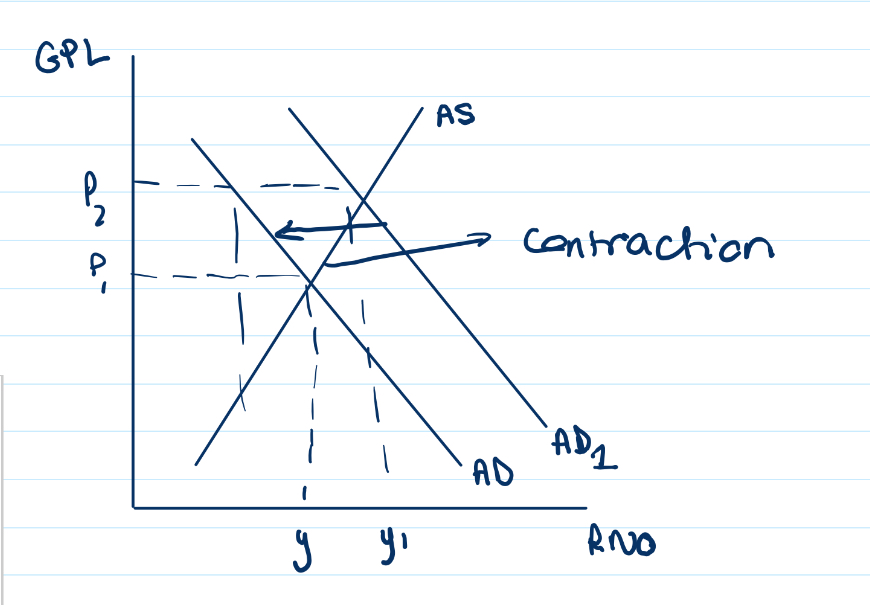
Draw what an aggregate supply curve would look like following an decrease in aggregate demand
An decrease in aggregate demand means an inward shift in the AD curve
Leading to a contraction along the supply curve
Because the price of the product decreases - so supply contracts
What does the gradient of a short run aggregate supply curve depend on?
The amount of spare capacity in the economy.
If there is lots of spare capacity
Define long run aggregate supply
The maximum output when all factors of production are fully and efficiently used (similar to a PPF)
Draw and label what a short run aggregate supply curve would look like when an expansion occurs
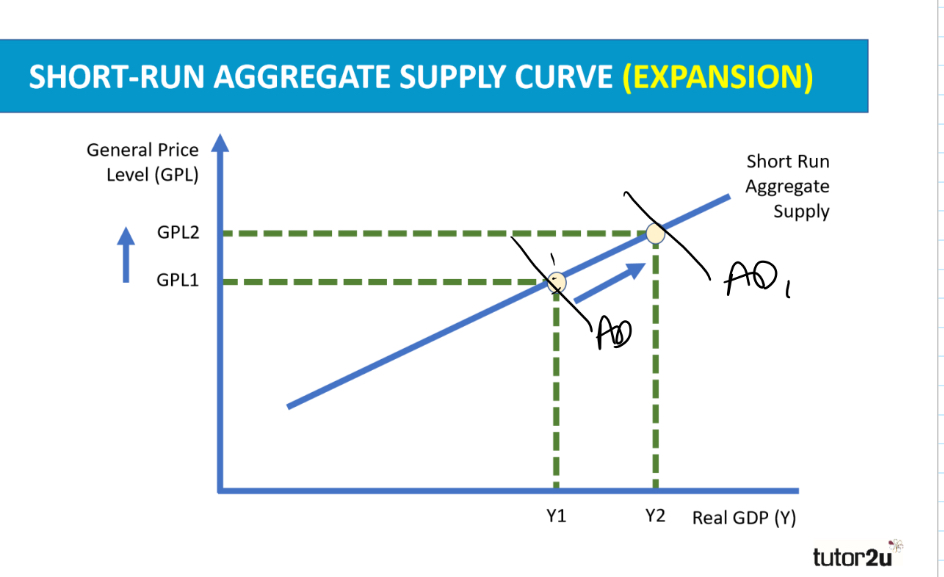
What stimulus an expansion in supply? Why?
