AP Psych - Learning
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
associative learning
* learning that certain events can occur together
* can be two stimuli (**classical conditioning**) or a behavior + consequence (**operant conditioning**)
* can be two stimuli (**classical conditioning**) or a behavior + consequence (**operant conditioning**)
2
New cards
classical conditioning
* one learns to link 2+ stimuli and anticipate events
* ex. **Pavlov**
* ex. **Pavlov**
3
New cards
learning
relatively permanent change in an organism's behavior bc of experience
4
New cards
behaviorism
view that psychology should be (1) an objective science that (2) studies behavior __without__ reference to mental processes
5
New cards
unconditioned response (UCR or UR)
* unlearned, naturally occurring response to an unconditioned stimulus
* ex. salivating when food is in mouth
* ex. salivating when food is in mouth
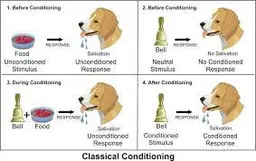
6
New cards
unconditioned stimulus (UCS or US)
stimulus that automatically triggers a response
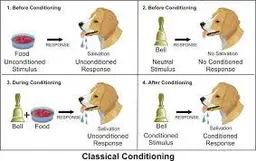
7
New cards
conditioned response (CR)
learned response to previously neutral (NS), but now conditioned stimulus (CS)
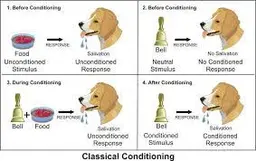
8
New cards
conditioned stimulus (CS)
originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association w/ unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response
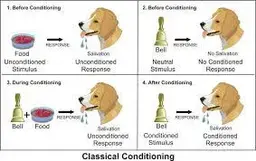
9
New cards
neutral stimulus (NS)
a stimulus that triggers no response
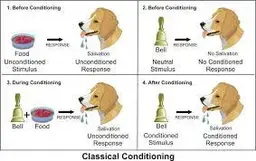
10
New cards
classical conditioning diagram w/ examples
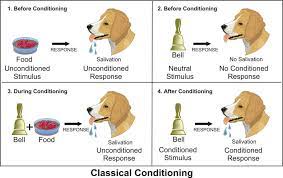
11
New cards
acquisition
* in **classical conditioning** - initial learning, where one links neutral stimulus and unconditioned stimulus, so that UCS begins triggering CR
* in **operant conditioning** - strengthening of reinforced response
* in **operant conditioning** - strengthening of reinforced response
12
New cards
higher-order conditioning
* process where **conditioned stimulus** is paired w/ a new **neutral stimulus**, creates a second (often weaker) **conditioned stimulus**
* ex. an animal that learns that a tone predicts food may learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone
* ex. an animal that learns that a tone predicts food may learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone
13
New cards
extinction
diminishing of **conditioned response**
* in **classical conditioning -** when an unconditioned stimulus does not follow a conditioned stimulus
* in **operant conditioning** - when a response is no longer reinforced
* in **classical conditioning -** when an unconditioned stimulus does not follow a conditioned stimulus
* in **operant conditioning** - when a response is no longer reinforced
14
New cards
spontaneous recovery
reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished **conditioned response**
15
New cards
generalization
the tendency for a similar stimulus to the **conditioned stimulus** to elicit a similar response
16
New cards
discrimination
the learned ability to distinguish between a **conditioned stimulus** and stimuli that have not been paired w/ **unconditioned stimulus**
17
New cards
respondent behavior
actions that occur as an automatic response to a stimulus
18
New cards
operant conditioning
type of learning where behavior is strengthened if followed by **reinforcer** or weakened if followed by **punisher**
19
New cards
operant behavior
behavior that operates on the environment, producing consequences
20
New cards
law of effect
**Thorndike's** principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely
21
New cards
operant chamber
(also known as a skinner box), container w/ bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain food or water reinforcer
22
New cards
shaping
**operant conditioning** procedure where reinforcers guide behavior to closer and closer approximations of final desired behavior
23
New cards
reinforcer
something that strengthens/encourages a behavior
24
New cards
punishment
something that weakens/discourages behavior
25
New cards
positive
adding something
26
New cards
negative
subtracting something
27
New cards
positive reinforcer
* stimulus added after a desired behavior that strengthens response
* ex. of positive reinforcement - giving a kid candy after they do their homework
* ex. of positive reinforcement - giving a kid candy after they do their homework
28
New cards
negative reinforcer
* stimulus that, when removed, strengthens response
* ex. of negative reinforcement - beep turns off after seatbelt is buckled
* ex. of negative reinforcement - beep turns off after seatbelt is buckled
29
New cards
positive punisher
* stimulus added after a desired behavior that weakens response
