10.ECG 606
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
How would you characterize the resting potential of cardiac pacemaker cells?
There is no standard stable resting potential in these cells. The membrane potential continuously shifts upwards until the cell reaches the threshold potential and enters the “0” phase of action potential.
How many chambers that the heart have from the anatomical point of view?
4
How many chambers does the heart have electrophysiological point of view?
2
Traditionally how many routine surface ECG leads are used?
12
List the routine ECG leads.
I, II, III
aVR, aVL, aVF
V1-6
Normally in which lead can you fimd the transition zone.
V3
To which direction(charge) does the dipole vector point?
From negative charge towards the positive charge
What is the normal range of heart rate for a healthy adult?
60-100/min
How long is the normal PR interval?
120-200 milliseconds (0.12-0.20 second)
What is the normal QRS duration?
80-100 milliseconds
What factors cause atrial dilatation/ enlargement? List the major causes of atrial enlargement.
Pressure and/or volume overload in atria
What are the characteristics of coronary T?
Pointed, symmetrical, negative/discordant T wave
What is the most characteristic ECG sigh of Prinzmetal angina?
Transient ST elevations
Which abnormality do you have to think about when you see the signs of localized injury in ECG?
Acute Myocardial Infarction(AMI)
Which chamber is affected by myocardial infarction in most cases?
LEFT ventricle
Which leads correspond to the apical part of the heart?
V5, V6
What is the typical range of heart rate in junctional escape rhythm(=Heart’s electrical signal starts from AV node/junction instead of SA node)?
40-60/min
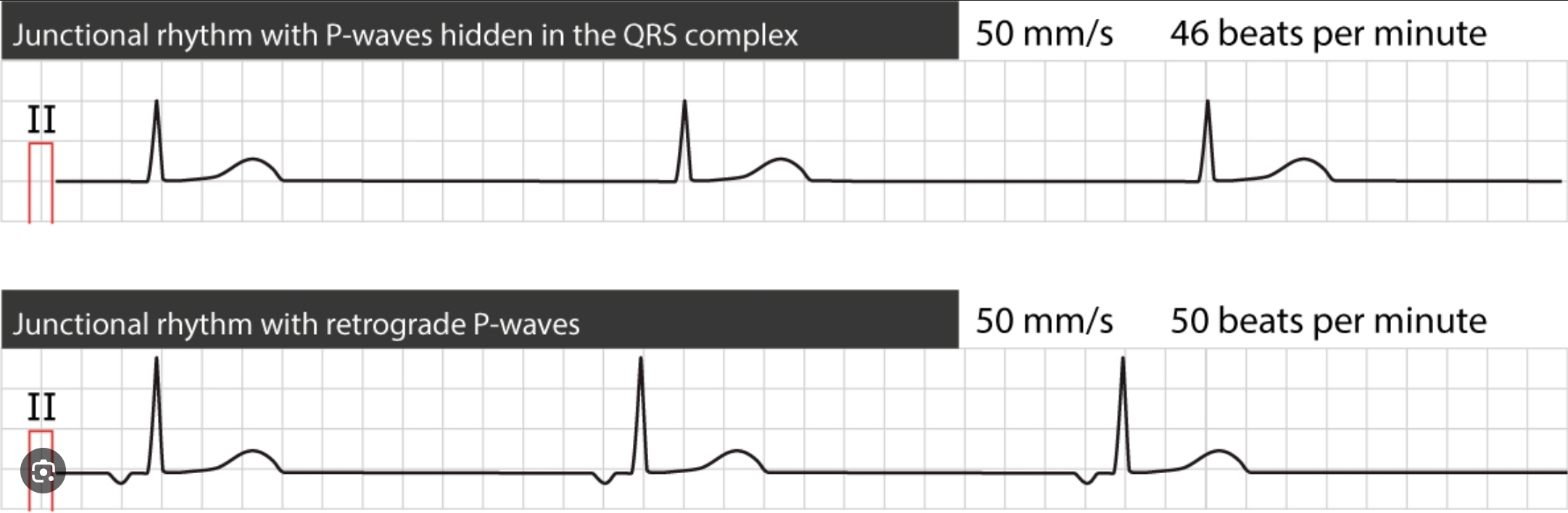
What is the typical range of heart rate in a ventricular escape rhythm(=compensatory heart rhythm that occurs when the heart’s natural pacemakers fail causing a slower rhythm to originate from the ventricles)?
20-40/min

Define allorhythmia.
Extrasystole is repeated with certain regularity.
