OCR GATEWAY GCSE BIOLOGY B3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
B3
Describe how the steps in a coordinated response
Stimulus = change in environment
Receptors = group of cells detection stimulus
Effectors = response occurs (muscles/glands). Muscles contract responding to impulse. Glands release hormones
Describe the structure of the nervous system
CNS= brain and spinal cord made of delicated nervous tissue protected by bones
Sensory neurones= carry electrical imoulses from receptor cells to CNS
Relay neurones= carry impulses from sensory neurones to motor
Motor neurone= Carry impulses from CNS to effectors
Sensory receptors= in sense organs
Explain how the components of the NS can produce a response
Stimulus-receptor cells-sensory neurones-spinal cord-brain-spinal cord-motor neurone-effector-response
Using named examples, explain a reflex action
Reflex actions are automatic and rapid. Occur for safety. The nerve pathway the impulse follows is called a 'reflex arc'
They can only occur in one direction bc at the synpase the nuerotransmitter only diffuses in one direction
E.G hand near hot flame
What are the steps in reflex actions?
Stimulus-receptor cell-sensory neurones-spinal cord-motor neurone-effector-response. Notice how there is no brain
Label the eye
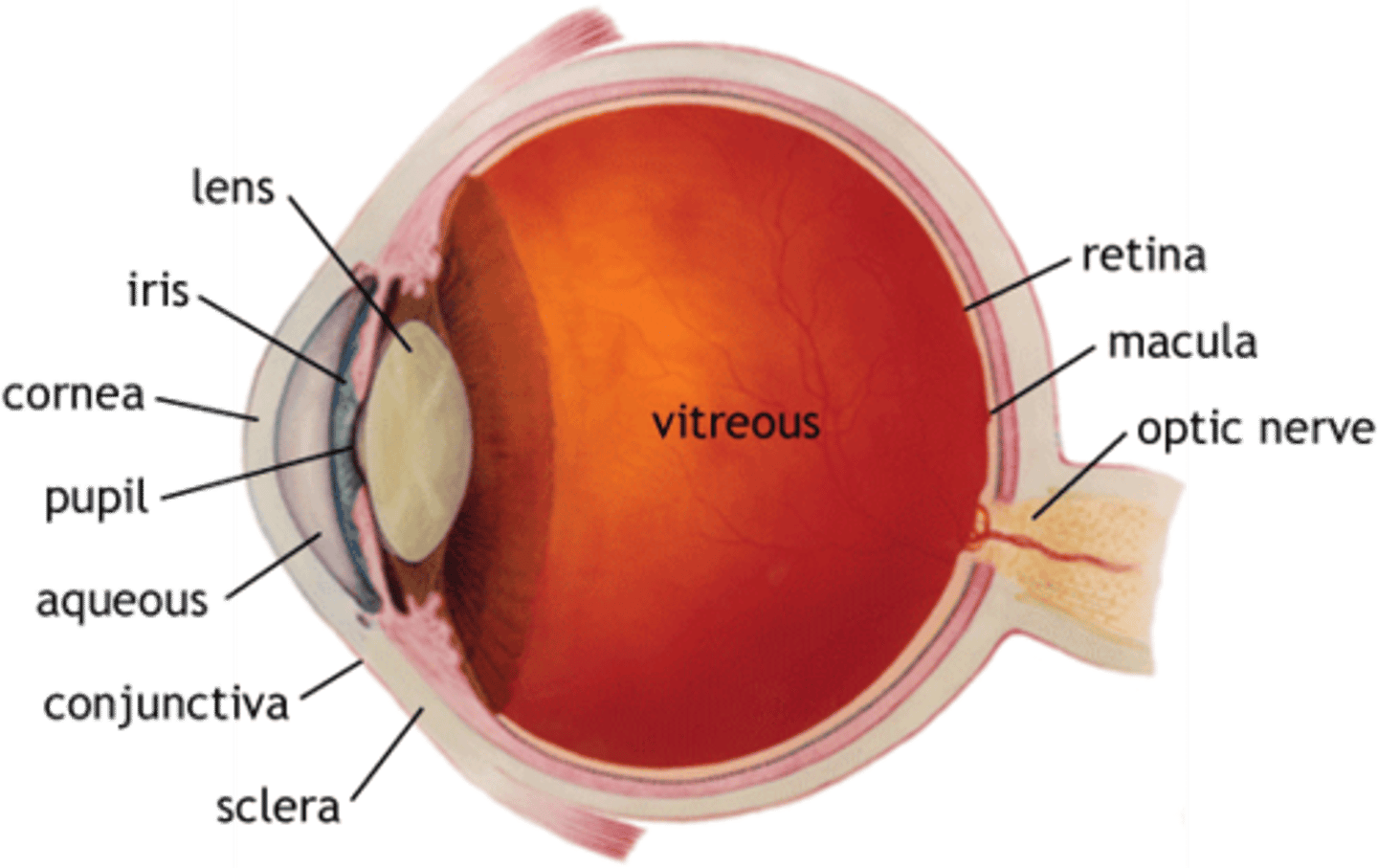
What does the cornea, pupil, iris do?
