lecture 5-10
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:53 AM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
Neuroimaging structural
CT, MRI, DTI
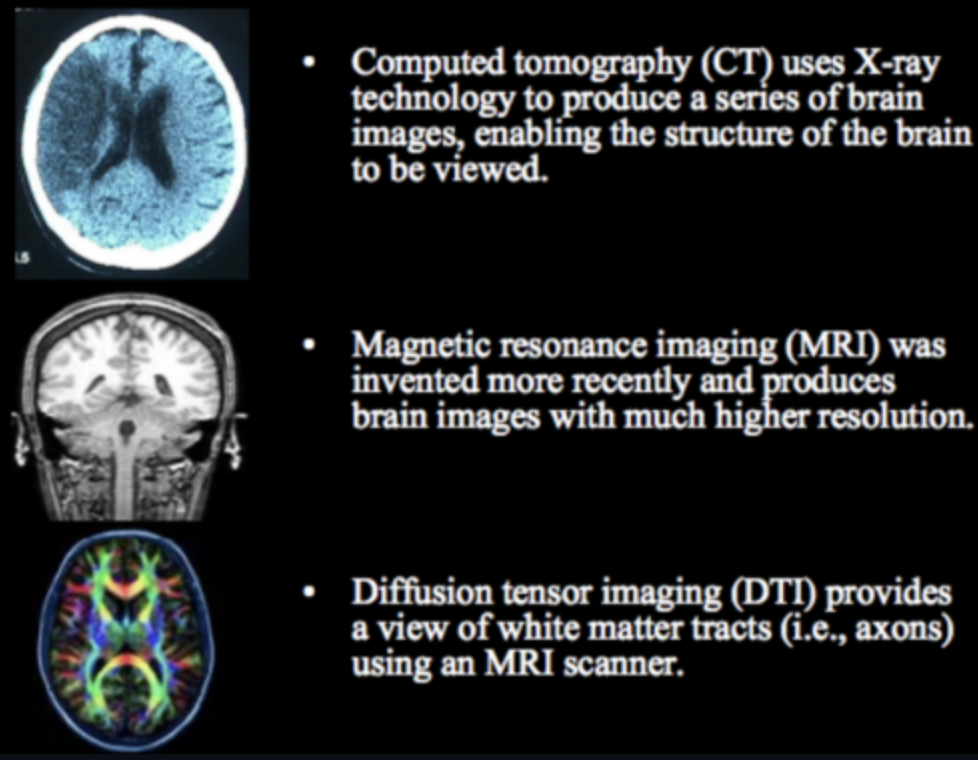
2
New cards
Neuroimaging: Functional
EEG, MEG, PET, fMRI
3
New cards
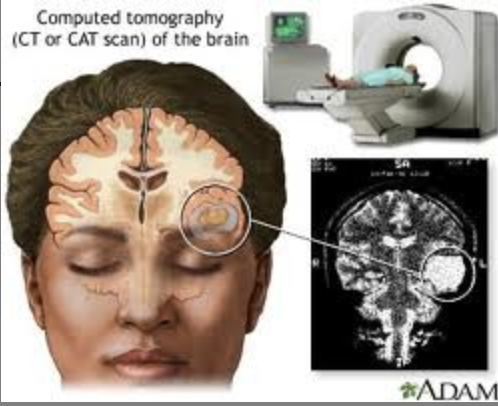
CT/CAT scan (structural) mechanism
\-3D x-rays @ diff angles
\-detect diff tissue density; bone-white; csf-dark
\-detect diff tissue density; bone-white; csf-dark
4
New cards
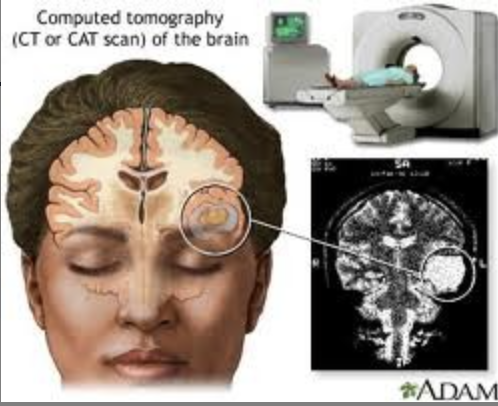
CT/CAT scan (structural) advantages
fast, not expensive
5
New cards
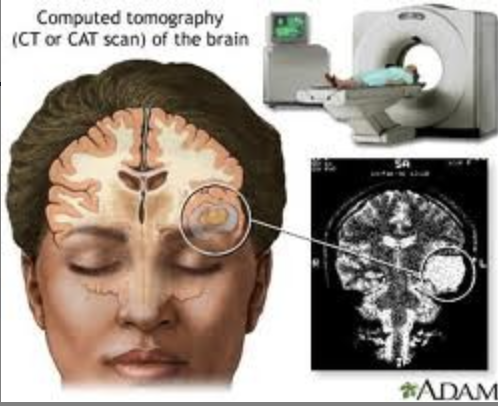
CT/CAT scan (structural) disadvantages
radiation, can't do too much
6
New cards
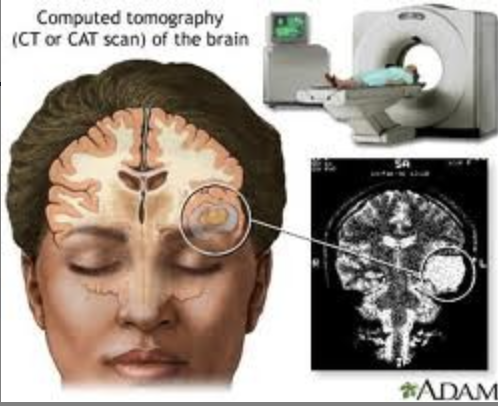
CT/CAT scan (structural) uses
diagnose: stroke, tumor, lesions, vascular malformations
7
New cards
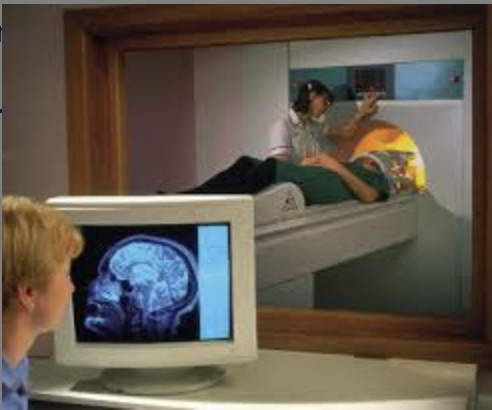
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), structural mechanism
1) radio frequency electromagnetic pulse knocks proton out of alignment
2) rate of proton in phase & realignment w/ one another make energy signal
\-rate depends on tissue (cerebral spinal fluid, white or gray matter)=diff realign=diff signal machine detects
2) rate of proton in phase & realignment w/ one another make energy signal
\-rate depends on tissue (cerebral spinal fluid, white or gray matter)=diff realign=diff signal machine detects
