Biology Unit 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
Species
A group of organisms that breed together and produce fertile offspring
2
New cards
Variation
different characteristics within a species
3
New cards
Characteristic
a feature in a species
4
New cards
inherited variation
is caused by genes mutations and DNA passed from your parents
5
New cards
inherited characteristics
eye colour, blood type
6
New cards
environmental characteristics
language, religion, piercings, scars, hair length
7
New cards
characteristics of both
height, skin colour, weight, hair colour
8
New cards
Mendel discovered
you inherit traits from both your parents
9
New cards
continuous variation
normally something you can measure. it’s a number in a range
10
New cards
discontinuous variation
Is something you have or don’t have. Something you can do or not do. I doesn’t have a number range.
11
New cards
continuous examples
height, weight, handspan
12
New cards
discontinuous example
eye colour, rolling your tongue
13
New cards
dependant variable
what you measure (y axis)
14
New cards
independent variable
what you change (x axis)
15
New cards
organisms competed for
water, light, space, food, mates, minerals
16
New cards
adaptions
when competing with other animals the best competitors are stronger, smarter and better at spotting prey. Spotting prey might require good hearing or sight. These features are called adaptions.
17
New cards
Hot climate adaptions
no reliance on sweat to cool down, Hunt during the night, thin layer of body fat under skin, camouflage isn’t white, survives on small amount of water, large thin ears, thin silky fur, large surface area to body mass ratio, not necessarily black eyes or nose
18
New cards
cold climate adaptions
small surface area to body mass ratio, survive on normal amount of water, large layer of fat under skin, thick fur, hunt during the day, normal reliance on sweat, black eyes and nose, camouflaged white or grey, small ears
19
New cards
the nucleus of the cell has
chromosomes
20
New cards
genes are sections of
dna , genes code for proteins, proteins produce characteristics
21
New cards
dna is made up of
bases
22
New cards
chromosome
long strand of dna
23
New cards
dna is a ……….. …….. shape
double helix
24
New cards
rosalind franklin studied dna using
x-rays
25
New cards
photo 51 was taken in
1952
26
New cards
every cell has …… chromosomes
46
27
New cards
what cells have 23 chromosomes
gametes
28
New cards
rosalind franklin discovered
dna was a double helix shape
29
New cards
evolution
