8. Radiographic interpretation Part 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
radiographic attenuation
The reduction in intensity of an X-ray beam as it travels through matter, caused by absorption or deflection
degree of attenuation depends on the material's thickness, its atomic number, and the energy of the X-ray beam; creates the contrast seen in a radiographic image
Areas w high attenuation, like bone, absorb more X-rays and appear white (radiopaque)
Areas w low attenuation, like air, absorb less and appear black (radiolucent)
photoelectric = absorbed vs compton scattering
high attenuation tissues appear more radiopaque or radiolucent?
radiopaque
low attenuation tissues appear more radiopaque or radiolucent?
radiolucent
bone high attenuation or low attenuation?
high attenuation, radiopaque
air high attenuation or low attenuation?
low attenuation, radiolucent
tissue that attenuates less photons
radiolucent
tissue that attenuates more photons
radiopaque
describe range of radiopaque or radiolucency of enamel, dentin, and cementum
most radiopaque: enamel, dentin, cementum
most radiopaque items
metal and restorations & cements
which is more radiopaque: cortical or cancellous bone?
cortical
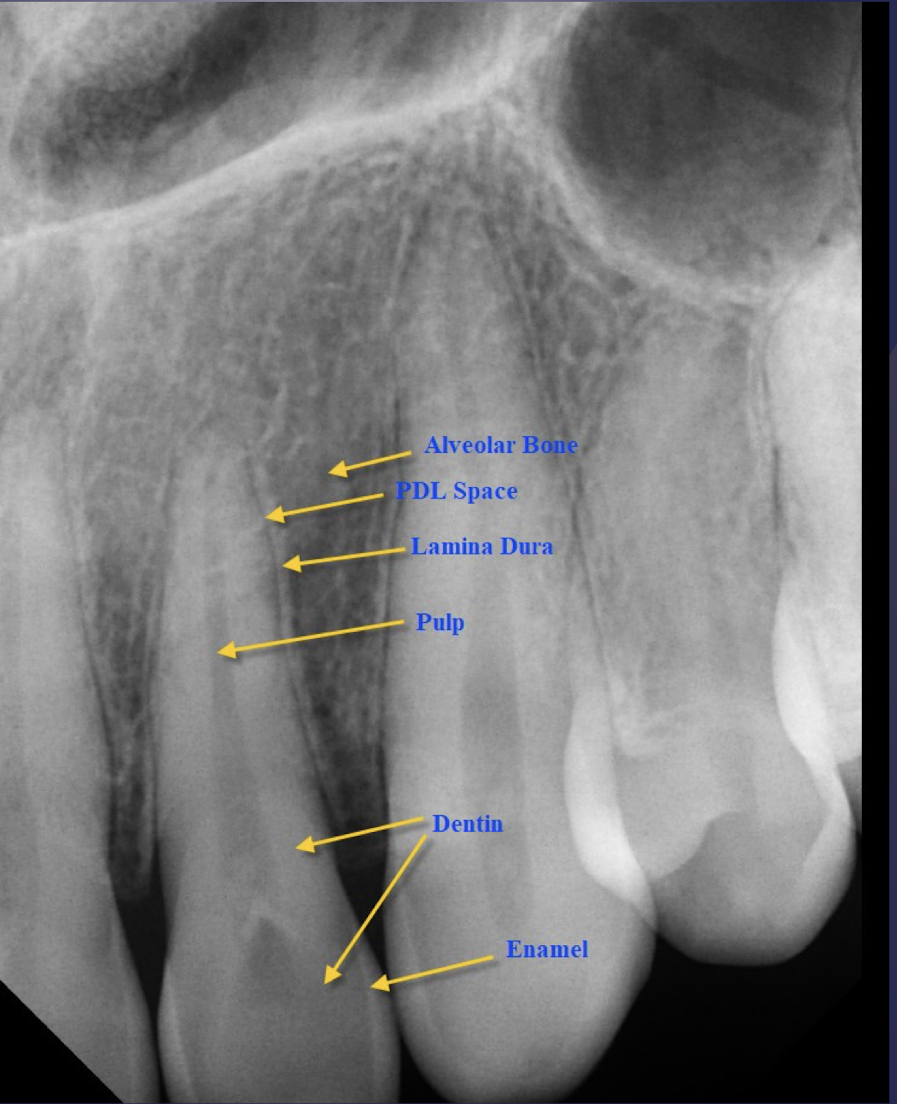
75% mineralized
dentin
tooth is primarily composed of
dentin
smooth and homogenous appearance
dentin
radiopaque similar to bone
dentin
cap is present over coronal portion
enamel
90% mineralized
enamel
causes greatest attenuation of x-rays bc of extreme mineralization making it the most radiopaque tissue
enamel
most radiopaque of the dental tooth tissues
enamel
why is it important to identify DEJ?
