Chapter 21 - The Evolution of Populations
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
do organisms evolve during their lifetime?
no they do not, populations of organisms evolve over many generations
natural selection acts on individuals, evolution is the result of the accumulation of changes made by natural selection to a population over time
microevolution
change in allele frequencies in a population over generations
phenotype
physical expression of the genotype
variation and how it translates to genotype/phenotype
variation in individual genotype leads to variation in individual phenotype
not all phenotypic variation is heritable
natural selection can only act on variation with a genetic component
how do geneticists measure variation within a population
population geneticists measure polymorphisms in a population by determining the amount of heterozygosity at the gene and molecular levels
average heterozygosity
measures the average percent of loci that are heterozygous in a population
nucleotide variability
is measured by comparing the DNA sequencies of pairs of individuals
mutations
changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA
cause new genes and alleles to arise
only mutations in cells that produce gametes can be passed to offspring
mutations in somatic cells always happen, but no negative effect
silent mutations have no effect
4 sources of genetic vartiation
formation of new alleles by mutation
altering gene number or position
rapid reproduction increases mutation rate
sexual reproduction
point mutation and effects
change in one base in a gene
effects can vary
if it causes a change in protein function, it is often harmful and usually deleted by natural selection
but sometimes this change in protein function can increase the fit between an organism and the environment (and instead preserved by natural selection)
mutations that alter gene number or position
chromosomal mutations that delete, disrupt, or rearrange many loci are usually harmful
but duplication of genes can arise from errors in meiosis
increases in gene number have played a major role in evolution
neofunctionalization and examples
when duplicated genes take on new functions by further mutation
important source of evolutionary novelty
ex. gene for luteinizing hormone has been duplicated six times to produce the chorionic gonadotropin gene family
ex. human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is important in the early maintenance of pregnancy
what was the original function of luteinizing hormone
to maintain early pregnancy by maintaining the corpus luteum (corpus luteum rescue)
luteinizing hormone and neofunctionalization
new copies of the LH beta gene (the chorionic gonadotropins) have new functions:
control invasion of the placenta into mother’s uterine endometrium during early embryo development in pregnancy
hCG also regulates maternal thyroid during gestation
also key to immunotolerance of the semi-allogenic fetus (immune system regulation)
mutation rates in plants and animals vs. prokaryotes and viruses
plants and animals
low mutation rates (average of 1 mutation in every 100,000 genes per generation)
lower than prokaryotes
prokaryotes and viruses
more generations per unit time
mutations can accumulate quickly
ex. HIV
2 day generation time
high mutation rate
mutations accumulate rapidly making drug treatments ineffective
sexual reproduction and genetic variability
sexual reproduction can shuffle existing alleles into new combinations
in organisms that reproduce sexually, recombination of alleles is more important than mutation in producing the genetic differences that make adaptation possible
Population
localized group of individuals that can interbreed and produce vertile offspring
gene pool
contains all of the alleles for all loci in a population
when is a locus fixed?
a locus is fixed if all individuals in a population are homozygous for the same allele
no variability
How to calculate the Frequency of an Allele in a Population
For diploid organisms:
total # of alleles at a locus = total # of individuals x 2
total # of dominant alleles at a locus = 2 alleles per homozygous dominant individual + 1 allele per heterozygous individual
^same thing for recessive alleles
Hardy-weinberg Principle
describes a population that is not evolving
if a population does not meet the criteria of the Hardy-Weinberg principle, then that population is evolving
states that frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population remain constant from generation to generation
allele frequencies don’t change even in a population where gametes contribute to the next generation randomly
Mendelian inheritance preserves genetic variation in a population
Why is the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem important?