Regular occurences of extrasystoles in an otherwise normal sinus rhythm e.g., bigeminy, trigeminy
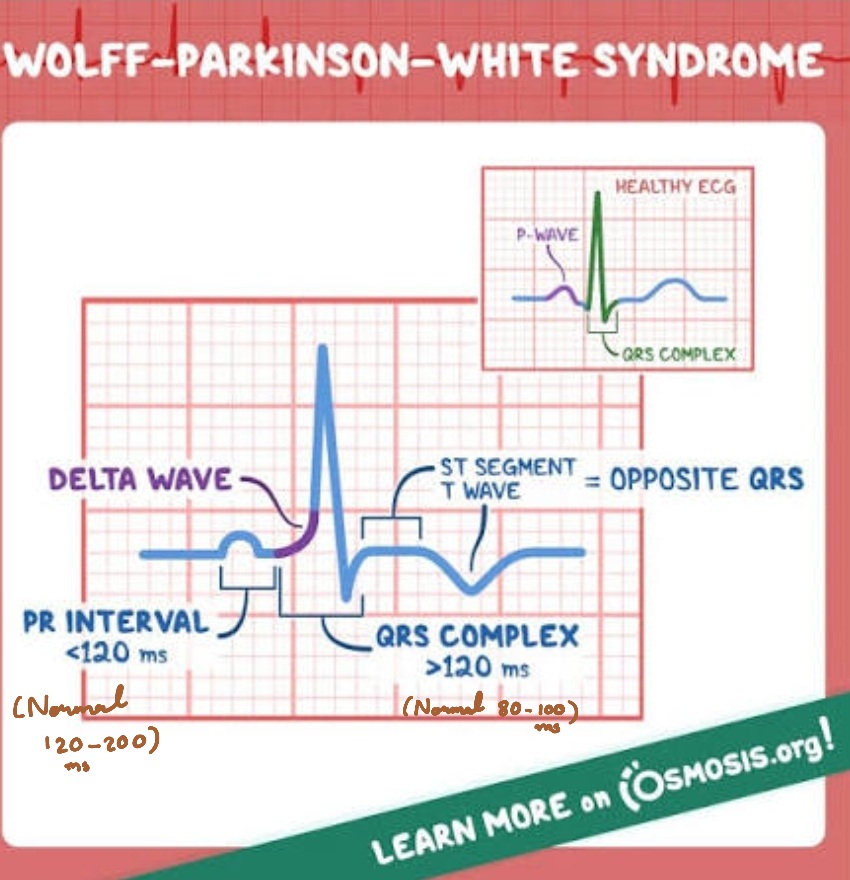
List the most common preexcitation syndrome.
WPW(Wolf-Parkinson-White)
LGL(Lown-Ganong-Levine)
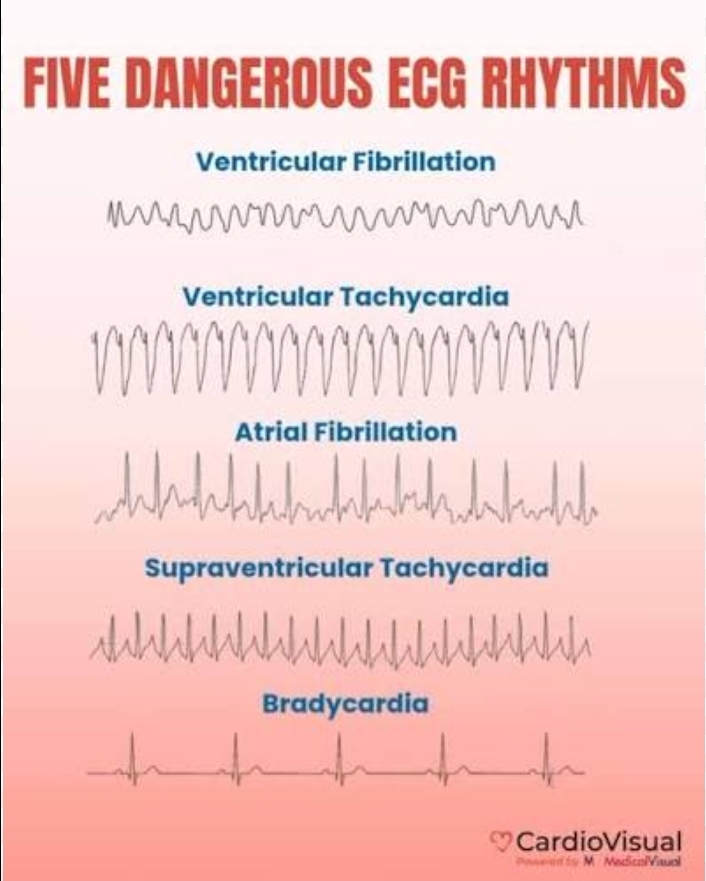
Characterize the cardiac output in ventricular fibrillation.