caries extent
50% mineralized
cementum
thin layer is present over root surface (~2 mm)
cementum
(BLANK) not visualized due to similar radiopacity of (BLANK)
cementum, dentin
what is visualized only with excessive formation
cementum
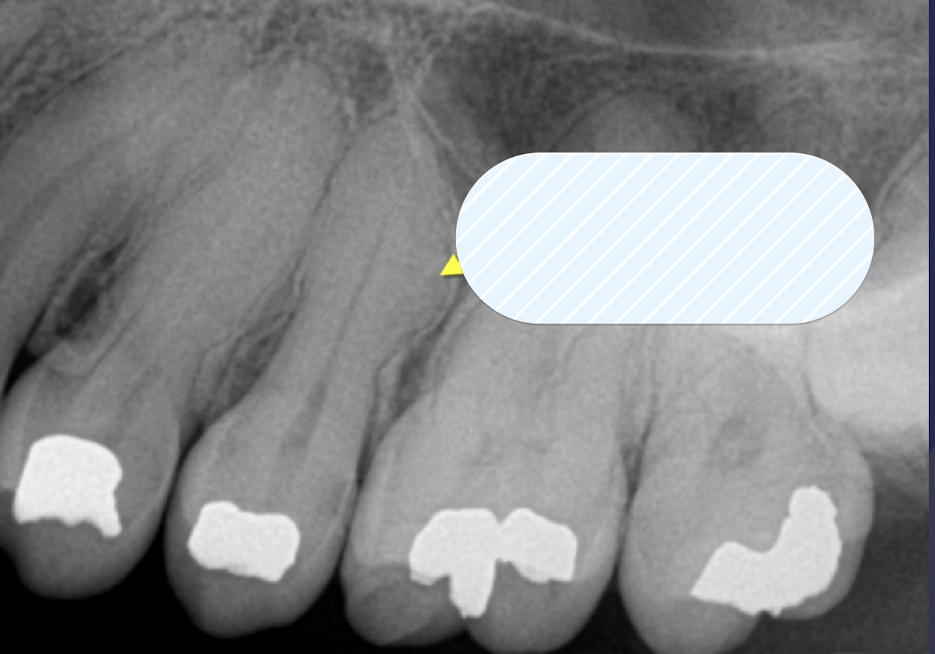
hypercementosis, only way cementum is visualized
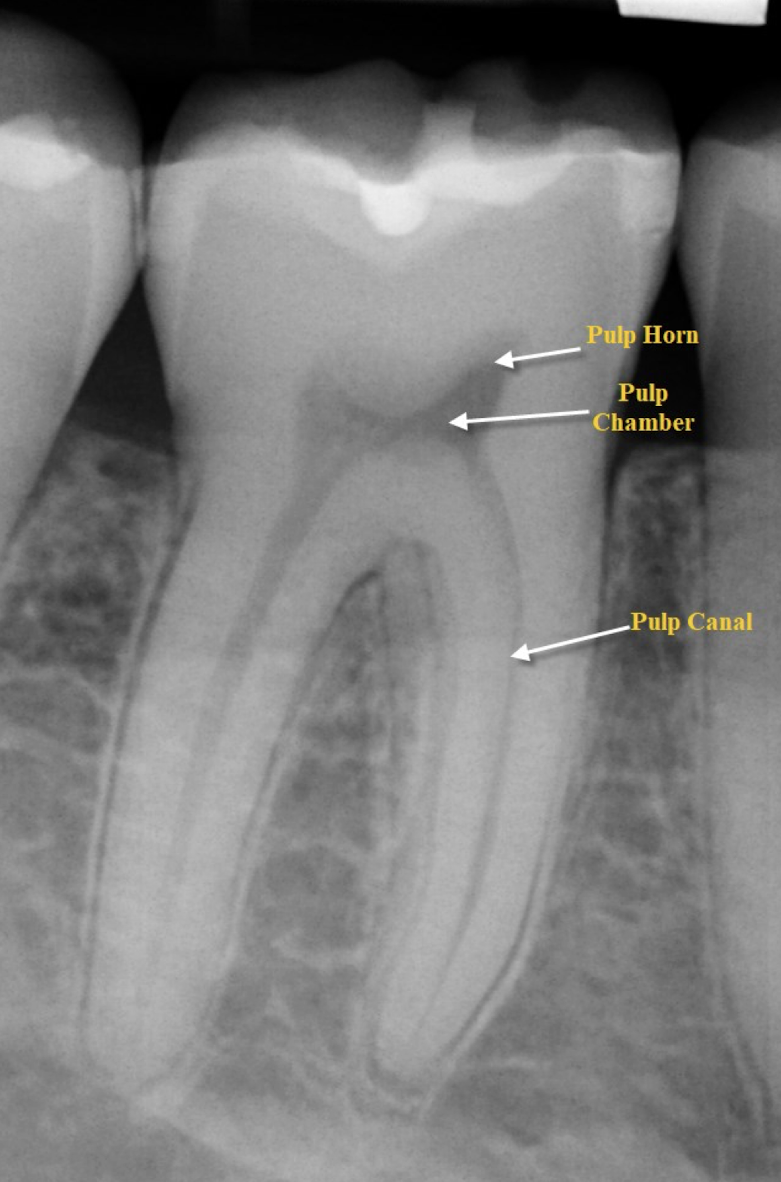
which view can you see cross-section of pulp chambers/canals?
axial
which view can you see mesial and distal of the teeth?
sagittal
which view can you see buccal and lingual of the teeth?
coronal
T or F: apical foramen is recognizable in fully formed teeth
true
T or F: apical foramen is always discernible in last 1 mm of length
false
describe the dental papilla of a developing tooth
root apex is open
radiolucent area surrounded by cortical bone: dental papilla bound by bony crypt
dental papilla
a small, cone-shaped mass of connective tissue located in the center of the developing tooth bud
root apex closed signifies
mature tooth
radiolucency with root apex open signifies
growing tooth
radiolucency with closed root apex signifies
lesion of adult tooth
what closes root apex?
pulpal walls in apical region constrict
close apposition = apex formation
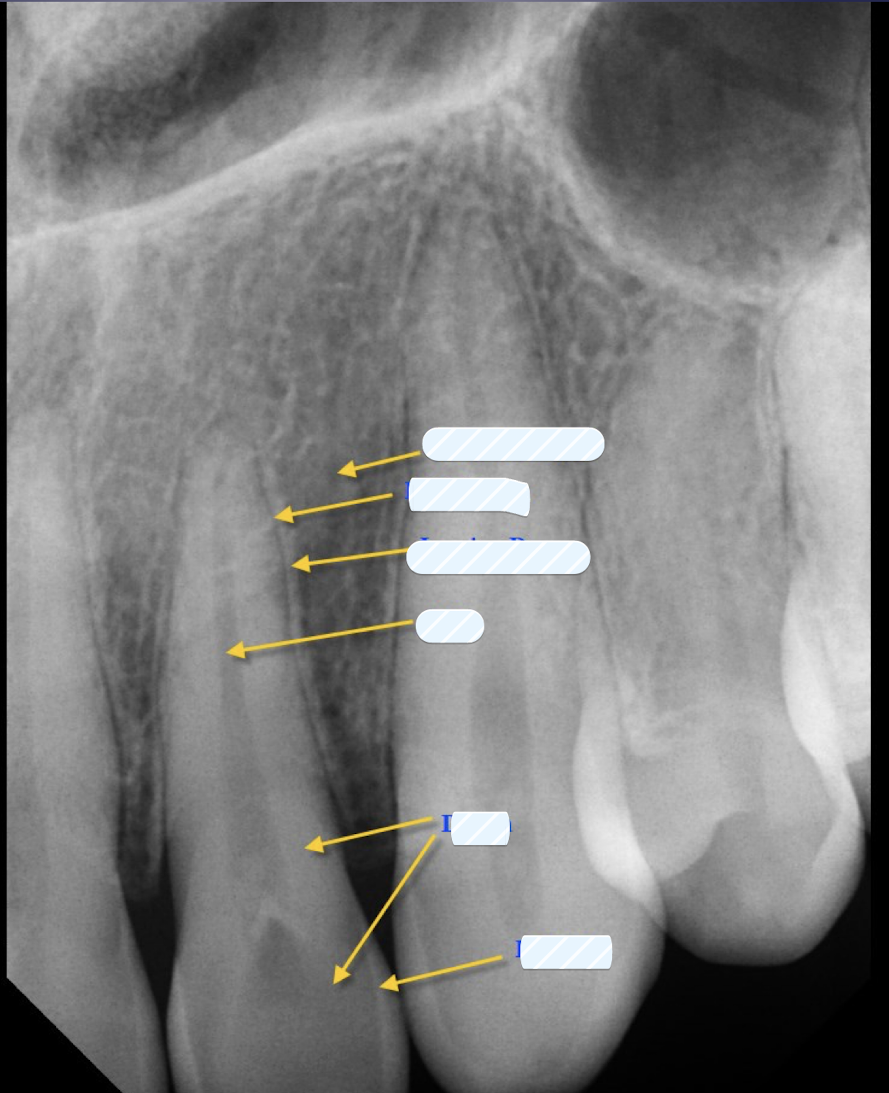
what are the five key supporting dentoalveolar structures?