C: Refracts light into the eye and protects
P: Controls how much light enters the pupil
I:allows light to enter the eye
What does the lens,ciliary body,suspensory ligaments do?
L; Focuses light onto the retina
CB:Connects ciliary muscle to lens
SL:
What does the optic nerve do?
Carries impulses from the receptors to the brain
How is a near/distant object formed as a image?
nearby: ciliary muscle contracts, lens becomes more thicker
distant: ciliary muscle relaxes, lens less thick
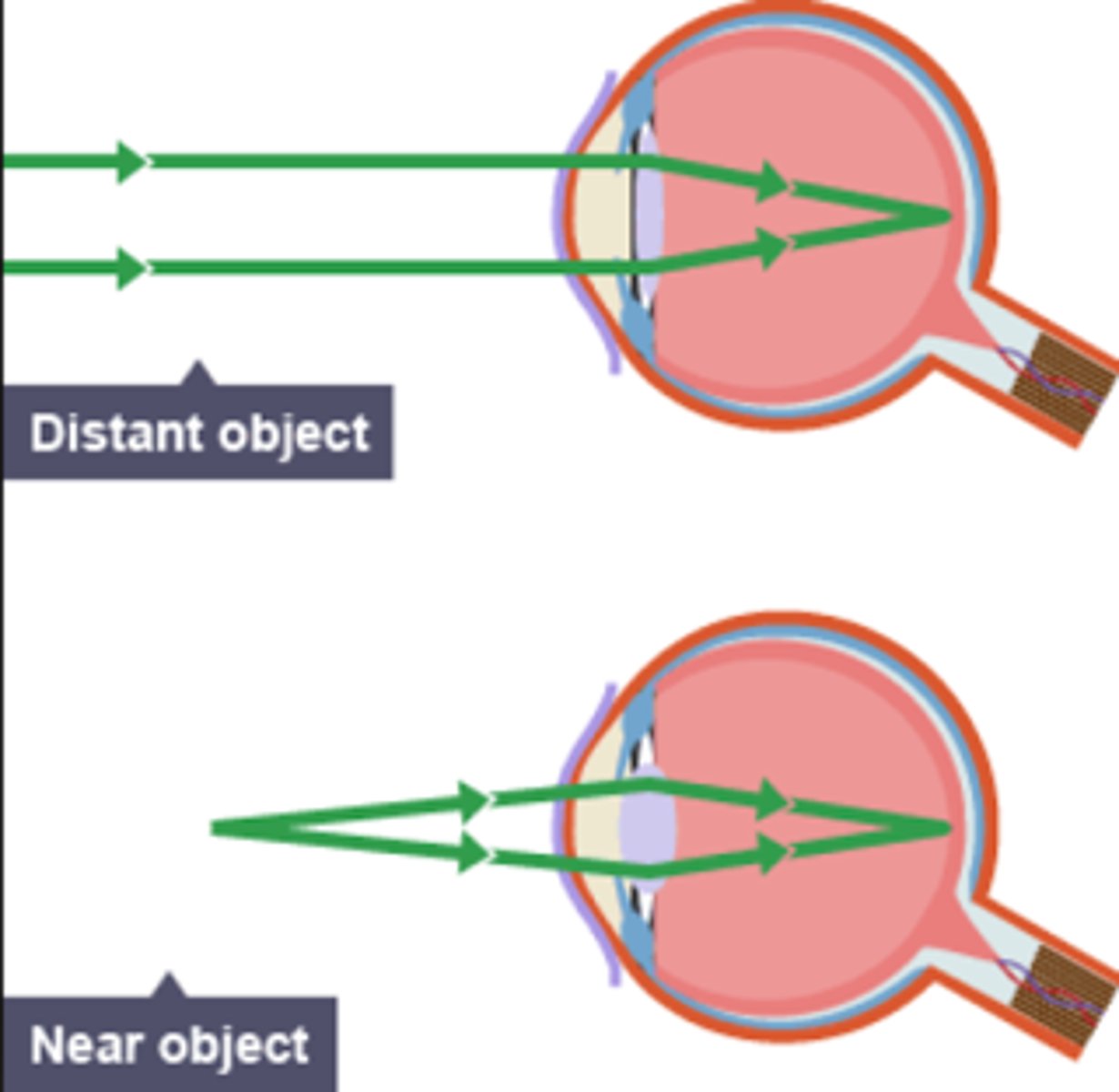
How is light reflected from an object to become an image interpreted by the brain?