Practically zero
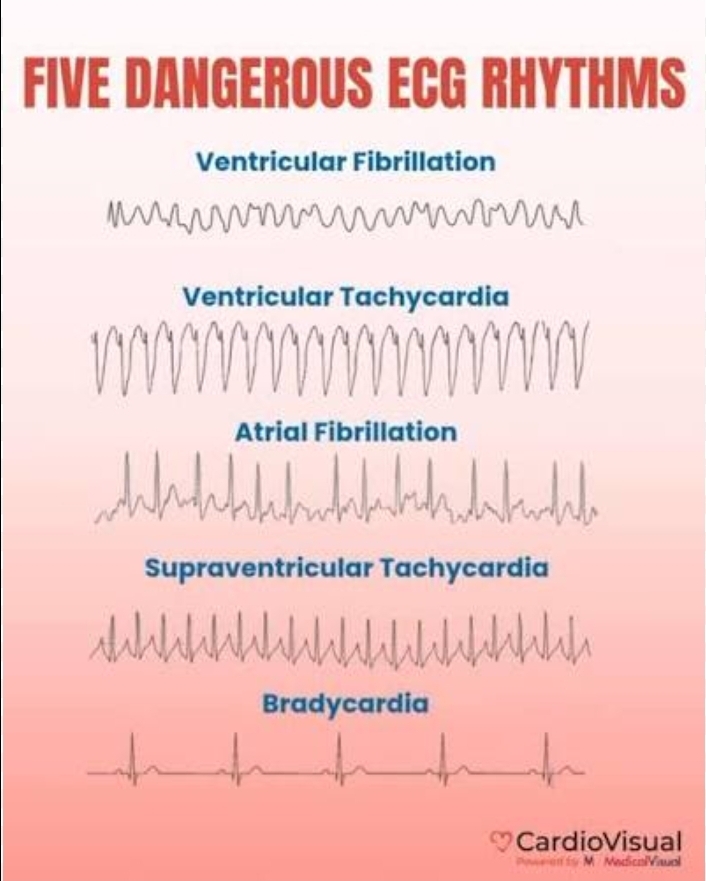
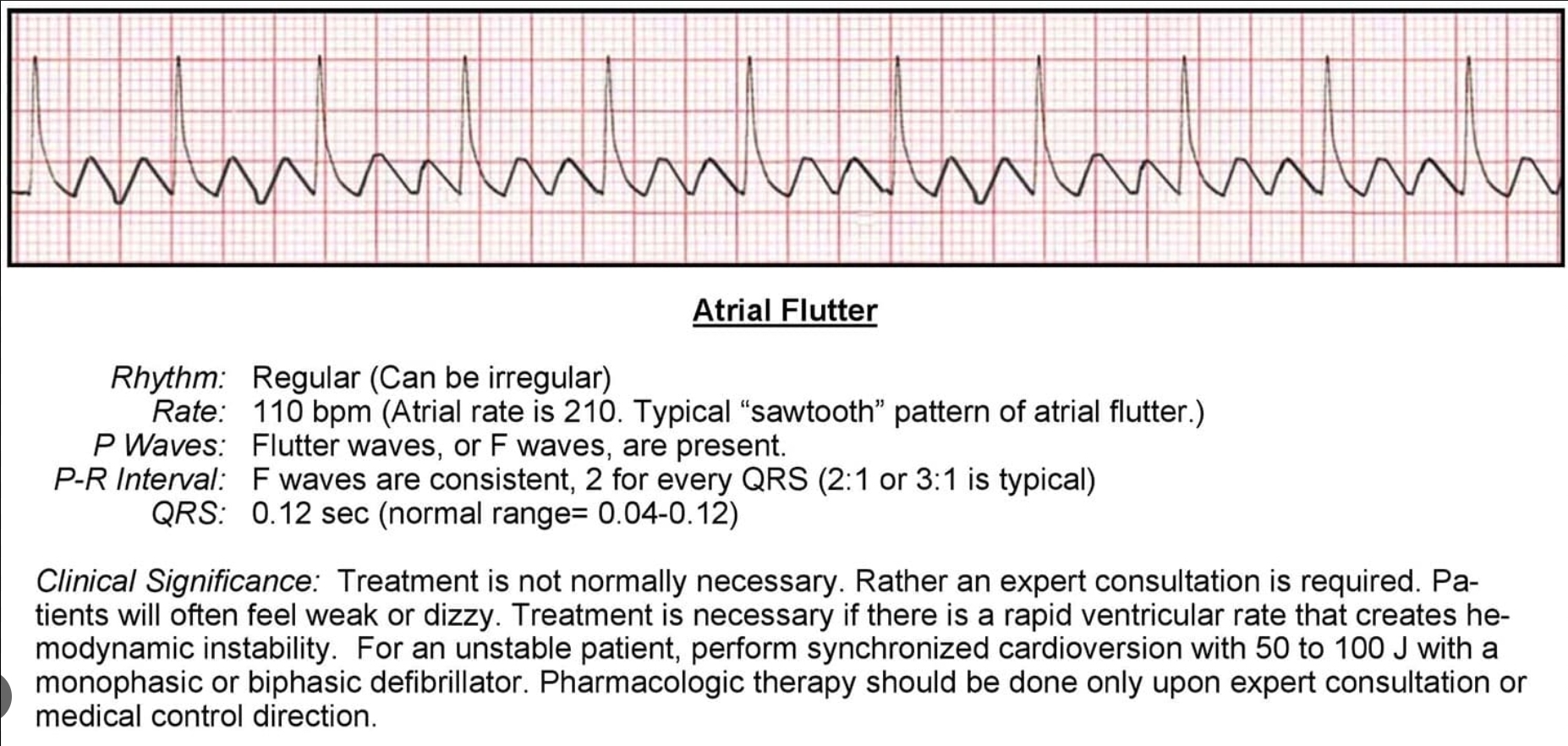
In which stimulus formation disorder(arrhthymia)can you see characteristic F waves in sawtooth pattern?
Atrial flutter
What is the QRS duration in complete bundle branch block?
More than 120 milliseconds(vs normal 80-100 milliseconds)
What electric charge does the surface of depolarized myocardial fibers show compared to the surface of resting myocardial fibers?
Negative
Define the direction of depolarization within the myocardial wall.
From subendocardial to subepicardial region
Define the direction of repolarization within the myocardial wall.
From subepicardial to subendocardial region
Which ECG leads are found in the frontal plane?
I, II, III,aVR,aVL,aVF
Draw the diagram of the hexaxial reference system. List the individual leads and their corresponding position.
I +0°
II +60°
aVF +90°
III +120°
aVR -150°
aVL -30°
What is the typical paper speed at which the ECG is recorded in Hungary?
25mm/s
What does the P wave of ECG represent?
Atrial depolarization
What does the PQ/PR interval represent in ECG?
Delay of atrio-ventricular conduction
What does the QRS complex represent in ECG?
Ventricular depolarization
What are the signs of ventricular repolarization in ECG?
ST segment, T wave
What is the direction of the normal T wave in the limb leads?
Concordant (i.e. positive T wave follows positive main deflection, negative T wave follows negative main deflection)