8
New cards
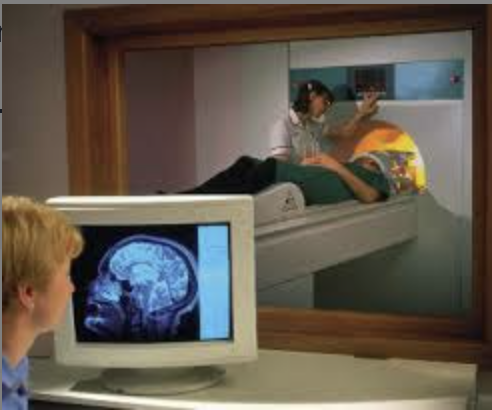
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), structural advantages
good spatial resolution, no radiation, differentiates tissues
9
New cards
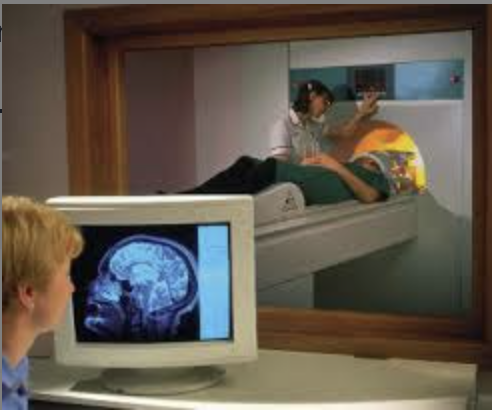
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), structural, disadvantages
expensive to use/run, no metal (pacemaker), longer than CT scan
10
New cards
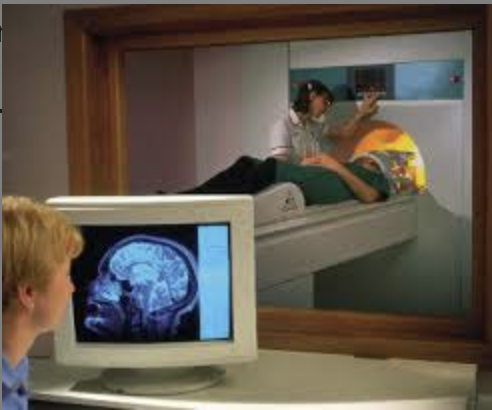
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), structural uses
detect tumor, bleeding degenerative diseases, evaluate treatment, guidance for neurosurgery
11
New cards
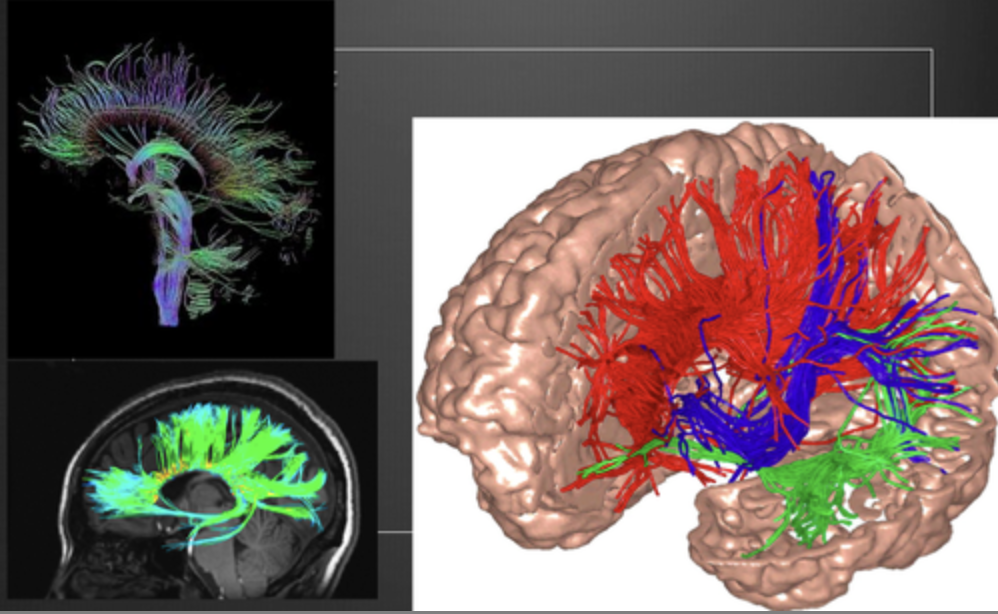
DTI (diffusion tensor imaging) structural mechanism
MRI technique detects flow of H20 along axon (like a straw); measure diffusion rate & direction
12
New cards
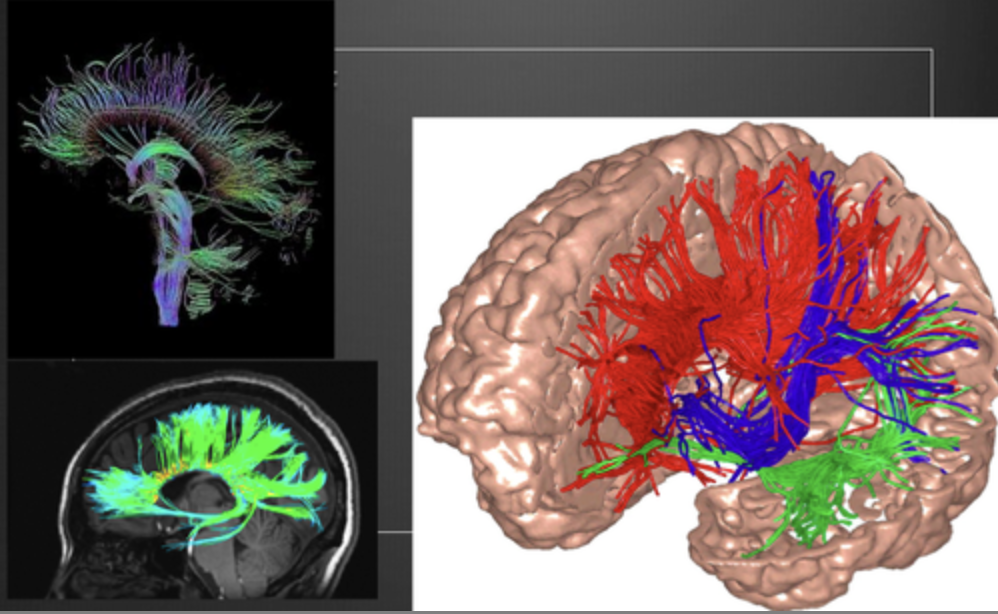
DTI (diffusion tensor imaging) structural advantages
high resolution & structural detail
13
New cards
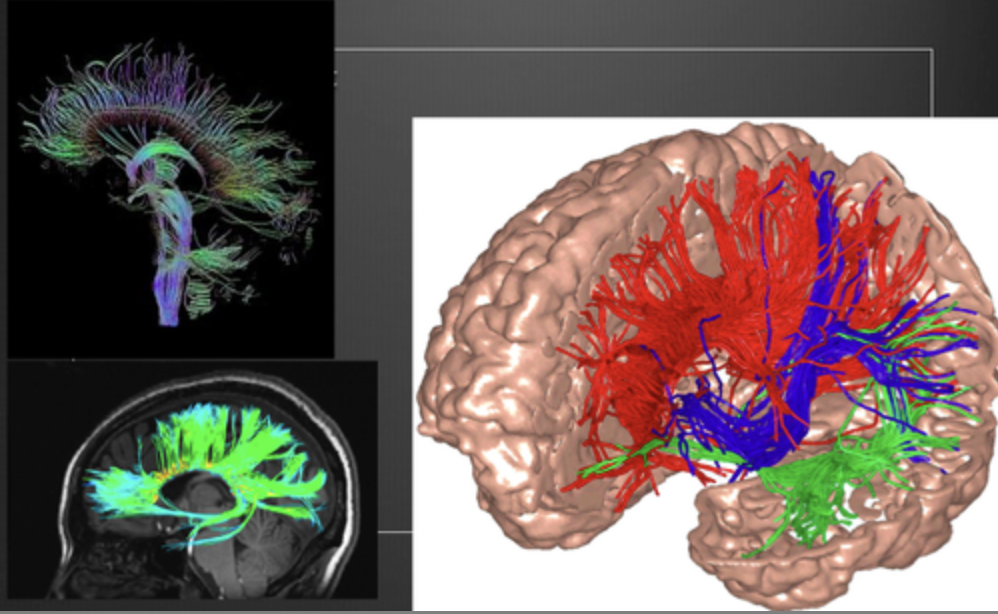
DTI (diffusion tensor imaging) structural disadvantages
can't trace to or from of fibers that bond/intersect (about 75% lost)
14
New cards
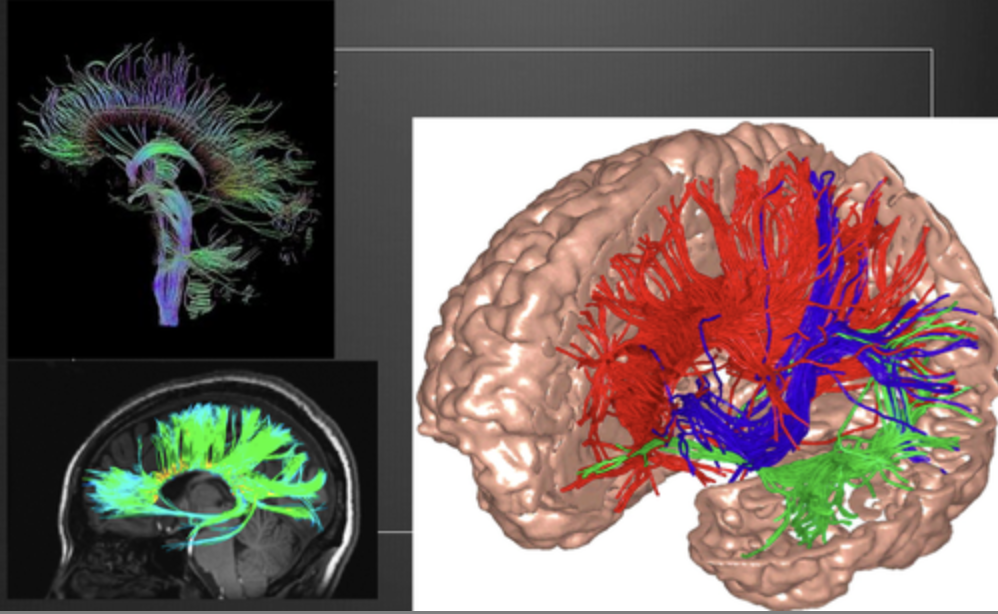
DTI (diffusion tensor imaging) structural uses
observe white matter (axons)
15
New cards
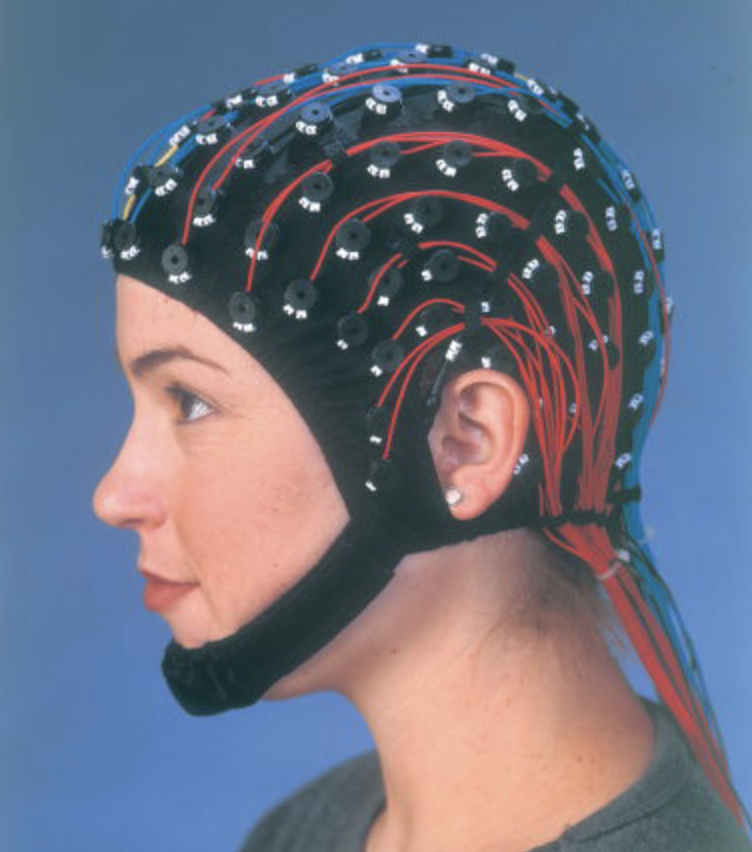
EEG (EEG (electroencephalogram) mechanism
\-functional, direct
\-functional, direct
