NE101 Lec 12: Neuroanatomy II
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Explores neural connections, synapses, connectomics, and communication pathways.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
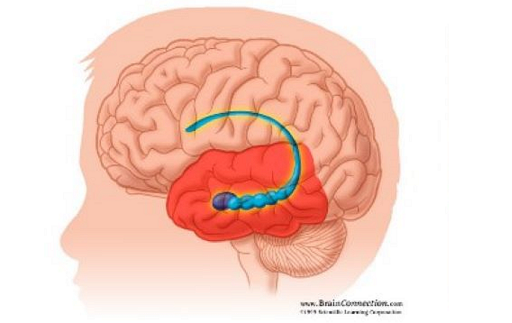
what location in the brain is this?
hippocampus
hippocampus function
memory
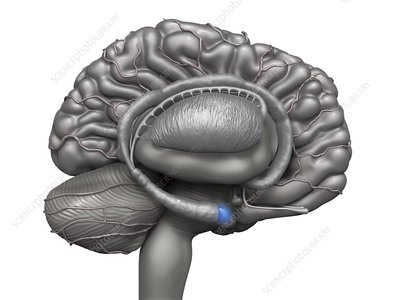
what location in the brain is this?
amygdala
amygdala function
emotion
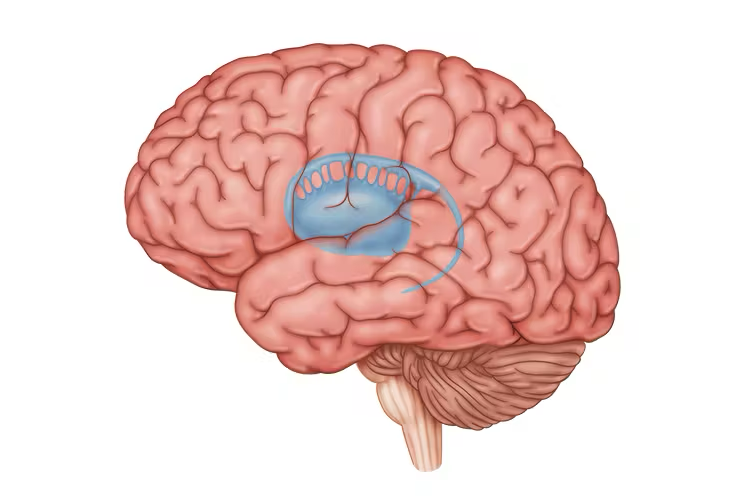
what location in the brain is this?
basal ganglia
basal ganglia function
movement and reward
Bell’s Palsy results from trauma or damage to the ________ nerve (CN VII).
facial
CN VII controls ________ and ________ of the face.
muscle control, sensation
Bell’s Palsy causes deficits on the ________ side of the face.
ipsilateral
The ______ tract connects the motor cortex to the cranial nerve nuclei in the brainstem.
corticobulbar
The ________ muscles are controlled by bilateral projections.
upper facial
The brain carries out computations at multiple levels, from single neurons to ________ networks.
cross regional
A single neuron represents level ________ of computation.
1
Microcircuits contain about ________ to ________ neurons.
tens, hundreds
Regional networks (like the hippocampus) contain up to ________ neurons.
billions
The cerebellum has approximately ________ billion neurons.
50
The entire brain contains about ________ billion neurons.
86
The ________ stain was used by Ramón y Cajal to study neuron morphology
golgi
Tracers are used to map ________ between brain regions.
connections
A limitation of tracers is that they must be used in ________ tissue.
post mortem
Tracers cannot establish a complete ________ diagram.
wiring
______ tracers identify cells that send connections to the injection site.
retrograde
______ tracers show where neurons in a region send connections.
anterograde
Injecting a retrograde tracer in the ventral horn would show expression in the ________ motor cortex.
contralateral
Injecting an anterograde tracer in the ventral horn would show expression in ________ muscle.
skeletal
Connectomics is the cataloging of all ________ between neurons.
connections
Challenge 1: The problem in mapping neurons is that tangled ________ and ________ make it hard to distinguish individual cells.
axons, dendrites
The solution to challenge 1 was to label neurons with different colors using the ________ transgenic mouse.
brainbow
Challenge 2: brain is difficult to see through because it is composed of ________.
lipids
The solution to challenge 2 is to remove lipids and make tissue ________.
transparent
Challenge 3: light microscopes cannot determine if neurons are connected because proximity doesn’t prove ________.
synaptic contact
The solution to resolving individual synapses is ________ microscopy.
electron
what problem is this? The human brain contains about 100 billion neurons and 125 trillion connections.
scale problem