lamina dura
PDL space
alveolar crest
cancellous/trabecular bone
cortical bone (best w CBCT)
lamina dura is
thin layer of cortical bone
which supporting dentoalveolar structure?
Thin radiopaque layer around the tooth root
Appearance may vary based on x-ray beam angulation
Appearance is a valuable diagnostic feature- the presence of an intact (BLANK) around the apex of a tooth strongly suggests a vital pulp
lamina dura
which supporting dentoalveolar structure?
composed primarily of collagen (soft tissue)
appears as a radiolucent line between tooth root and lamina dura
width varies between individuals, tooth to tooth and location to location
PDL space
widening of PDL space signals
loss of cortical bone (trauma, lesion, inflam)
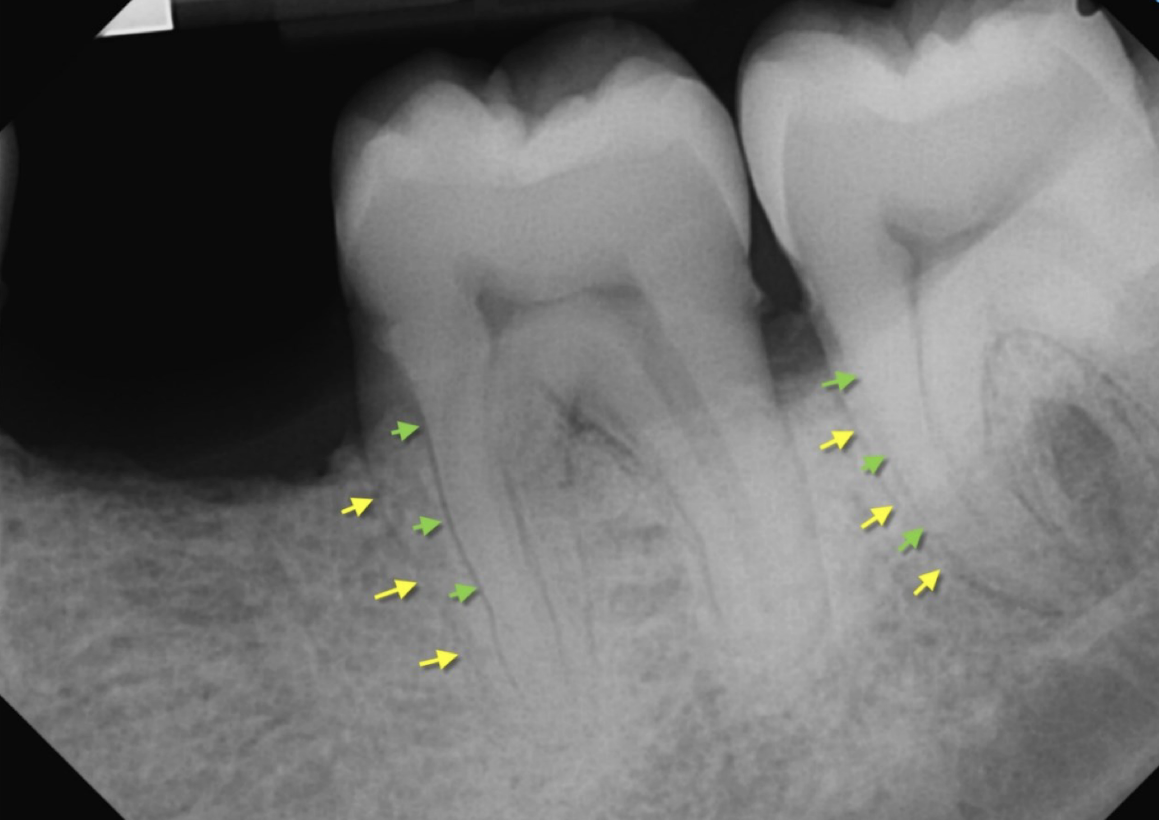
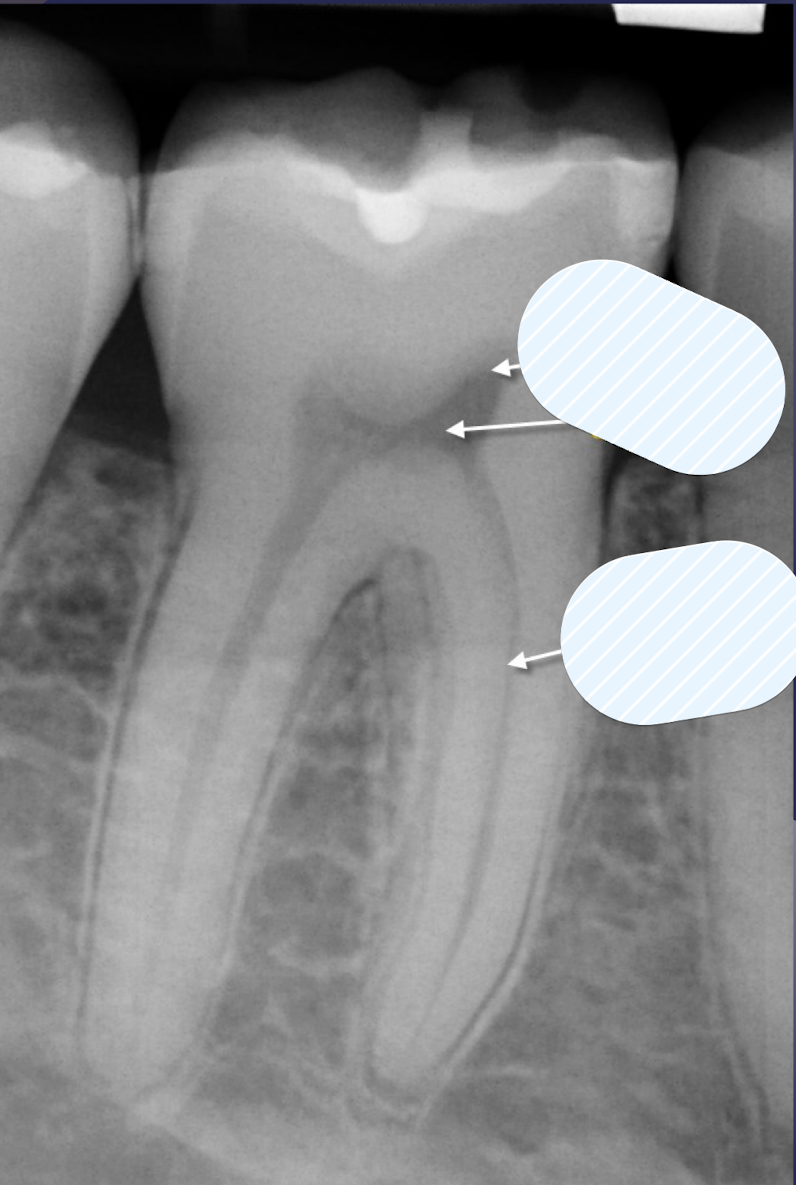
