ACS Organic Chemistry I & II Reactions Reagents, and Functional Groups
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
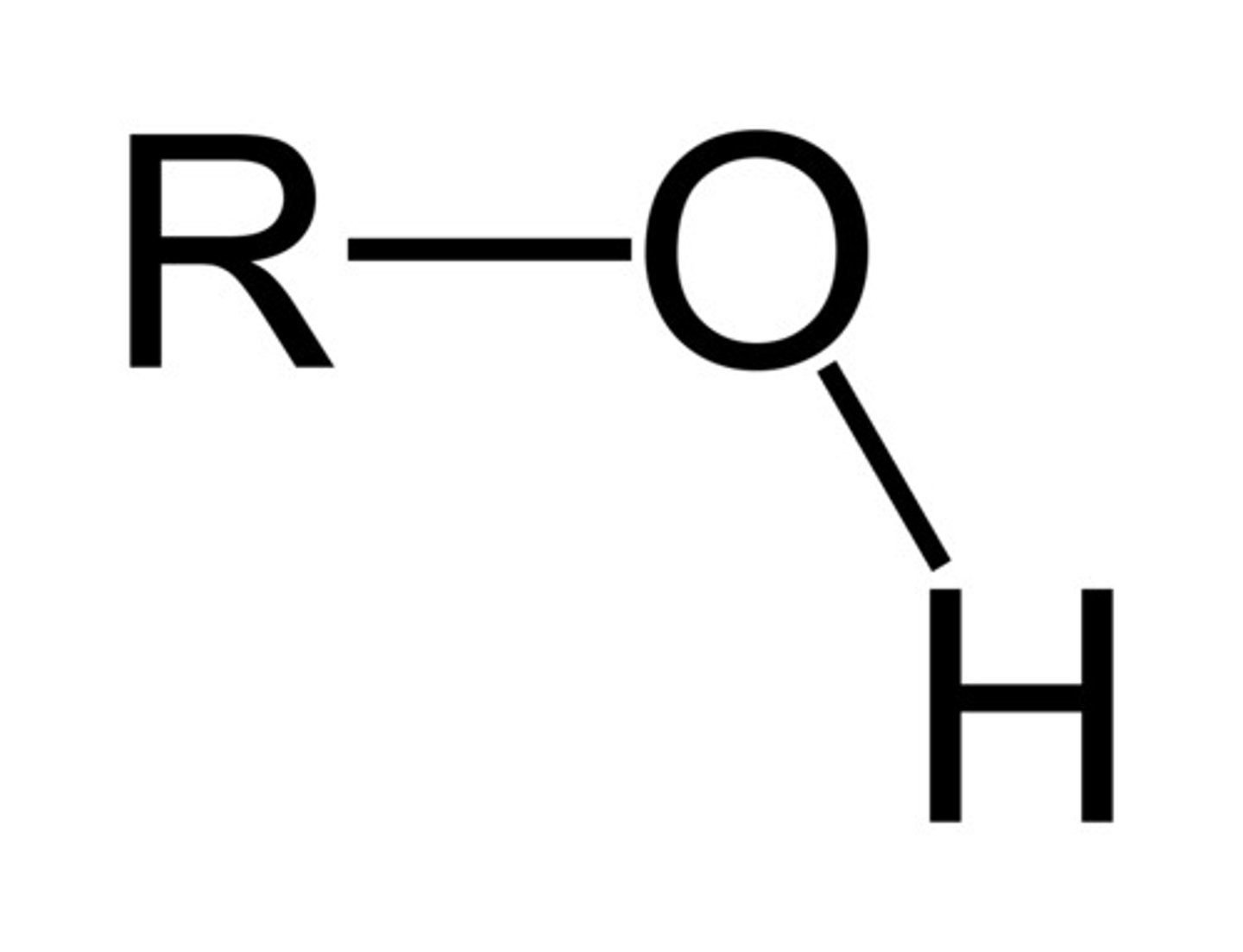
Alcohol
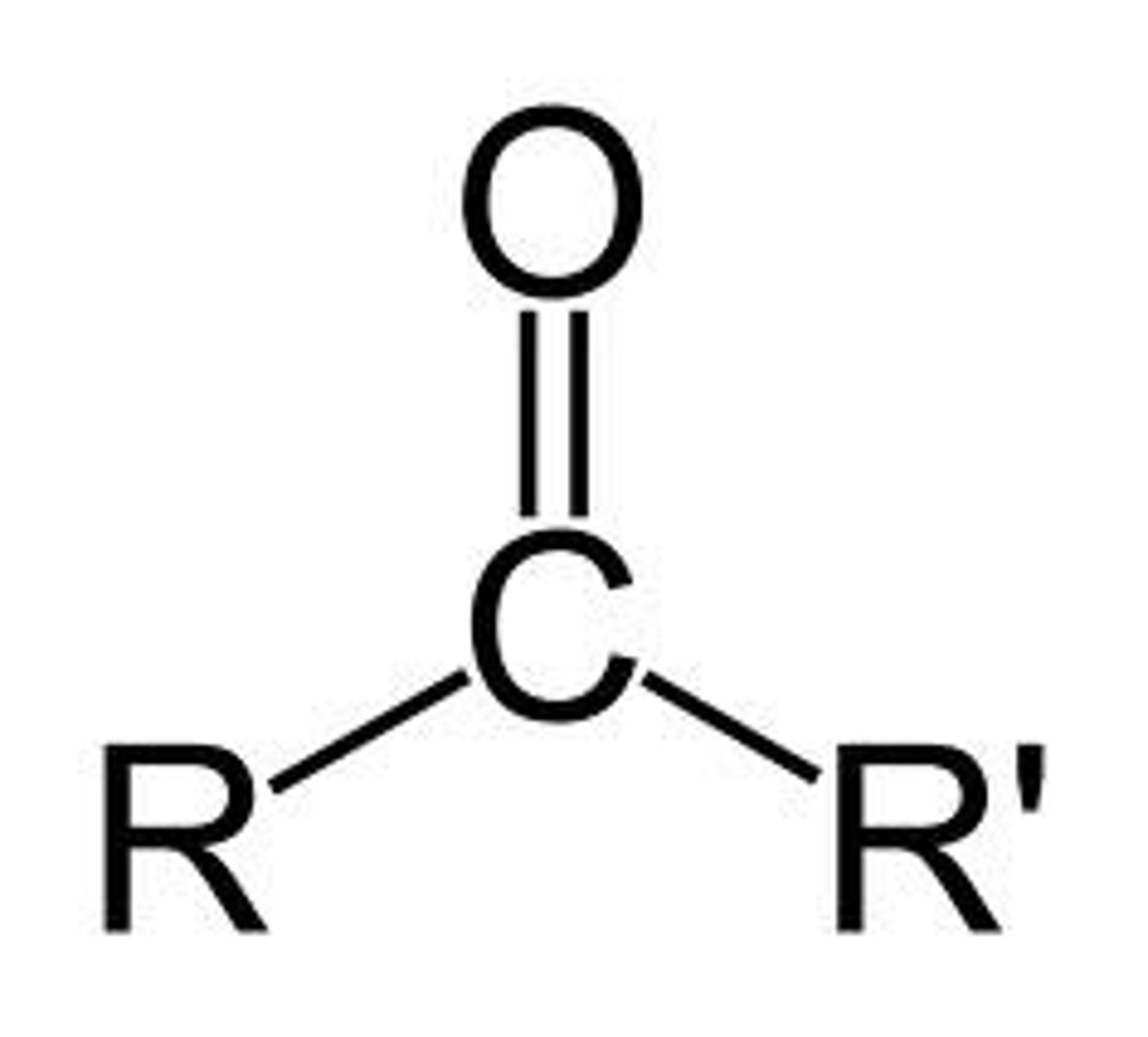
Ketone
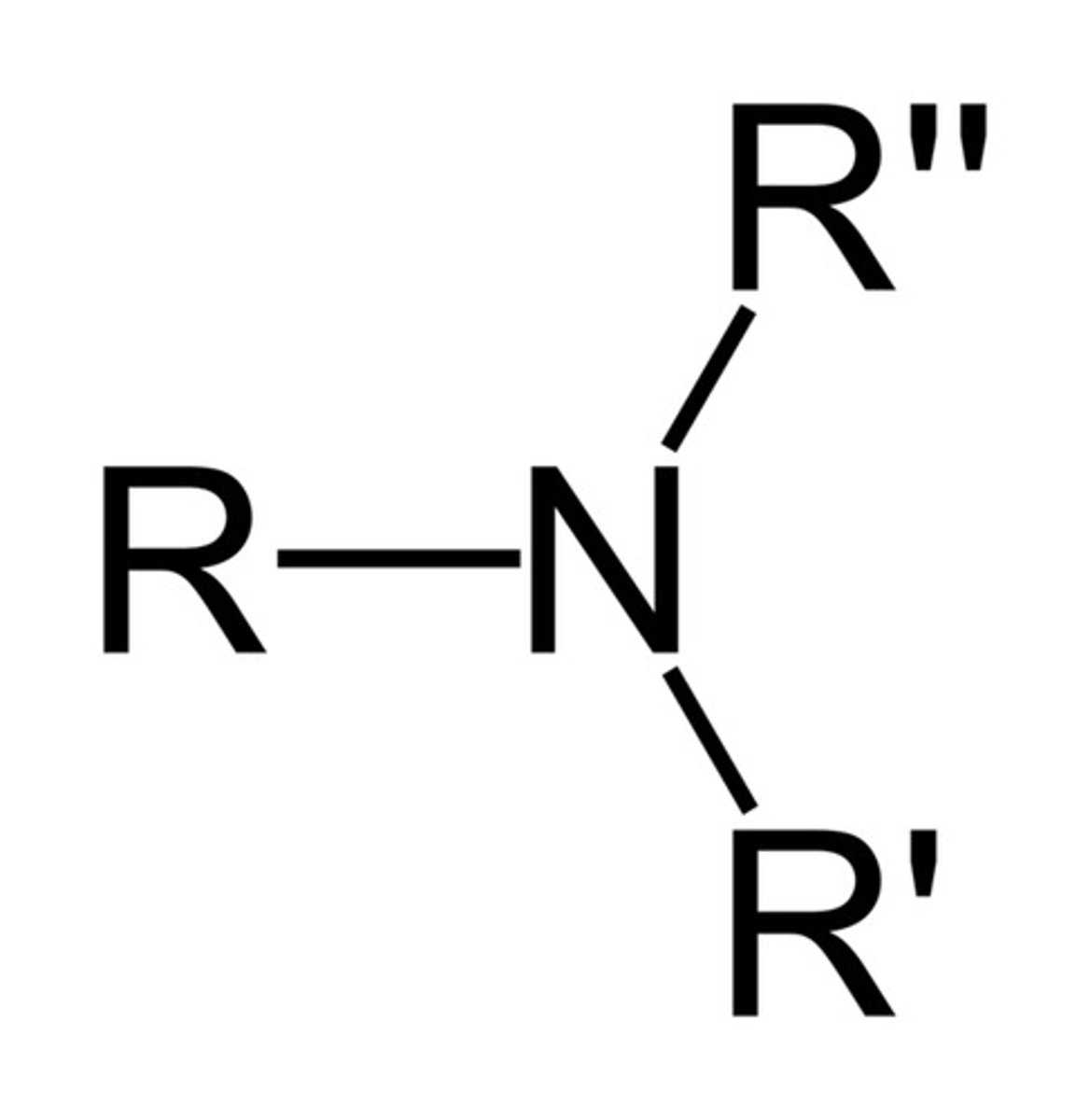
Amine
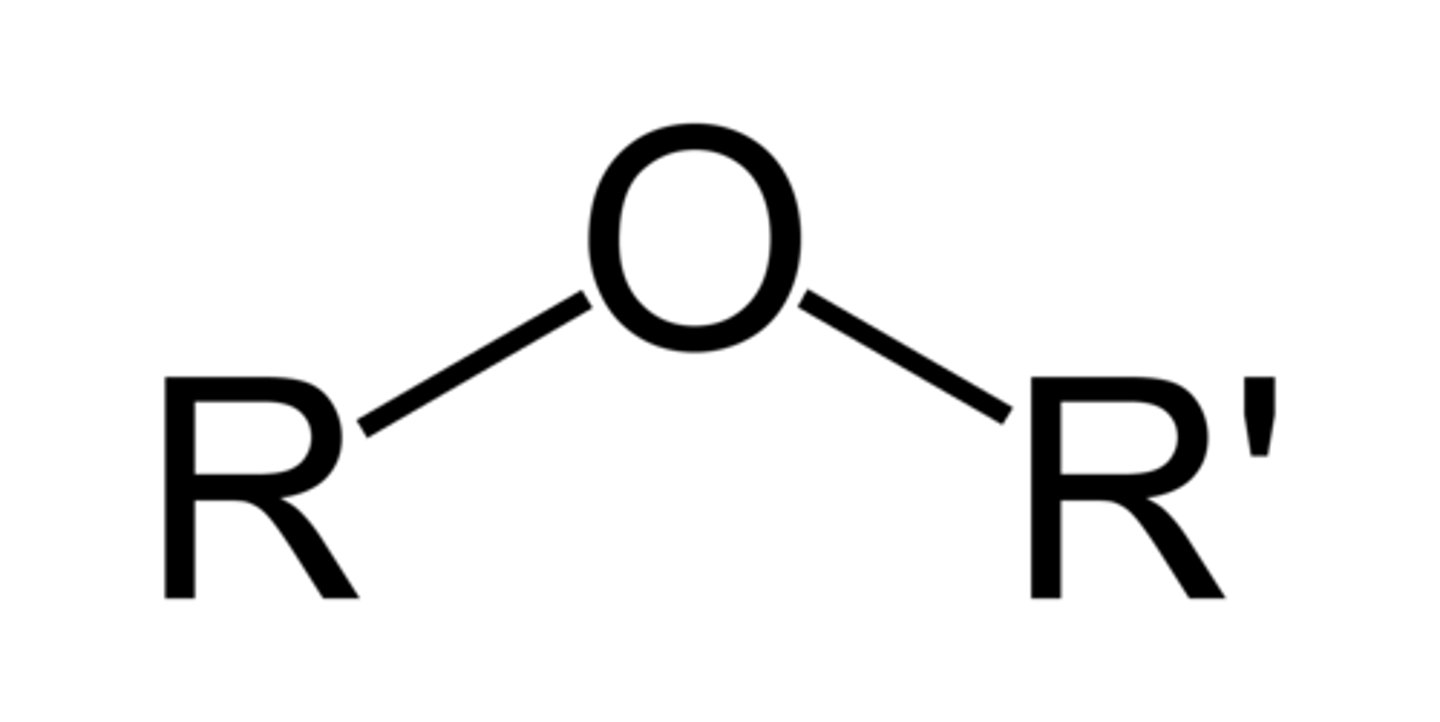
Ether