Iris controls how much light enters the pupil
Cornea refracts light onto the retina. Re
Retina passes impulse to optic nerve which carries the impulse to the brain
What causes short sightedness?
Eyeball too long or lens too strong. Light rays meet in front of retina not on it. Can be corrected with concave lens that refracts light outward before entering eye
What causes long sightedness?
Eyeball too short/ lens too weak. Light rays don't meet at retina. Convex lens can bend rays inward before entering eye.
What causes colour blindness?
retina contains cells that are sensitive to red, green or blue light. People with colour blindness have a lack of receptors, or defects in them.
Function of brain
Processed info collected by receptor cells about changes in internal/external environment.
function of cerebellum, medulla oblongata
Cerebellum: balance and coordination and involuntary movements
MO: Controls heart/breathing rate
Function of cerebrum, hypothalamus
Cerebrum: Controls complex behaviour eg learning, memory, personality
H;body temperature, sleep, appetite, emotions, control of the pituitary gland
function of pituitary gland
produces/stores hormones
Explain why it is difficult to investigate brain function
-brain is sensitive tissue may cause more damage
-cannot repair itself
-difficult to do in isolated areas
- can lead to cancer as you're leaving it open to radiation
- ethics
Explain the limitations in treating damage/disease in the brain and NS
BRAIN: healthy brain tissue around tumour will be damaged
NS: ^ and leads to permament loss of function/disability. Spinal cord is .15cm in diameter and contains MANY nerve fibres
Describe the principles of hormonal coordination and control by the human endocrine system
-cause a response and regulate functions of specific cells and target organs
-control body processes that need constant adjustment eg body temperature
-made in endocrine glands and transported in blood plasma around in the body
-slow and long lasting eg testosterone
-BUT scan be quick eg adrenaline in response to danger
Describe the role of thyroxine
-produced in thyroid gland
-regulates body's metabolic rate so it controls how much energy is available to cells
-function is to take iodine and turn it into thyroxine by combining it w tyrosine
Describe the role of adrenaline
-produced by adnreal glands near kidney
-prepares body for intensive action
-'fight or flight'
Explain the purpose of a negative feedback system
-small changes are detected by sensory receptors and then effectors work to reverse the change and restore the conditions back to their base levels
How are thyroxine levels controlled?
body needs energy, hypothalamus causes pituitary gland to release TSH
-TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to release the hormone
-this increases metabolic rate allowing cells to transfer additional energy
How are adrenaline levels controlled?
-body responds by respiring more quickly to increase rate of ATP production, diverting blood away from areas eg digestive system towards the muscles, increasing rate of breathing to cop w extra demand for oxygen
-once stress is removed signals to adrenal glands so stop so the glands stop producing adrenaline and the body returns to normal state
Stages of menstrual cycle
-lining of uterus starts to thicken ready for a fertilised egg
-at the same time a egg matures in one of the ovaries which then gets released from the ovary (ovulation) 14 days later
-lining of uterus remains thick
-if egg is fertilised it may implant in the uterus lining where its protected n receives nutrients and oxygen so the woman is PREGGERS
-BUt if egg isnt fertilised uterus lining and egg are removed from the body through menstrutation
What controls the menstrual cycle?
FSH is secreted by pituitary gland and causes egg to mature in ovary. Triggers ovaries to produce Oestro
OESTROGEN causes lining of uterus to build up (made/secreted) by ovaries. When Oestro is rising it inhibits the production of FSH which usually stops more than 1 egg maturing (twins,triplets etc). Triggers the pituitary gland to release LH
LH triggers ovulation when it reaches a peak in the middle of the cycle
PROGESTRONE maintains the uterus lining. When preggers levels are high. INHIBITS LH
What are the 2 types of contraception?
NON-HORMONAL = barrier methods that prevent sperm contacting egg. physical devices that release chemical compounds that kill spermicides
E.G condom, cervical cap, IUD
HORMONAL = use hormones to disrupt normal female reproductive system
E.G IUS, Prog/Oestro pill
Least effective to most?
Diaphragm and cap is least
Intrauerine system and oesto/proges pill are most effective
Male condom is better than female
What is and why do couple need fertility treatment?
-blocked sperm ducts
-lack of mature eggs in the ovaries
-failure of ovaries to release egg
How is FSH used?
-artificial fertility drug
-stimulates eggs to mature in ovaries
-triggers oestro production
-increases chances of one or more eggs being released
What is IVF?
-collecting eggs from mother and fertilising them w sperm OUTSIDE of the body. FSH and LH are given to mother to increase the chances of eggs maturing and harvested
Why is IVF not the best?