double PDL space
buccal and lingual eminences on mesial surface of #18 and #19
how does double PDL space occur?
created when x-ray beam directed so that two convexities of root surface appear on image
what could be mistaken for vertical root fracture?
double PDL space
double PDL space of #19
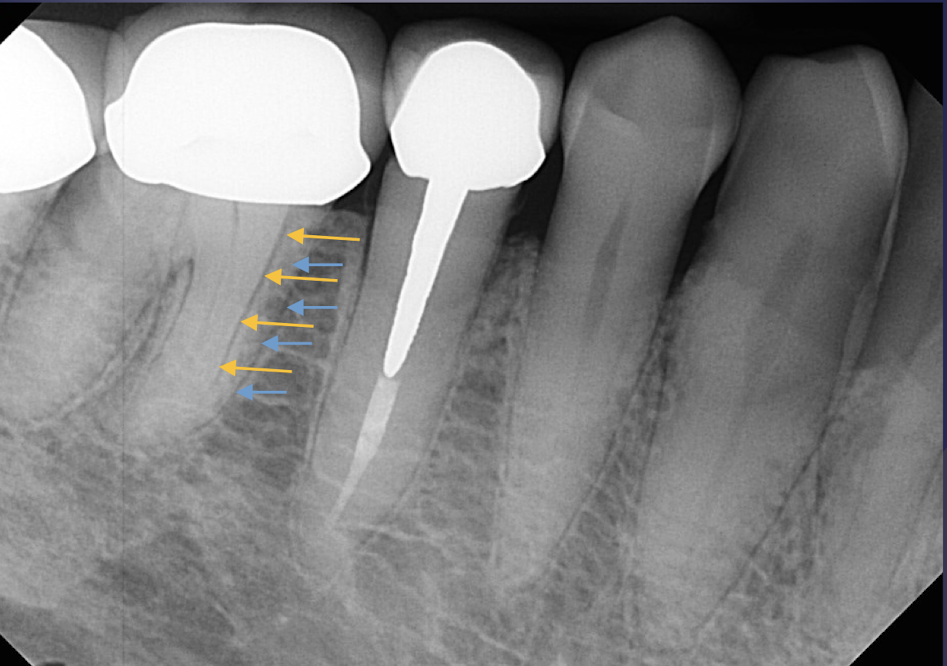
which supporting dentoalveolar structure?
The gingival margin of alveolar process between teeth
Appears as a radiopaque line
alveolar crest
alveolar crest is continuation of
lamina dura
alveolar crest is (perpendicular/parallel) to imaginary line connecting (BLANK) of adjacent teeth
parallel, CEJs
normal level of alveolar crest
distance btwn crest and CEJ is under 2mm
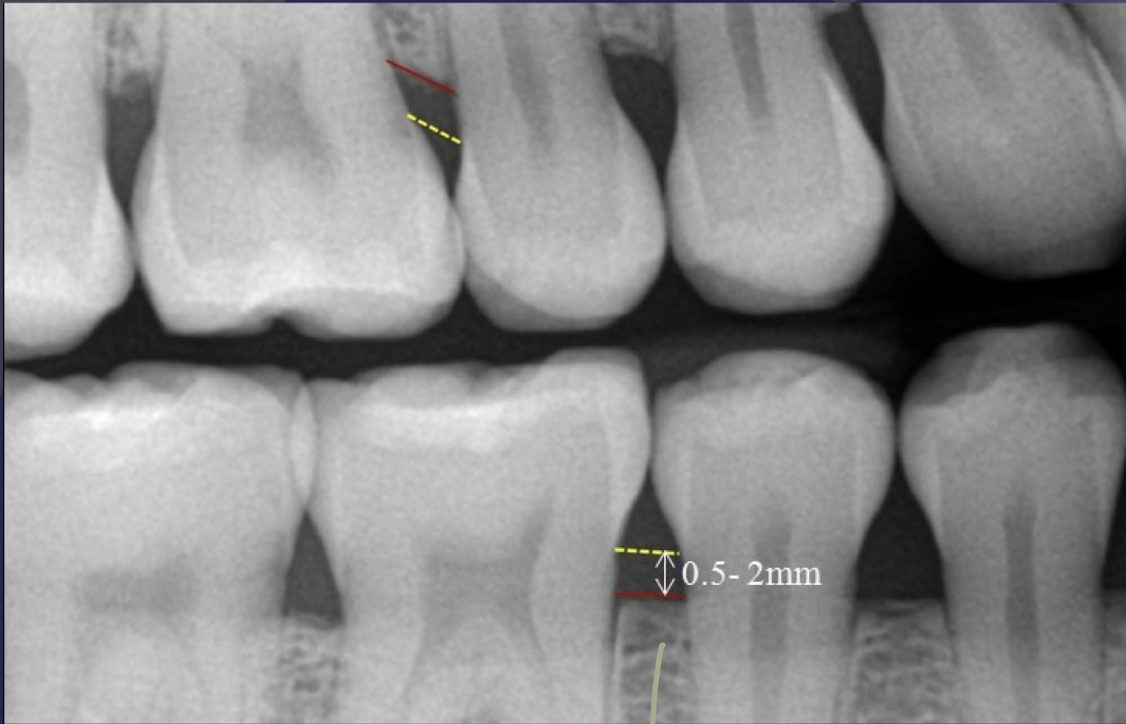
alveolar crest
which dentoalveolar structure?