record electric energy (neuron fire) of brain from scalp, measures group of neurons firing
16
New cards
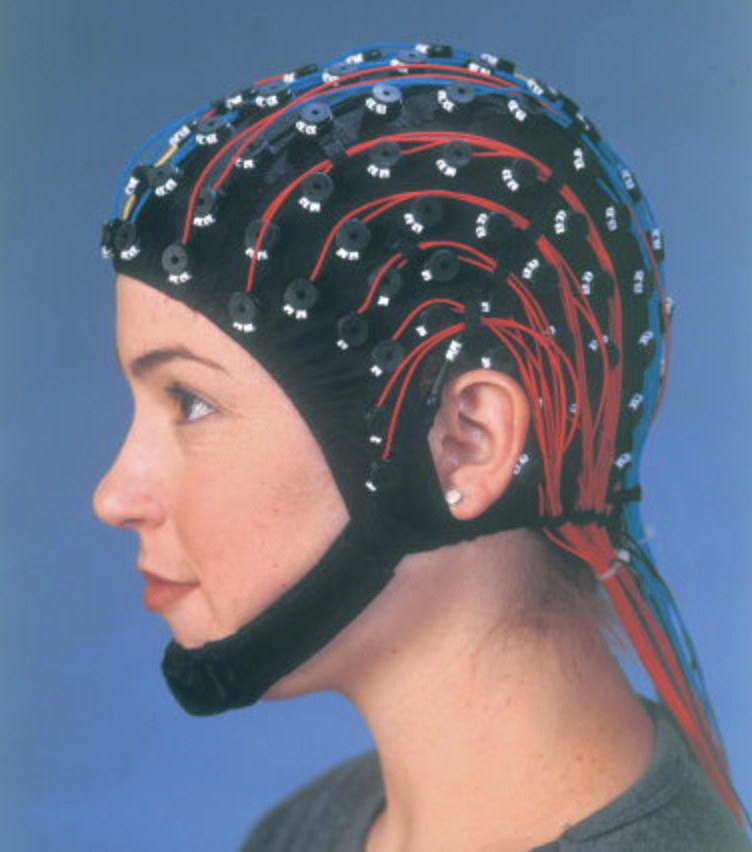
EEG (electroencephalogram) advantages
\-functional, direct
\-functional, direct
good temporal resolution (m/s), not invasive (no radiation), behavioral response unnecessary (can use on baby)
17
New cards
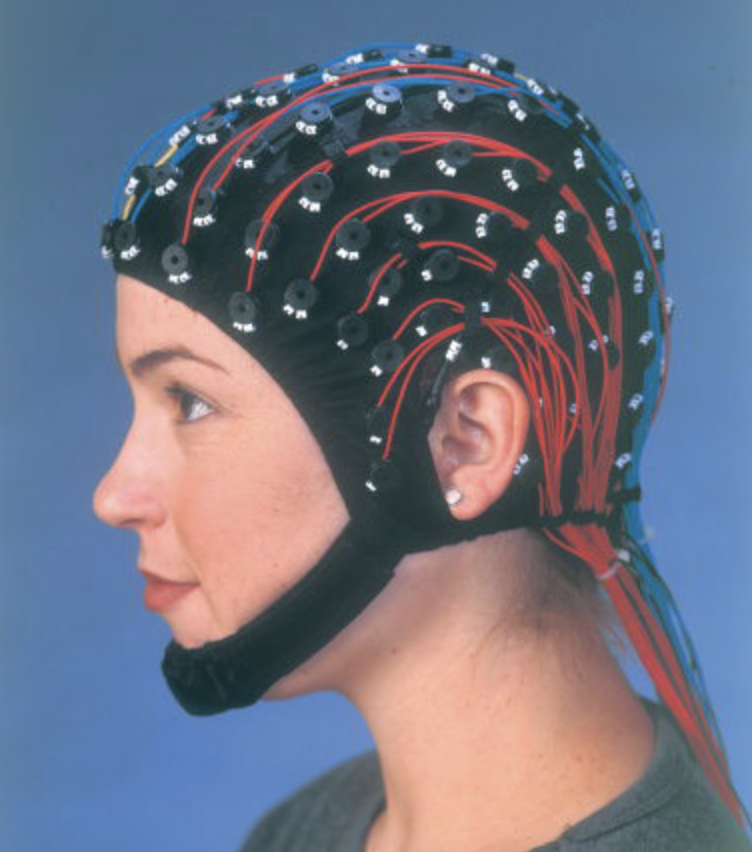
EEG (electroencephalogram) disadvantages
\-functional, direct
\-functional, direct
poor spatial resolution; only a general area
18
New cards
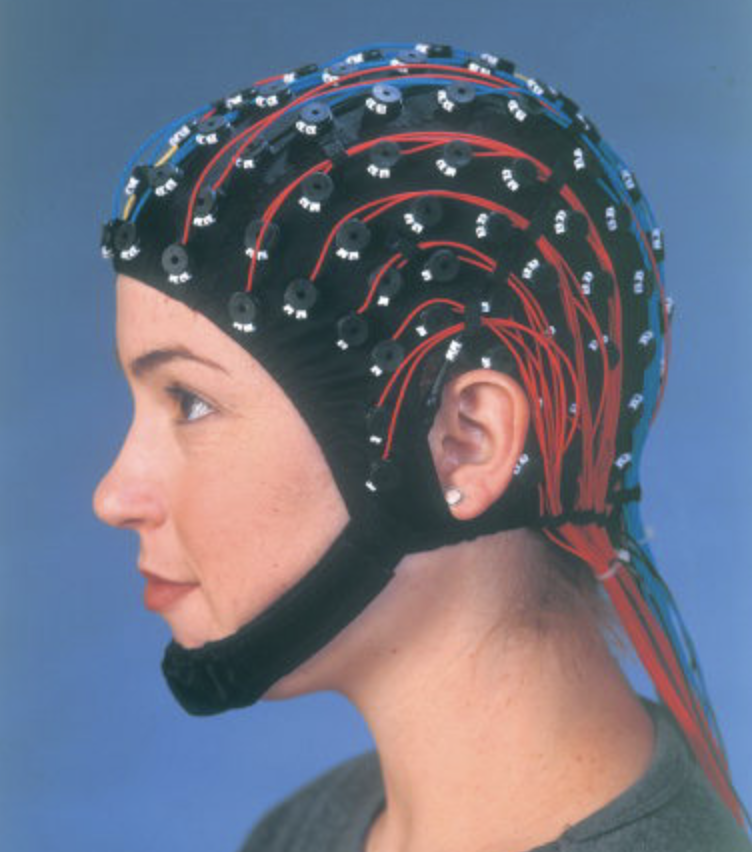
EEG (electroencephalogram) uses
\-functional, direct
\-functional, direct
research: event-related potential (ERP), time locked stimuli to measure brain response
\
hospital diagnostics: seizure, stages of sleep & awake, stimuli response
\
hospital diagnostics: seizure, stages of sleep & awake, stimuli response
19
New cards
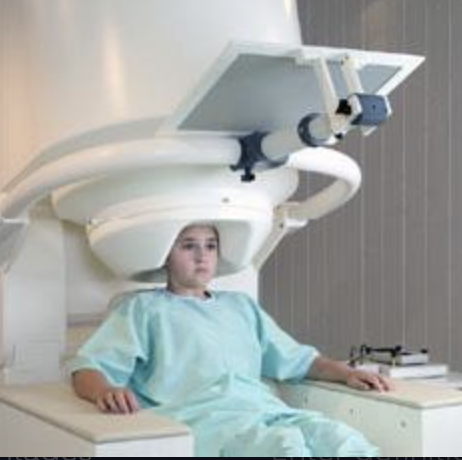
MEG (magnetoencephalography) mechanism
\-functional direct
\-functional direct
measure electrical activity from large group of neurons firing synchronously using a magnet
20
New cards
MEG (magnetoencephalography) advantages
\-functional direct
\-functional direct
good temporal resolution (m/s), better spatial resolution than EEG, magnetic field less distorted than electric fields, combined w/ fMRI=>very strong localization
21
New cards
MEG (magnetoencephalography) disadvantages
