Nervous System test review (A&P)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
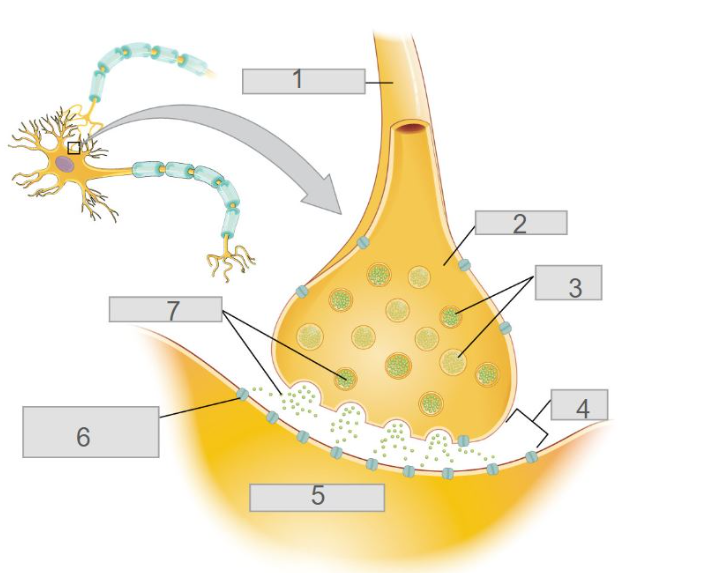
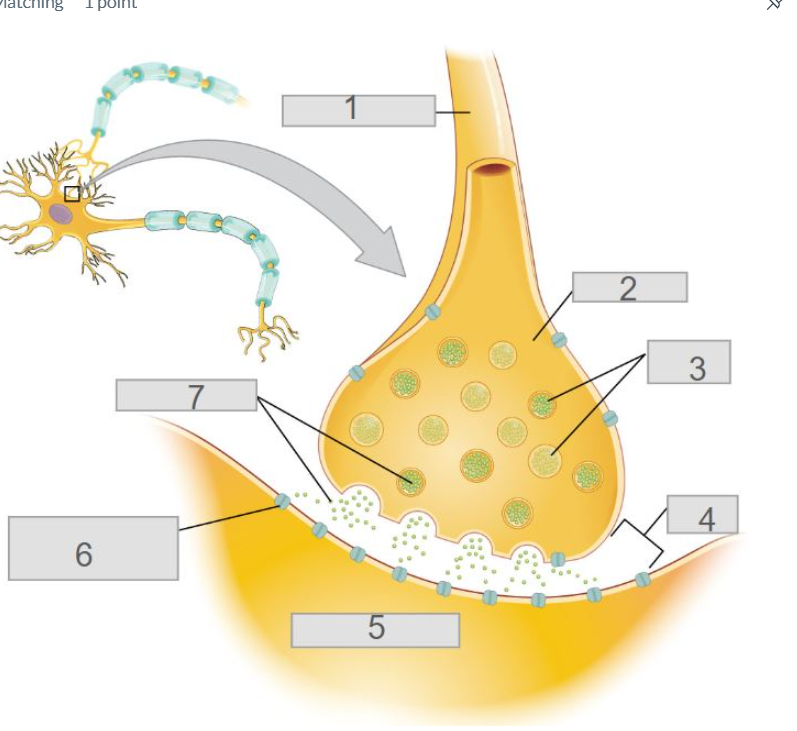
3
synaptic vessicles
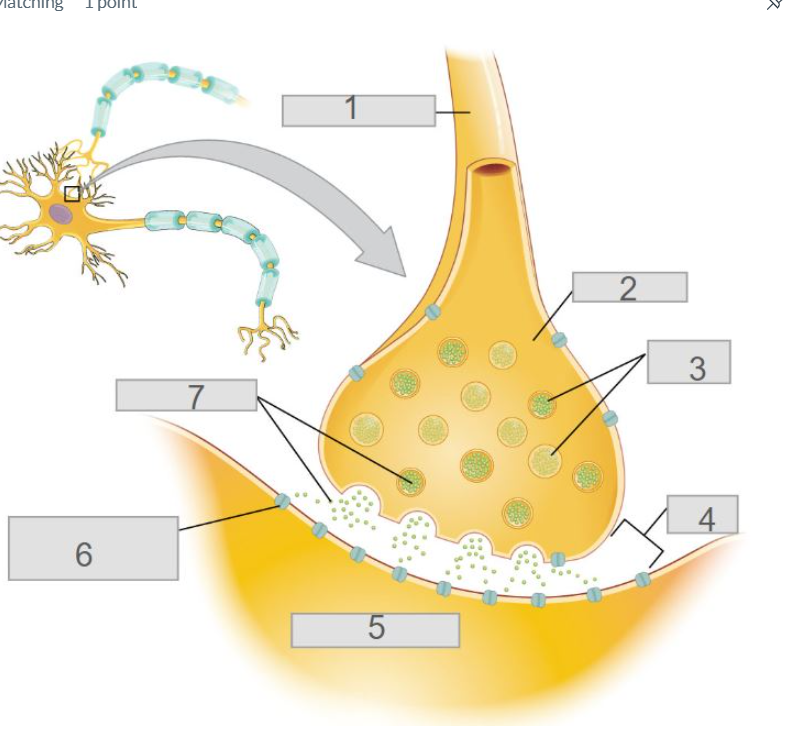
6
ligand-gates channels w/ receptors for neurotransmitters
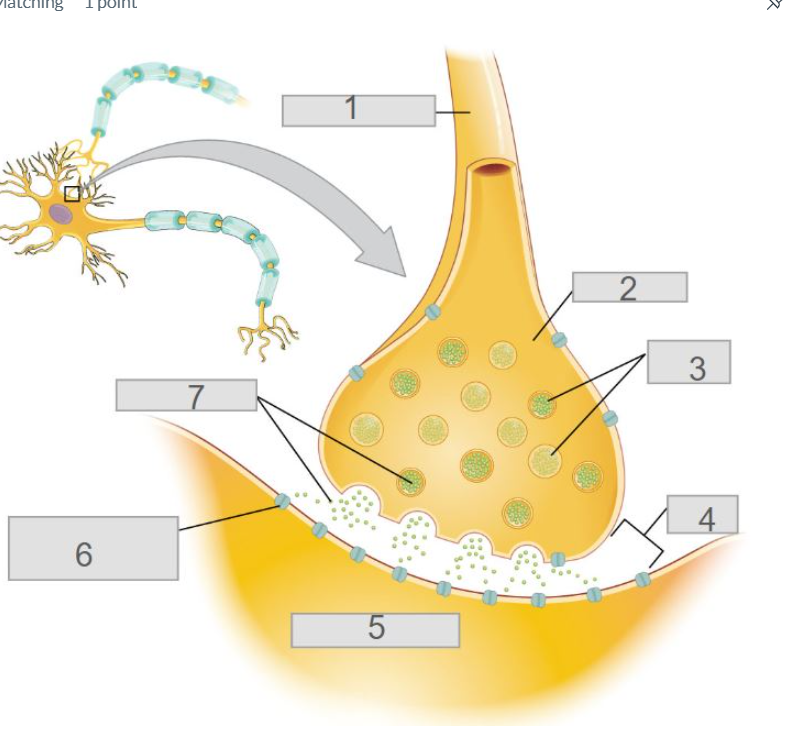
4
synaptic cleft
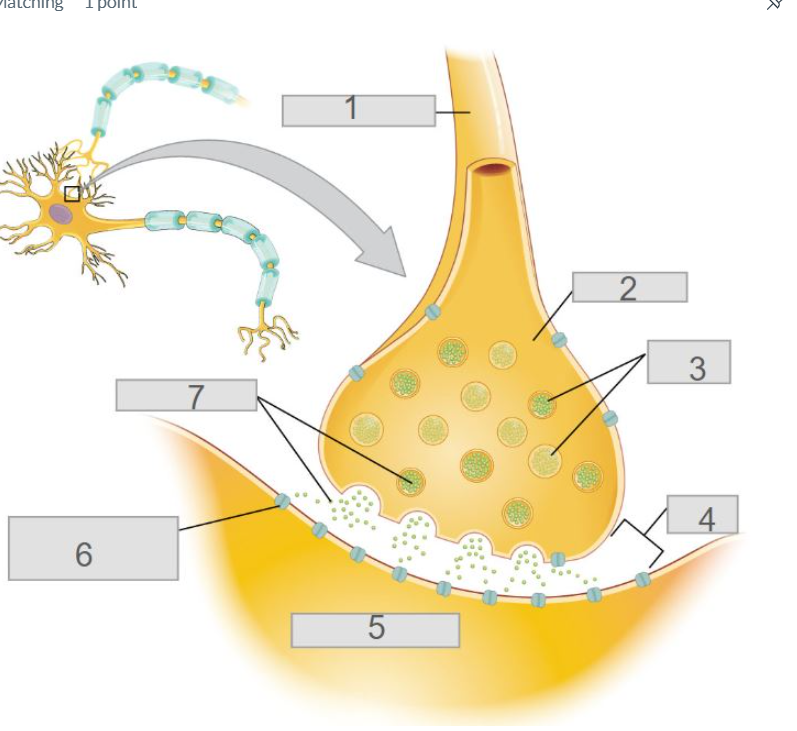
5
post-synaptic neuron
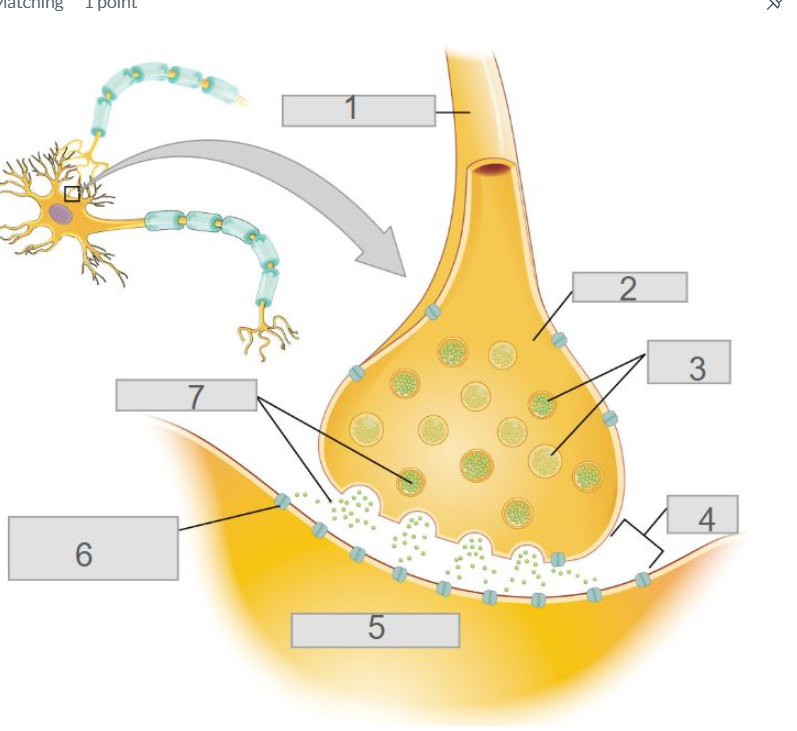
2
axon terminal
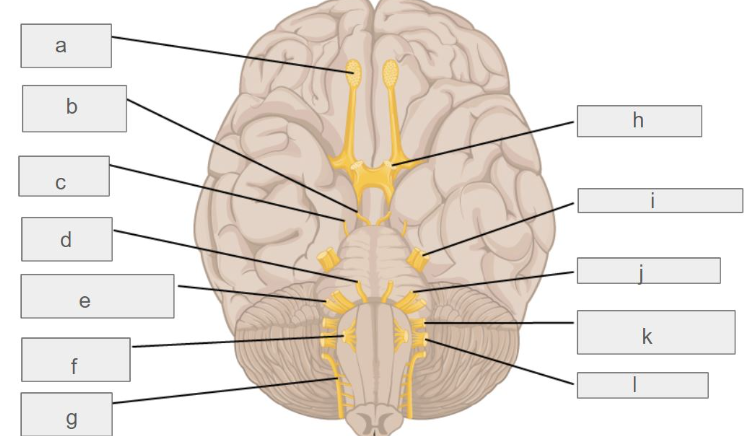
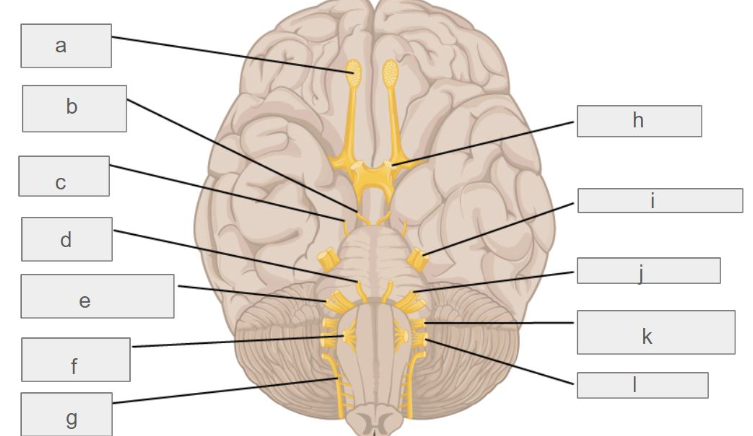
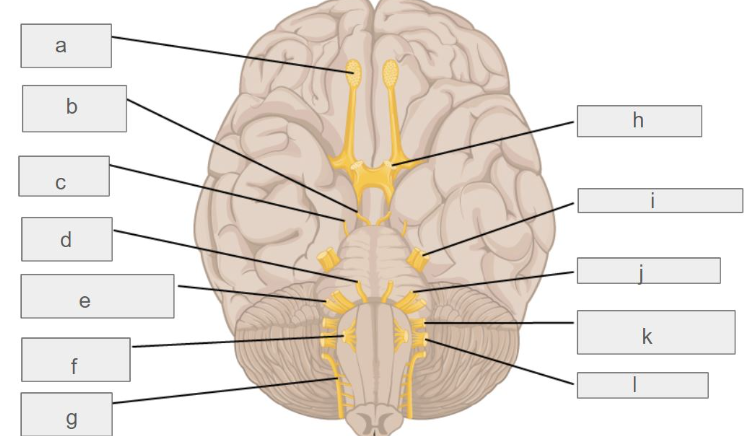
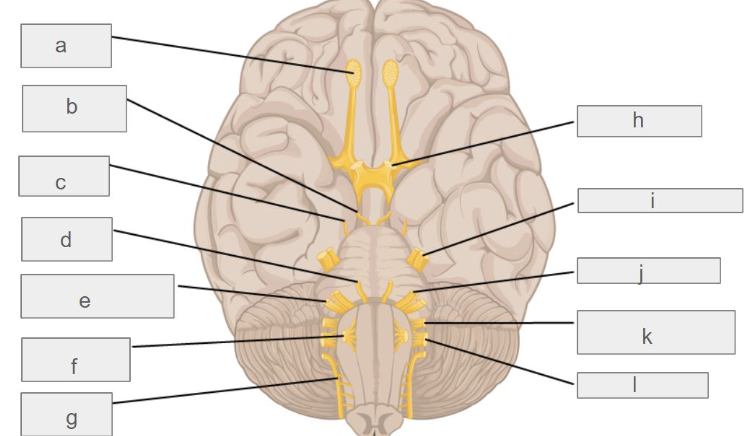
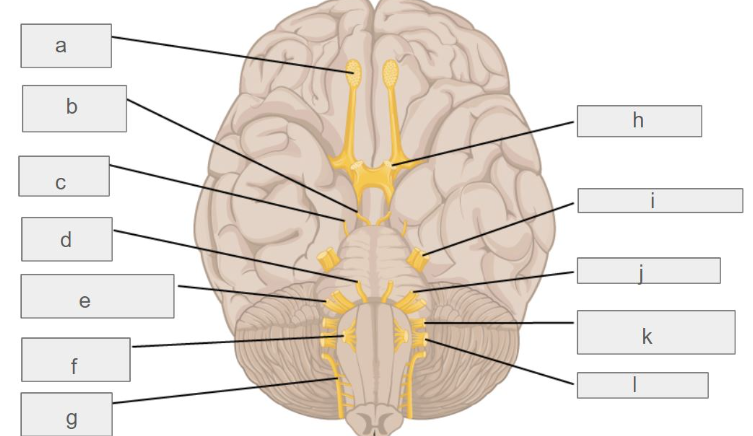
g
accessory nerve
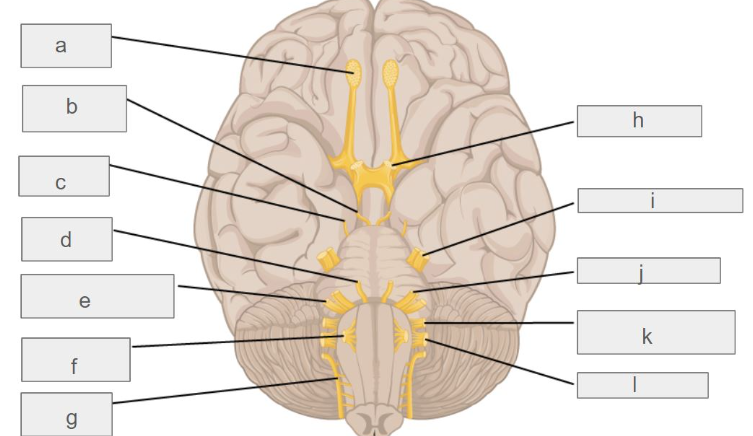