it is the entry point to the study of population genetics
in real populations, allele and genotype frequencies do change over time
but Hardy-weinberg theorem allows us to determine the cause of changes in gene frequencies
Hardy Weinberg Equation
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
p - dominant allele frequency
q - recessive allele frequency
p² - probability of a homozygous dominant individual
q² - probability of a homozygous recessive individual
2pq - probability of a heterozygous individual
used to compute genotype frequencies if we know the allele frequencies
genotype frequencies must add up to 1.0
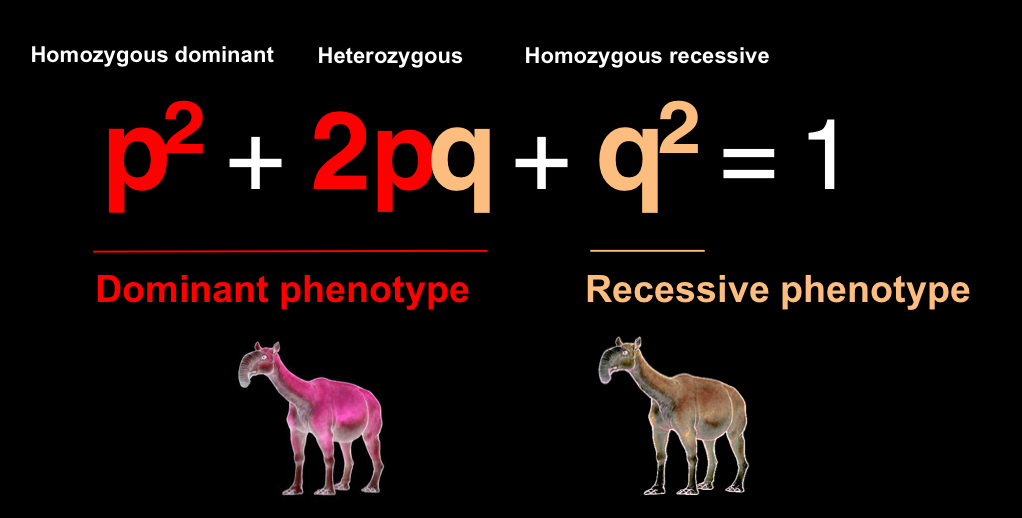
Steps on how to apply Hardy-Weinberg equation
start with genotype frequencies
use Hardy-Weinberg equation to help compute the allele frequencies
allow random breeding, then use Hard-Weinberg equation to compute genotype frequencies in the next generation
5 assumptions/conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
No mutations
Random Mating
No natural Selection
Extremely large population size
No gene flow
PKU and applying the Hardy-Weinberg Equation
We can assume the locus causes Phenylketonuria (PKU) is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium since:
PKU gene mutation rate is low
Mate selection is random
Natural selection can only act on rare homozygous individuals who do not follow dietary restrictions
population is large
migration has no effect as many other populations have similar allele frequencies
3 factors that alter allele frequencies
Natural Selection
Genetic drift
gene flow
Natural Selection
A successful reproduction results in certain alleles being being passed to the next generation in greater numbers
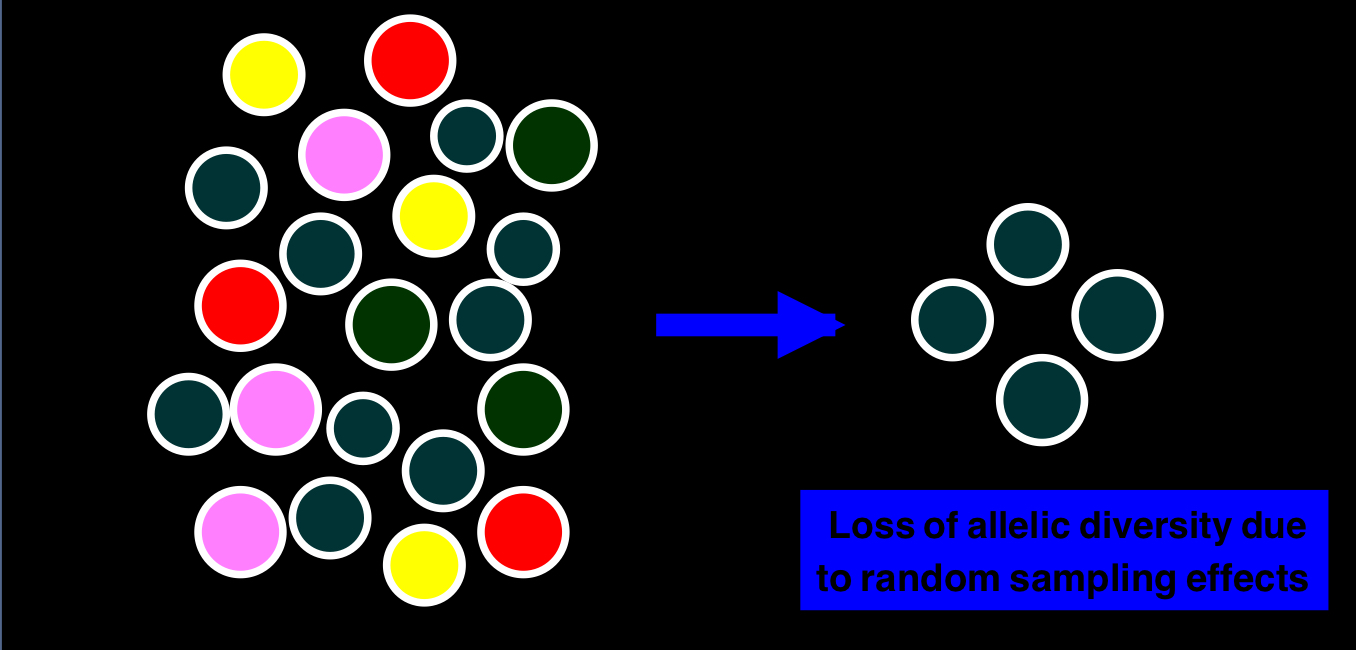
Genetic drift
Random change in allele frequencies
tends to reduce genetic variation through losses of alleles
the smaller a sample, the greater chance of deviation from a predicted result
Founder Effect
when a few individuals become isolated from a large population and start a new population
allele frequencies in the small founder population can be different from those in the larger parent population
can also result in loss of allelic diversity due to random sampling effects
Huntington’s disease
first autosomal dominant disease discovered