\-functional direct
\-functional direct
only surface image, can't have metal
22
New cards
MEG (magnetoencephalography) uses
\-functional direct
\-functional direct
only research
23
New cards
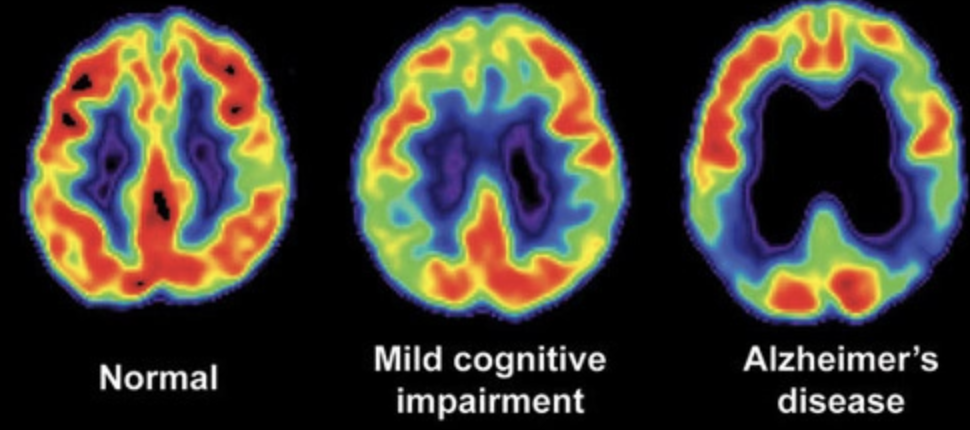
PET (positron emission tomography) scan mechanism
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
radiotracer (radioactive form of glucose) injected into bloodstream, bind to target, accumulate @ highest target concentration, detector ring detects gamma rays radiotracer emits
24
New cards
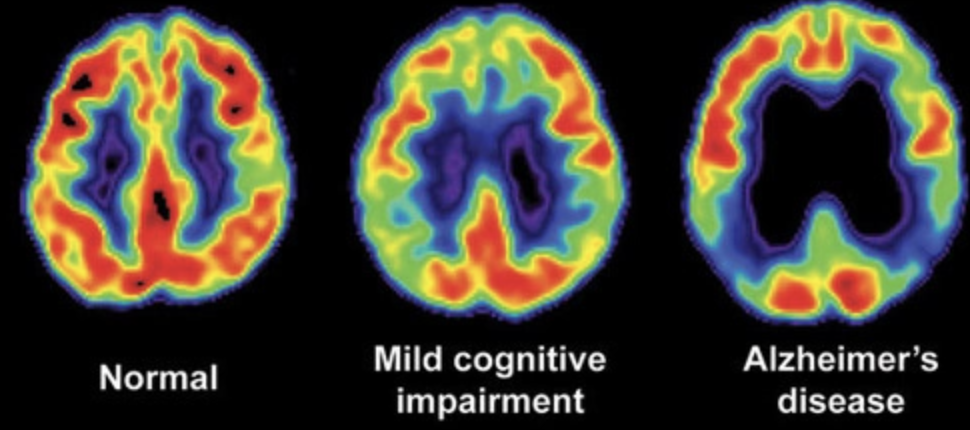
PET (positron emission tomography) scan advantages
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
measure function, baseline (body function=blood flow, oxygen use)
25
New cards
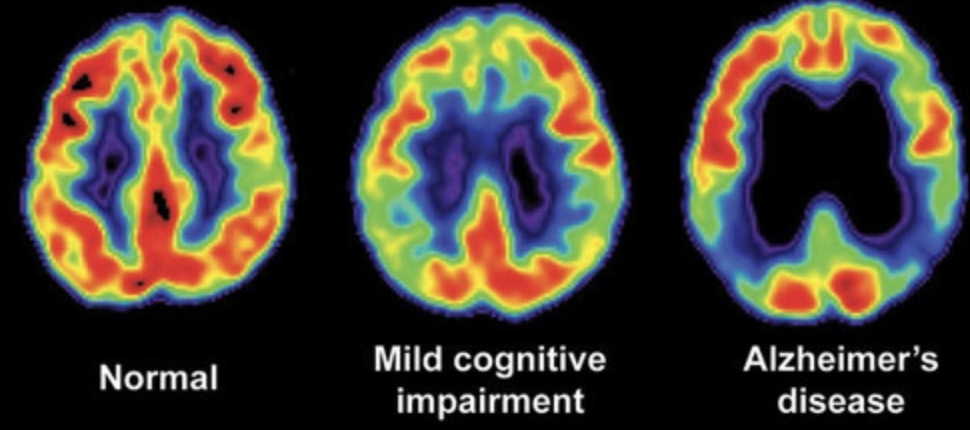
PET (positron emission tomography) scan disadvantages
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
radiation=invasive, poor resolution, expensive
26
New cards
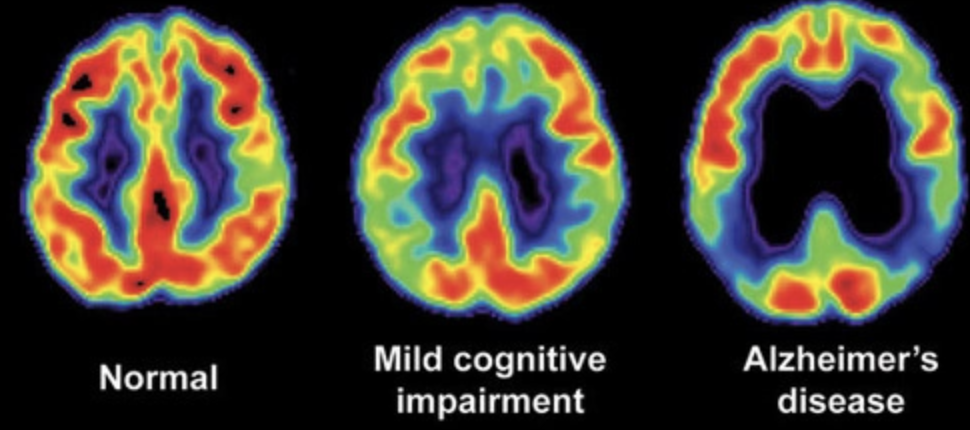
PET (positron emission tomography) scan uses
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
oncology, diagnose diffuse brain disease, research examining brain activity during tasks
27
New cards
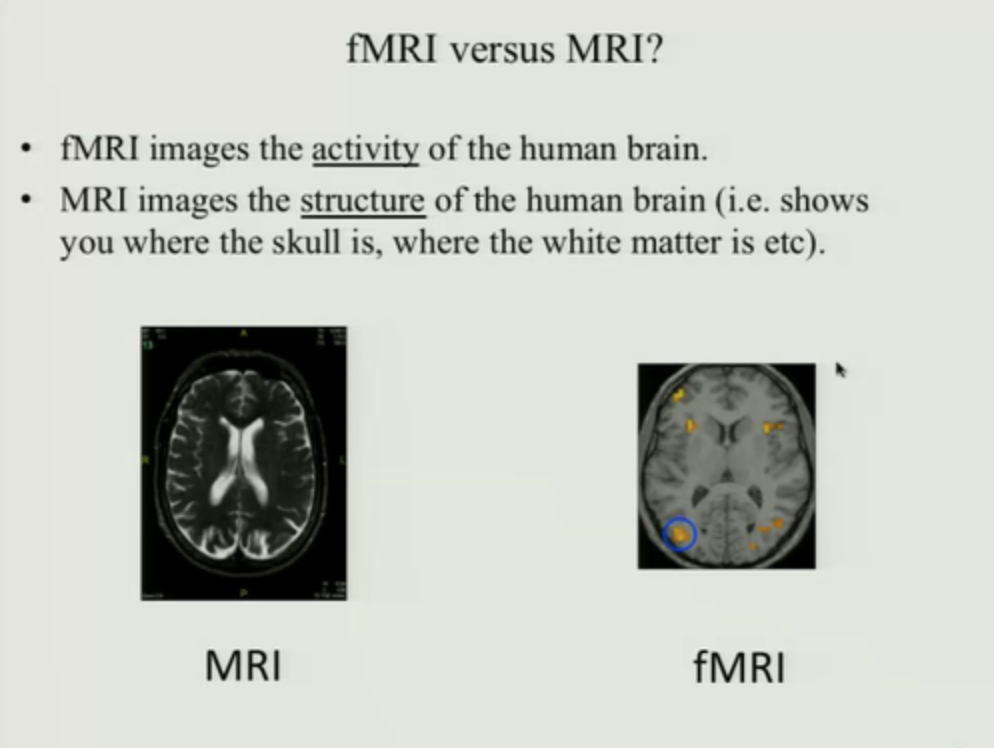
fMRI (functional MRI) mechanism
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
measure BOLD (blood oxygenation level dependent), neural activity increases=increase blood oxygenate (blood flow)=increase MR signal