c
trochlear nerve
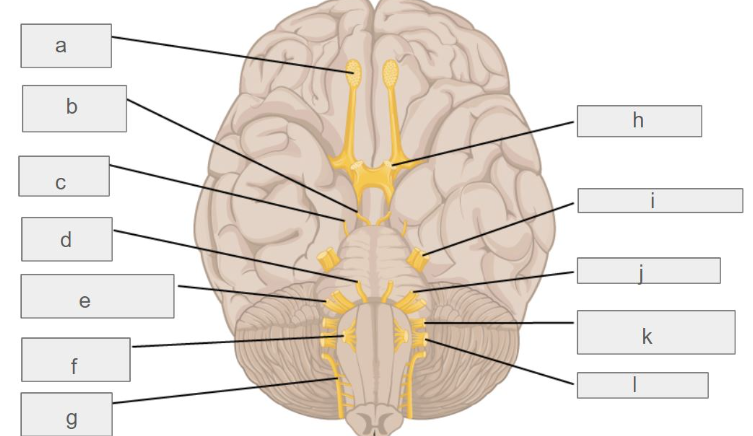
l
vagus nerve
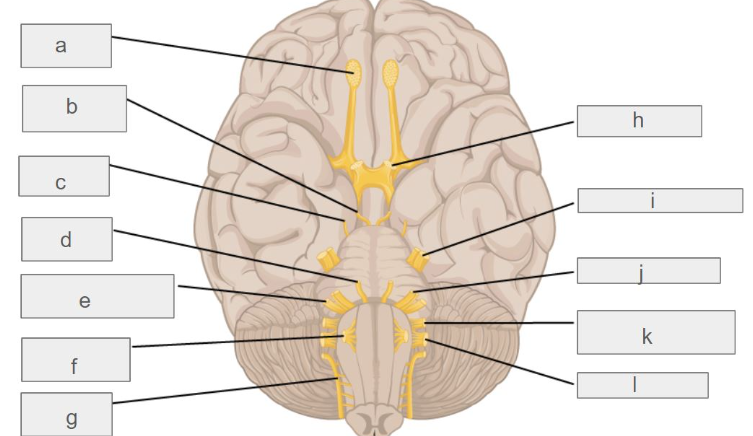
d
abducens nerve
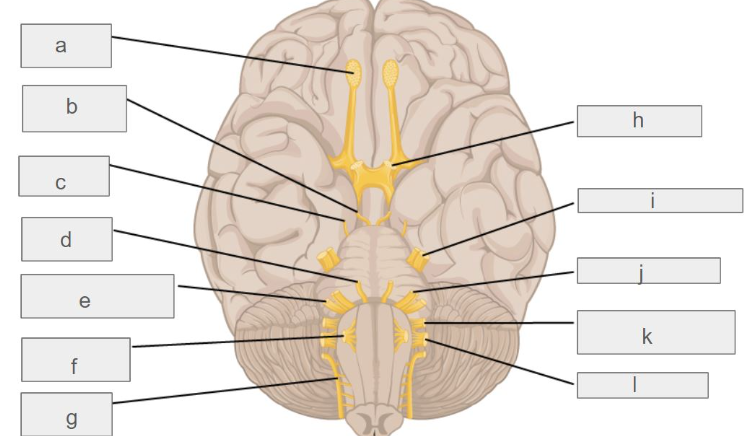
i
trigeminal nerve
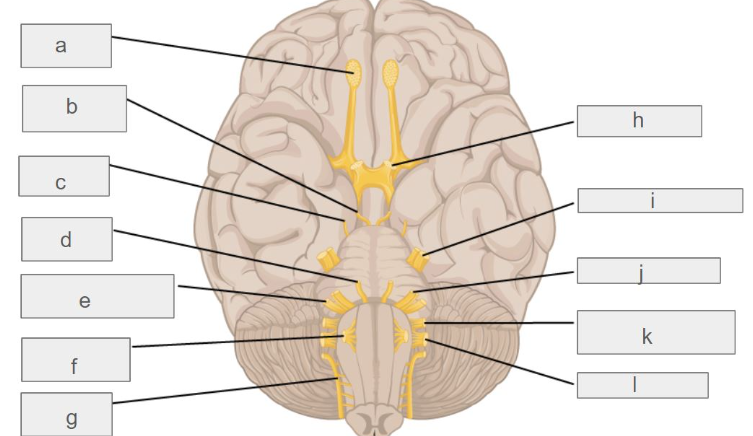
k
glossopharyngeal nerve
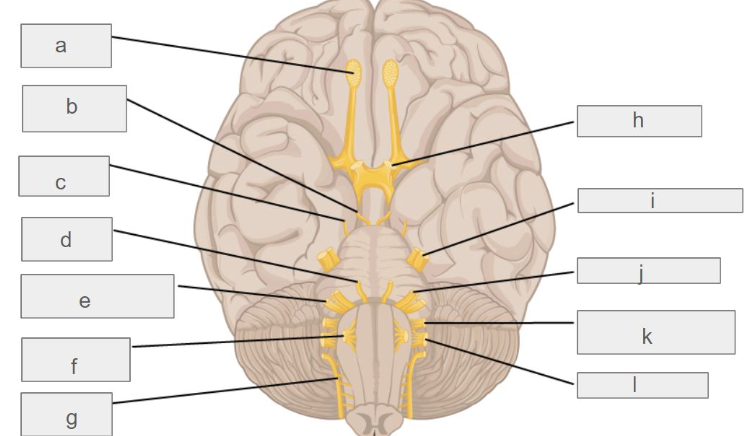
e
vestibulochlear nerve
f
hypoglossal nerve
b
oculomotor nerve
h
optic nerve
j
facial nerve
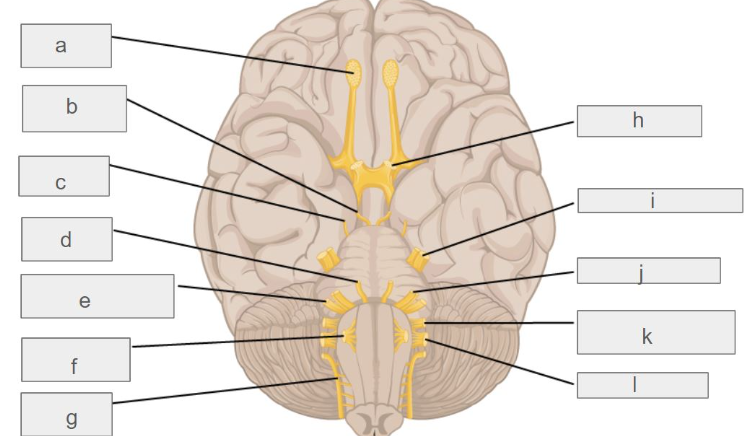
a
olfactory nerve
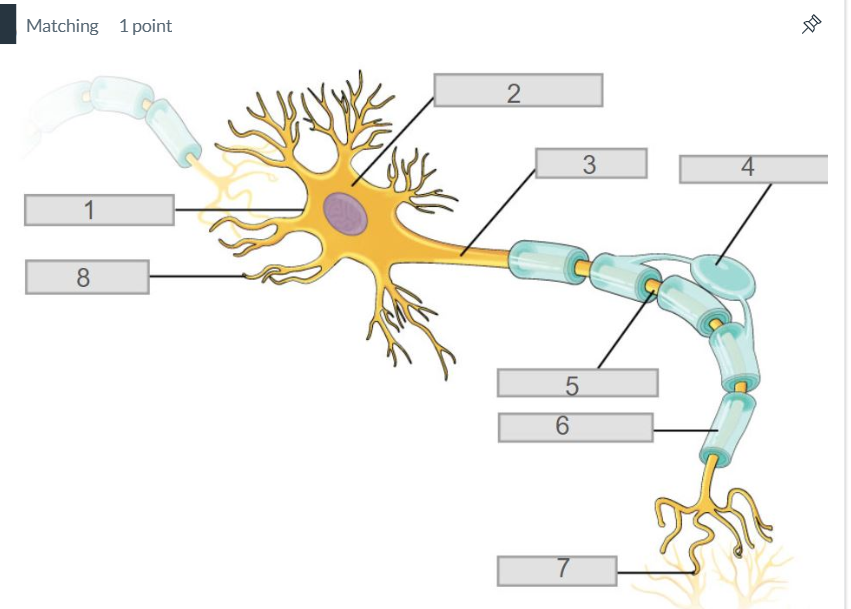
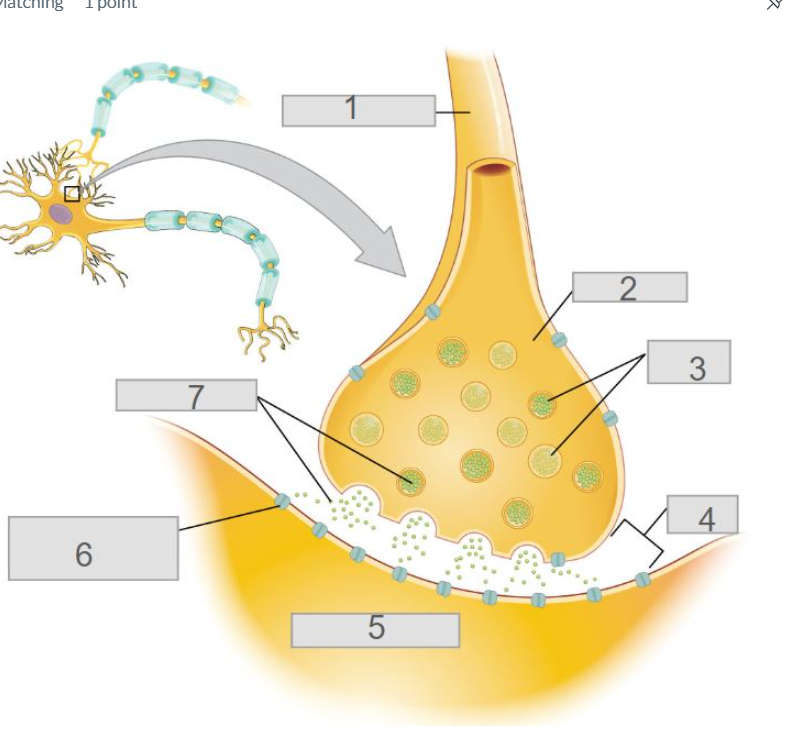
3
axon
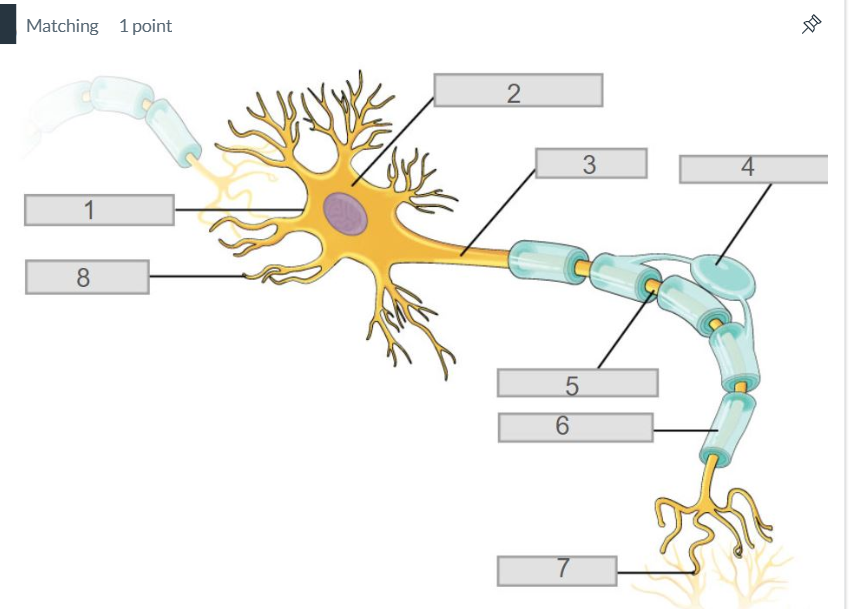
7
synapse
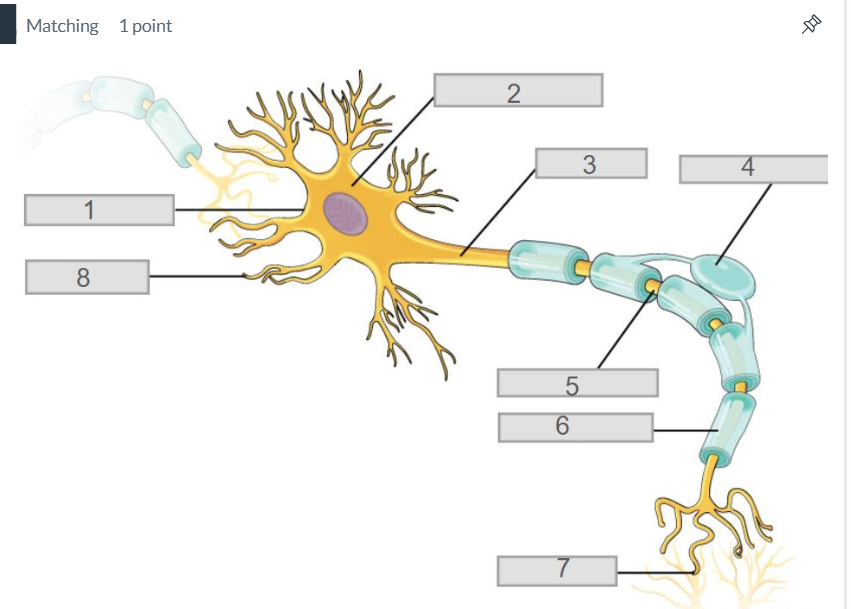
4
oligodendrocyte
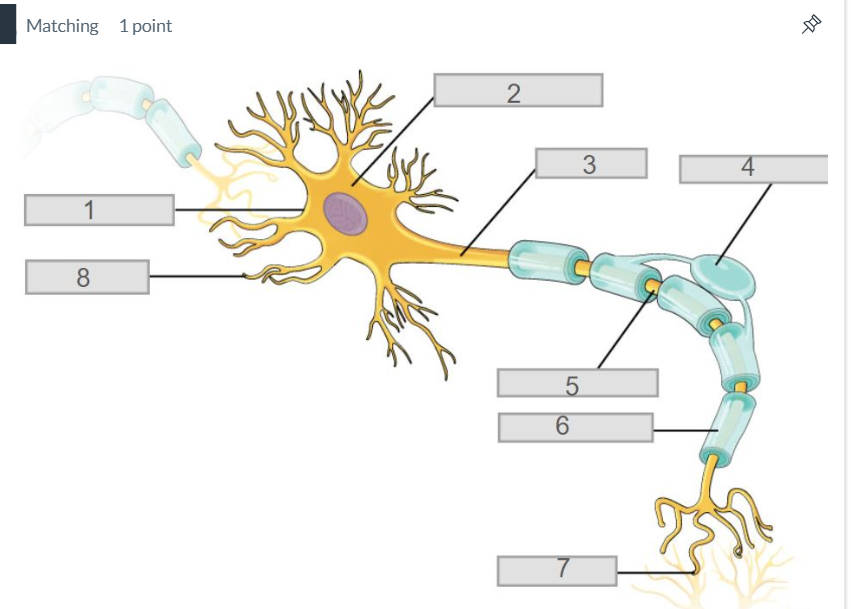
5
node of ranvier