Rising demand and prices,
Because producers are assumed to respond to the profit motive when the market demand is increasing, and the general price level is rising.
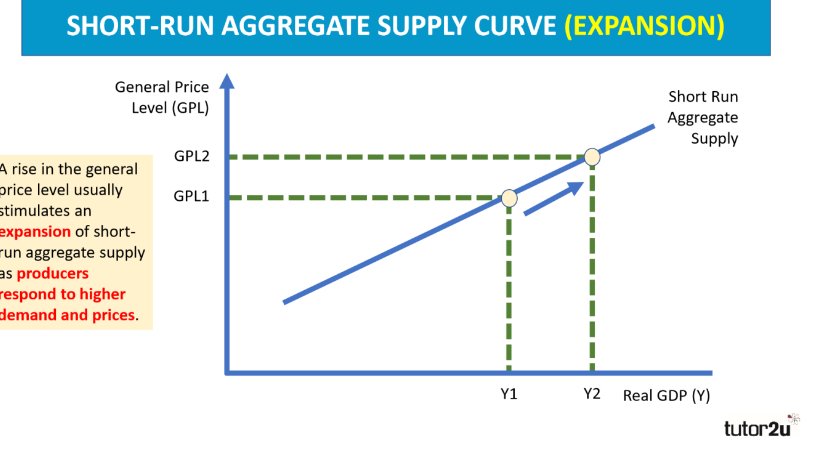
What does a rise in the general price level stimulate in a short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve? Draw this
an expansion in SRAS
as producers respond to higher demand and prices
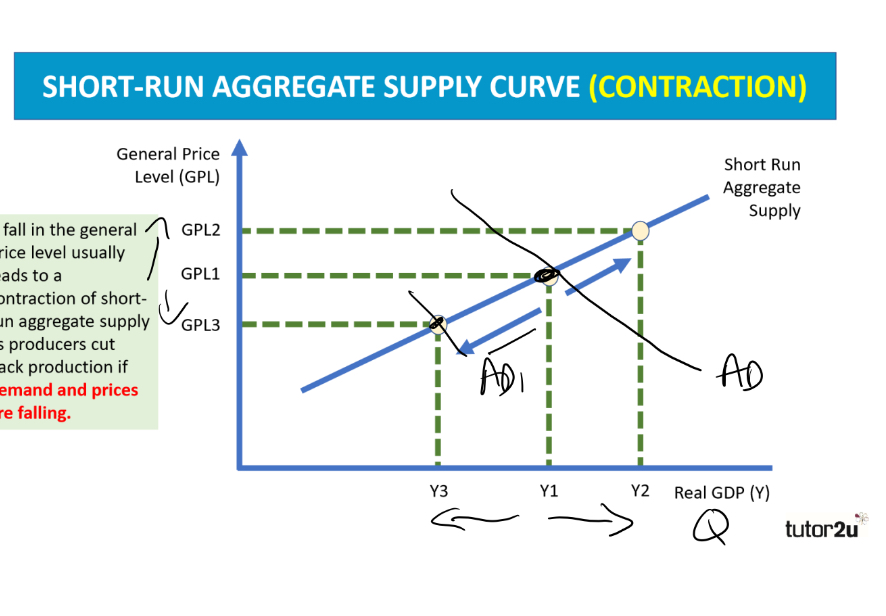
What does a fall in the general price level stimulate in a short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve? Draw this
a contraction in the SRAS curve
as producers cut bascule production if demand and prices fall
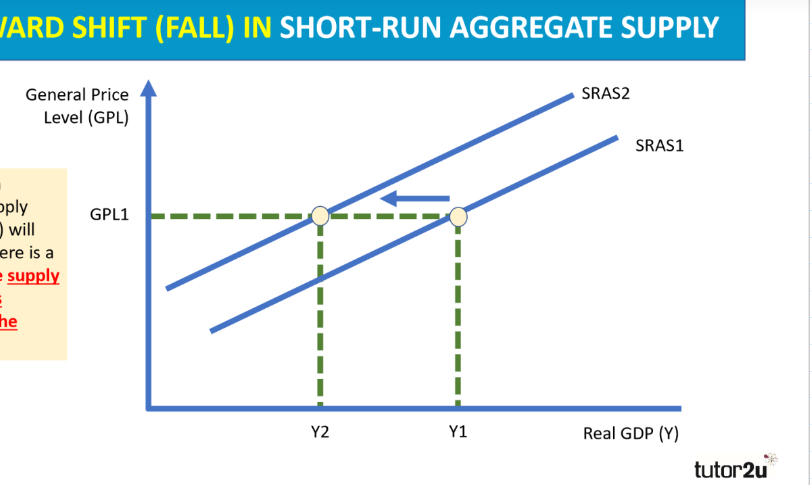
What effect does an increase in the SUPPLY costs for firms throughout the economy has on a short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve? Draw this
causes an inward shift in SRAS
because less can be produced at every price level
What effect does a decrease in the SUPPLY costs for firms throughout the economy has on a short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve?