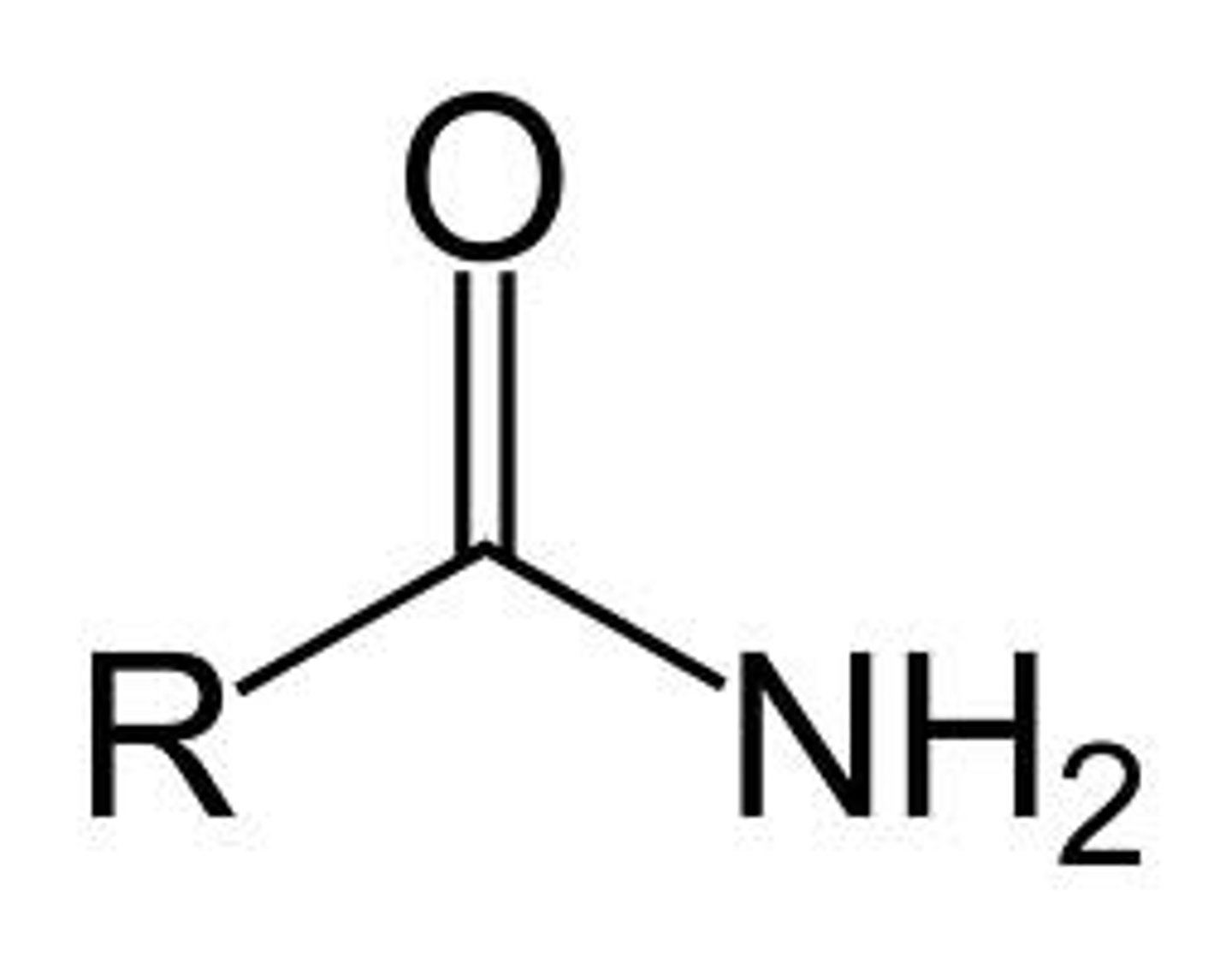
Amide
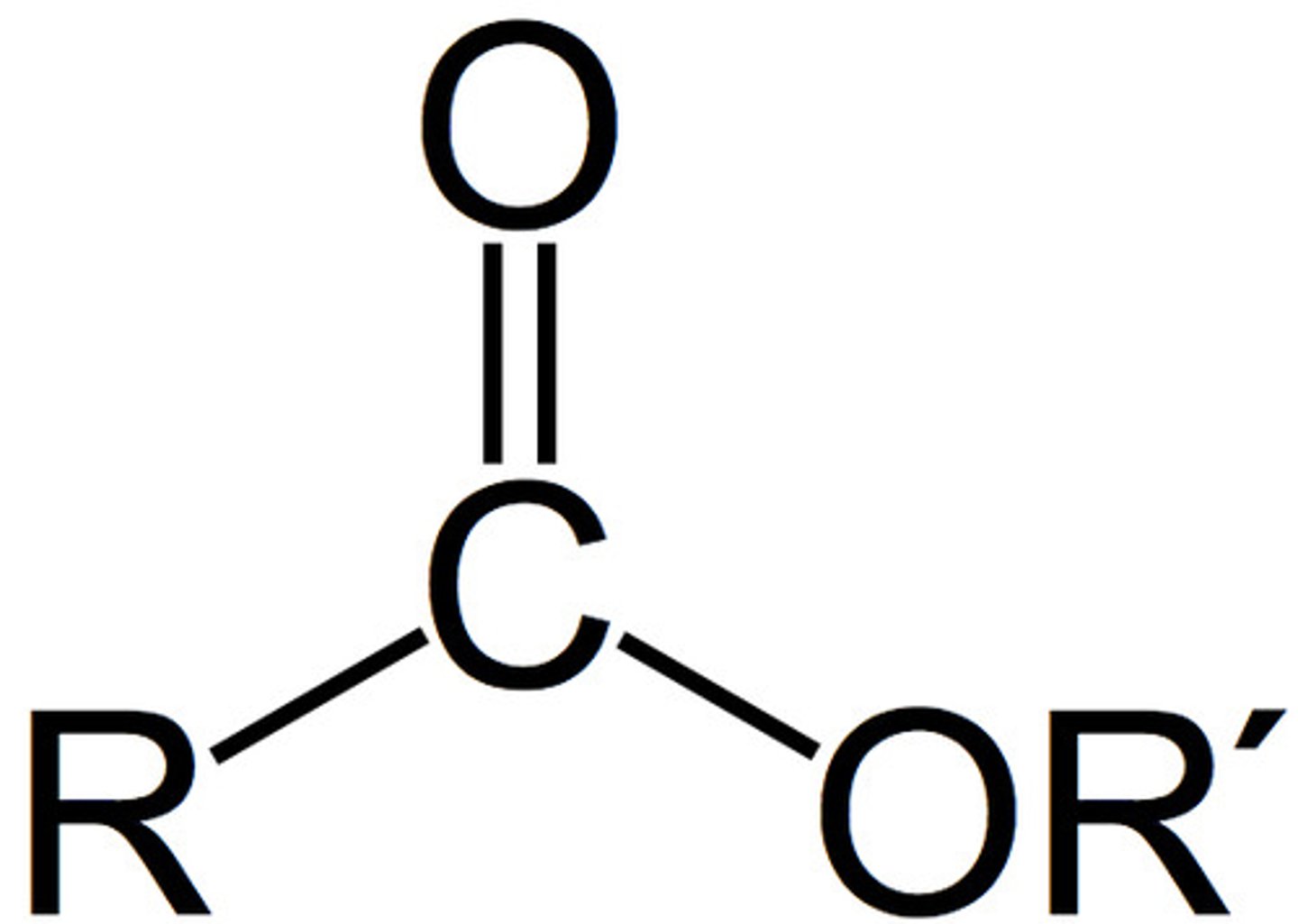
Ester
functional groups
Alkyl
An alkane missing a hydrogen
Aromatic compound
Cyclic, planar, with every atom of the aromatic ring having a p orbital, while obeying hackles rule of 4n+2 pi electrons
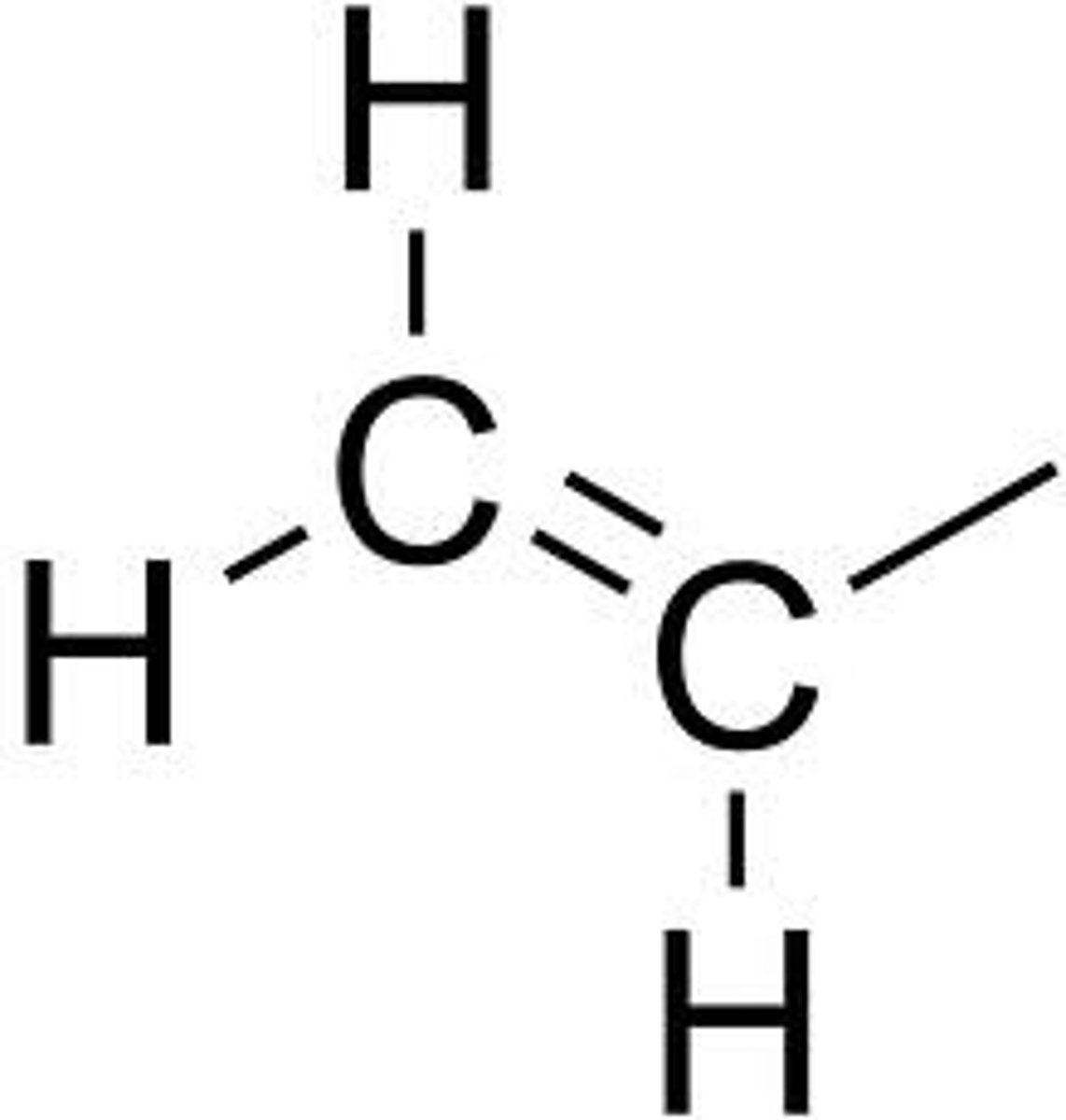
Vinyl
Hydrolysis Reaction