Lies between cortical plates in both jaws
Composed of thin radiopaque plates and rods (BLANK1)
Surrounded by many radiolucent pockets (BLANK 2)
cancellous/trabecular bone BLANK 1: trabeculae BLANK 2: marrow spaces
cancellous bone
anterior/posterior mandible/maxilla:
Trabeculae are thin & numerous
Form a fine, granular, dense pattern
Marrow spaces are small and relatively numerous
anterior maxilla
cancellous bone
anterior/posterior mandible/maxilla:
Trabeculae are thicker & less numerous (coarser pattern)
Trabecular plates oriented more horizontally
Marrow spaces are larger
anterior mandible
cancellous bone
anterior/posterior mandible/maxilla:
thicker trabeculae, oriented horizontally
Trabeculae reduce in number inferior to the molar root
posterior mandible
cancellous bone
anterior/posterior mandible/maxilla:
Finer and more trabeculae than in posterior mandible
More marrow spaces
posterior maxilla
alteration in number and pattern may suggest disease in asymptomatic pts
in cancellous bone, systemic disease like osteoporosis, renal issue, etc
what are the landmarks of the maxilla?
intermaxillary suture
incisive/nasopalatine foramen
incisive/lateral fossa
which landmark of the maxilla?
radiolucent line in midline of maxilla btwn central incisors surrounded by radiopaque lines of thin cortical bone
intermaxillary suture
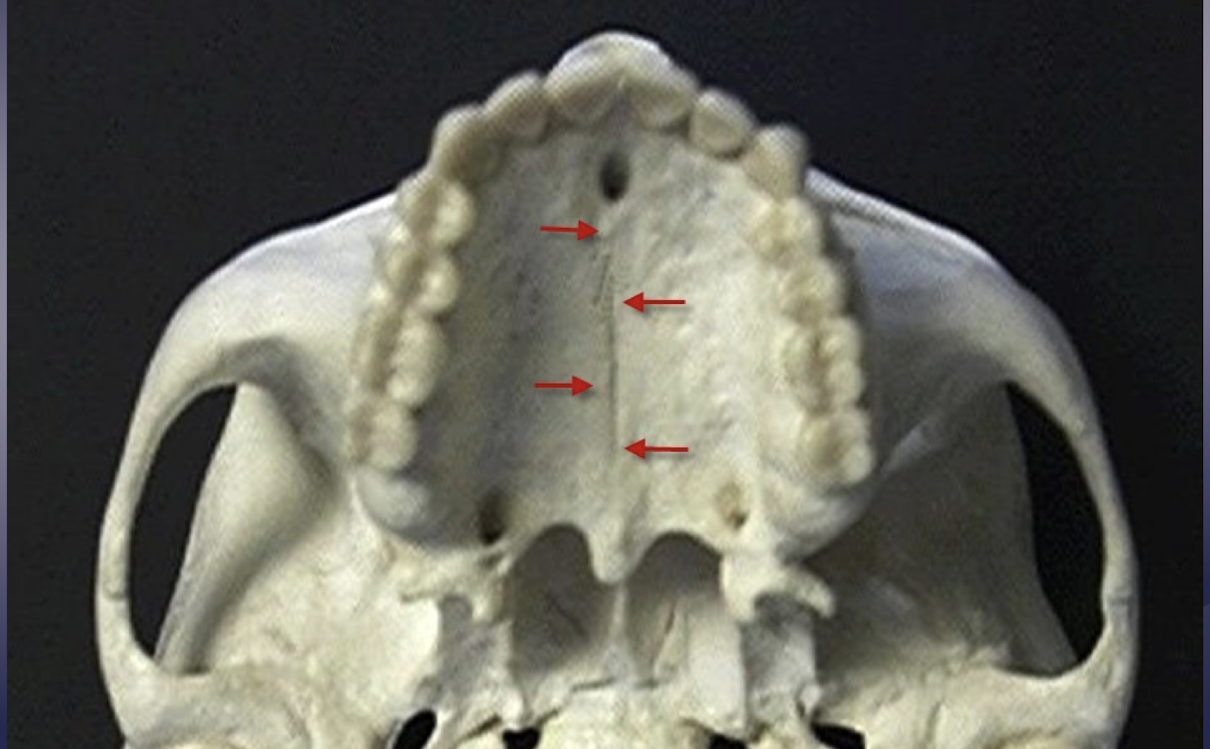
intermaxillary suture aka midpalatine suture aka median palatine suture
intermaxillary suture
how do you tell the difference btwn intermaxillary suture and a fracture?