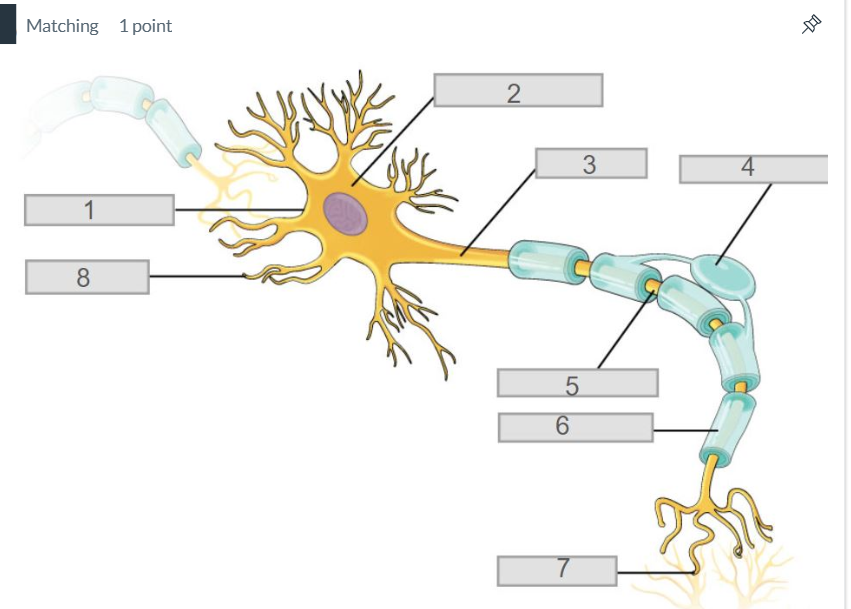
6
myelin sheath
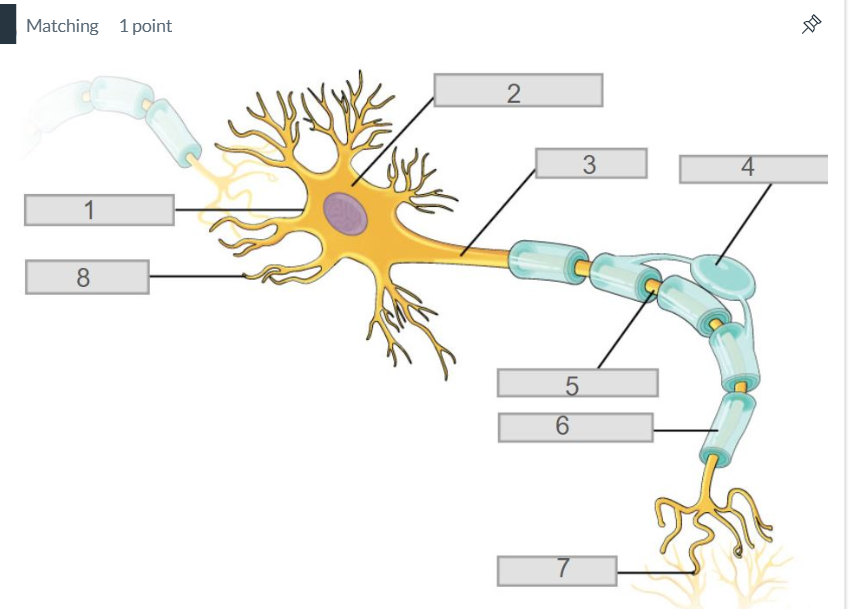
2
cell body (soma)
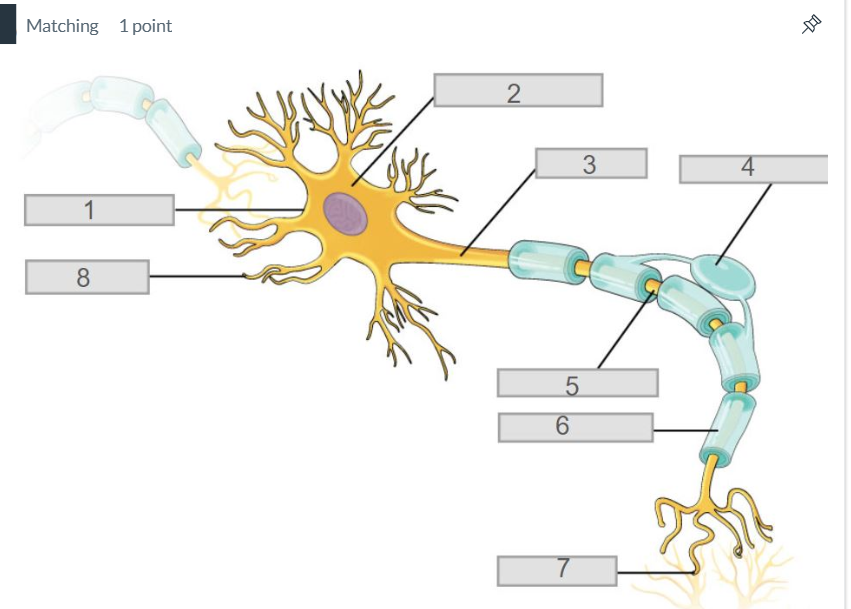
8
dendrites
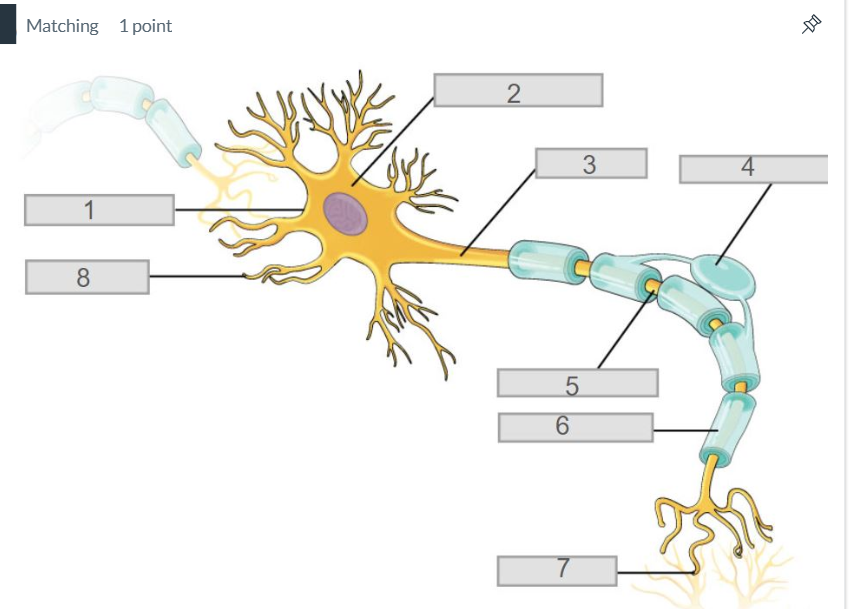
1
cell membrane
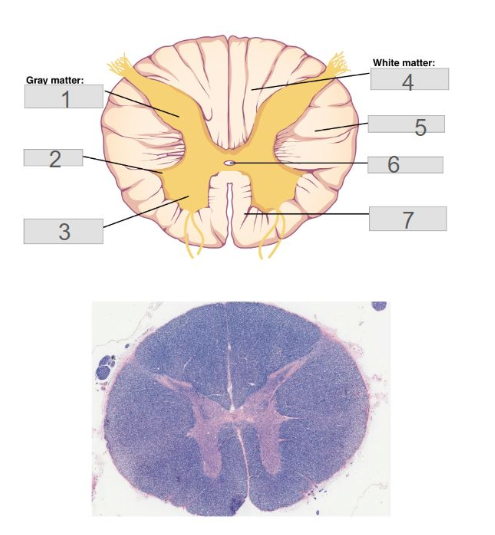
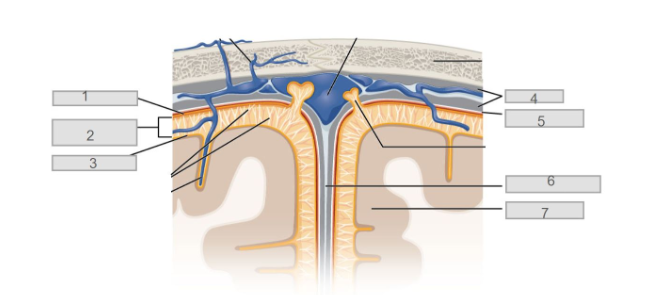
6
Central Canal
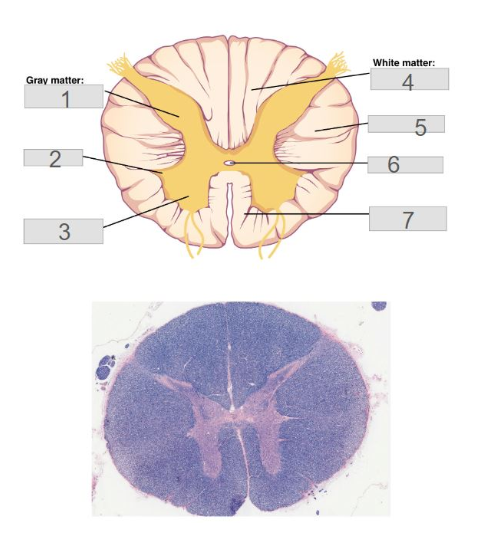
3
Anterior (ventral) horn
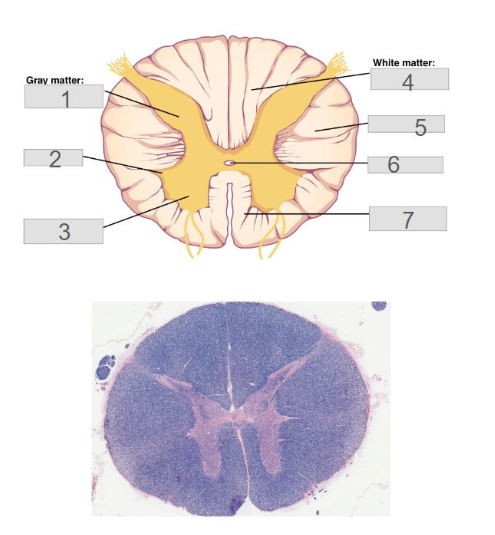
5
Lateral Columns
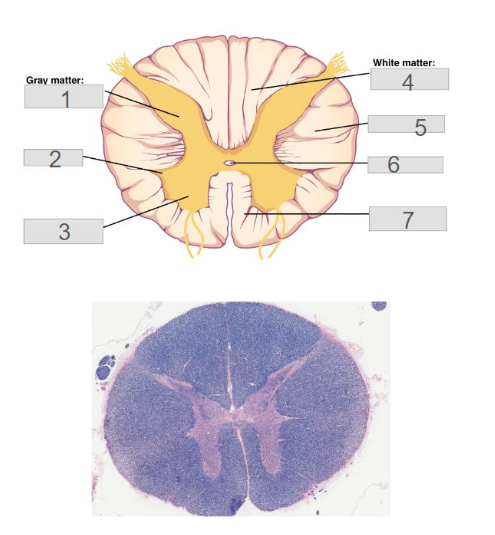
1
posterior (dorsal) horn
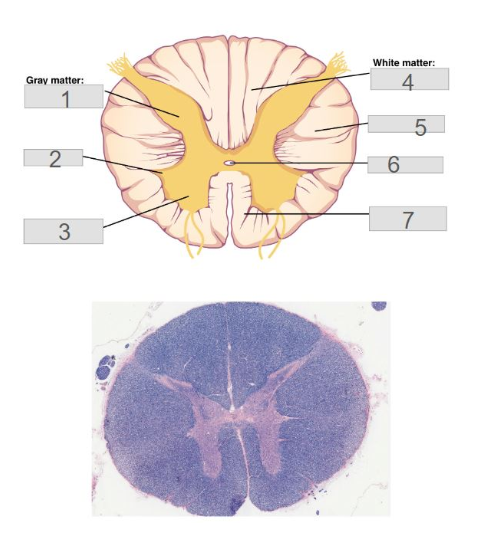
4
posterior (dorsal) columns
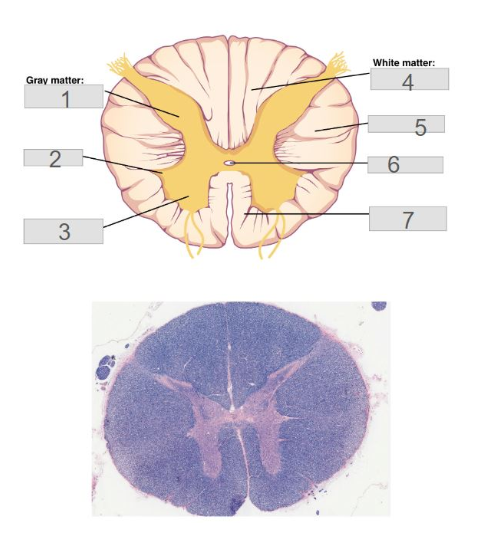
7
anterior (ventral) columns
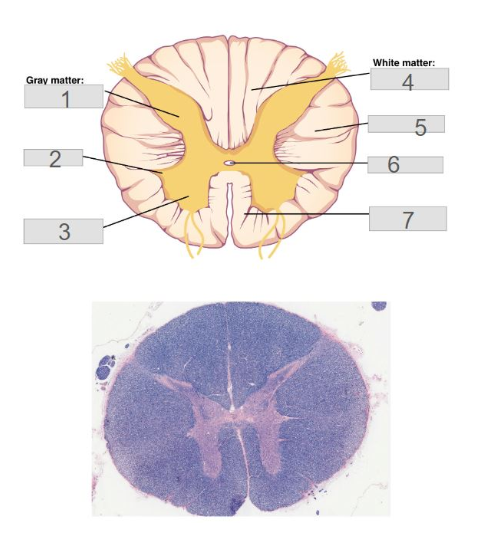
2
lateral horn
7