the process by which living things can gradually change over time
30
New cards
evolution takes ……………. of years
millions
31
New cards
according to scientists all animals have a common ……………, which was a …………. …………
ancestor, simple organism
32
New cards
3 types of evidence for evolution
fossil, dna, observational evidence
33
New cards
mutation
a change in the DNA sequence of an organism. some of these cause variations that are advantageous to the animal
34
New cards
natural selection
organisms with characteristics most suited to their environment can reproduce and pass on their genes are characteristics
35
New cards
example of natural selection
peppered moths, giraffes, praying mantis
36
New cards
extinction
is when all members of a species die, this normally happens when a species isn’t adapted to it’s environment
37
New cards
causes of extinction
travelling, urbanisation, virus, climate change, loss of habitats, poaching, hunting, pollution, invasive species, predators, natural disasters
38
New cards
interdependency
if one animal in the food chain becomes extinct it can make other animals in the chain at risk
39
New cards
a gene bank
stores genetic material of plants and animals to preserve species, they are conservation efforts
40
New cards
seed banks
\-18 degree freezers
41
New cards
tissue banks
buds and other cells of plants stored
42
New cards
cryobanks
seeds or embryos are stored at very low temperatures using liquid nitrogen
43
New cards
there are 4 types of banks, seed banks, tissue banks, cryobanks, and
pollen banks
44
New cards
selective breeding
a sped up artificial evolution where parents are chosen to replicate desired traits
45
New cards
after 1 round of selective breeding
the best offspring from the parents are selected and bred together
46
New cards
selective breeding takes
decades
47
New cards
cloning
is making a genetically identical copy of an individual
48
New cards
cloning happen naturally in
asexual reproduction
49
New cards
plant can be cloned by
cutting them and planting then in growth hormones
50
New cards
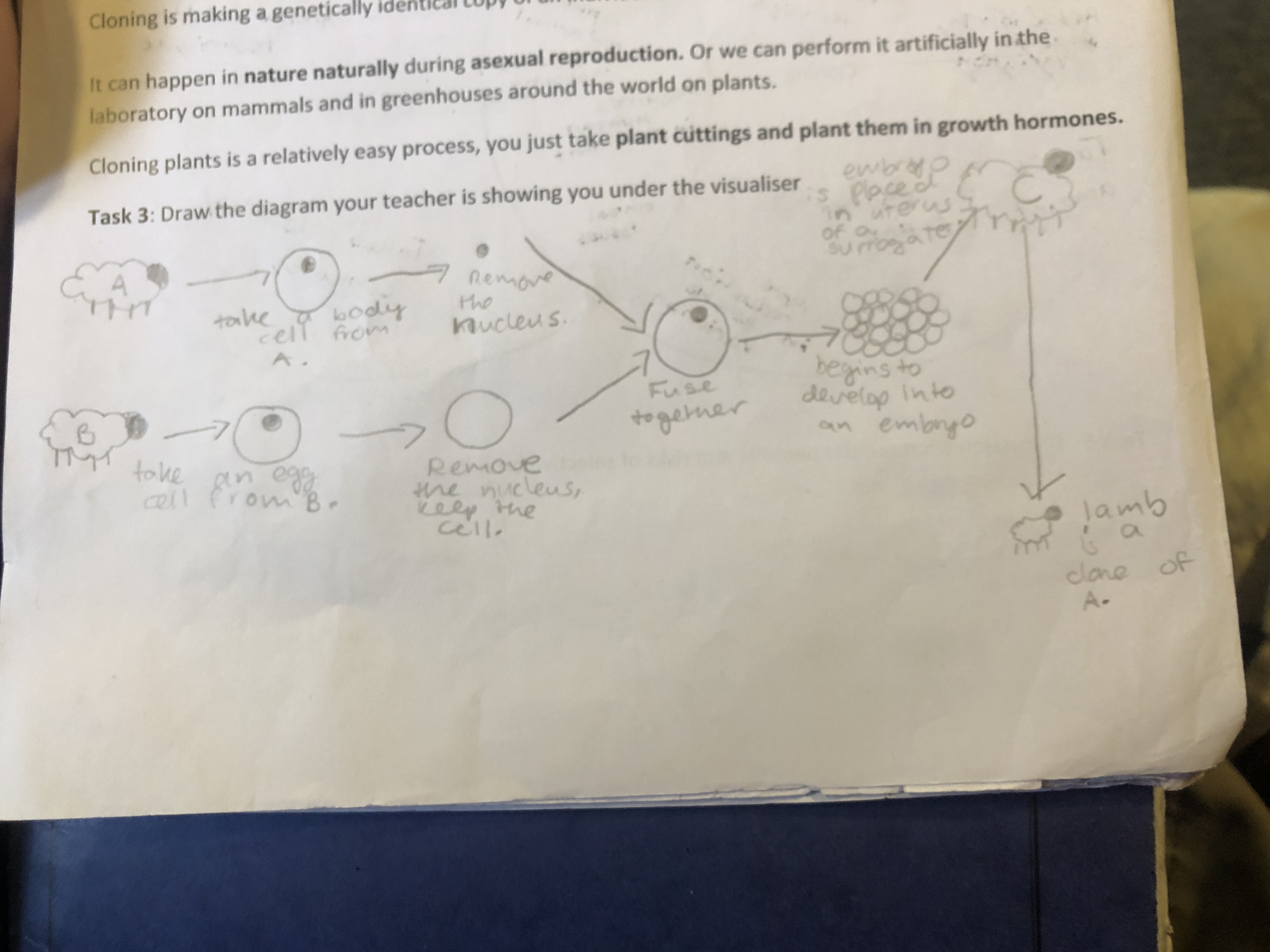
cloning diagram
51
New cards
cloning and selective breeding similarities
ethical issues, requires human involvement, reduce in genetic variation, reproduction/new animal, enhances or replicates desired traits
52
New cards
only cloning
is lab dependent, helps prevents extinction, modern technique, takes shorter amount of time, more reduction in genetic variation
53
New cards
only selective breeding
doesn’t rely on labs, is an ancient technique, takes decades