suture is a radiolucent line sandwiched btwn two radiopaque lines
fracture would be only a radiolucent line
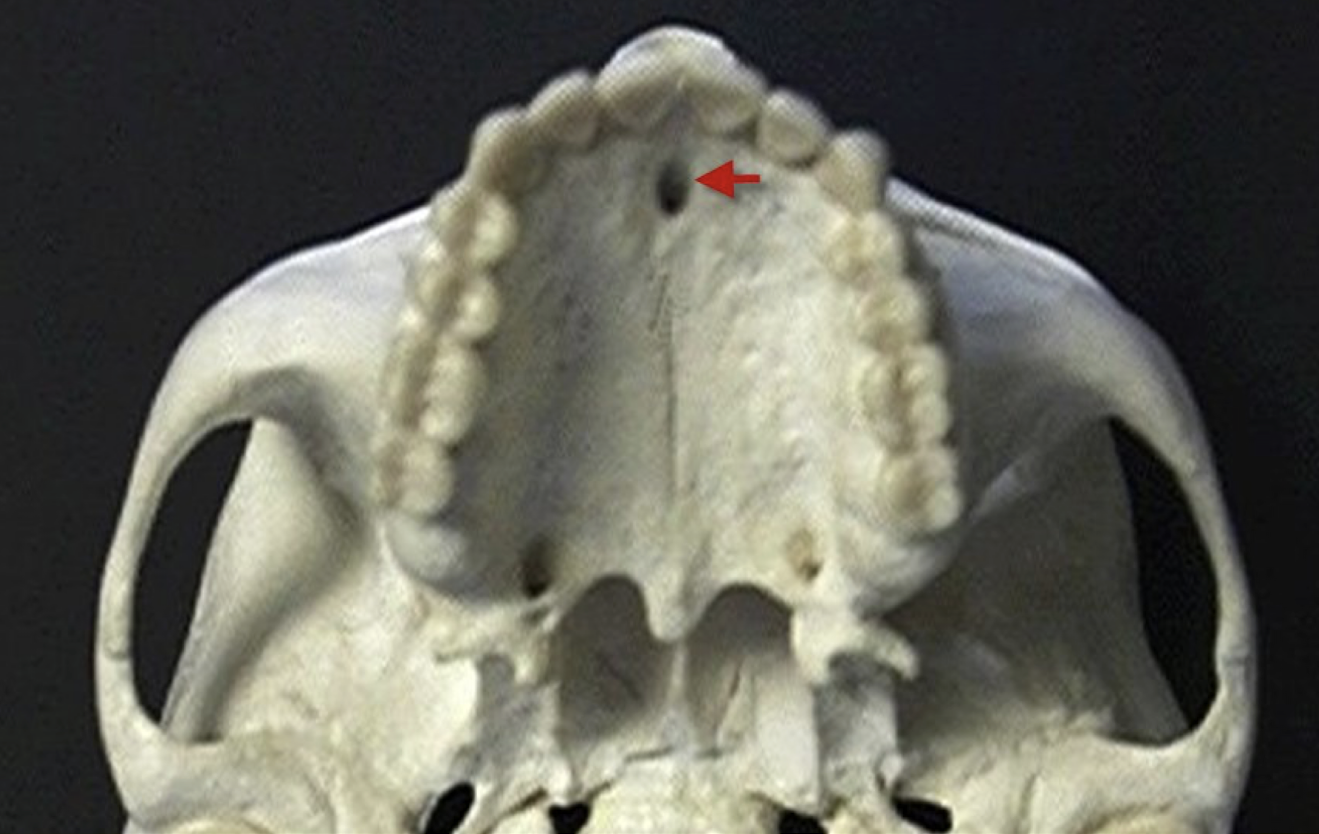
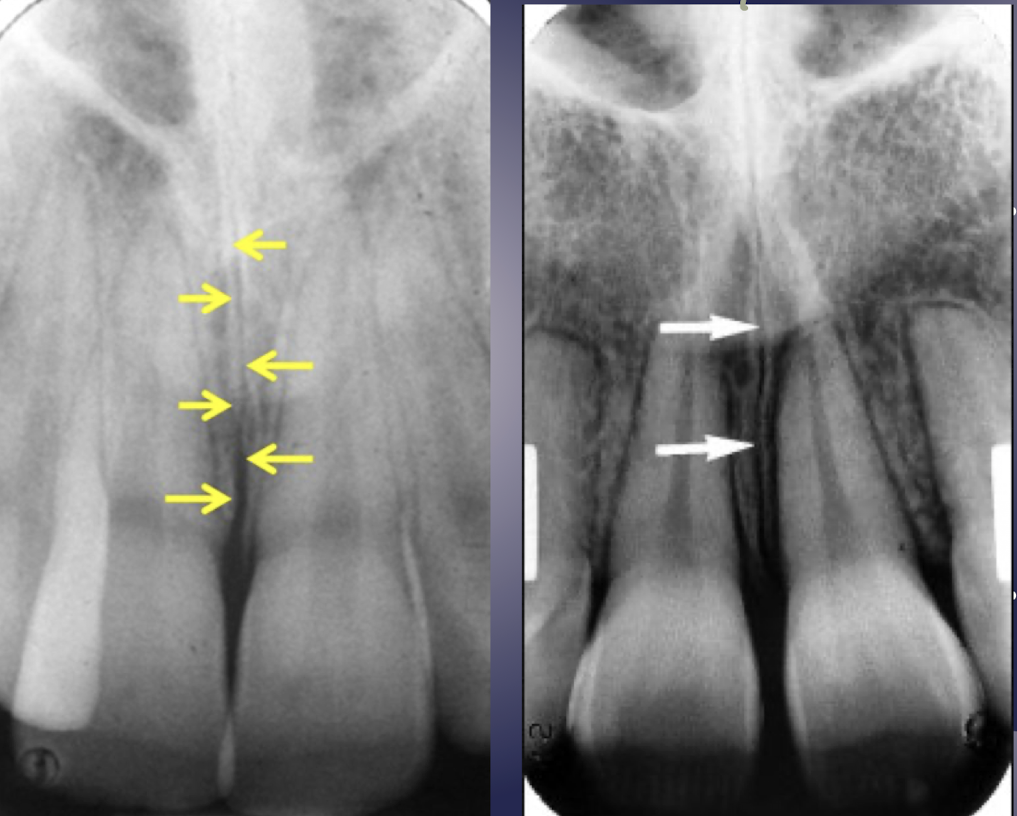
incisive/nasopalatine foramen
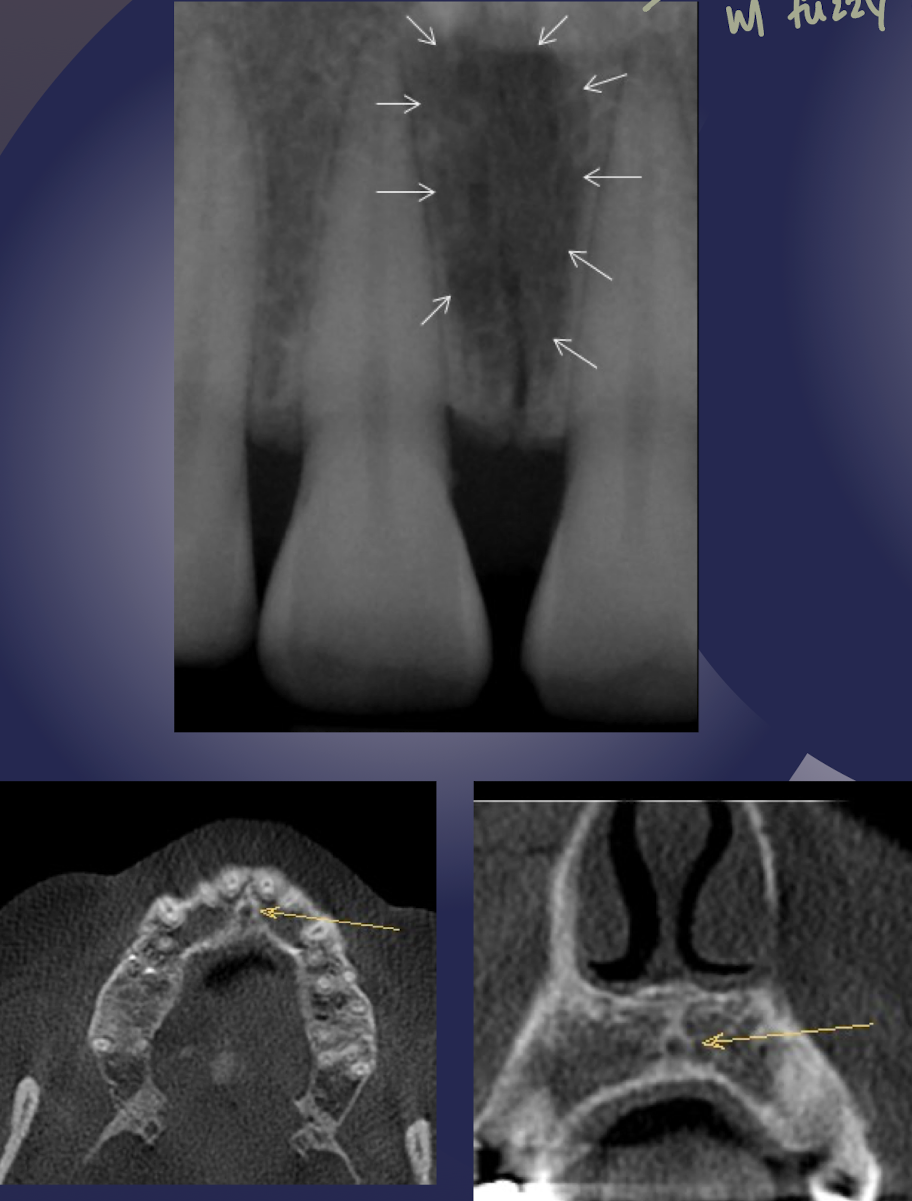
incisive/nasopalatine foramen
which landmark of the maxilla?
oral terminus of nasopalatine canal
Image is found between roots of central incisors
Ovoid radiolucency (fuzzy outline w sagittal view)
