Bio 181
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/191
Earn XP
Last updated 9:32 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
1
New cards
independent variable
something that you change, "I control"
2
New cards
Intersexual selection
males compete for females attention by displaying gift or characteristics
- peacock feathers
- penguins making nests/presenting pebbles
- peacock feathers
- penguins making nests/presenting pebbles
3
New cards
Bishop Ussher
calculated the age of the earth using genesis
- earth created Oct. 23 404 BC
- earth created Oct. 23 404 BC
4
New cards
1st law of thermodynamic
matter can not be created or destroyed, only transformed
5
New cards
hypothesis
testable, expands past observations --> critical thinking
null --> nothing will happen
alternative --> something with change
null --> nothing will happen
alternative --> something with change
6
New cards
2nd law of thermodynamics
every time energy is transformed some is lost (heat)
7
New cards
why can't viruses be considered alive? They can't...
read and code for DNA
reproduce on their own
harness energy convert energy
reproduce on their own
harness energy convert energy
8
New cards
eukaryotes
nucleus
large
multi and single celled
in plants, animals, fungi, protists
large
multi and single celled
in plants, animals, fungi, protists
9
New cards
negative selection
decreases the frequency of bad alleles
10
New cards
types of mutations
somatic or germline
11
New cards
somatic mutations
nonreproductive cells, do not get passed from gen to gen
12
New cards
germline mutation
sex cells, passed from gen to gen
13
New cards
humans role in evolution
genetic engineering
poaching
creating environments that allow for over-population
poaching
creating environments that allow for over-population
14
New cards
ecology
how organisms interact with each other and their environments
15
New cards
biology
the study of how life works
16
New cards
translation
RNA to tRNA, through proteins
17
New cards
transcription
turns DNA into RNA
18
New cards
Jean-Baptist Lamarck
French naturalists --> claimed evolution had a goal, a tendency toward perfection
--> inheritance of acquired characteristics
--> selective use and disuse (body parts that were used more
got bigger)
--> inheritance of acquired characteristics
--> selective use and disuse (body parts that were used more
got bigger)
19
New cards
Thomas Malthus
english economist, if humans pop kept growing --> we would run out of resources to care for them
20
New cards
Charles Lyell
scottish geologist, uniformitarianism: thought the earth was millions of years old
- observed natural phenomes
- observed natural phenomes
21
New cards
prokaryotes
- small
-shaped: spheres, rods, cubes, spiral
no nucleus or organelles
well wall
-shaped: spheres, rods, cubes, spiral
no nucleus or organelles
well wall
22
New cards
The cell
smallest unit of life
23
New cards
types of natural selection
directional
stabilizing
disruptive
balancing
- heterozygous advantage
stabilizing
disruptive
balancing
- heterozygous advantage
24
New cards
Balancing selection - heterozygous selection -
maintaining two or more alleles in a pop because of different environment pressure
25
New cards
disruptive selection
both extremes are at an advantage
