Forensic science exam 2
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Forensic anthropology
Bones
Osteology
Study of bones, 206 in body
Function of bones
Structure, protect organs, muscle attachments, detoxify body
Information from skeletal remains
Age, sex, ancestry, height, trauma, body type, cause of death and PMI
Epiphysis
Growth plate found at ends of long bones, determines age in sub adults
Cranial sutures
Lines between skull bones that fuse with age, estimate age
Sexual dimorphism
Male: larger and robust
Female: smooth and small
Subpubic angle
Narrow in males, wide in females
Acetabulum
Hip socket, larger in males
Skull sex differences
Males: more robust, sloping forehead, pronounced brow ridges, rectangular chin.
Females: smoother bones, vertical forehead, rounded skull, smaller jaw
Ancestry determination
European: long narrow nasal, oval eyes, triangle palate
African: wide nasal, square orbits, rectangle palate
Asian: rounded nasal, rounded orbits, parabolic palate
Shovel shaped incisors
Front teeth with scooped backs, asian and native american
Carabellis cusp
Small extra cusp on upper first molars, european
Human stature(height) estimation
Lengths of long bones (femur, tibia, humerus, radius)
Odontology
Dental
Adult teeth
32
Deciduous teeth
baby teeth, 20
Teeth identification
Hardest substance in body, unique to person, dna in pulp
Antemortem records
Teeth xray before death
Postmortem records
dental collected after death
Burning and teeth
Last to disintegrate, survive for identification
Clyde snow
Anthropologists, wored on Josef mengele and john wayne
Josef mengele
Nazi doctor remains identified in brazil through anthropology
King richard 3 case
skeleton found in 2012, identified using radiocarbon dating, mitochondrial dna
Bill bass
Founded body farm at University of tennessee
Body farm
Study human decomposition
Dacyuloscopy
Study of fingerprints
Bertillion system
Identification system using body measurements
Sir Francis Galton
Established individuality of fingerprints, first classification method
Juan Vucetich
Created own fingerprint classification system, first conviction using fingerprint evidence
Edward Henry
Developed classification system, Henry classification system,
Gilbert Thompson
First known use of fingerprints in the U.S.
Henry PDeforrest
Systematic fingerprinting within New York Civil Service
Will west case
Proved bertillion system flaws, 2 men same measurements different fingerprints
FBI fingerprint system
National fingerprint database
Permanence principle
FIngerprint unchanged through life
Ridge patterns
for classification
Friction ridges
Raised portion of the skill formed by papillae under dermis, sweat pores
Minutia-lines
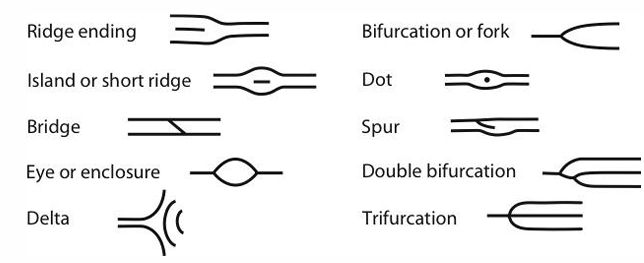
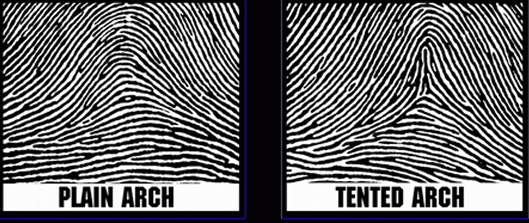
Arches picture
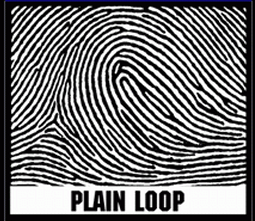
Loop picture
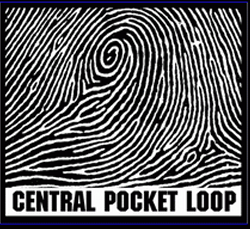
Whorl-Plain picture