outward shift in SRAS
because more can be supplied at every price level
Define costs of production
How much it is to produce goods / services. i.e wages, rent, raw materials
What effect will a stronger UK pound have of SRAS
A strong pound will lead to:
a fall in production costs
So an outward shift in SRAS
What if the acronym for the strength of the pound?
SPICED
S- strong
P- pound
I- imports
C- cheap
E- exports
D- dear (expensive)
If the government increase national wages by 10% what effect will this have on SRAS?
increased cost of production (due to higher wages)
so an inward shift SRAS
If the government increase national minimum wages by 4% and labour productivity rises by 10% what effect will this have on SRAS?
Will decrease costs of production
So will result in an outward shift/ increase in SRAS
If the UK leaves the EU without a trade deal and the UK imposes average tariffs of 11% on EU imports what effect will this have on SRAS
cost of production will increase
so SRAS will shift inwards/ decrease
If the government cuts a subsidy paid to UK farmers what effect will this have of SRAS?
cost of production will increase
so SRAS will decrease/ shift inwards
If there is a rise in the global price of raw materials imported into the UK economy what effect will this have on SRAS?
cost of production will increase
so SRAS will decrease/ shift inwards
What are the 6 factors which cause shifts in SRAS - explain them
unit wage costs (perhaps rising from higher minimum wage)
Labour productivity (increased efficiency lowers the unit costs of supply)
key raw material and components prices (e.g glass, cement, rubber) and energy costs (such as oil, gas, electricity & renewables prices
Business indirect t taxes, substantial, VA, environmental & employment taxes
Cost of imported materials (affected my movements in a country’s exchange rates + fluctuations in global prices)
supply shocks (e.g a hurricane, impact of drought, flooding or political crisis, impact of a lockdown because of a public health crisis)
How would the following affect SRAS:
Increase in price of raw materials
Decrease in price of energy
Appreciation of the £
Depreciation of the £
Increase in direct taxation
Increase in government subsidies
Inwards shift/ decrease in SRAS
Outward shift/ increase in SRAS
Outward shift/ increase in SRAS
Inward shift/ decrease in SRAS
Inward shift/ decrease in SRAS
Outward shift/ increase in SRAS
What is indirect tax?
Taxes on expenditure (goods and services)
E,g VAT , sugar tax, tobacco tax
What is direct tax?
Taxes on income. E.g income tax (on individual workers), corporate tax (on firms)
What is a supply shock?
A unexpected event that changes the cost of production for firms, causing the SRAS curve to shift.
Supply-side shocks affect short run aggregate supply and can also affect a country’s long run productive potential.
give some examples of supply shocks
strong rises in oil and gas prices or other commodities used in production
Political turmoil/ civil u rest/ major strikes
Supply shut-downs caused by a public health crisis
Natural disasters causing a sharp fall in production
Unexpected breakthrough in production technology (example of favourable supply shock)
What is the difference between SRAS and LRAS?
The SRAS curve is upward sloping because firms can increase output in the short term by using existing factors of production more intensively.
Whereas the LRAS curve is vertical at the economy’s potential output because, in the long run, all factors of production are variable.
What is the relationship SRAS between and LRAS?
SRAS shows the output fluctuations based on short-term cost changes,
whereas LRAS indicates the maximum sustainable output determined by the quantity and quality of the economy’s resources and technology