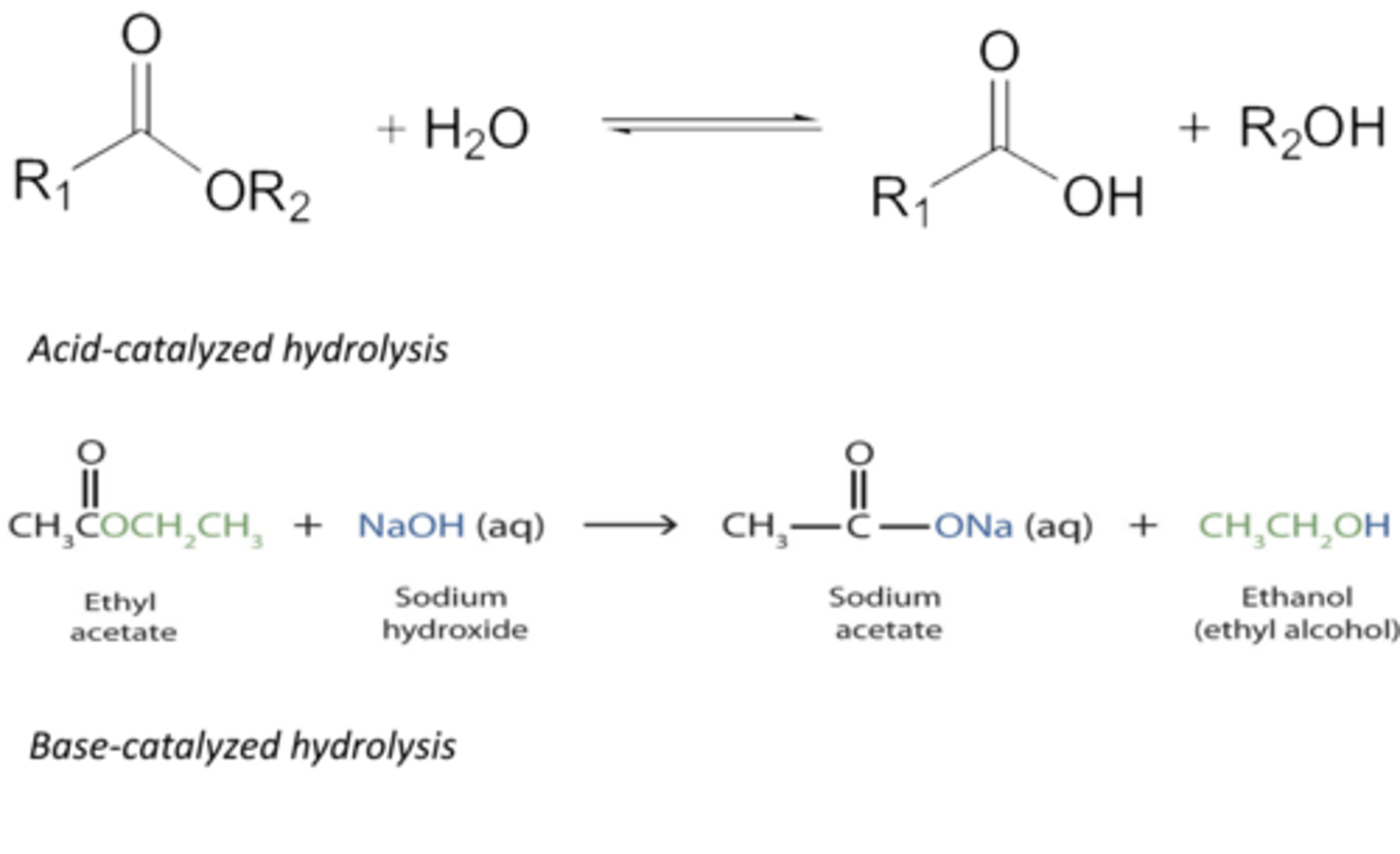
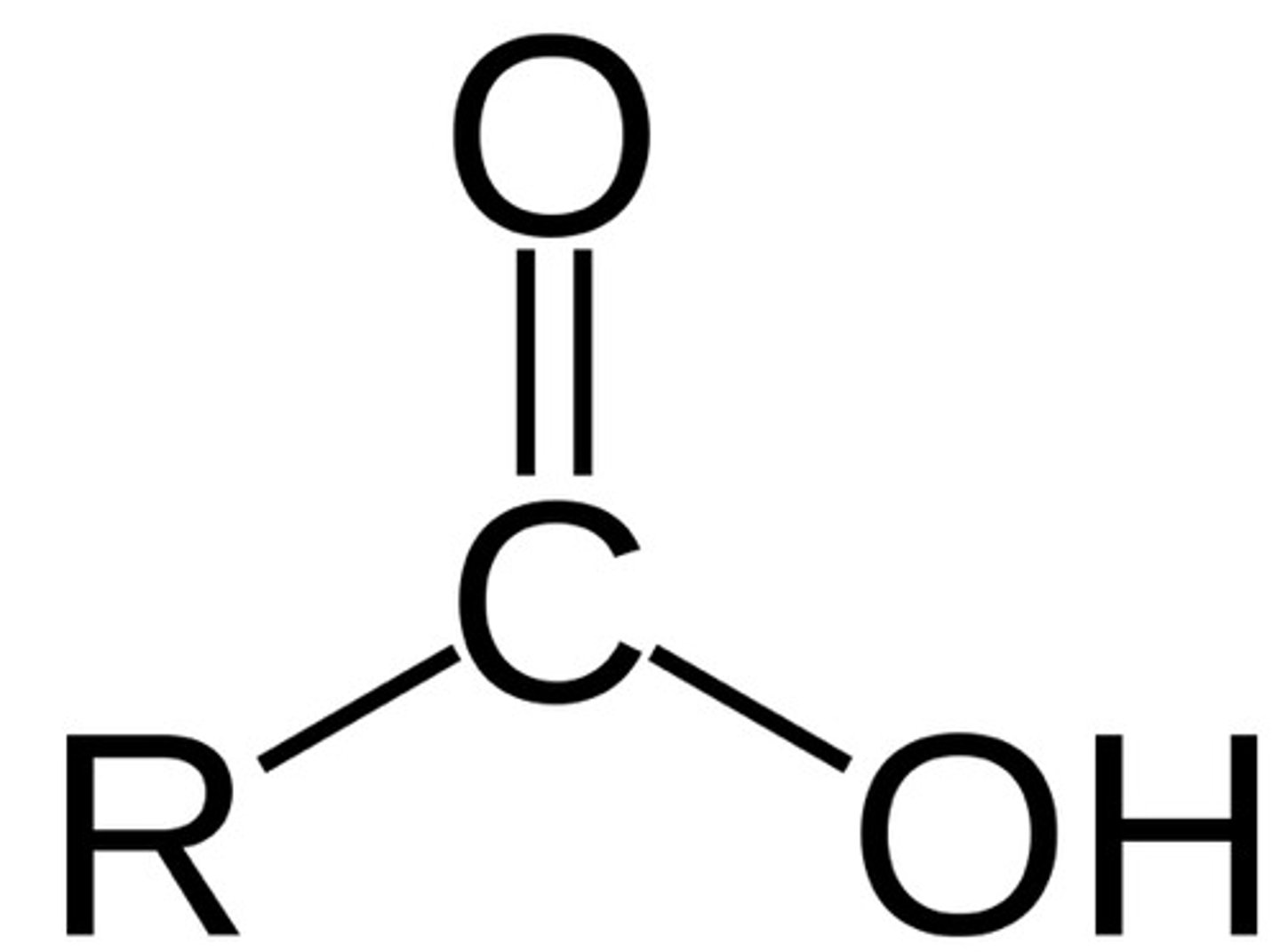
Carboxylic Acid
pKa ~ 5
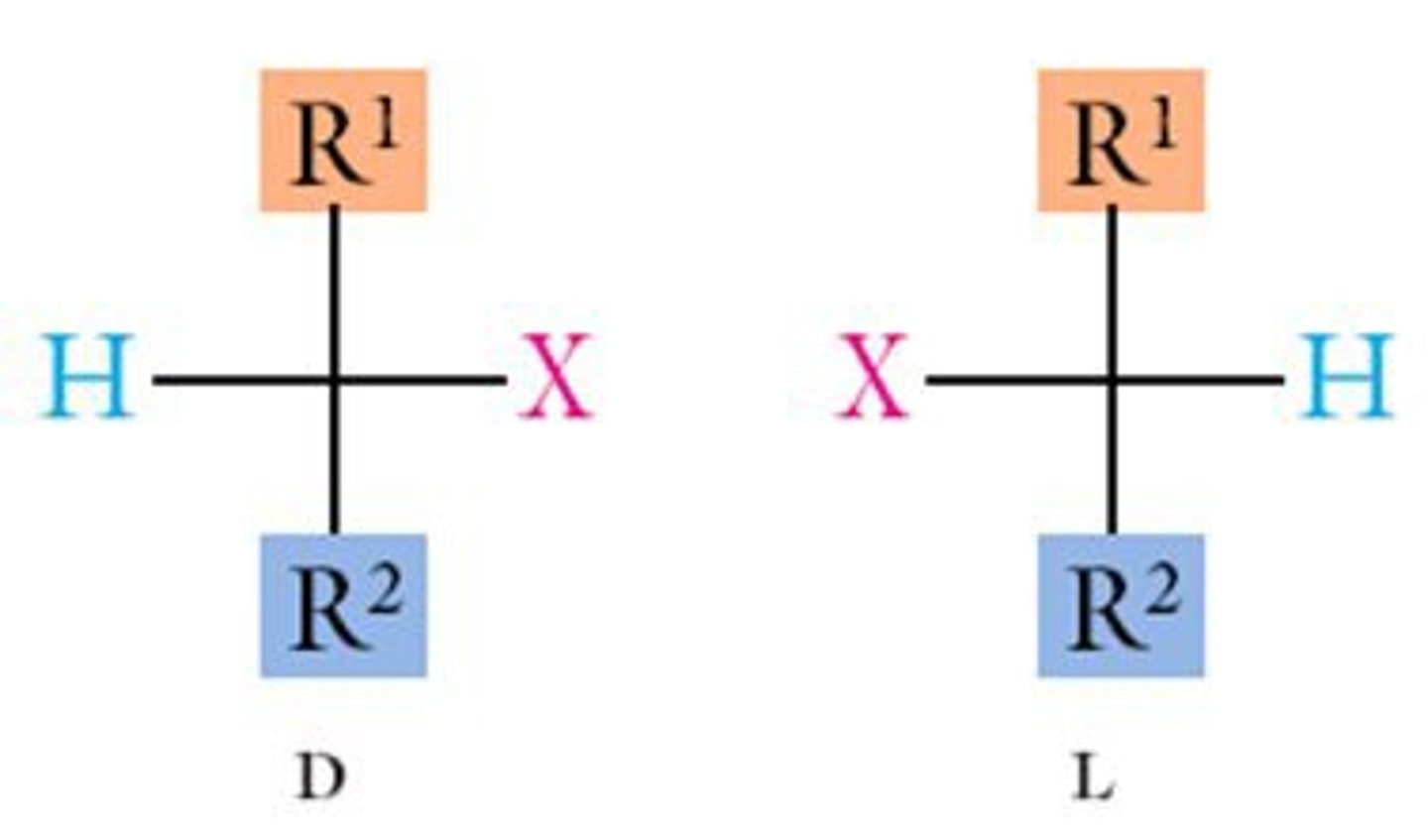
Enantiomers
stereoisomers that are non super imposable mirror images
Diastereomers
- Same molecular formula, same bond connections, NOT mirrors images, NOT the same compound.