practical application of founder effect
high frequency of the disease in the Lake Maracaibo region of northwest Venezuela
all of those with the disease have ancestry with a European sailor who had the disease in 1800 and had children
Bottleneck effect
sudden reduction in population size due to a change in he environment
resulting gene pool may no longer reflect the original population’s gene pool
if the population remains small, it may be further affected by genetic drift
Genetic drift impact on Greater Prairie Chicken
loss of prairie habitat caused a severe reduction in the population
surviving birds had low levels of genetic variation
affected reproduction (only 50% of eggs hatched)
Cheetahs and population bottleneck
underwent a severe population bottleneck during the pleistocene (roughly 10,000 years ago)
Cheetah’s lost 90-99% of genetic variation during the bottleneck
there is so little variation that they do not reject skin grafts
Summary of the effects of Genetic Drift
significant in small populations
causes allele frequencies to change at random
can lead to a loss of genetic variation within populations
can cause harmful alleles to become fixed
Gene flow
the movement of alleles among populations
alleles can be transferred through the movement of fertile individuals or gametes (ex. pollen)
tends to reduce differences between populations over time
is more likely than mutation to alter allele frequencies directly
can decrease the fitness of a population
what is the ONLY mechanism that consistently causes adaptive evolution
Natural Selection
Natural selection
increases the frequencies of alleles that enhance survival and reproduction
adaptive evolution
when the match between an organism and its environment increases
Natural selection and adaptive evolution
only natural selection consistently results in adaptive evolution
genetic drift or gene flow can cause adaptations sometimes, but not consistently
causes adaptive evolution by acting on the phenotype of an organism in its current environment
Relative fitness
the contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of other individuals
3 modes of selection
directional selection - favours individuals at one end of the phenotypic range
ex. NBA makes population of its players towards taller players