neurotransmitters
1
pre-synaptic neuron
5
subdural space
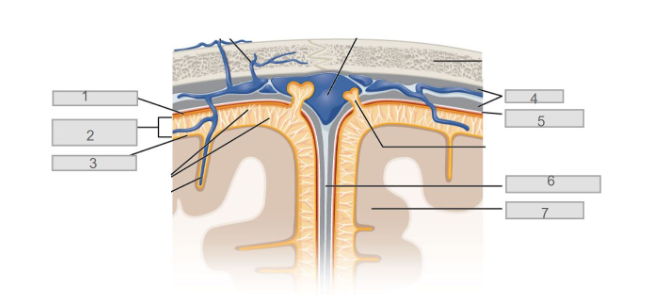
7
cerebral cortex
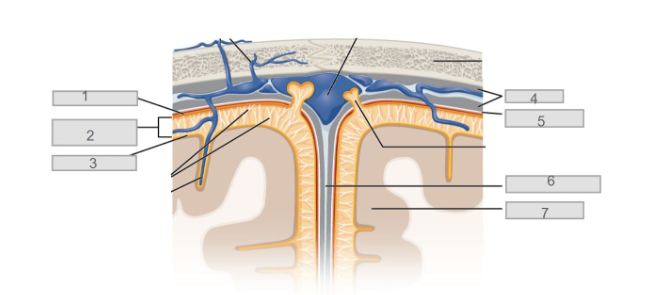
6
longitudinal fissure
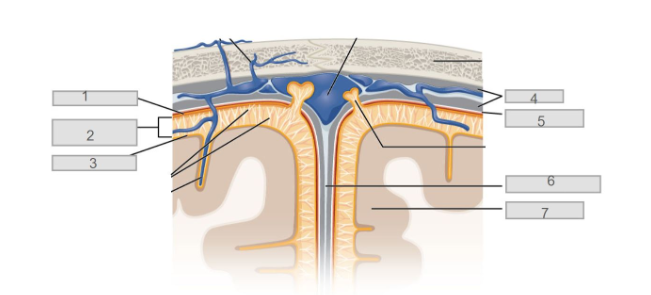
4
dura mater
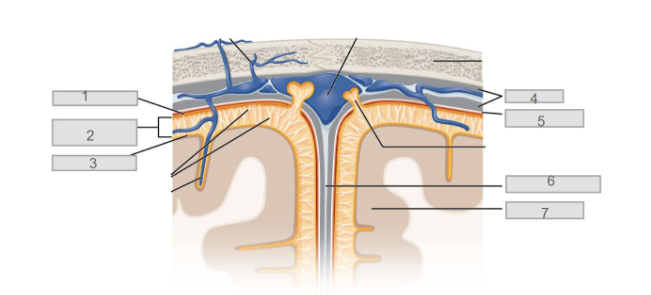
2
subarachnoid space
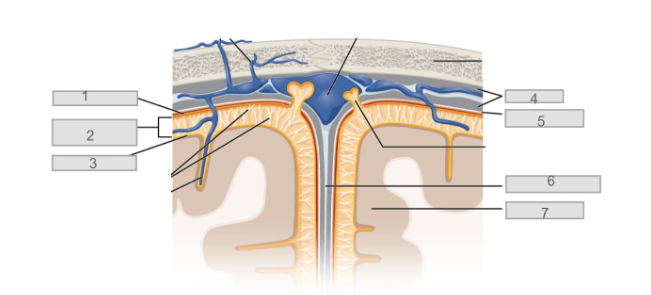
3
pia mater
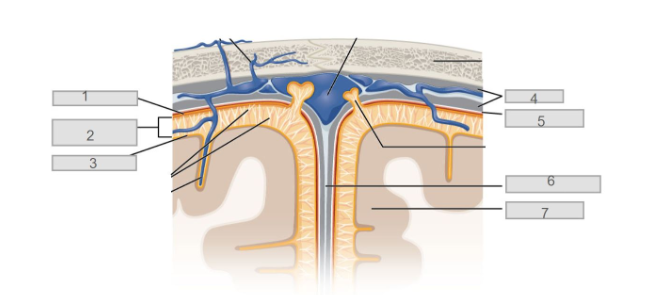
1
arachnoid mater
10
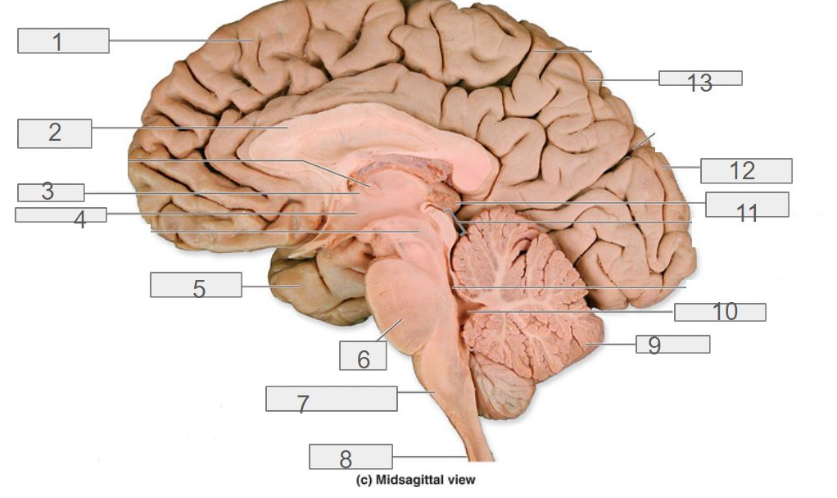
fourth ventricle
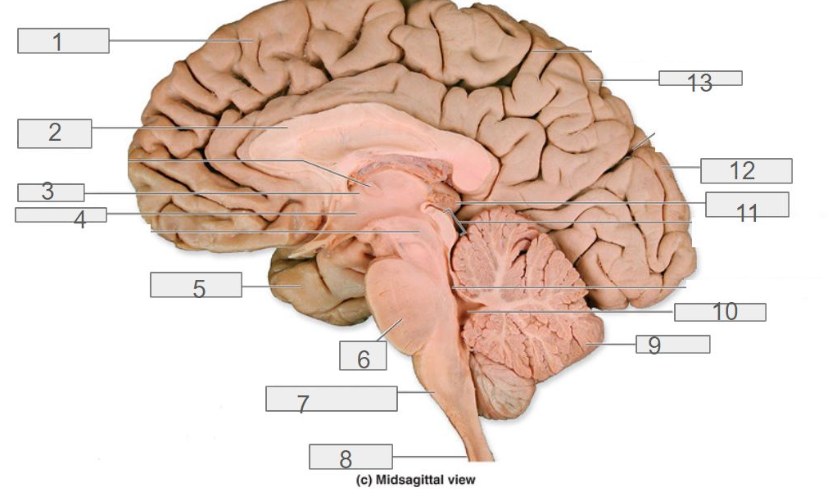
7
medulla oblongata
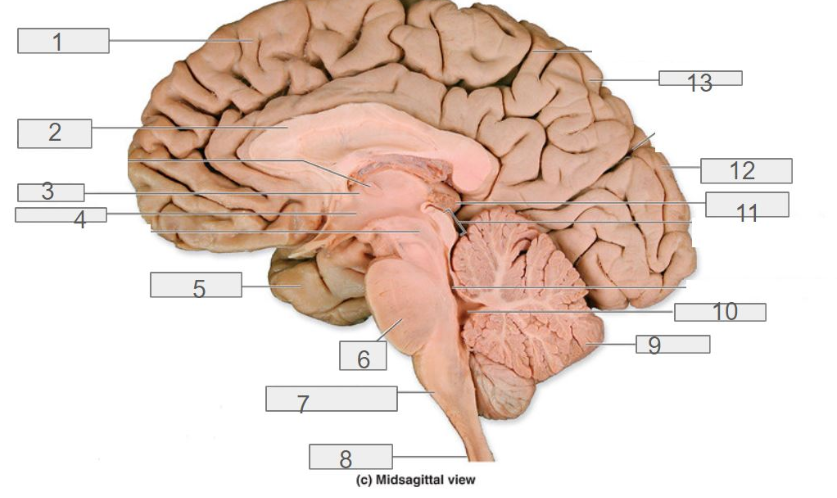
1
cerebral cortex
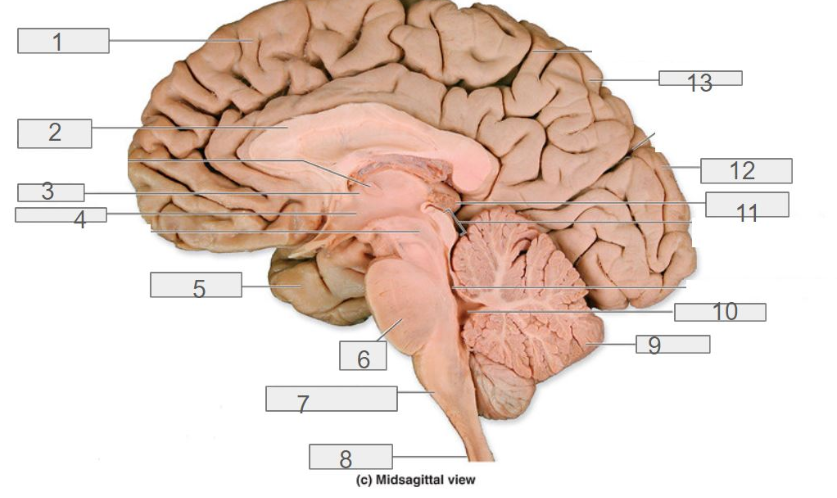
4
hypothalamus
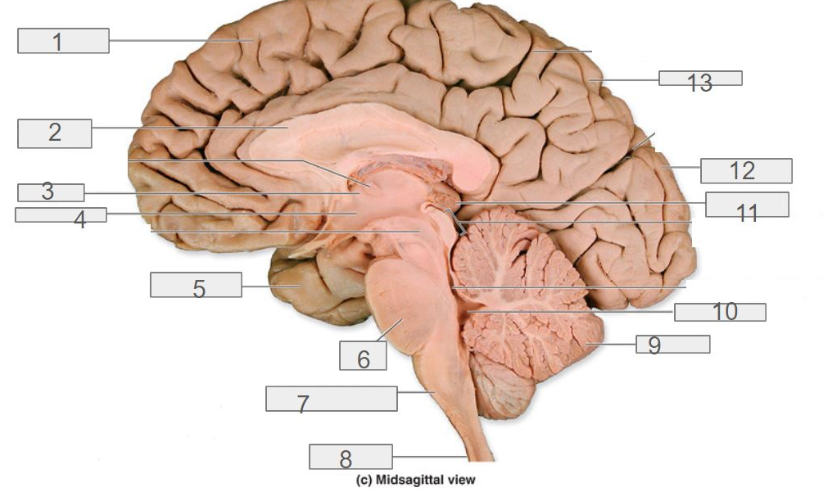
13
parietal lobe
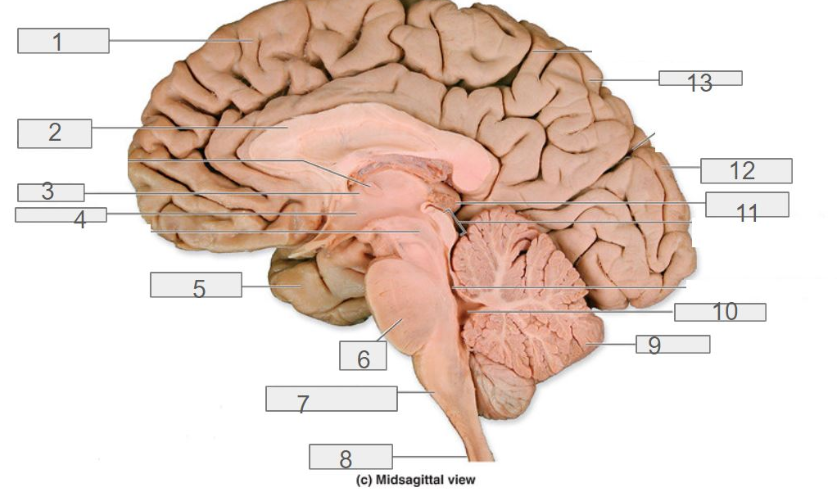