What is the direction of the normal T wave in the chest leads?
Positive
What are the ECG signs of left atrial enlargement?
Mitral P(normal amplitude, increased duration), P terminal force

What is the Sokolov-Lion index?
Positive index indicates left ventricular hypertrophy RV5+SV1>= 35mm.
What are the ECG signs of stable angina pectoris?
Transient, generalized ST depressions induced by exercise or stress
Whatbare the ECG signs of pericarditis?
Diffuse ST elevations, low voltage
What are the signs of myocardial necrosis?
Pathological Q wave
Reduction of R wave
In which phase of the myocardial infarction does the ST elevation occur?
Hyperacute phase
What are inferior leads?
II, III, aVF
Which endocrine disease may lead to atrial fibrillation?
Hyperthyreodism
What is the bigeminy?
A type of allorhythmia in which a normal sinus beat always followed by extrasystole(premature beat). Consequently, every second beat is an extrasystole.
In a right bundle branch block, which leads are characterized by a prolonged VAT (Ventricular Activation Time)?
V1, V2
In left bundle branch block, which leads are characterized by a prolonged VAT(Ventricular Activation Time)?
V5, V6
What is the cause of pre-excitation syndrome?
A congenital atrio-vetricular accessory bundle
What are the ECG signs of WPW syndrome?
Short PQ/PR-interval
Delta wave
Slightly widened QRS
Secondary ST/T abnormalities