Stereocenter
sp3 hybridized and bounded to different subsitutents
Chiral
objects with non-superimposable mirror images; 'handedness'
Meso
Achiral compound that contains stereocenters
Cahn-Ingold Prelog
R/S Nomenclature
E2
3⁰ with strong base, 2⁰ with strong base, 1⁰with strong, non-nucleophilic base
E1
3⁰ with weak base in polar, protic solvents, 3⁰ in polar, protic solvents, with poor nucleophiles, 2⁰ with poor nucleophiles in polar, protic solvents
SN2
1⁰ with strong bases, 1⁰with weak bases, 2⁰ with weak bases
SN1
2⁰ or 3⁰ in weak bases or poor nucleophiles in polar, protic solvents
CH₃OK/CH₃OH
Favors SN2 or E2
Acetone
SN2
OH⁻
Nucleophilic Displacement Reaction
Nucleophile
Electrophilic Additions
Attracted to C=C because of it being oxygen rich
Forms a carbocation intermediate that rearranges to a more stable carbocation that is immediately susceptible to nucleophilic attack, completing the addition to the double bond. Attack is on most stable carbon.
CH₃OH/H⁺
The H⁺ attacks first. The oxygen of the methanol is the nucleophile
NaH
ROH to RO- Na+
NaBH4, MeOH
Ketone to alcohol
H2/Pt
Reducing to cis
1. LAH 2. H2O
Reducing to trans
1. RMgX 2. H2O
Add R group
TMSCl, Et3N
Protection group of alcohols
TBAF
Remove alcohol protecting group
1. TsCl, py 2. NaBr
Make water good leaving group. The sn2
SOCl2, py
Chlorination of alcohol
H2SO4, heat
Elimination
-OEt
Elimination
Jones
Secondary alcohol= ketone
Primary alcohol= carboxylic acid
PCC
Primary alcohol= aldehyde
1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O or ROH 2. NaBH4
Markinov addition
MCPBA
Epoxide ring
1. Br2, H2O 2. NaOH
Epoxide ring
NaOH, H2O
Opening epoxide ring
1. Nuc 2. H2O
Opening epoxide ring
HX
Markinov addition
HBr, ROOR
Anti markinov
1. BH3.THF 2. H2O2, NaOH
Anti markinov n syn
OsO4
Syn OH addition
Electro cyclic
Syn hv syn