8
spinal cord
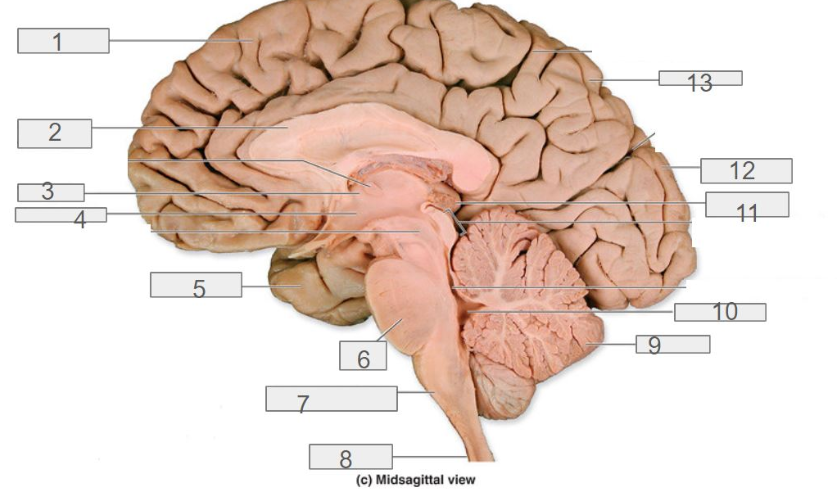
6
pons
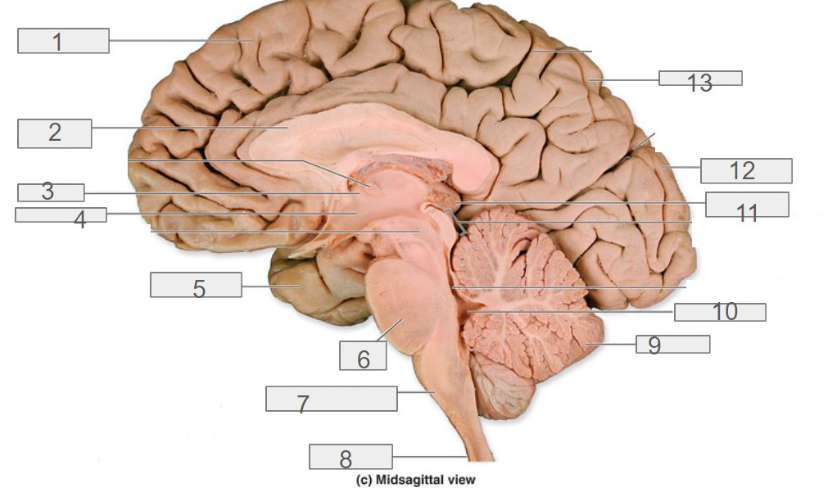
2
corpus callosum
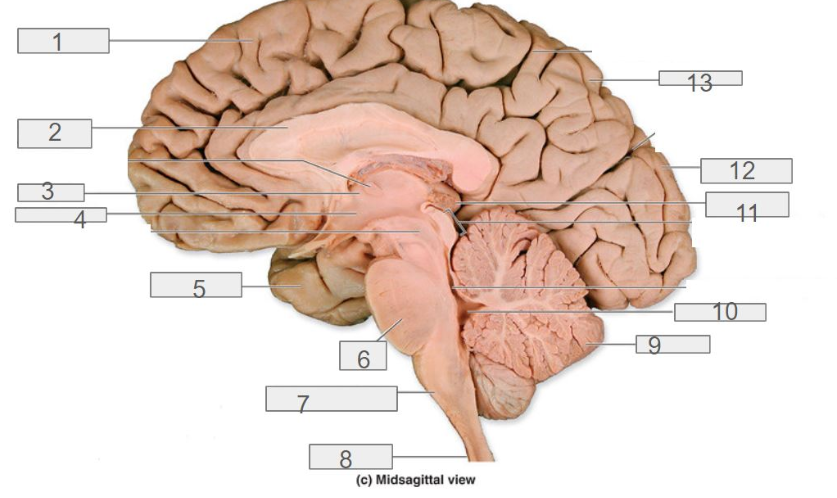
12
occipital lobe
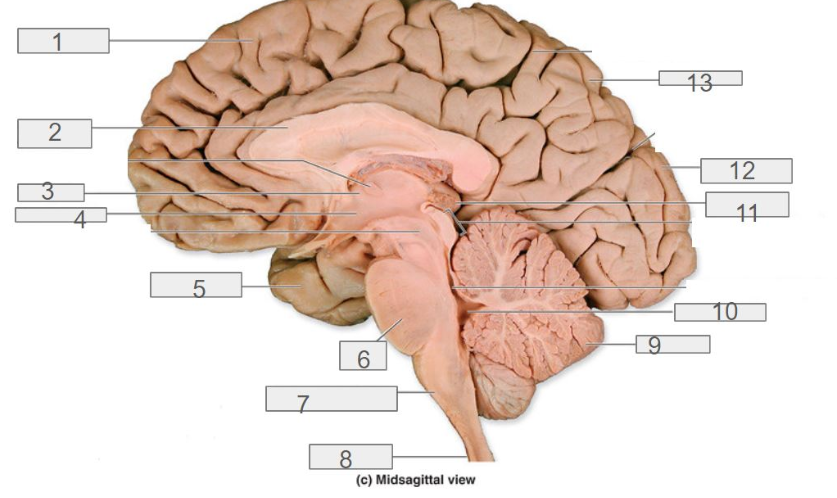
9
cerebellum
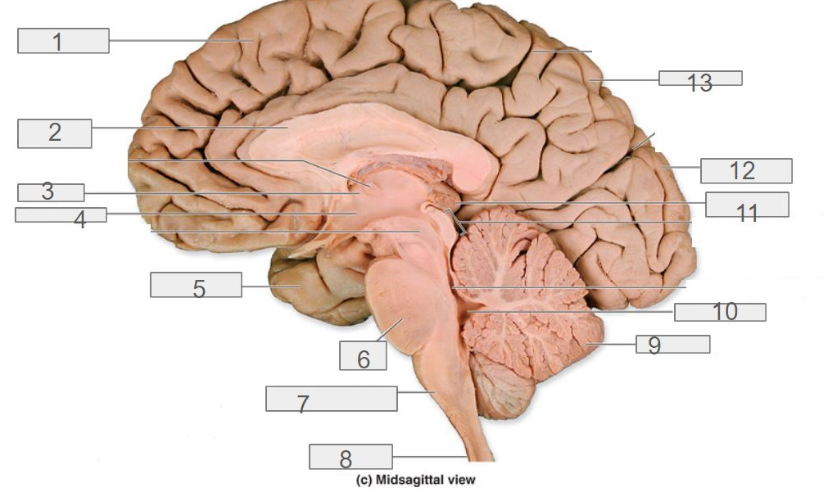
5
temporal lobe
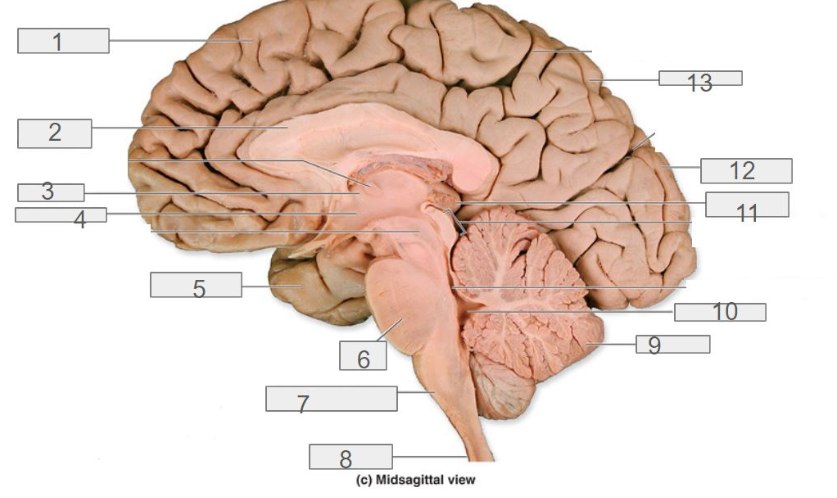
3
thalamus
11
pineal gland
what is poliomyelitis?
a viral disease causing paralysis
what type of neurons does poliomyelitis destroy?
motor neurons
what is the arachnoid mater?
middle meningeal layer
what is the main function of the arachnoid mater?
forms subarachnoid space
through which opening does the spinal cord exit the cranium?
foramen magnum
what is parkinson’s disease?