* ex. of positive punishment - physical abuse as an attempt to discourage a behavior
* ex. of positive punishment - physical abuse as an attempt to discourage a behavior
30
New cards
negative punisher
* stimulus subtracted after a desired behavior that weakens response
* ex. of negative punishment - a time out (removing choice, attention, time) as an attempt to discourage a behavior
* ex. of negative punishment - a time out (removing choice, attention, time) as an attempt to discourage a behavior
31
New cards
primary reinforcer
* innately reinforcing stimulus, often that satisfies a biological need
* ex. food, painful headache going away
* ex. food, painful headache going away
32
New cards
conditioned/secondary reinforcer
* stimulus that gains it's reinforcing power through its association w/ a primary reinforcer, may have no value otherwise
* ex. money
* ex. money
33
New cards
continuous reinforcement
reinforcing desired response each time it occurs
34
New cards
partial (intermittent) reinforcement
* reinforcing a response only sometimes
* results in slower acquisition but greater resistance to extinction than continuous reinforcement
* results in slower acquisition but greater resistance to extinction than continuous reinforcement
35
New cards
fixed-ratio schedule
* reinforces behavior after a specified number of responses
* (ex. 1:1 \[1 occurrence of a behavior to 1 reward\], 3:1 \[3 occurrences of a behavior to 1 reward\])
* (ex. 1:1 \[1 occurrence of a behavior to 1 reward\], 3:1 \[3 occurrences of a behavior to 1 reward\])
36
New cards
variable-ratio schedule
reinforces behavior after an unpredictable and inconsistent number of responses
37
New cards
fixed-interval schedule
reinforces response only after a consistent time has elapsed
38
New cards
variable-interval schedule
reinforces response after an inconsistant, unpredictable time has elapsed
39
New cards
cognitive map
mental representation of the layout of one's enviroment
40
New cards
latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it
41
New cards
intrinsic motivation
desire to perform behavior for its own sake
42
New cards
extrinsic motivation
desire to preform behavior to receive reward/avoid punishment
43
New cards
observational learning
learning through the observation of others
44
New cards
modeling
observing and imitating a certain behavior
45
New cards
mirror neurons
frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions/observing another doing so
46
New cards
prosocial behavior
positive, constructive, helpful, behavior
47
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
* physician/neurophysiologist
* studied digestive secretions in dogs
* **classical conditioning**
* studied digestive secretions in dogs
* **classical conditioning**
48
New cards
John B. Watson
* Together w/ **Rosalie Rayner**, trained "little Albert" to fear rats, using **classical conditioning**
* Also showed **generalization**, as Albert became afraid of white fuzzy things
* Also showed **generalization**, as Albert became afraid of white fuzzy things
49
New cards
Rosalie Rayner
* Together w/ John B. Watson, trained "little Albert" to fear white rats, using classical conditioning
* Also showed **generalization**, as Albert became afraid of white fuzzy things
* Also showed **generalization**, as Albert became afraid of white fuzzy things
50
New cards
John Garcia
studied taste aversion and nausea w/ Robert Koelling
51
New cards
Robert Koelling
studied taste aversion and nausea w/ John Garcia
52
New cards
Robert Rescorla
* Developed theory emphasizing the importance of cognitive processes in **classical conditioning**
* Said that subjects had to determine (think) whether **CS** was a reliable predictor of **UCS**
* Said that subjects had to determine (think) whether **CS** was a reliable predictor of **UCS**
53
New cards
Edward L. Thorndike
* Named the **law of effect**
* Created puzzle boxes for research on cats
* **Operant conditioning**
* Created puzzle boxes for research on cats
* **Operant conditioning**
54
New cards
B. F. Skinner
* Elaborated on **Thorndike's law of effect**
* **Skinner boxes**, pigeons
* Behaviorist
* **Skinner boxes**, pigeons
* Behaviorist
55
New cards
Edward Tolman
* Behavioral psychology
* Studied **latent learning** and **cognitive maps** using rats in a maze
* Critical of behaviorism
* Studied **latent learning** and **cognitive maps** using rats in a maze
* Critical of behaviorism
56
New cards
Albert Bandura
* Studied **observational learning**, consequences a model has on subjects
* Bobo doll experiments
* Studied delayed gratification w/ **Mike Mahoney**
* Bobo doll experiments
* Studied delayed gratification w/ **Mike Mahoney**
57
New cards
Mike Mahoney
Studied delayed gratification w/ **Albert Bandura**