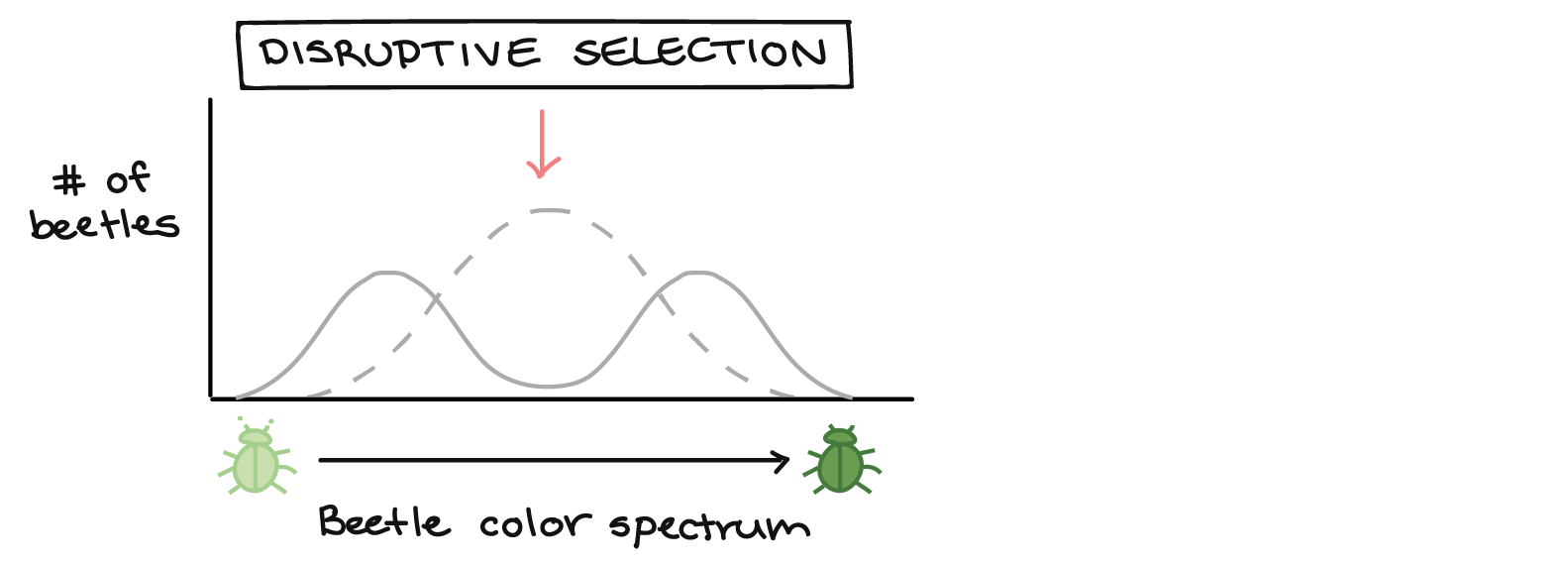
26
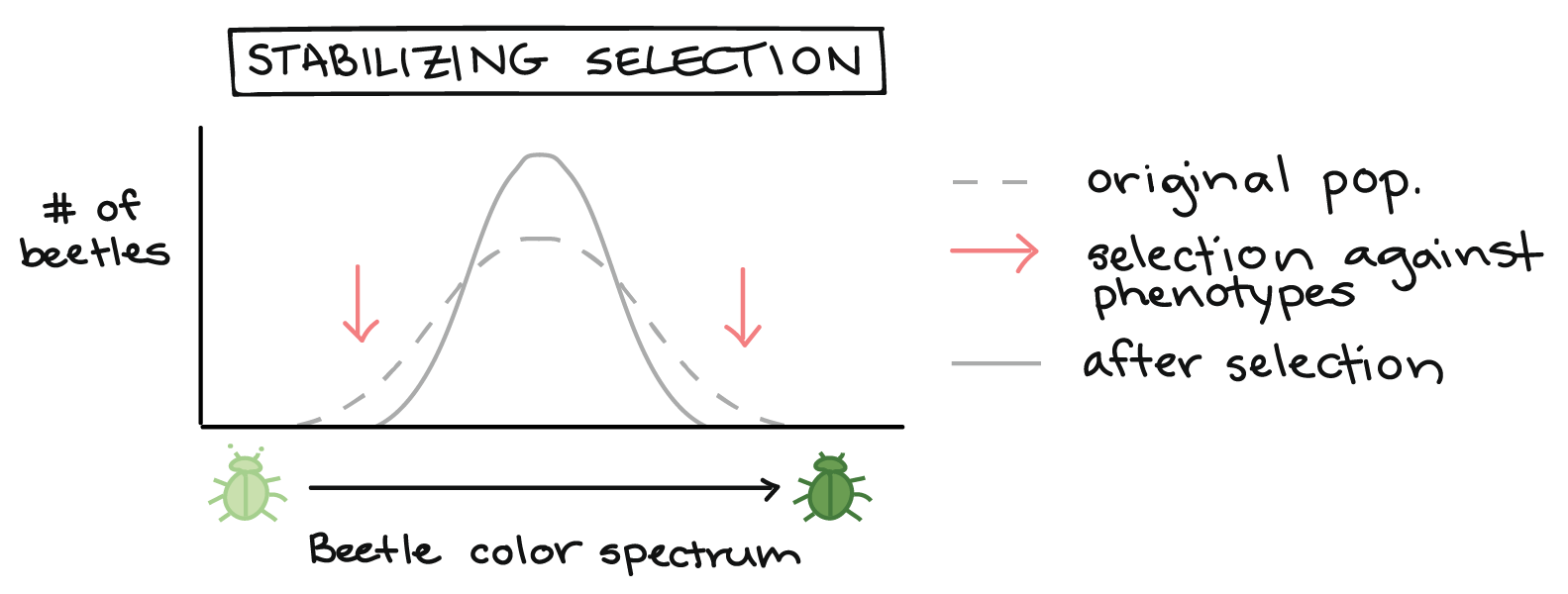
New cards
stabilizing selection
selecting for the average --> in between two exchanges
example - birth weight
example - birth weight
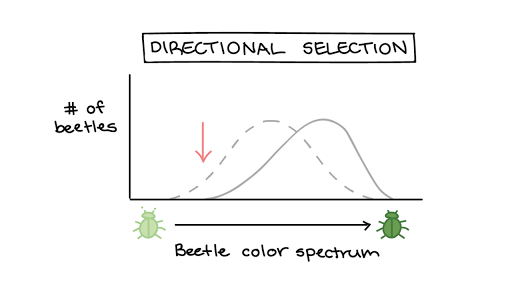
27
New cards
directional selection
favors one individual phenotypes
--> towards the extreme
--> moves one direction
--> towards the extreme
--> moves one direction
28
New cards
evolution
change in allele frequency over times
change in populations
change in populations
29
New cards
Hardy Weinberg equilibrium
1. no natural selection
2. no mutation
3. no migration
4. large population
5. random mating
2. no mutation
3. no migration
4. large population
5. random mating
30
New cards
population
interbreeding groups of organisms of the same species living in the same area
31
New cards
gene pool
all the different alleles/genotypes in the population
32
New cards
species
Reproductively isolated
33
New cards
Darwin's History
Born in england, dropped out of med school, became of clergyman
HMS Beagle Voyage --> Galapagos Islands --> finches
HMS Beagle Voyage --> Galapagos Islands --> finches
34
New cards
gene flow/ migration
introduces or removes genes into/from populations
35
New cards
post modern synthesis
natural selection and genetics(DNA), ecology/evolution, and population genetics all working together
36
New cards
characteristics of life
- organization
- energy required
- change in response to environment
- ability to reproduce
- evolve
- energy required
- change in response to environment
- ability to reproduce
- evolve
37
New cards
genetic drift
random change in allele frequency
- Bottleneck event
- Founders event
- Bottleneck event
- Founders event
38
New cards
Bottleneck event
an event natural/human caused --> only small amount of individuals survive
39
New cards
founder event
few individuals start new population
40
New cards
controlled experiment
tests hypothesis
quantifiable and repeatable
two groups
- control: baseline, no treatment
- experimental/test: introduce varible
quantifiable and repeatable
two groups
- control: baseline, no treatment
- experimental/test: introduce varible
41
New cards
experimental study
direct manipulation: treatment, observe response to variables
can determine causation
can determine causation
42
New cards
observational study
no intervention/manipulation: just watching what is happening
correlation not causation
correlation not causation
43
New cards
dependent variable
constant, already occurs
gets affected by the independent variable
gets affected by the independent variable
44
New cards
intrasexual selection
members of one sex compete with each other for the other sex
45
New cards
sexual selection
nonrandom mating
types --> inter and intra
types --> inter and intra
46
New cards
fitness
the ability for an animal to survive and reproduce
the longer they live the more offspring they have, the more their genes are present in the population
the longer they live the more offspring they have, the more their genes are present in the population
47
New cards
raw material of evolution
genetic material/variation - sexual recombinations, mutations
survival of the fittest
survival of the fittest
48
New cards
Darwin's Natural Selection