28
New cards
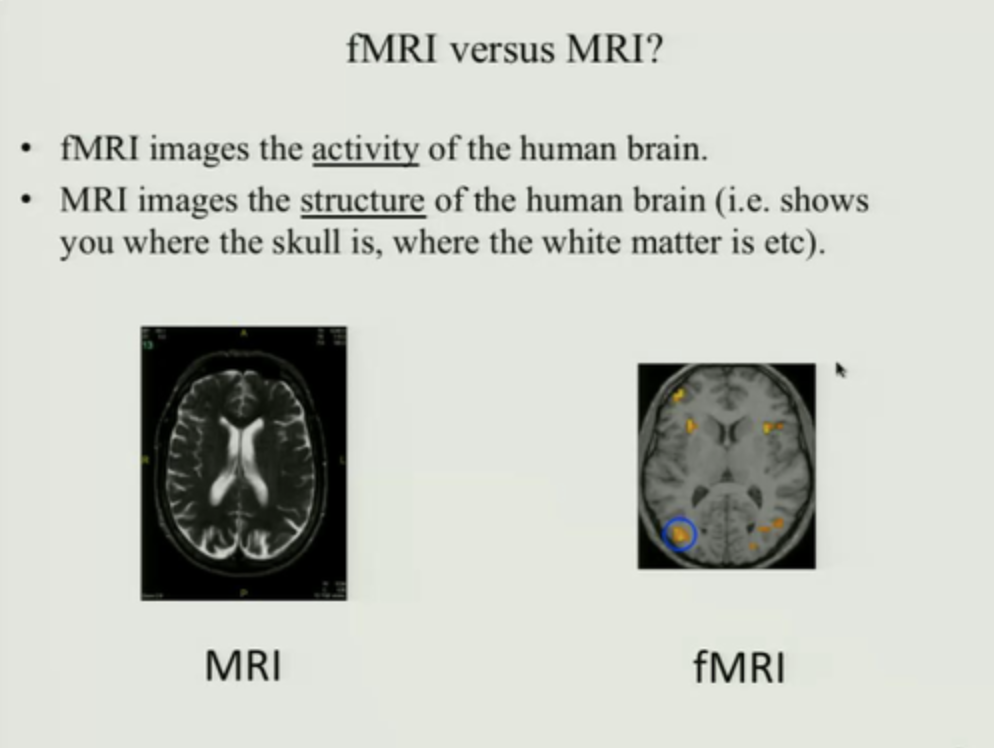
fMRI (functional MRI) advantages
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
no radiation, increase spatial resolution
29
New cards
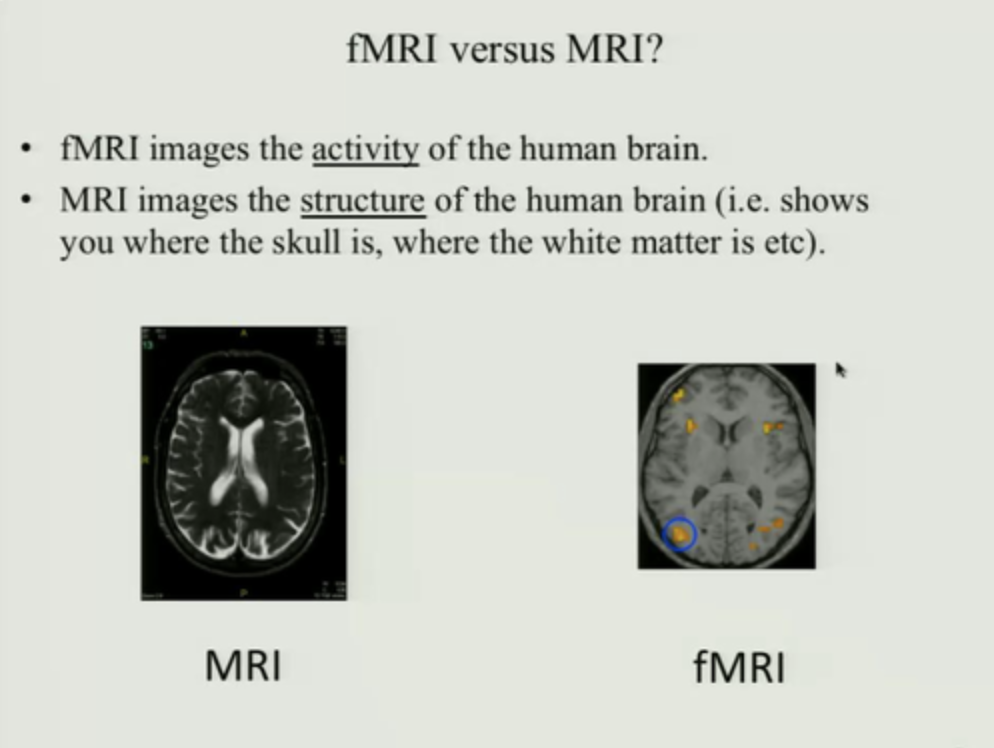
fMRI (functional MRI) disadvantages
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
ethics; not used well (ex: no lie MRI)
30
New cards
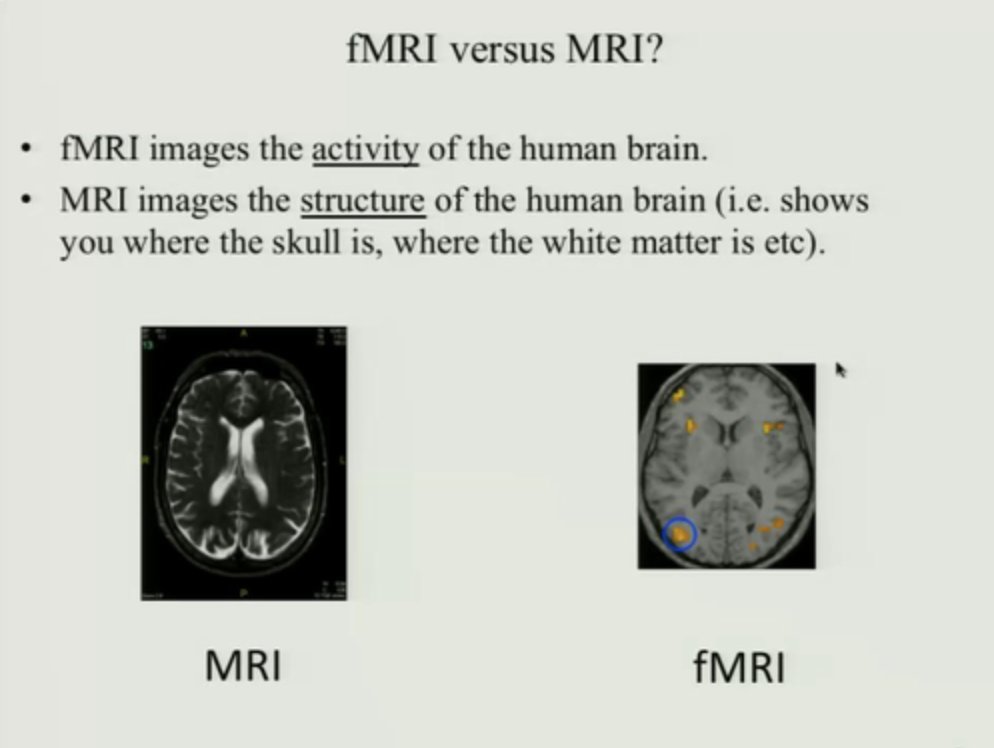
fMRI (functional MRI) uses
\-functional indirect
\-functional indirect
neuropsychology
31
New cards
Define neurophysiology
the study of life processes w/in neurons
32
New cards
electric signal (neuron fire) communication w/in or between neuron?
w/in neuron
33
New cards
chemical signal (neurotransmitter) communication w/in or between neuron?
between neurons
34
New cards
Define ions, cations, and anions.
ions- two oppositely charged atoms
Cations- positive charged ions (+)
Anions- negatively charged ions (-)
Cations- positive charged ions (+)
Anions- negatively charged ions (-)
35
New cards
cations in neurons
K+, Na+, Ca +2
36
New cards
anions in neurons
Cl-, anions (large neg proteins)
37
New cards
outside of neuron
positively charged
salty milk: Na+, Cl-, Ca 2+
salty milk: Na+, Cl-, Ca 2+
38
New cards
inside of neuron
negatively charged
negative banana: K+, Al-
negative banana: K+, Al-
39
New cards
Cell membrane (plasma membrane)