a neurodegenerative disorder
which neurotransmitter is lacking in parkinson’s disease?
dopamine
which brain structure maintains homeostasis?
hypothalamus
what are the functions of the hypothalamus
acts as the body’s main control center, maintaining homeostasis by regulating crucial autonomic, endocrine, and somatic functions
what is the pineal gland
a tiny, pincone-shaped endocrine gland located in the center of the brain that plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles
what hormone does the pineal gland release?
melatonin
what causes a stroke (cerebral apoplexy)?
interrupted blood flow to the brain
what is a fissure?
a deep brain groove
what is a gyrus?
a raised brain fold
which love is responsible for vision?
occipital lobe
which meningeal layer is most superficial?
dura mater
what is the main role of the dura mater?
protection and support
what are motor (efferent) nerve fibers?
nerves that carry impulses away from the CNS
in which direction do motor nerves carry impulses?
away from the CNS
what neurotransmitter is involved in fight-pr-flight?
epinephrine
what neurotransmitter is linked to pleasure and addiction?
dopamine
what are the meninges
protective membranes of the CNS
where is cerebrospinal fluid found?
ventricles and subarachnoid space
why is cerebrospinal fluid important?
cushioning and protection
what is the cauda equina?
a bundle of nerve roots located at the base of the spinal cord that resembles a tail, extending to control sensation and movement in the bladder, bowels, legs, and sexual organs
what type of impulses do ascending tracts carry?
sensory impulses
what is the cerebral cortex?
outer gray matter of the brain
which love controls planning and decision making?
frontal lobe
what is the arbor vitae?
network of tree-like white matter located deep within the cerebellum
where is the arbor vitae found?
cerebellum
where does crossing over of nerve tracts occur?
medulla oblongata
which structure links the nervous and endocrine systems?
hypothalamus
which cranial nerve controls smell?
olfactory nerve
which division of the autonomic nervous system controls fight-or-flight?
sympathetic division