Disruptive or diversifying selection - favours individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
least common
stabilizing selection - favours intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes
most common
Stabilizing selection for birth weight in humans
very small and very large babies have lower survival rates
since bigger babies are more likely to get stuck in the birth canal
Balancing selection
Some selection may preserve variation at some loci, thus maintaining two or more phenotypes in a population
2 types:
heterozygote advantage
frequency-dependent selection
Heterozygote advantage
when heterozygotes have a higher fitness than both homozygotes
natural selection will tend to maintain two or more alleles at that locus
ex. sickle-cell allele causes mutations in hemoglobin but also gives malaria resistance
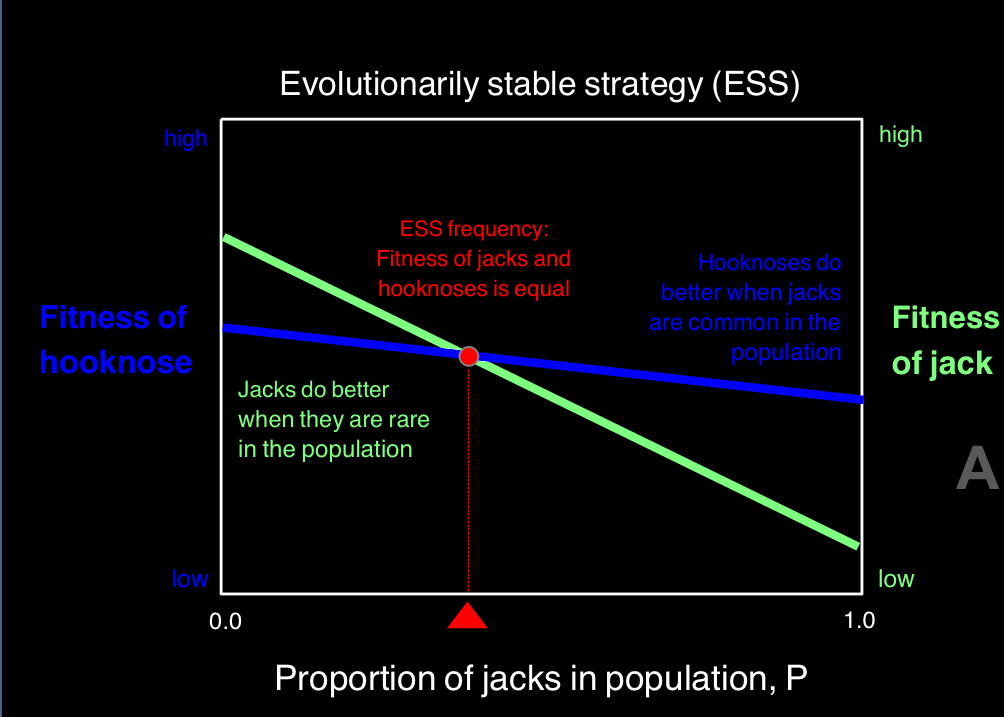
Frequency-dependent selection
fitness of a phenotype declines if it becomes too common in the population
selection can favour whichever phenotype is less common in a population
Frequency-dependent selection in salmon
large hooknoses fight to get close to the females and small jacks sneak
small jacks do better when they are more rare in the population, large hooknoses do better when jacks are common in the population
Sexual selection
natural selection for mating success
can result in sexual dimorphism
sexual dimorphism
differences between sexual characteristics of males and females
ex. male red-winged blackbirds are about 1/3 larger than females
2 main types of sexual selection
intrasexual selection
intersexual selection
intersexual selection
involves competition among individuals of one sex for mates of the opposite sex
it is often, but not always, males competing with males
intersexual selection
when individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting their mates
often called mate choice
males can be showy due to mate choice, which can increase their chances of attracting a female, but also decreasing their chances of survivals
4 reasons why natural selection cannot make perfect organisms
Natural selection can only act on existing variations
evolution is limited by historical constraints
adaptations are often compromises
chance, natural selection, and the environment interact