phospholipid bilayer that surrounds all cells and regulates what enters and leaves the cell
\-semipermeable: hydrophobic & small uncharges polar molecules shall pass
\-semipermeable: hydrophobic & small uncharges polar molecules shall pass
40
New cards
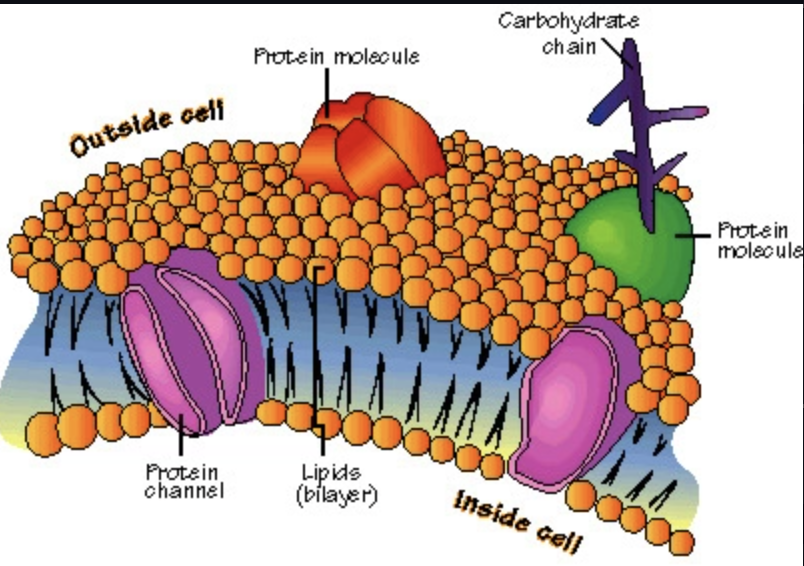
plamsa membrane
outer wall of cell
41
New cards
Phospholipids
molecule that forms the bilayer of the cell's membranes
hydrophobic tail: water hater, nonpolar
hydrophilic head: water lover, polar
hydrophobic tail: water hater, nonpolar
hydrophilic head: water lover, polar
42
New cards
membrane potential (Vm)
diff in distribution of charged ions across cell membrane
\-2 passive & 1 active processes
\-2 passive & 1 active processes
43
New cards
membrane resting potential
\-50 to -80 mV
44
New cards
2 passive processes in membrane potential
1) concentration gradient
2) electrostatic force
2) electrostatic force
45
New cards
1) concentration gradient
high to low concentration across membrane
46
New cards
2) electrostatic force
like charge repel & opposites attract
47
New cards
equilibrium potential
concentration gradient (K+ out) and electrostatic force (K+ in) balance/act against each other; -60mv K+
48
New cards
why is resting potential (between -50 & -80 mv) so similar to equilibrium potential for K+ (-60 mv)?
cuz cell membrane is mostly permeable to K+
49
New cards
active process for membrane potential is? & how?