1. all organisms are genetically different
2. more offsprings are produced than the environment can support to reproductive age
3. the offspring that do survive, have a genetic advantage
4. over time these characteristics become more common in the population
2. more offsprings are produced than the environment can support to reproductive age
3. the offspring that do survive, have a genetic advantage
4. over time these characteristics become more common in the population
49
New cards
Darwin after the voyage
he researched and cataloged his finding for 20 years until Wallace sent him a letter detailing his similar findings, Darwin published his book within a year.
50
New cards
positive selection
natural selection that increases frequency of an advantageous allel
51
New cards
ordovician
climate change, falling seas
85% death rate
85% death rate
52
New cards
permian
volcano eruption, global warming, increase in chemicals
95% death rate
95% death rate
53
New cards
Triassic causes
increase in Methane and CO2, global warming
76% death rate
76% death rate
54
New cards
Devonian
asteroid impact, rapid global cooling
70% death rate
70% death rate
55
New cards
K-T
asteroid impact, volcanic eruption, falling sea level
80% death rate
80% death rate
56
New cards
6 mass extinction events
1. Ordovician
2. Devonian
3. Permian
4. Triassic
5. K-T
6. present time
2. Devonian
3. Permian
4. Triassic
5. K-T
6. present time
57
New cards
present extinction
human activity --> unsustainable use of energy, natural resources
climate change
climate change
58
New cards
climate change
increase natural selection, fewer species will survive
causes an increase in natural disasters
causes an increase in natural disasters
59
New cards
volcanic eruptions
releases chemicals/lava --> destroy habitats
increases planet temp
increases planet temp
60
New cards
root
end of the phylogenetic tree, where the ancestry begins
61
New cards
synopomorphy
shared common trait
62
New cards
biotic factors
biological, living organism
63
New cards
monophyletic
common ancestors + all decedents --> clade
64
New cards
demography
analytical study of population characteristics
65
New cards
k - strategists
parental investment, internal fertilization, stable environments, fewer offspring
type one survivorship curve
type one survivorship curve
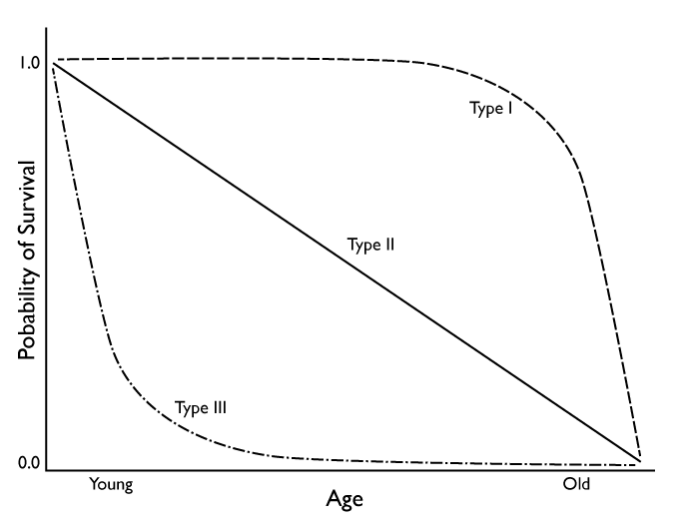
66
New cards
asteroid impacts
debris in air, collision destroys habitat
67
New cards
R-strategist
no parental investment, external fertilization, unstable environments, many offspring
type 3 on the survivorship curve
type 3 on the survivorship curve
68
New cards
metapopulation
population that has been separated by habitat fragmentation
usually by human infrastructure
usually by human infrastructure
69
New cards
community ecology
the study of many different populations of different species,
how they interact with each other
how they interact with each other
70
New cards
antagonistic
at least one organism is losing because of the interaction
71
New cards
types of antagonistic relationships
competition
predation
herbivatory
parasitism
predation
herbivatory
parasitism
72
New cards
interspecific competition
competition between two different species
73
New cards
intraspecific competition
