Psych 101 - Unit 6 : Cognitive Learning
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Learning
A process by which knowledge or behaviour change as a result
of experience
Physical and chemical changes in the brain (Changes to chemical aspects of neurotransmission)
How we learn
By Association (associating things together)
Classical Conditioning (Two stimuli occur together; involuntary response; almost always physiological)
Operant Conditioning (Relationship between (voluntary) behaviour & consequence)
By Cognition
Mental representation of events
By Observation
Watching others
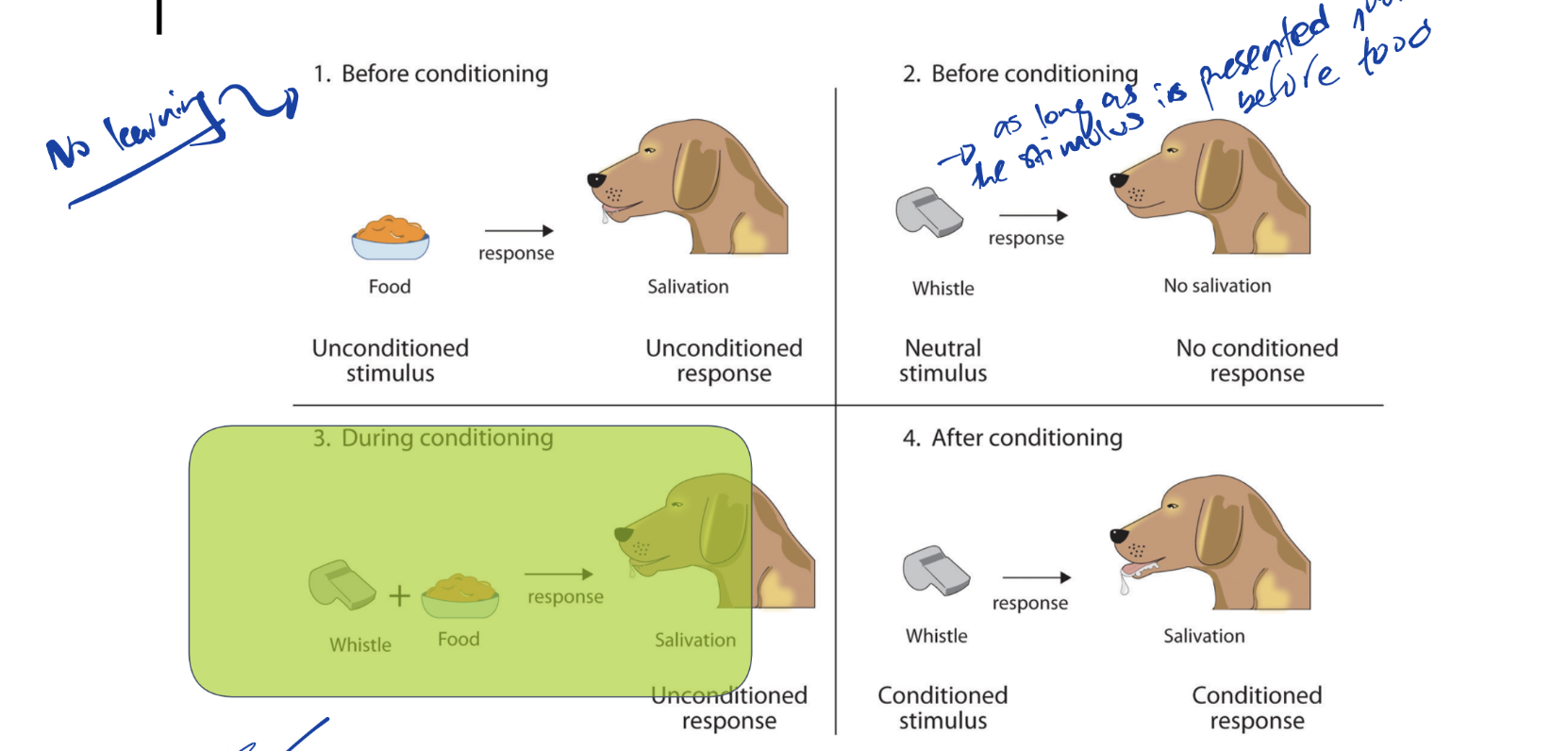
Classical Conditioning
• Unconditioned stimulus (US)
A stimulus that naturally elicits a response
• Unconditioned response (UR)
The natural response to a stimulus
• Conditioned stimulus (CS) aka...Neutral Stimulus
An originally neutral stimulus that, through repeated pairing, will eventually elicit a response
• Conditioned response (CR)
A learned response to a previously neutral stimulus
The CR and the UR are usually the same behaviour (not always)
Key Principles of classical conditioning
Intensity
The strength of association depends on the vividness of the stimuli; If particularly vivid, several pairings are not necessary
Generalization
Stimuli similar to the CS can elicit the CR
Discrimination
Learn not to respond to similar stimuli
Extinction and Spontaneous Recovery
CS no longer elicits CR response but can then reappear
Operant Conditioning
Relationship between (voluntary) behaviour and consequence
Doing chores = Allowance (reward)
Who measured the time it took cats to learn to escape from puzzle
boxes & what is the law of effect?