energy dependent pump (sodium-potassium pump)
\-3Na+ out for every 2+ pumped in
\
\-help distribution of ions (electrical chemical gradient) revert back to normal
\-3Na+ out for every 2+ pumped in
\
\-help distribution of ions (electrical chemical gradient) revert back to normal
50
New cards
action potential
the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
51
New cards
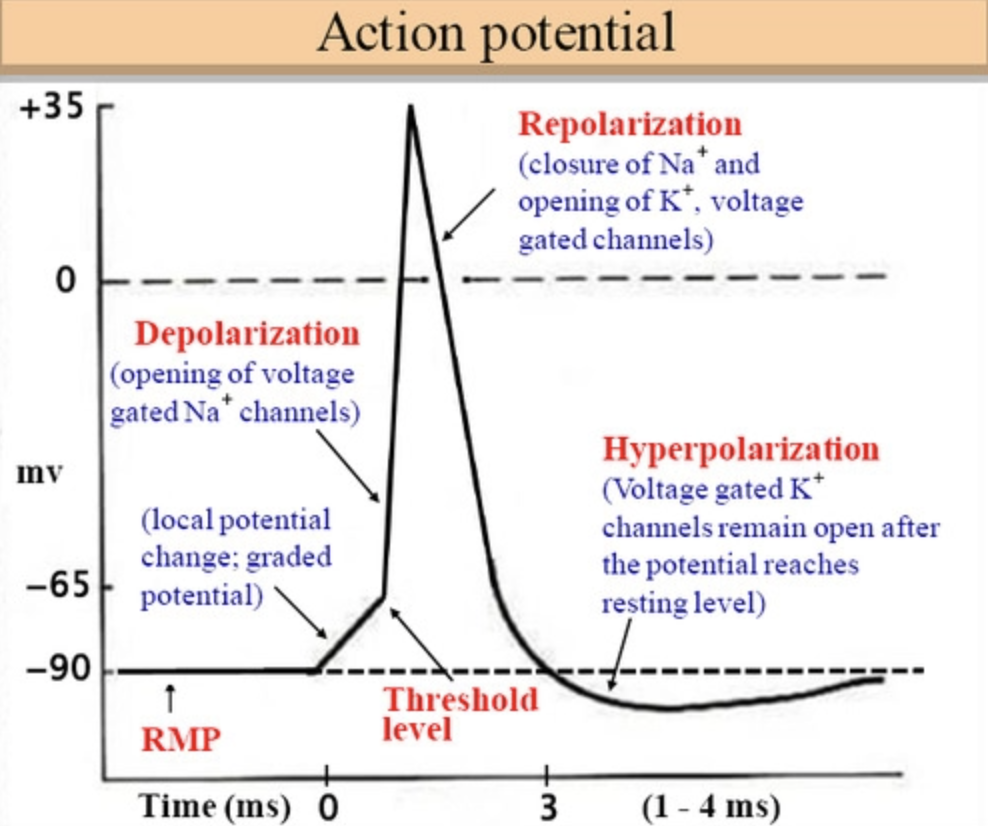
action potential steps
1 - Stimulus disturbs the plasma membrane
2 - Sodium Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to flow into the cell, lessening the polarization/difference in charge at that location
3 - This change causes nearby voltage-gated sodium channels to open, allowing more Na+ to flow into cell
4 - That area of the inside of the cell is now slightly more positive, and the outside, slightly more negative
5 - This affects other nearby voltage-gated Na+ channels and depolarization moves down the membrane = action potential
6 - These channels close and voltage-gated potassium K+ channels open, potassium flows out of the cell repolarizing the membrane
7 - Sodium-potassium pumps then restore resting potential and reestablish proper concentrations of Na+ and K+
2 - Sodium Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to flow into the cell, lessening the polarization/difference in charge at that location
3 - This change causes nearby voltage-gated sodium channels to open, allowing more Na+ to flow into cell
4 - That area of the inside of the cell is now slightly more positive, and the outside, slightly more negative
5 - This affects other nearby voltage-gated Na+ channels and depolarization moves down the membrane = action potential
6 - These channels close and voltage-gated potassium K+ channels open, potassium flows out of the cell repolarizing the membrane
7 - Sodium-potassium pumps then restore resting potential and reestablish proper concentrations of Na+ and K+
52
New cards
all-or-none property of action potentials
the neuron fires at full amplitude or not at all-does not reflect increased stimulus strength (no variation)
53
New cards
permeability changes
1) Na+ depolarize
2) K+ repolarize
2) K+ repolarize
54
New cards
depolarization (+) and repolarization (-)
For an action potential to occur, the neuron will first experience local __________ when sodium rushes into the cell, and then __________ as potassium leaves the cell and the impulse continues down the axon.
55
New cards
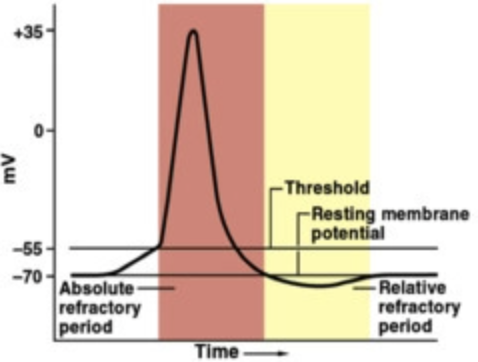
absolute refractory period
The minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin, completely insensitive to further stimulation
56
New cards
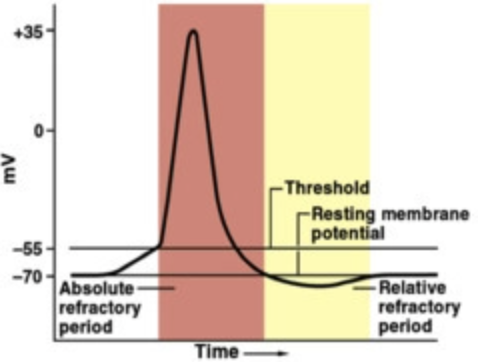
relative refractory period
A period after firing when a neuron is returning to its normal polarized state and will fire again only if the incoming message is much stronger than usual; reduced sensitivity to further stimulation
57
New cards
1) electrotonic conduction
passive current flow through neurons that accompanies activated electrical currents, passive decays w/ time distance from initiation site (smaller over time)
58
New cards
2) active conduction
repeated renewal of a long-range electrical signal along the axon, action potential from axon hillock to axon terminal, not lessen over length of axon, opening Na+ voltage gate channels depolarizes
59
New cards
3) saltatory conduction
Potential moves from electric field to field between nodes of Ranvier
= much faster than as it doesn't require inducing changes all along, Na + currents faster & farther, need less regeneration
= much faster than as it doesn't require inducing changes all along, Na + currents faster & farther, need less regeneration
60
New cards
synaptic transmission
The relaying of information across the synapse by means of chemical neurotransmitters. presynaptic axon terminal to postsynaptic dendrites
61
New cards
synaptic transmission steps
1\. action potential arrives at the axon terminal
2\. voltage gated Ca 2+ channels open
3\. Ca 2+ enters the cell
4\. Ca 2+ signals to vesicles
5\. vesicles move to the membrane
6\. docked vesicles release neurotransmitter by exocytosis
7\. neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse and binds to receptors
8) EPSP or IPSP
9) enzyme breaks down excess NT
10) reuptake & recycle of NT slows synaptic action
11) NT binds to autoreceptors of presynaptic membrane
12) spatial or temporal summation
2\. voltage gated Ca 2+ channels open
3\. Ca 2+ enters the cell
4\. Ca 2+ signals to vesicles
5\. vesicles move to the membrane
6\. docked vesicles release neurotransmitter by exocytosis
7\. neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse and binds to receptors
8) EPSP or IPSP
9) enzyme breaks down excess NT
10) reuptake & recycle of NT slows synaptic action
11) NT binds to autoreceptors of presynaptic membrane
12) spatial or temporal summation
62
New cards
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