Varies in shape, size, sharpness
Shape and size may vary based on differing projection geometry
Increase in size may indicate a cyst involving the nasopalatine canal
cyst is presumed if it exceeds 1 cm
incisive/nasopalatine foramen
if this maxilla landmark is large you should investigate
incisive foramen
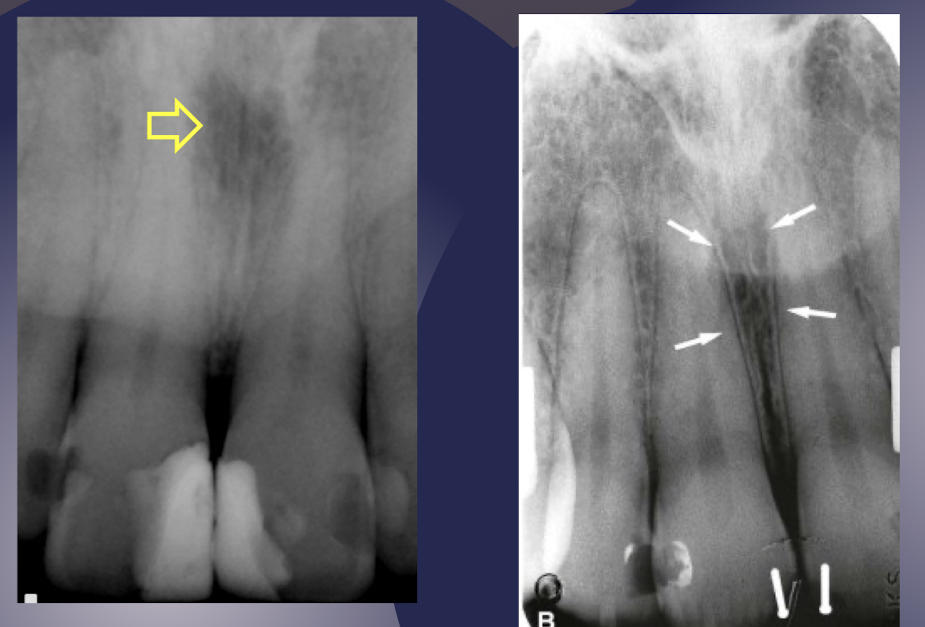
incisive foramen
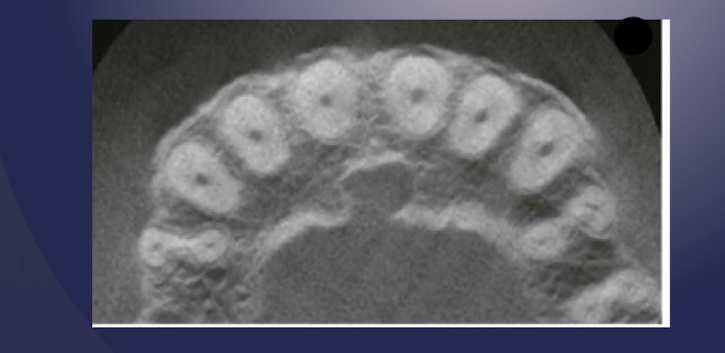
incisive foramen