Syn heat anti
Anti heat syn
Anti hv anti
NBS heat
Free radical bromination
Na, CH3OH, NH3 Birch reduction
Aromatic ring to two alkynes
FeBr3, Br2
Bromination of aromatic ring
AlCl3, Cl2
Chlorination of aromatic ring
Fuming H2SO4
Sulfonation of aromatic ring
Dilute H2SO4
Remove sulfonation of aromatic ring
HNO3, H2SO4
Nitration of aromatic ring
1. KMnO4, NaOH heat 2. H3O+
Methylbenzene to methyl carbolic acid
HO--OH
Acetal protecting group
H2O
Remove acetal protecting group
Witting reaction
C=C produced
RCO3H
Produced esters
1. CO2 2. H3O+
Grignard to carboxylic acid
1. LDA 2. RX
Alkylation to alpha
Low temp less sub
High temp more sub
Sulfuric acid
Proton source
NaNH2
Elimination
PBR
Bromination of primary alcohol
Heat
Cyclo reactions
1. DIBAH 2. H2O
Ester into aldehyde
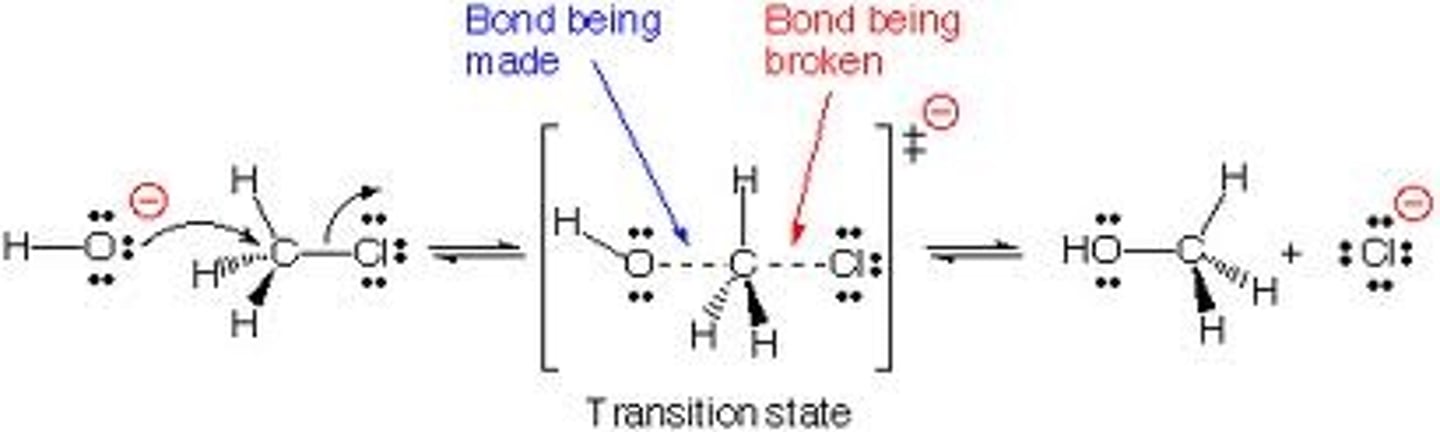
SN1
-2 steps
-Rate limiting step, so reaction rate is dependent on concentration of R-X
-Weak nuc/weak base (typically solvolysis) for secondary and tertiary carbons; also competes with E1 reactions
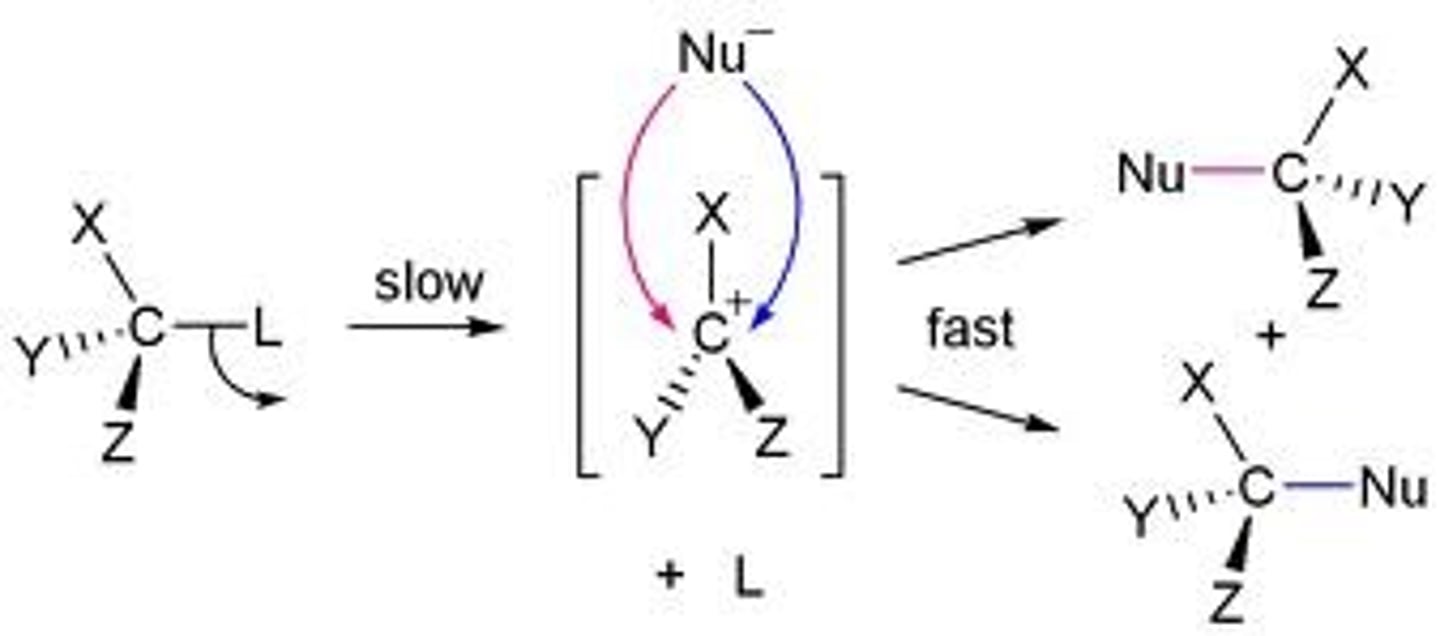
SN2
-1 step (concerted)
-Reaction rate is dependent on concentration of R-X and Nuc
-Prefers methyl, primary, or secondary carbons
-Strong nuc/strong base (OH-) or strong nuc/weak base (I-, CH3CO2-) required for methyl, primary, and secondary
E1
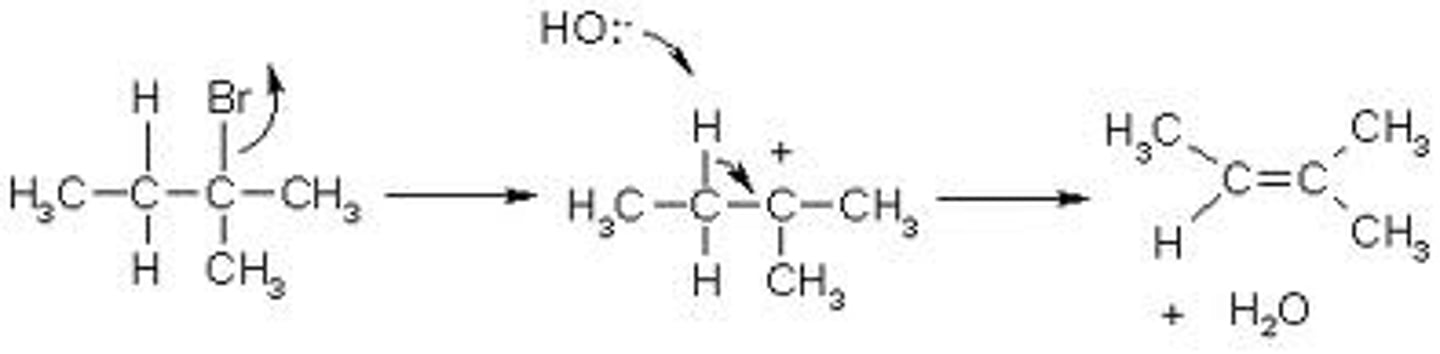
-2 steps
-Rate limiting step, so reaction rate is dependent on concentration of R-X
-Weak nuc/weak base (typically solvolysis) for secondary and tertiary carbons; competes with SN1 (without heat)
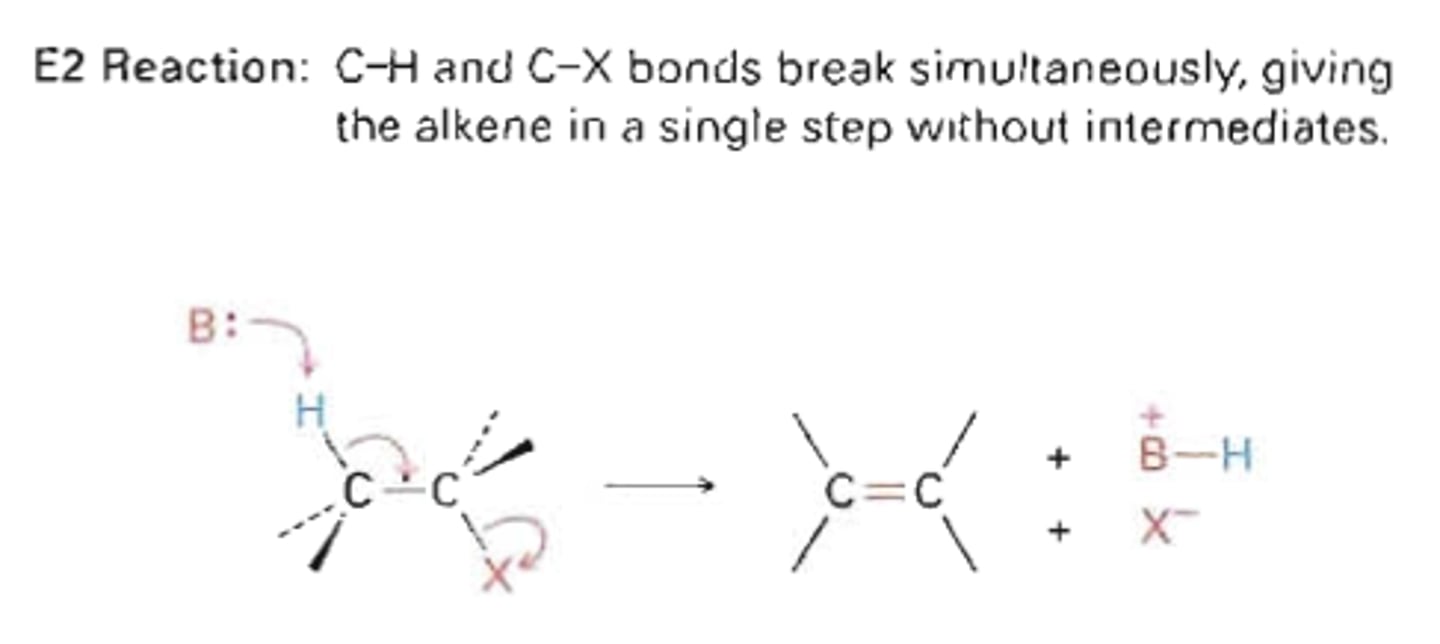
E2
-1 step
-Reaction rate is dependent on concentration of R-X and Nuc
-Weak nuc/strong base (potassium tert butoxide or LDA) for primary carbon
-Strong nuc/strong base or weak nuc/strong base for secondary and tertiary carbon