Whorl central pocket picture
Double loop

Accidental picture

Arch pattern- 5 percent
Ridges enter from one side, rise, and exit other side
NO DELTAS AND NO CORES
Loop pattern- 60 percent
Ridges enter and exit from same side
ONE DELTA AND ONE CORE
Whorl pattern- 30 percent
At least one ridge complete
TWO DELTAS
Henry classification system
Categorize fingerprints into 1024 categories
Whorl value system
Fingers paired and assigned values based on whorls, arches and loops are 0
(16, 8, 4, 2, 1)
Courts accept 8-12 matching points
Points of similarity
Entomology
insects
Pmi
Post morterm interval by insects
Goff’s 5 stages
Fresh: death until bloating
Bloated: abdomen inflates
Decay: skin breaks, body deflates
Post decay: 20 percent or less body remains
Skeletel: bones and hair
Autolysis
breakdown of tissues by body own chemicals, releases gas
Putrefaction
Decomposition by bacteria, skin slippage
Adipocere
Wax by fat
Necrophagous Arthropods
Insects feed directly on corpse
Early physical change
Body is pale and waxy, blood settles (livor mortis)
Necrophagous species
Feeds directly on corpse like flies and bettles
Predators and parasies
Feed on necrophagous species, like burying beetles, ants, bees, and wasps
Opportunistic species
Use corpse as habitat like spiders and mites
ORDER YOU NEED TO KNOW
Flies Larva Beetles Ants Spiders
Blow fly (calliphoridae)
Common necrophages species arrive within minutes, feed on fluids
Blow fly life cycle
Egg, larva, pupa, adult
Instars: developmental stages
Responsible personnel
Death investigator, technician, anthropologist collect information
Visual, temperature, insects inside the body, insects beneath body
Aerial collection
Using a net to collect flying insects, kill with ethyl acetate, preserve in ethyl alcohol
Hand collection
Maggots with forecetps, scald in boiling water, store in alcohol
Live sampling “Maggot motel”
Place live larvaw in contain, allow to DEVELOP INTO ADULTS to identify
Scene temperatures
REcord maggot mass, body surface, ground surface, and under body temperatures
Ambient temperature
Affects egg and larval development
Maggot mass temperature reaches up to
125 F
Accumulated degree hours
Thermal energy required for insect to develop into next stage, used for PMI
Crime scene insects
M lee goff
Toxicology
Poisons in body
Types toxicology
Environment, consumer, medical
Father of forensic toxicology
Mathieu orfilla
developed chemical nature of poisons
Arsenic detection
Marsh test
Highly sensitive test to detect arsenic
Paracellsus principle of poison
Depends on dose
Ronald clark
Killed boy with cyanide candy
Georgi markov
Poisoned with ricin under umbrella pellet
Ideal poison
No odor, no taste, is soluable, undetectable, low dose can kill, not traceable
Poison kills the
CNS- depression
Respiratory- suffocation
cardivascular-hypotension
cellular-hypoxia
LD 50 definition
Dose kills half population within 4 hours
Order of hymenoptera
Ants bees wasps
Forensic art
arts for legal
4 main art methods
Composites
age progression
facial reconstruction
superimposition techniques
Composite imagry
graphic images by combining describes facial features from witness (hand drawn)
Age progression
current facial from abducted children using technology
Facial reconstruction
After determining age, sex, ancestory, create a face
3d vs 2d construction
skull using tissue depth markers (gatliff snow method)
vs
taught at fbi academy
Facial landmarks
anatomical points on skull for tissue thickness, muscle origin
3d facial steps
Establish age and sex and ancestory
plot landmarks
mount eyes
add fatty tissue
cover with skin
Karen taylor
Forensic artist for composit sketches and 2d construction
Betty pat gatliff
forensic artists developed 3d facial recognition
Super imposition
placement of image over another. matching skull to photograph
Rehydration tattoo
store tattoos
Types of poison symptoms
Lye: burn around lips
Carbon monoxide: red lividity
cyanide: burnt alomds
Metals: dirrhea, nausea
alcohol: blind
Elements prove poisoning
Crime committed, intent, access to poison, access to victum, death by poison, homicideal
Poison type s
specific
motive: money, jealous, political