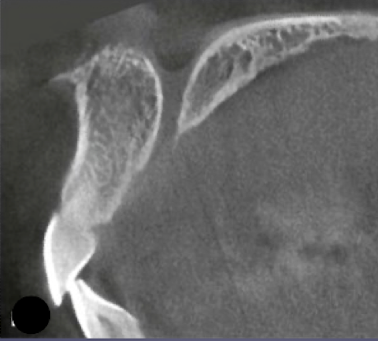
incisive foramen
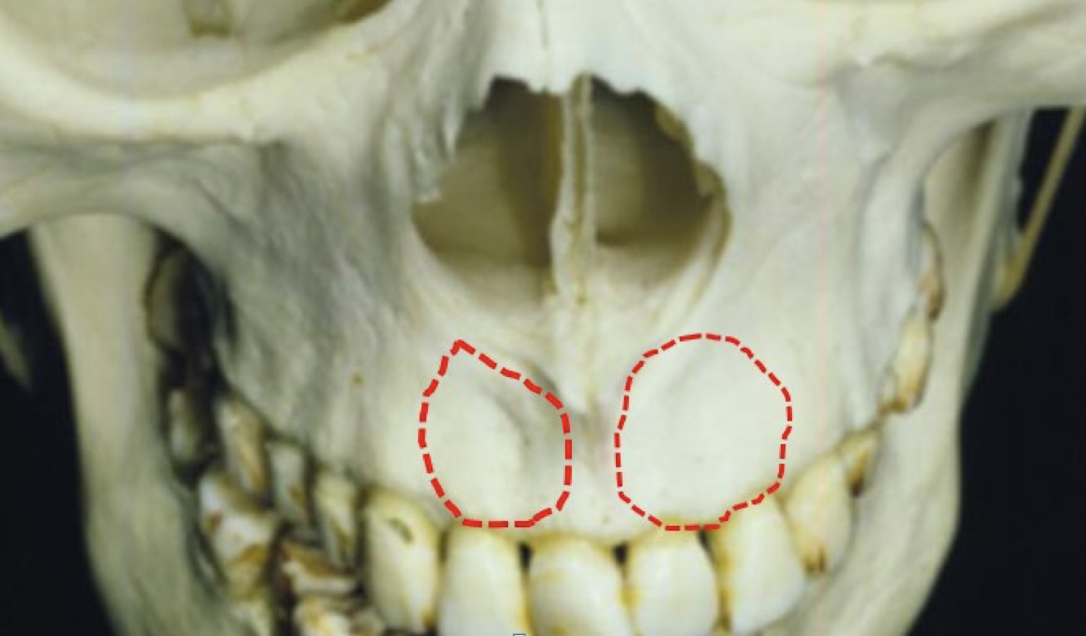
incisive/lateral fossa
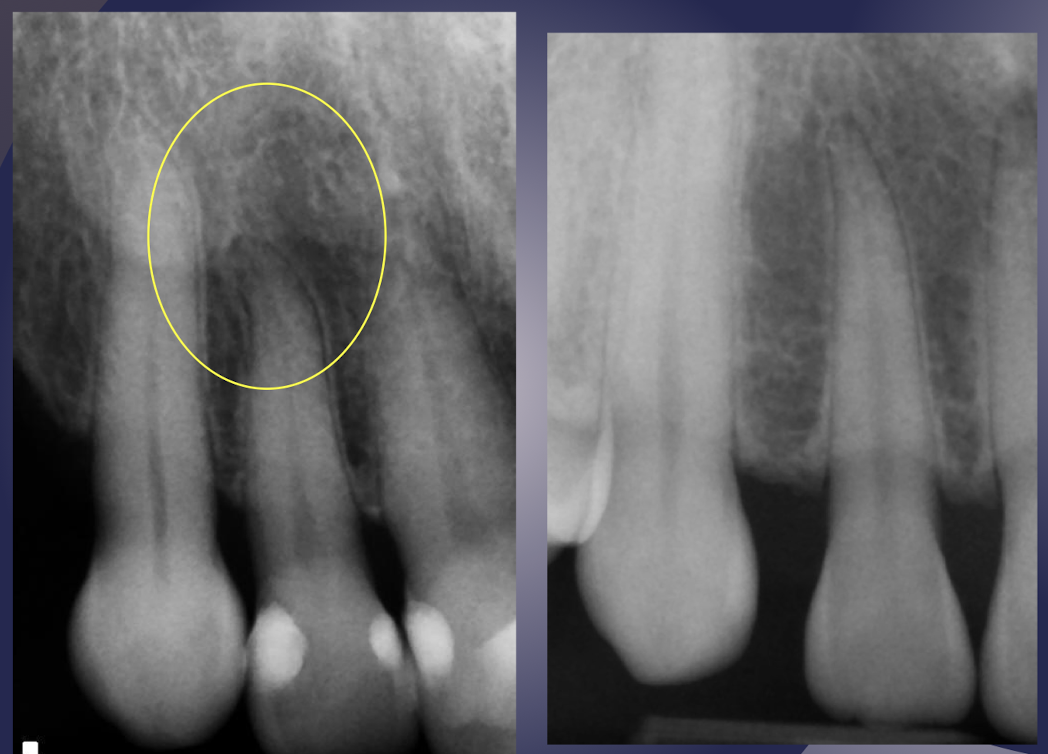
incisive/lateral fossa
which maxillary landmark?
Gentle depression near root apex of lateral incisor of maxilla
Casts a diffusely radiolucent shadow in periapical radiographs
Often misinterpreted as pathologic condition
Intact lamina dura may help rule out pathology
incisive/lateral fossa