-Beta hydrogen must be anti to leaving halide
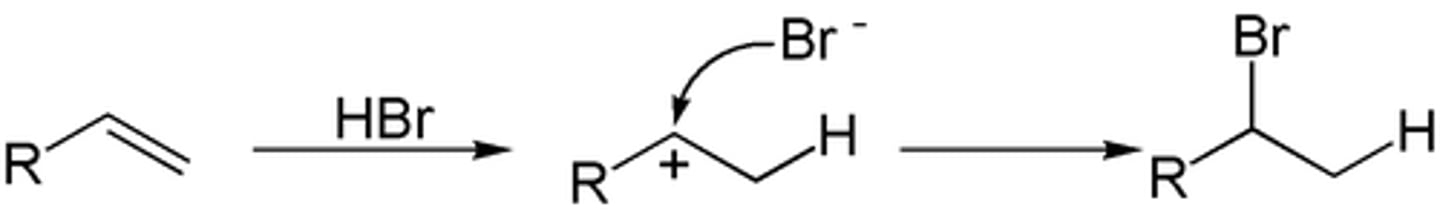
Hydrohalogenation of alkenes
-Reagents: HCl, HBr, or KI + H3PO4
-Addition
-Carbocation intermediates, rearrangements possible
-Markovnikov addition
-No stereochemical preference
Radical hydrohalogenation of alkenes
-Reagents: Peroxides, heat/light
-Chain reaction
-Radical intermediates
-Anti-Markovnikov addition
-No stereochemical preference

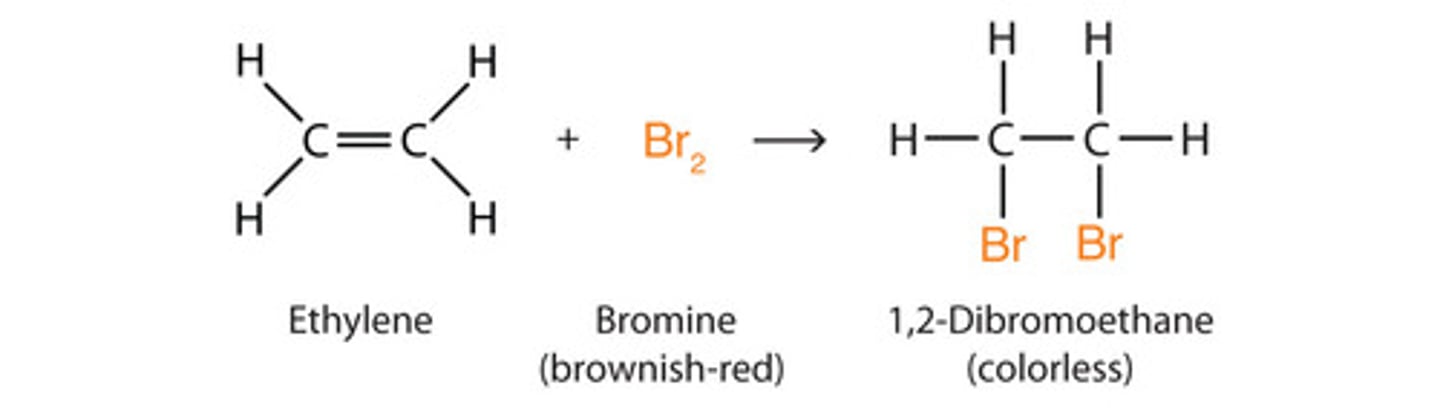
Halogenation of alkenes (anti addition)
-Reagents: Br2, Cl2, or I2 in CH2CL2 or CCl4
-Addition
-Bromonium or chloronium intermediates
-Anti addition stereochemical preference
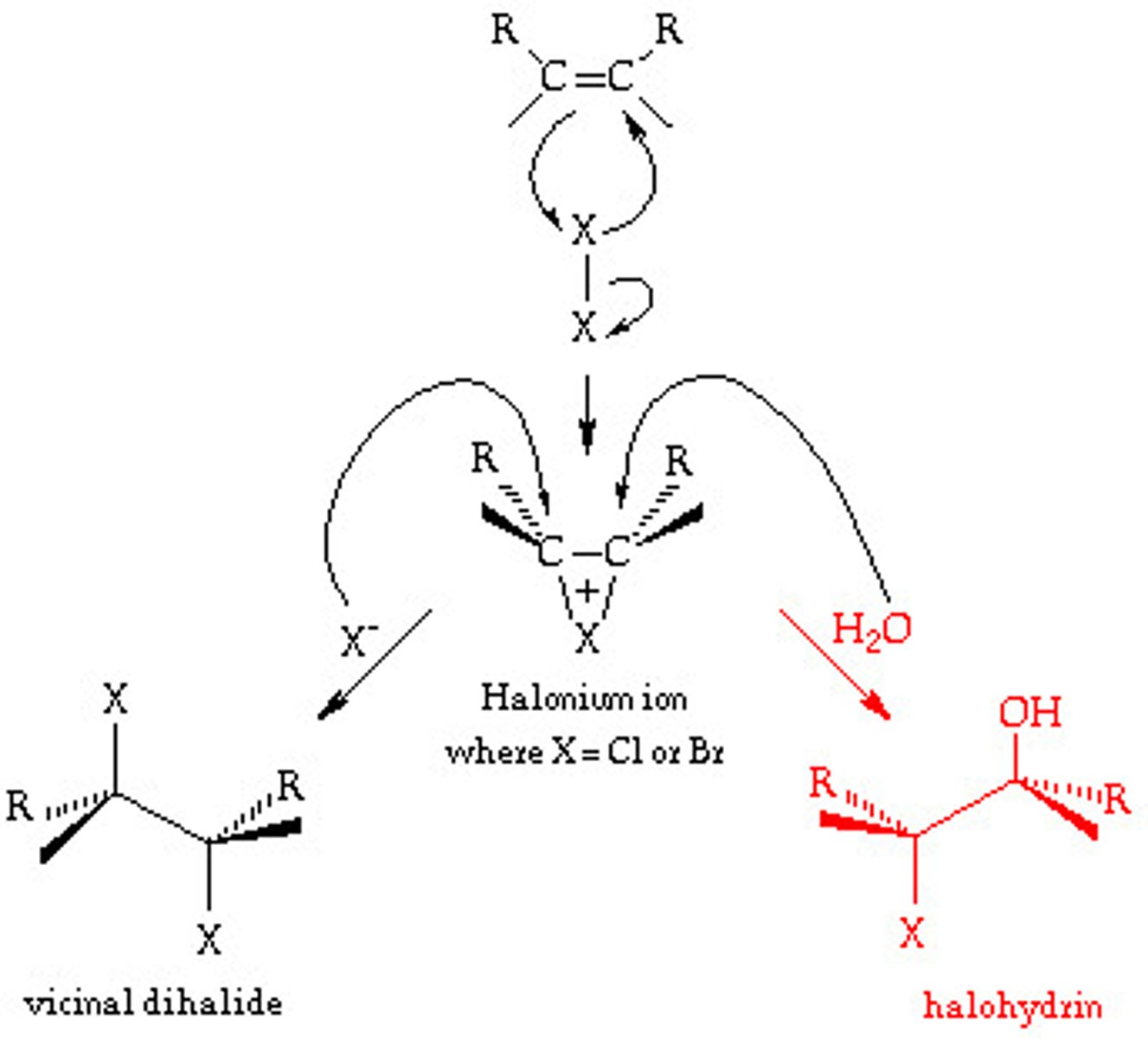
Halohydrin
-Addition of X2
-Reagents: Br2 or Cl2 in H2O
-Bromonium or chloronium ion intercepted by H2O
-Markovnikov addition of H2O
-Anti addition stereochemical preference
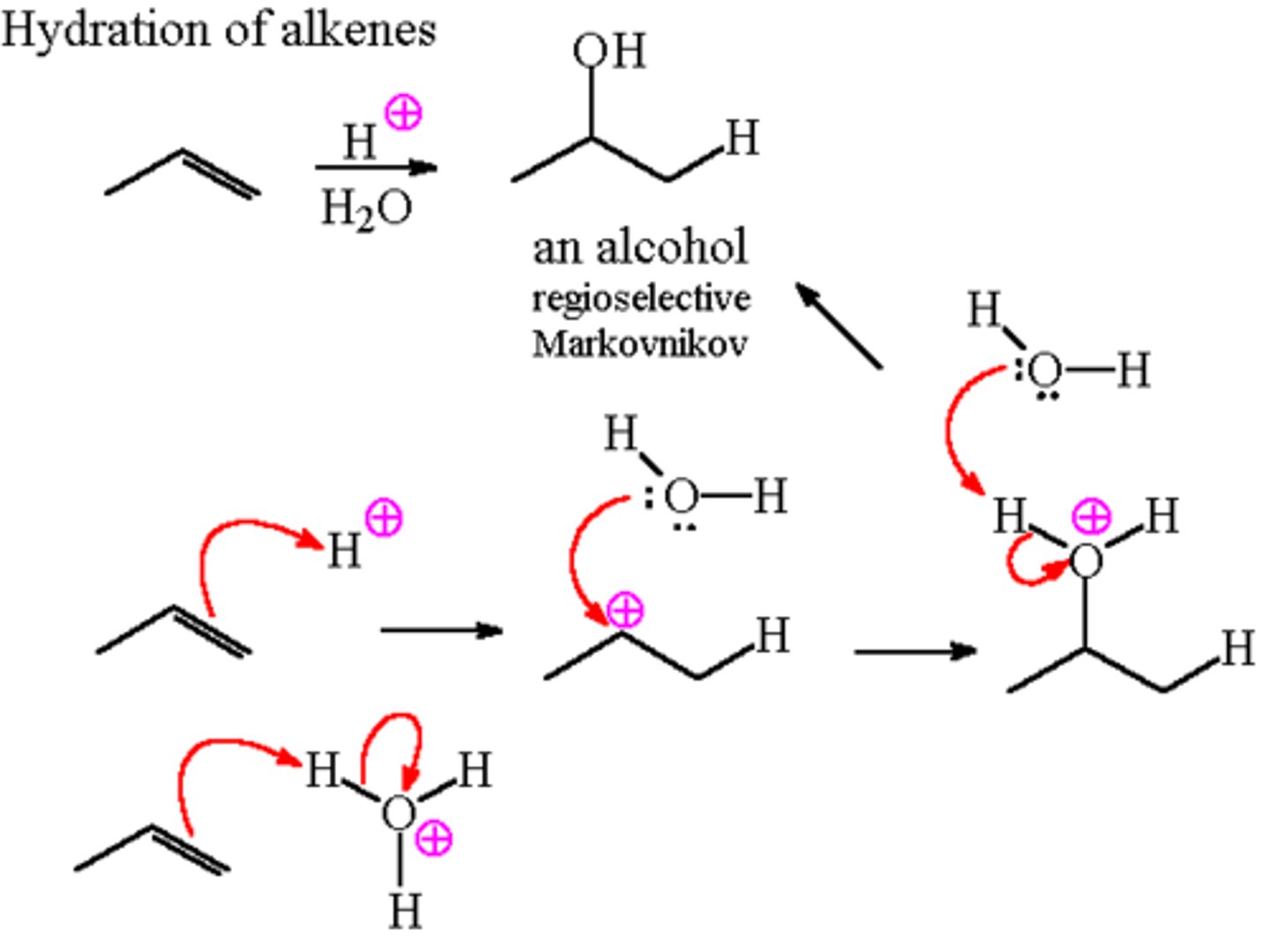
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes
-Reagents: H2SO4, HClO4, H3PO4; high temperature
-Can be reveresed to form alkenes from alcohols
-Addition
-Carbocation intermediates
-Markovnikov addition
-No stereochemical preference
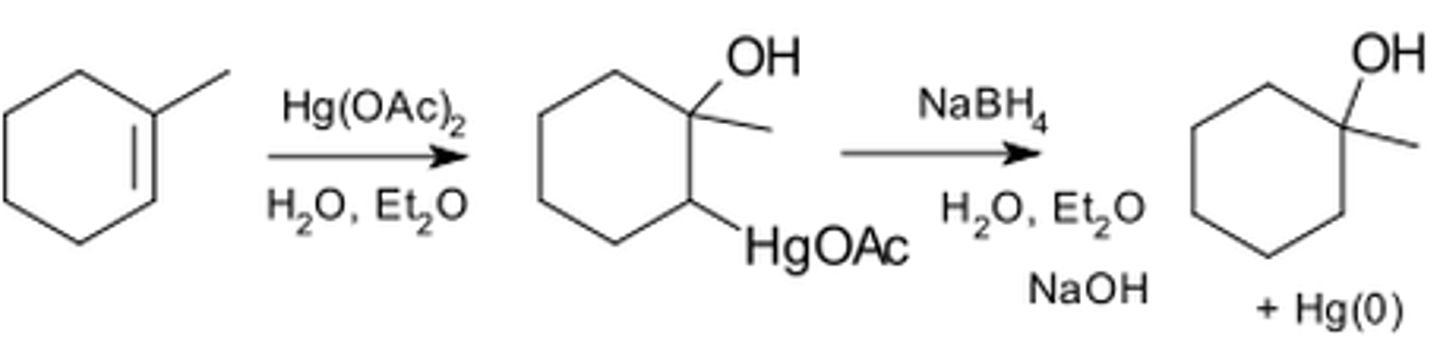
Oxymercuration-demercuration of alkenes
-Reagents: 1) Hg(OAc)2 in H2O or THF/H2O, 2) NaBH4
-Addition of mercury compound
-Mercurinium ion intermediate intercepted by H2O
-Markovnikov addition of H2O
-Addition of H2O is anti, but reduction (NaBH4) scrambles stereochemistry, no preference
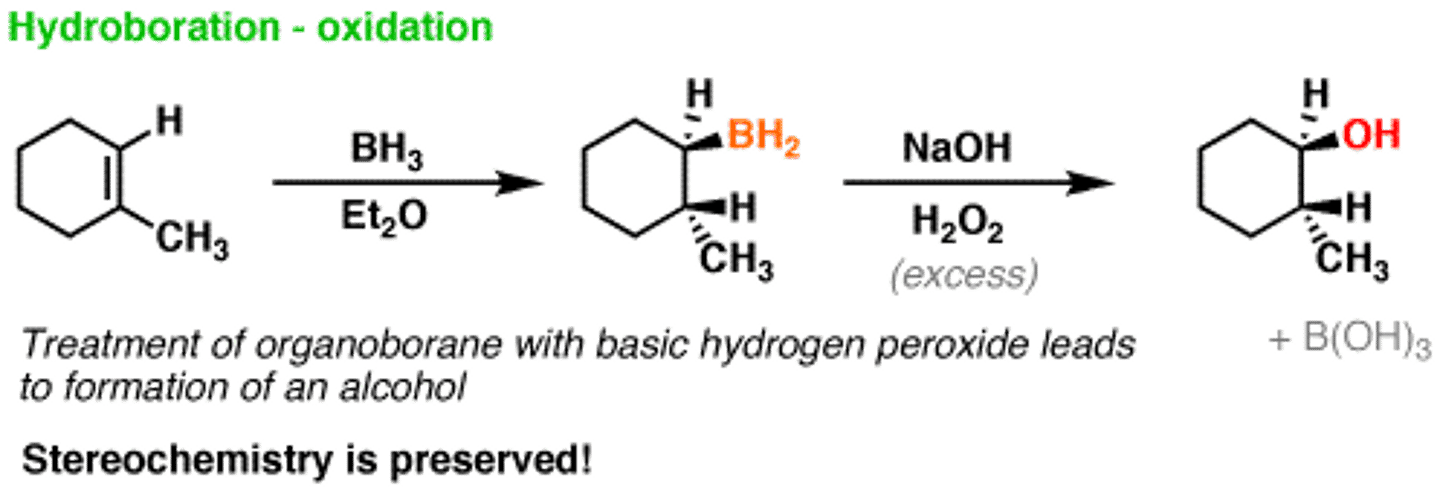
Hydroboration of alkenes
-Reagents: 1) BH3-THF (Forms trialkylboranes/R3B), 2) H2O2/-OH; room temperature or heat
-Addition of BH3
-Cyclic transition state puts boron on least substituted carbon of the double bond
-Syn addition stereochemical preference
-Anti-Markovnikov addition of -OH
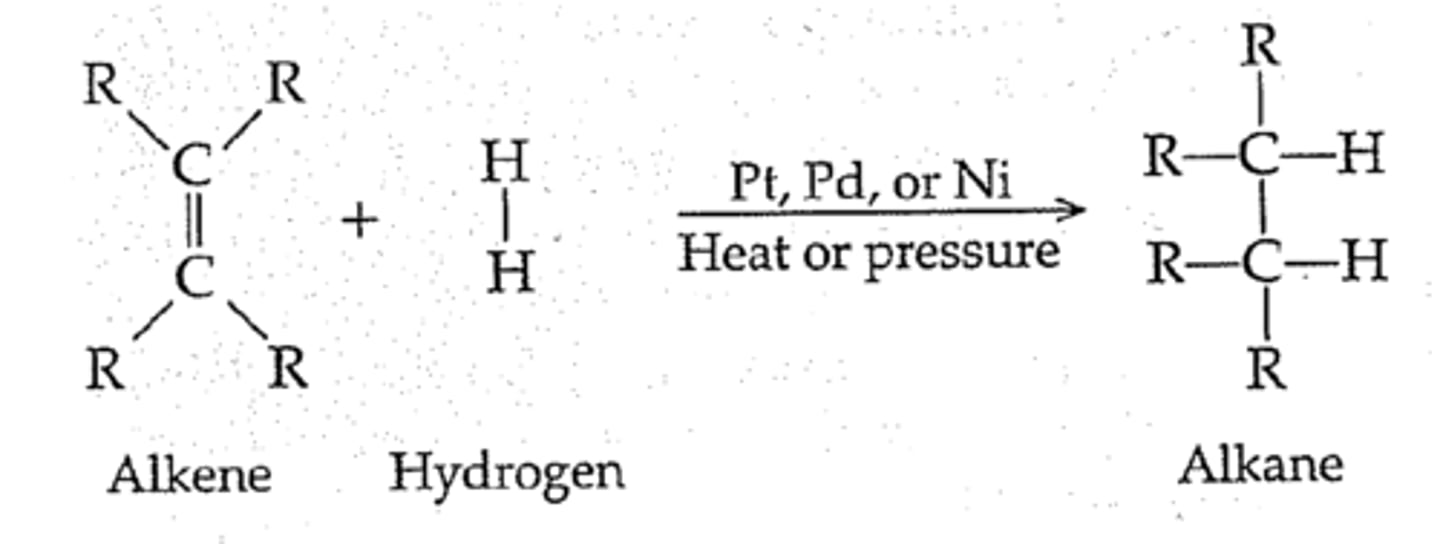