Thorndike (1898)
Law of effect: Behaviour is a function of consequences (satisfiers & annoyers)
ABCs: Antecedent, Behaviour, Consequence
B.F. Skinner and Skinner Boxes
1930
Reward only when light is lit
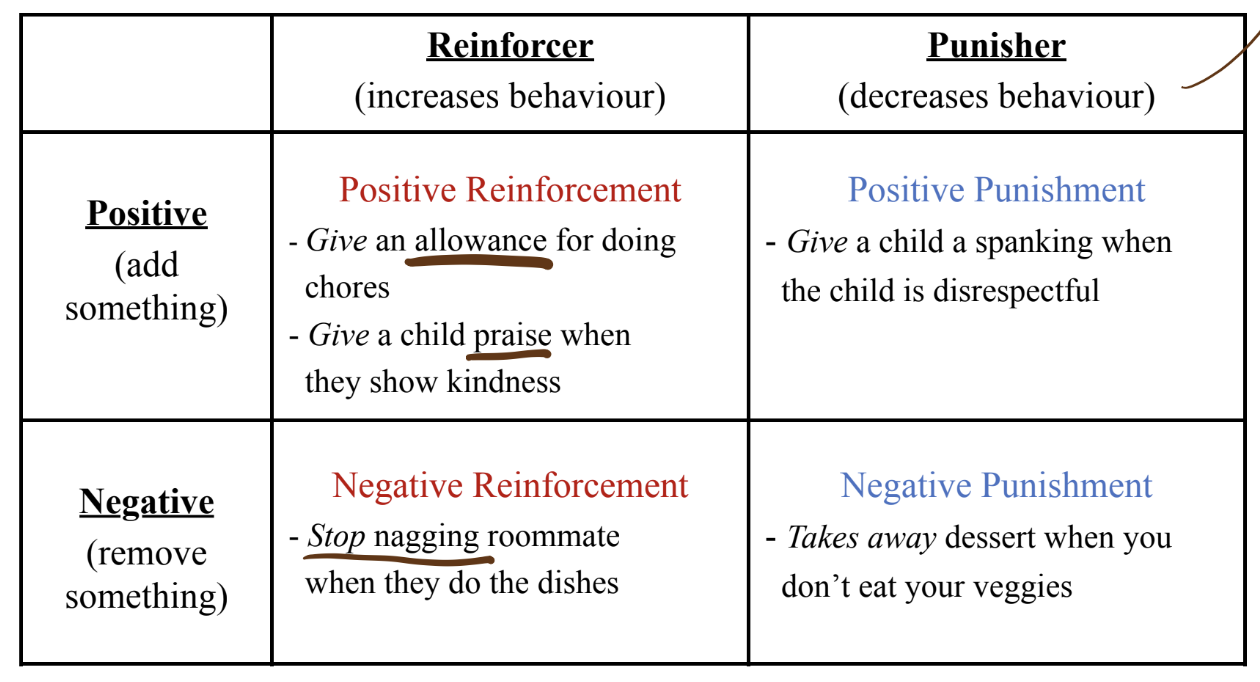
Reinforcement and punishment
Reinforcement vs. Punishment
Reinforcement
Consequence that increases the likelihood that behaviour will occur again
Can be positive (adds something) or negative (takes something away)
Punishment
Consequence that decreases the likelihood that behaviour will occur again
Can be positive (adds something) or negative (takes something away)
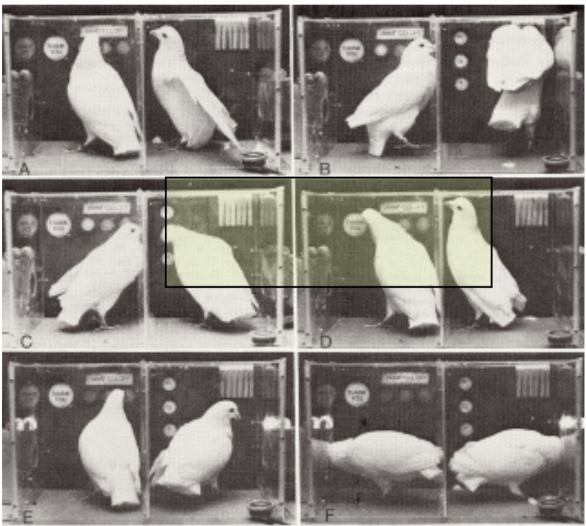
Shaping
BF Scanner
Encouraging a new behaviour by reinforcing successive approximations (reward small behaviour towards the goal)
Important point: GRADUAL change

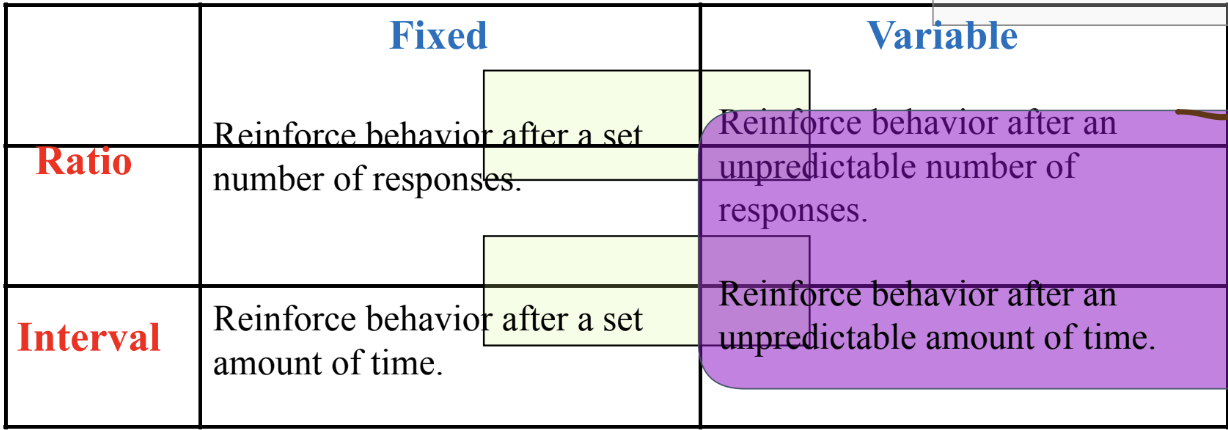
Reinforcement Schedules
How often and under what circumstances does the individual receive the reinforcement or punishment?
Continuous reinforcement schedule (every single time)
Not a good way for it to be sustainable
Partial reinforcement schedules (only sometimes)
Variable ratio schedules tend to generate high rates of responding
John Watson
Behaviourism
→ Believe that the only thing that matters is what you learn (+ experience)
Insight Learning
Latent Learning
Superstitious Conditioning
Insight Learning:
Koehler: Set up puzzles for chimps (e.g.,hanging a banana out of reach); Developed insight (more than learning
from reward)
Latent Learning:
Tolman: Rats learn mazes without reward (just exploring) -rats that explored first escaped faster than those who didn’t
Superstitious Conditioning:
Individual believes that a particular behavior, thought, or action is directly related to an outcome or event, often as a result of coincidental reinforcement.
Observational Learning
Social Learning (learning by observing and imitating others)
Mirror Neurons (forming connection even if just watching)
Fires when an animal performs an action, and when the animal observes someone else performing the same action