-may result in no pregnancy
-multiple pregnancies
-emotionally distressing
-not natural process
-very expensive only limited within NHS
What's good about IVF?
-allows parents to conceive who couldnt previously
-enables older parents
-allows younger women to focus on their careers
Success rate for IVF?
35>x<37 is 32.2%
older than 44 is 1.9%
What's phototropism?
-growing towards light
-plant can photosynthesise more so more food so increases plants chances of survival
What's gravitopism?
-growing in same direction as gravity
-growing deeper into soil provides anchorage and closer to water
-important for germinating seeds
-scattered seeds often are the wrong way up so these responses ensure plant grows correctly
What are auxins?
- enables plant to grow towards or away from stimulus
-near tops of plant shoots or roots
-the response to a stimulus is bc of uneven distribution of auxin
-causes unequal growth rate so shoot/root elongates unevenly
What are the commercial uses of plant hormones?
killing weeds(auxins),
promoting root growth(auxins),
delaying ripening(auxins),
ripening fruit(ethene),
producing seedless fruit(auxins),
controlling dormancy (auxins/gibberllins)
TAKE A BREAK

Explain the importance of maintain a constant internal environment
THis is homeostasis
Explain the function of skin in the control of body temperature
-thermoregulatory centre in brain relies on signals received from receptor cells in skin(external temp) and from internal receptor cells (temp of blood)
What happens when youre too hot?
ENZYMES WILL DENATURE
-body hairs lower so its flat preventing a insulating layer of air being trapped around body
-sweat glands produce sweat containing salt and urea as sweat evaporates energy is transferred by heating from body to environment
-blood vessels near surface of skin widen increasing blood flow, increasing heat loss by radiation. this is vasodilation
What happens when you're too cold?
ENZYMES WILL WORK TOO SLOWLY
-body hairs rise n trap layer of air close to skin for insulation
-sweat glands stop producing sweat
-blood vessels near surface of skin. vasoconstriction reducing heat loss
-shivering makes cells respire more quickly transferring energy by heating
What hormones act to maintain constant blood sugar level?
Insulin if too high
Glucagon if too low
What happens if blood glucose concentration is too high?
-pancreas detects
- secretes insulin
- travels to liver
-liver turns glucose to glycogen
-glycogen is stored in liver
-less glucose in blood
-blood sugar level falls
What happens if blood glucose concentration is too low?
-pancreas releases hormone glucagon
-liver changes glycogen back to glucose
-glucose released into blood
-sugar levels increase
Describe Type 1 diabetes
-cannot produce insulin
-immune system destroyed pancreatic cells that make insulin
-condition begins in childhood
-controlled by regular injections of insulin and balanced diet w regular exercise
Describe Type 2 diabetes
-cannot effectively use insulin
-cells dont produce enough or body cells dont respond correctly
-controlled by regulating person's carbohydrate intake thru diet and exercise
-often overweight people
-drugs/insulin injections are used to stimulate insulin production
How does our body maintain water balance?
-salt and water enter through food and drink
-water also produced from respiration
-excretion through sweating and in urine, water vapour when you exhale
Explain the effects on cells of osmotic changes in the body
-water level in blood plasma must be constant
-too much will cause lysis
-too little or too much of solute, water will diffuse out causing crenation
How's urine produced?
-small molecules like water glucose urea n salts pass into tubes in kidney
-blood cells r too big so remain within capillaries
-then kidneys put any useful substances into blood incl glucose any salts n some water(selective reabsorption)
What do kidneys look like inside?
-capsule is outer membrane, helps maintain kidney shape and protect it from damage
-cortex is outer part of kidney
-medulla is inner part of kidney
Where's urine produced?
-microscopic tubules called nephrons inside kidney
-each kidney has approx 1 mil nephron
-top of nephron is in cortex, lower is in medulla
What goes on in the kidney? (P1)
-blood enters under high pressure from renal artery
-renal artery has many branches leading to a glomerulus
-each glomerulus has a knot of capillaries
-blood vessels narrow at exit to the glomerulus increasing blood pressure
-increased blood pressure forces small molecules(eg urea) out thru capillary wall into capscule
What goes on in the kidney?(P2)
-large molecules (proteins) stay in the bloodstream
-selective reabsorption takes place
-as filtrate moves through nephron tubule glucose is reabsorbed w water n salts needed
-filtrate passes through end of nephron (Henle) and collecting ducts
-can reabsorbing extra water/salt if needed
-excretion occurs
Explain the effects of ADH
dehydrated= morea adh = more reabsorption= less urine concentrated
healthy= less adh= less resabsorption needed= more urine dilute
3 groups of sport drinks
HYPERTONIC high levels of glucose and salts
HYPOTONIC low levels of glucose and salts
ISOTONIC ion concentrations equal to those in blood plasma