Hydrogenation of alkenes
-Reagents: H2 over metal catalyst (Pd/C, Pt, PtO2)
-Surface reaction
-Syn addition from the less crowded/sterically hindered face
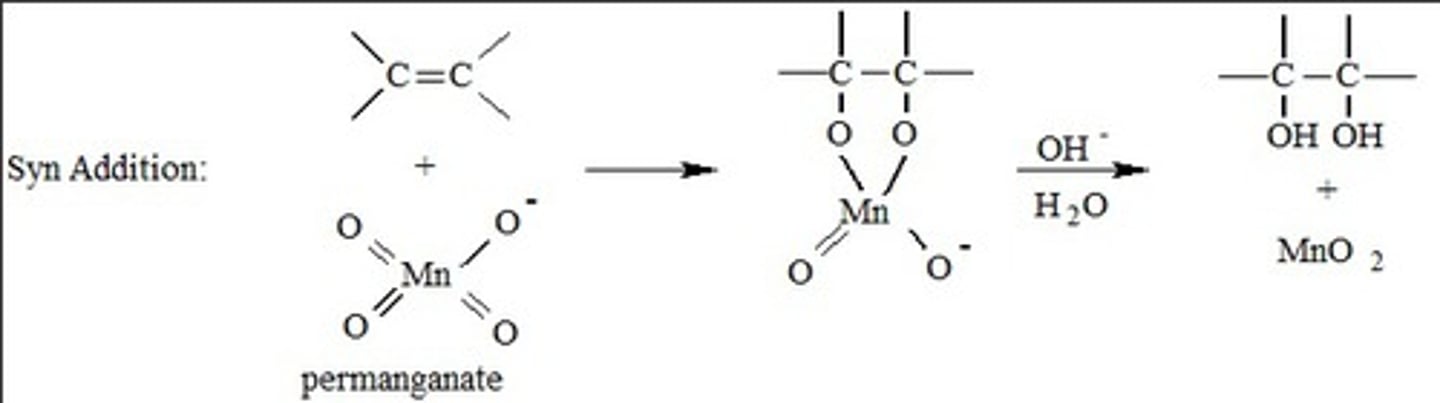
Hydroxylation of alkenes (syn addition)
-Reagents: KMnO4/-OH (lower yield) or OsO4/pyridine (higher yield, but dangerous and expensive) or catalytic OsO4 with NaHSO3
-Cyclic transition state and intermediate
-Syn addition of -OH groups
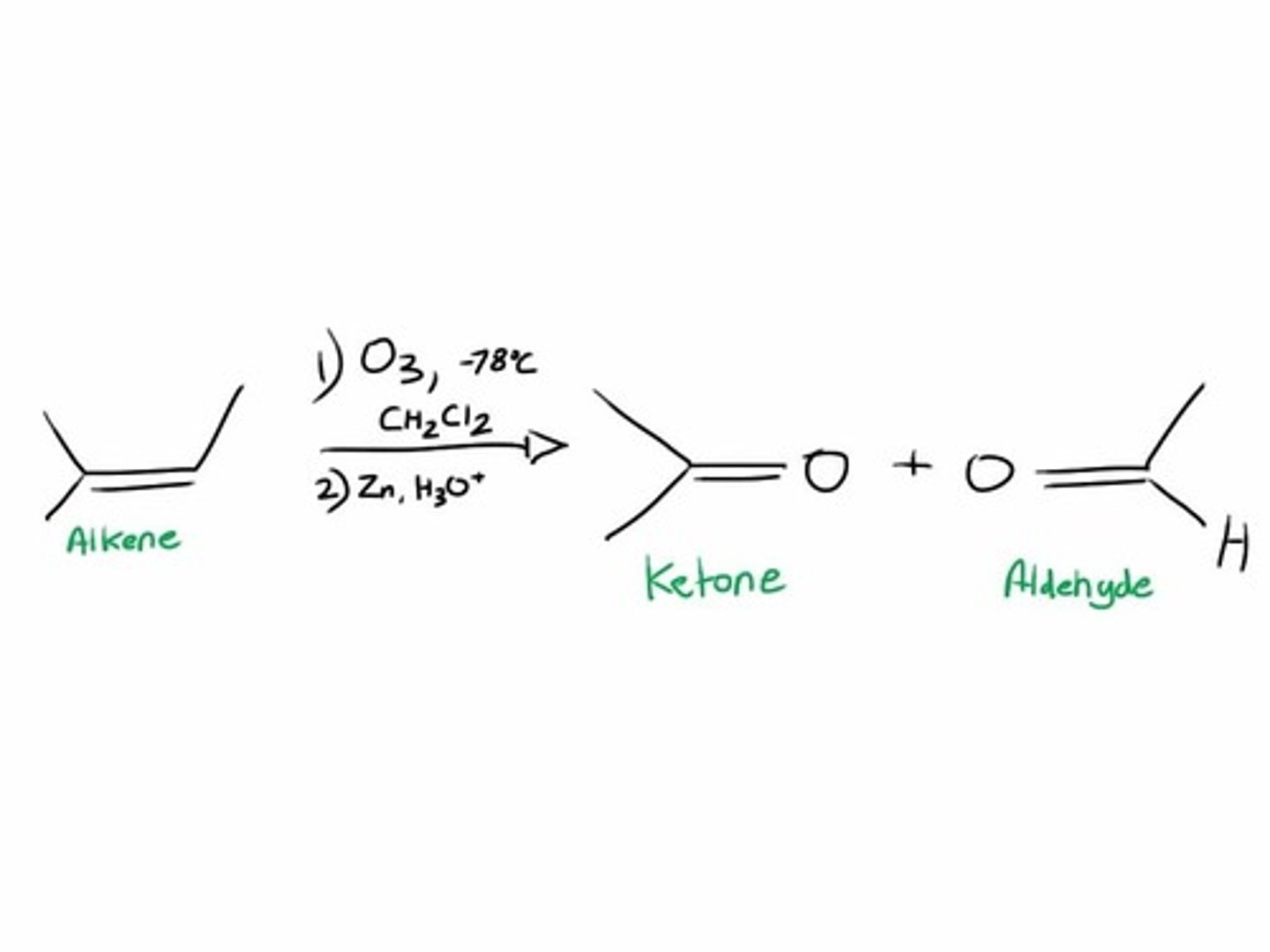
Ozonolysis of alkenes
-Reagents: 1) Ozone (O3) at low temperature, 2) Zn/AcOH
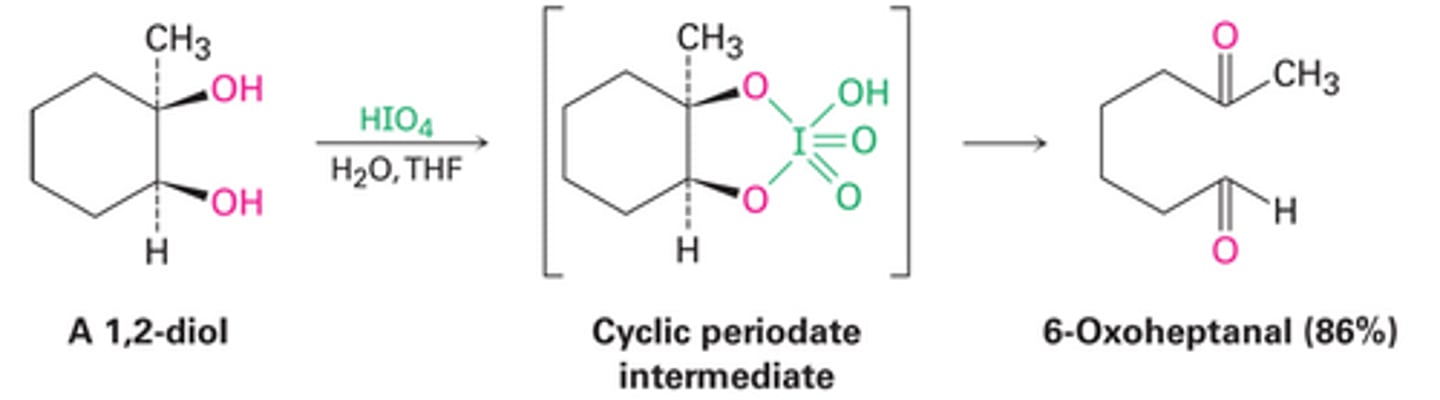
Oxidation of diols
-Reagents: 1,2-dioltreated by HIO4 in H2O/THF
-Cyclic intermediate with HIO4
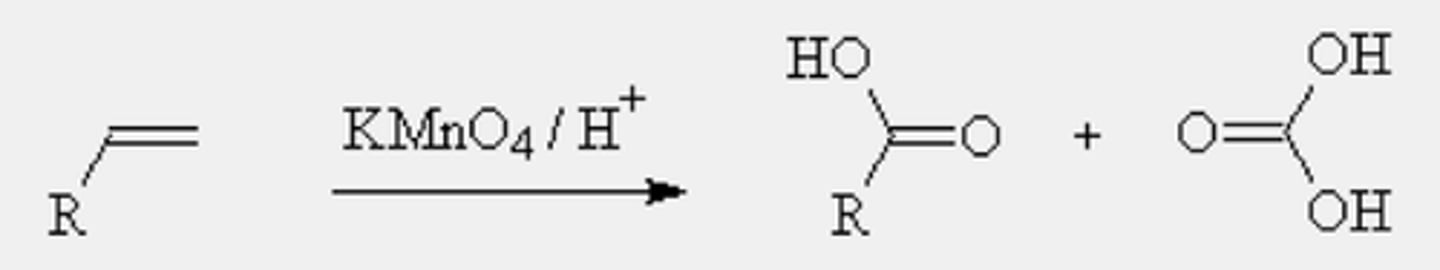
Oxidation of alkenes with permanganate
-Reagents: potassium permanganate (KMnO4) under acidic/neutral condition (H+)
-Oxygen inserts into all former vinylic C-H bonds
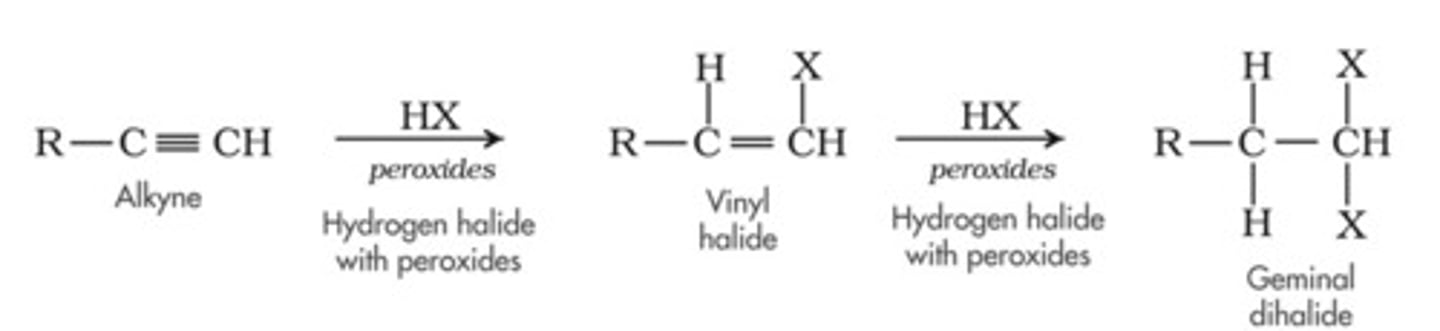
Hydrohalogenation of alkynes
-Reagents: HCl, HBr in acetic acid
-Addition
-Vinyl halide as intermediate
-Markovnikov addition
-Mixed stereochemistry, but first addition is usually trans, often followed by second addition (less reactive than alkenes)
-Excess HX --> geminal dihalides and excess X2 ---> tetrahalides
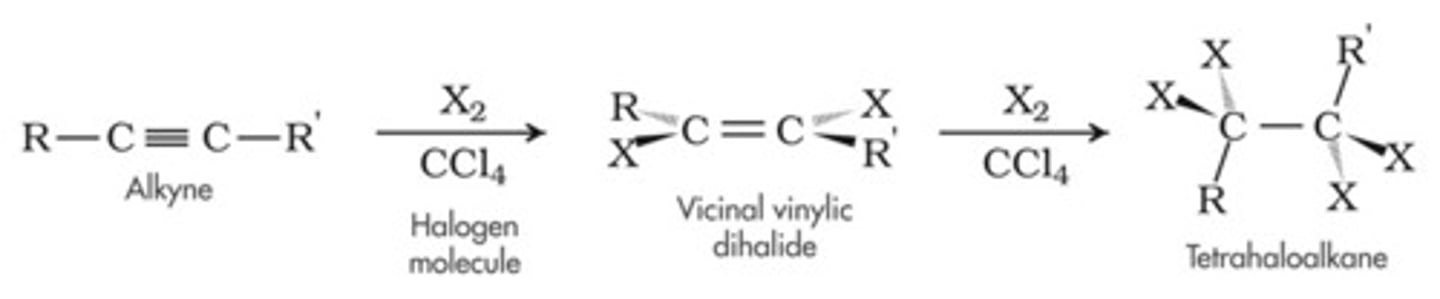
Halogenation of alkynes
-Reagents: Br2 or Cl2 in CCl4
-Addition
-First addition is usually trans
-Markovnikov addition
-Excess X2 ---> tetrahalides
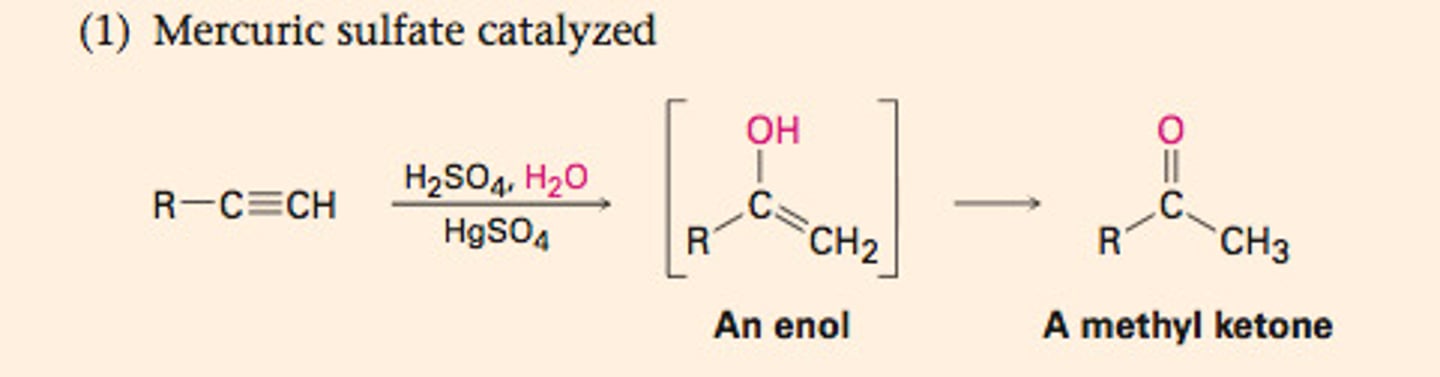
Hydration of alkynes (HgSO4)
-Reagents: HgSO4/H2O/H2SO4
-Addition catalyzed by Hg2+, no mercurinium ion invovled
-Primary product is an enol (less stable tautomer of a ketone)
-Markovnikov addition
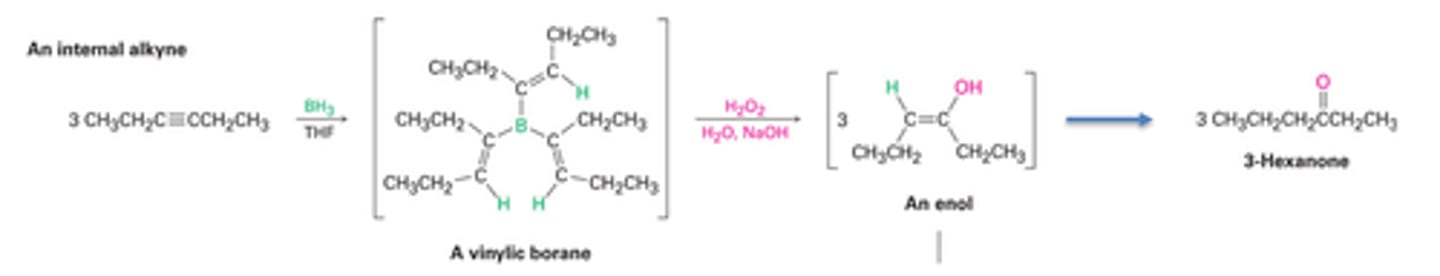
Hydroboration of alkynes
-Reagents: 1) BH3/THF, 2) H2O2/OH-