between members of the same species
74
New cards
competitive exclusion
one species goes extinct due to competition
75
New cards
resource partitioning
species with similar niches change their niiche so that they can co-exist
76
New cards
role of disturbance in the environment
causes a rapid change in the environment, community/ecosystems become more adaptable to change
succession
succession
77
New cards
succession
predictable changes in a community over time, after a disturbance
78
New cards
primary succession
when there is no soil
79
New cards
pioneer species
lichens, moss --> help break up ground for soil
80
New cards
branch
only the main branch shows evolutionary time
- common ancestor population
- common ancestor population
81
New cards
what fossils teach us
1. evolutionary history
2. record of the past/extinct animals
3. puts evolution in context of the history of life
4. helps build phylogenetic trees
2. record of the past/extinct animals
3. puts evolution in context of the history of life
4. helps build phylogenetic trees
82
New cards
secondary succession
with soil
83
New cards
climax community
reached it's full potential, no more changes, stable
84
New cards
what ecologist study
the distribution, range, relationships, abundance between organisms, population, and species to each other and the environment
85
New cards
levels of ecology
Biosphere
ecosystem
community
population
organism
ecosystem
community
population
organism
86
New cards
taxonomy
the study of naming and classifying organisms
87
New cards
phylogeny
evolutionary history of species, common ancestor/decedents/evolution of characteristics
88
New cards
minimum viable population
the smallest number of individuals a population can have and still be successful
89
New cards
carrying capacity
the most about of individuals a population can have and still be successfulsi
90
New cards
sister group
species groups that are more closely related to each other than any other group
91
New cards
factors of emigration
loss of resources, availability of dispersal mechanisms
92
New cards
density dependent factors
factors that change population based on its density
- limiting
- limiting
93
New cards
growth rate with carrying capacity
r*N((k-n)/k)
r = per capita growth rate
n = population total
k = carrying-capacity
r = per capita growth rate
n = population total
k = carrying-capacity
94
New cards
factors that increase population size - Birth
the number of reproductive episodes per lifetime
the number of offspring per reproductive episode
age at first reproductive episode
the number of offspring per reproductive episode
age at first reproductive episode
95
New cards
factors of immigration
availability of dispersal mechanisms, and suitable habitat
96
New cards
factors that decrease pop size - Death
poaching, disease, predation, nutrient availability
97
New cards
changes in sea level
rise: flooding --> destroys habitats, kills animals
drop: glacial periods
drop: glacial periods
98
New cards
oxygen in atmosphere
to little --> ozone layer will lessen, expose earth to sun
99
New cards
abiotic factors
nonliving, effect organism
100
New cards
parsimony
most likely outcome of a phylogenetic tree
- least amount of evolutionary events
- least amount of evolutionary events