a slight graded depolarization of a postsynaptic cell, bringing the membrane potential of that cell closer to the threshold for an action potential (+, cations), slower than action potential
63
New cards
inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
graded hyperpolarization (-, anion) of postsynaptic membrane, lowers probability of action potential firing, slower than action potential
64
New cards
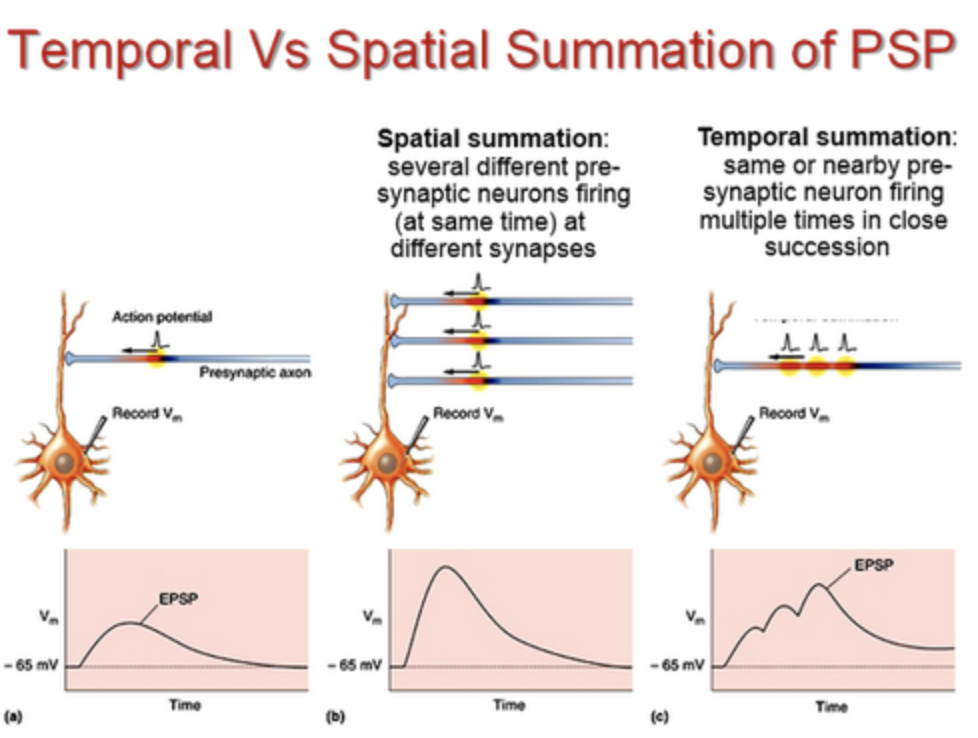
spatial summation
The sum of multiple synapses firing at different locations at one time to create a net effect, input across space, closer=better
65
New cards
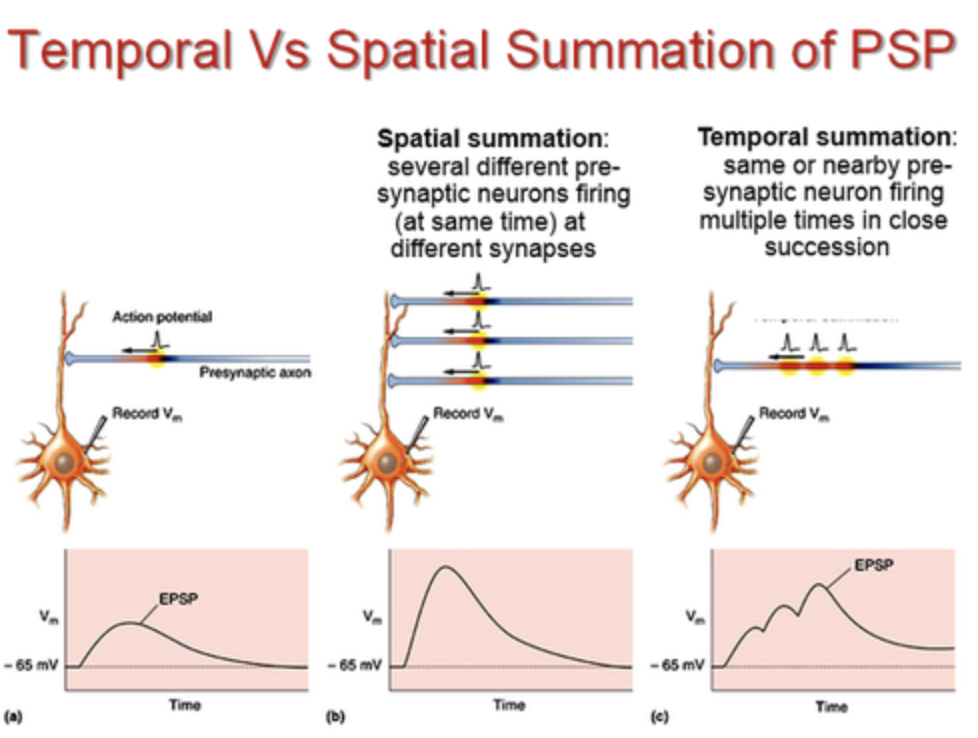
temporal summation
Summation by a postsynaptic cell of input (EPSPs or IPSPs) from a single source over time, input across time, time closer together=better
66
New cards
receptor & neurotransmitter is analogous to...
lock=receptor
neurotransmitter=key
neurotransmitter=key
67
New cards
ionotropic receptors
receptors that are coupled to ion channels and affect the neuron by causing those channels to open
\-mediate fast EPSP (cation, depolar), IPSP (anion, hyperpolar)
\-mediate fast EPSP (cation, depolar), IPSP (anion, hyperpolar)
68
New cards
Acetylcholine
quaternary
\-found in basal forebrain
\-project to cortex, amygdala, hippocampus
\-found in basal forebrain
\-project to cortex, amygdala, hippocampus
69
New cards
Acetylcholine role
sleep, attention, learning and memory
70
New cards
Acetylcholine disease
Alzheimer's disease
71
New cards
Acetylcholine broken down by
acetylcholinesterase (AChe) very fast
72
New cards
acetylcholine receptors
nicotinic (ionotropic) and muscarinic (metabotropic)
73
New cards
Dopamine (monoamine)
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) from substantia nigria (midbrain) to striatum (part of basal ganglia)
2) central tegmental (midbrain to limbic system & cortex
2) central tegmental (midbrain to limbic system & cortex
74
New cards
Dopamine role
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) motor control
2) reward & pleasure
2) reward & pleasure
75
New cards
Dopamine disease
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) Parkinson's disease
2) schizophrenia, addictive behaviors
2) schizophrenia, addictive behaviors
76
New cards
Dopamine reuptake
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
dopamine transporter (DA), slow
77
New cards
Dopamine broken down
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
monoamine oxidase (MAG) target of antidepressants
78
New cards
Dopamine receptors
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
1) mesostrial system
2) mesostriatial system
D1 (excitatory) and D2 (inhibitory)
both metabotrophic & G-protein
both metabotrophic & G-protein
79
New cards
Norepinephrine monoamine
project from locus coerolous (midbrain) & lateral tengmental (pons) to thalamus, amygdala, cortex, cerebellum
80
New cards
Norepinephrine role
sleep, stress, mood, alertness, sexual behavior
81
New cards
Norepinephrine disease
depression, ADHD
82
New cards
Norepinephrine reuptake
norepinephrine transporter (NET) slow
83
New cards
Norepinephrine broken down
monoamine oxidase (MAO)
84
New cards
Norepinephrine receptor
alpha , beta
\-metabotrophic, G protein
\-metabotrophic, G protein
85
New cards
Serotonin (monoamine)
project from raphe nuclei (brainstem) to hippocampus, basal ganglia
86
New cards
Serotonin role
sleep and mood
87
New cards
Serotonin disease
also depression & ADHD
88
New cards
Serotonin reuptake
serotonin transporter (SERT)
89
New cards
Serotonin receptors
5-HT 1-7=metabotrophic, G-protein
\
5-HT2=ionotrophic
\
5-HT2=ionotrophic
90
New cards
Glutamate (amino acid)
The principal excitatory neurotransmitter in limbic, basal ganglia circuits
91
New cards
Glutamate role
learning and memory some level all behavior
92
New cards
Glutamate diseases
glutamate excitotoxicity, Alzehimer's disease, Mild Cognitive disease (MCI), Impairment Amyotrophic (ALS)
93
New cards
Glutamate reuptake
Glutamate Transporters (excitatory amino acid transporters - EAAT1-5)
fast astrocytes contribute, recycled into vesicles for later
fast astrocytes contribute, recycled into vesicles for later
94
New cards
Glutamate receptors
AMPA and NMDA (inotropic), memory formation
95
New cards
GABA (amino acid)
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter found throughout brain, predominantly interneurons
96
New cards
GABA role
involved in all behavior at some level
97
New cards
GABA disease
drug increase GABA to treat anxiety, epilepsy, stress
98
New cards
GABA reuptake
GABA transporters on astrocytes and neurons
\- GABA transporters (GAT)
\- recycling breakdown
\- GABA transporters (GAT)
\- recycling breakdown
99
New cards
GABA receptors
GABAa (ionotropic) and GABAb (metabotropic)
100
New cards
Neuropeptides: Opioid Peptides
endogenous peptides (made form body naturally)mimic opiate drugs such as morphine and reduce the perception of pain, anxiety