-Two-step addition of borane followed by oxidation with basic hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
-Syn addition only (keto-enol tautomerization) for disubstituted alkynes
-Anti-Markovnikov addition with terminal alkynes; forms aldehydes
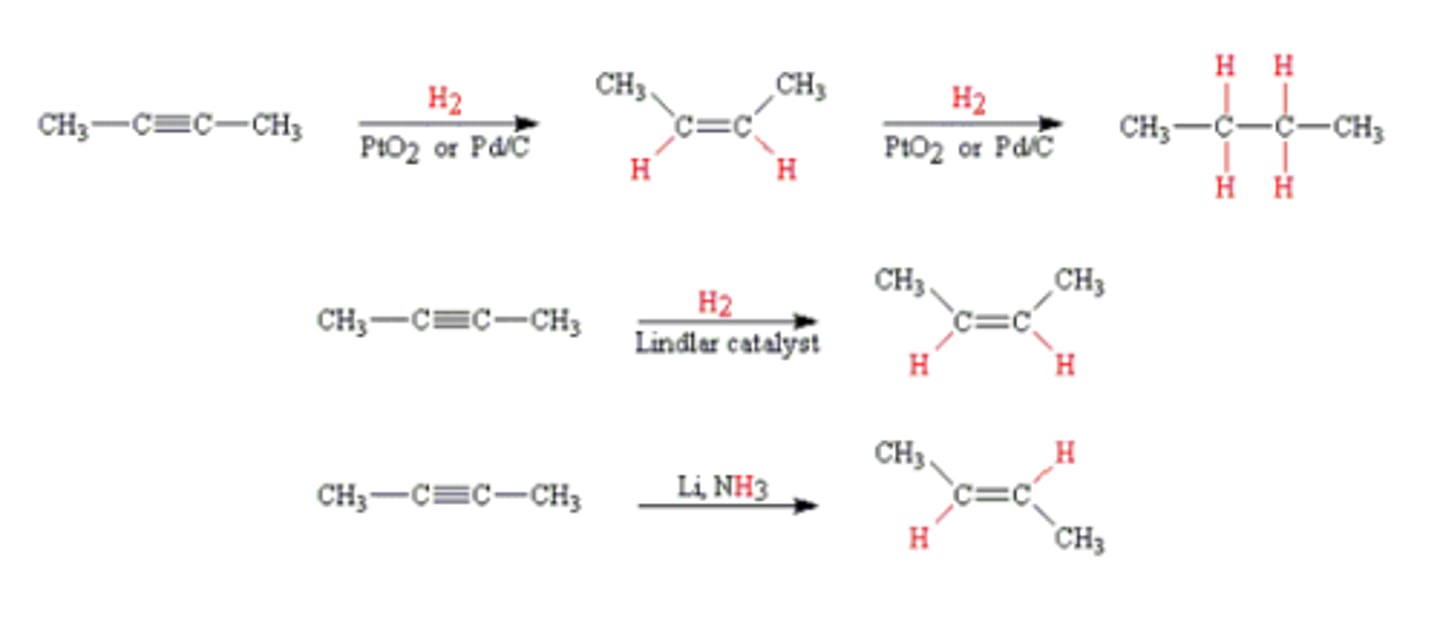
Hydrogenation of alkyne to alkene
-Reagents: H2 and Lindlar's catalyst (cis product) or Na, NH3 (trans product)
Alkylation of acetylide anion (Organic synthesis)
-Reagents: 1) NaNH2, 2) R1X
-Only occurs with terminal alkynes and occurs best with primary alkyl halides
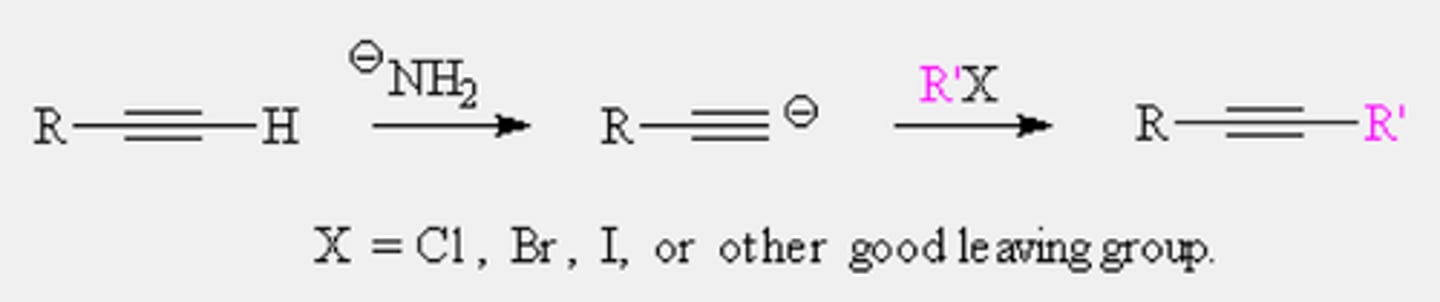
Opening of epoxides/Anti dihydroxlation
Oxidative cleavage of alkynes
-Reagents: 1) O3, 2) H2O
-Terminal yields carboxlyic acid and CO2
-Disubstituted yields two carboxlic acids
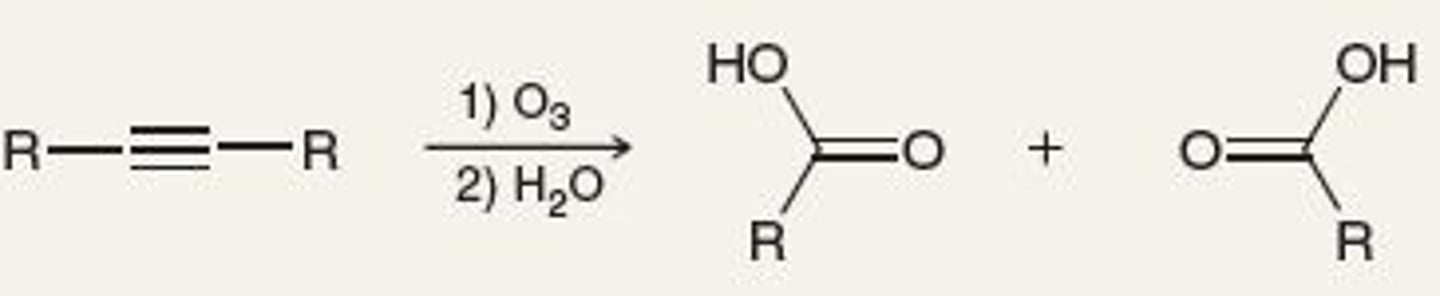
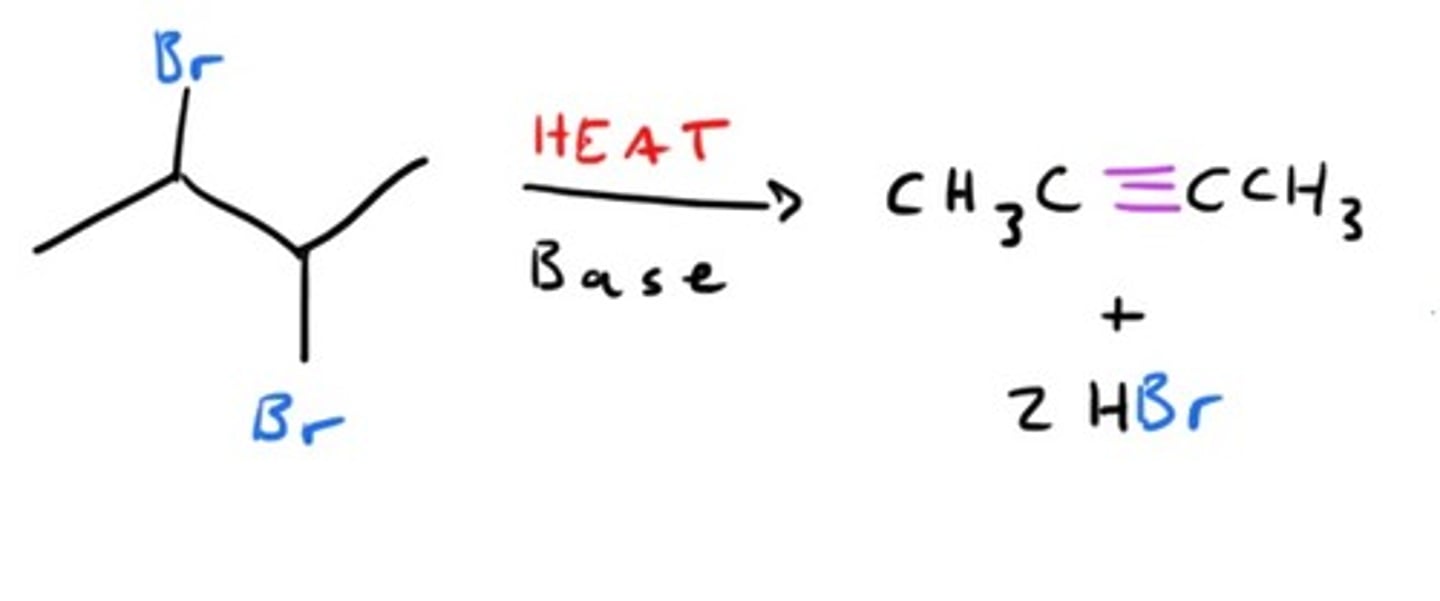
Synthesis of alkynes
-Elimination of halides (E2)
-Vicinal dihalide (alkane) ---(2 eq. KOH, ethanol or 2 NaNH2, NH3)--> alkyne
-Vinylic halide (alkene) ---(NaNH2/NH3)--> alkyne
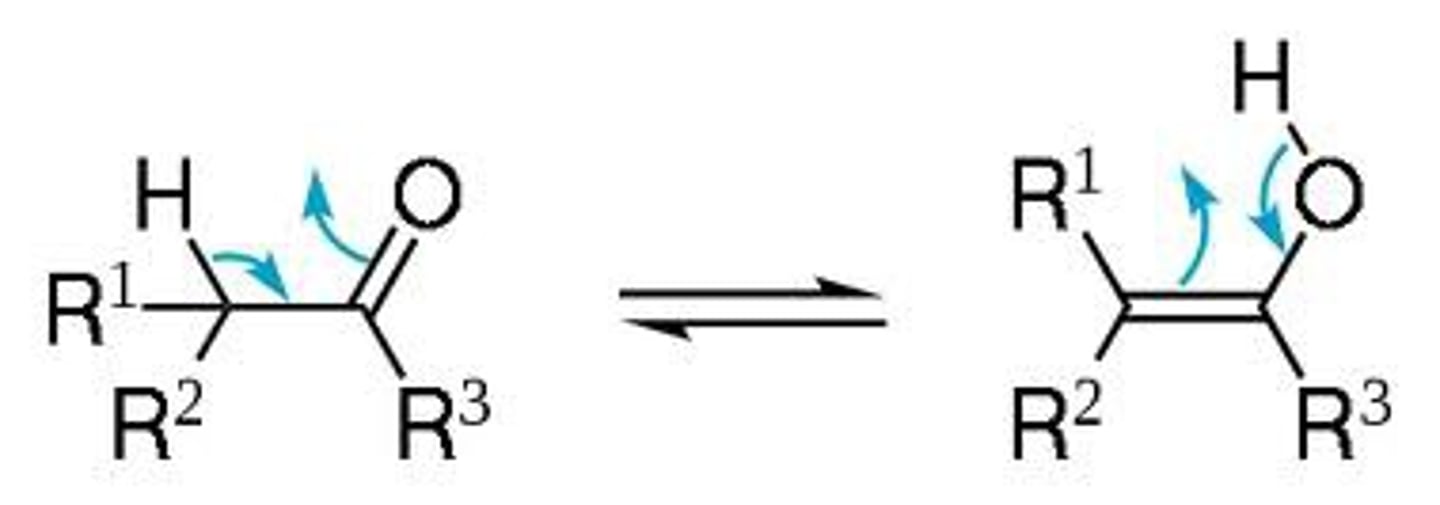
Keto-enol tautomerism
-Conversion of enols to ketones
-Occurs in hydroboration of alkynes and
hydration of alkynes with HgSO4
regioselective
preference of one direction of chemical bond making or breaking over all other directions
stereospecific
single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers
regiospecific
one structural isomer is produced exclusively when others are theoretically possible
radicals
form when bonds break homolytically via heat, using fishhook arrows to indicate single electron movement
very unstable, but can be stabilized by resonance/hyperconjugation; radical reactivity follows radical stability trend (tertiary > secondary > primary); geometry of free radical carbon allows for halogen abstraction to occur on either side of the plane with equal probability