ANSC327 Genetics Exam 1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
where are genes stored?
genes are stored in the chromosomes located in the nucleus
describe the findings of Frederick Griffith’s experiment in 1928:
Griffith discovered that non-virulent bacteria (R-strain) could transform into virulent forms (S-strain) when exposed to heat-killed virulent strains, suggesting that physical traits can be passed from one cell to another, giving the first hint that DNA was the genetic material, and that genetic transformation was possible. His experiment used streptococcus pneumonia.
outline the steps of Griffith’s experiment:
living S (smooth) cells injected into a mouse kills the mouse. Can isolate live S colonies from dead mouse tissue.
Living R (rough) cells injected into a mouse do not kill it. Heat-killed S cells injected into a mouse do not kill
Living R cells are mixed with heat-killed S cells and injected, the mouse dies, and live S cells are recovered. Can isolate colonies of both R and S cells.
Thus, the R cells “transformed” the heat-killed S cells.
describe the findings of Avery, MacLeod, and McCarthy’s experiment in 1944:
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty demonstrated that DNA is the transforming principle by showing that only DNA extracted from heat-killed S-strain bacteria could transform R-strain bacteria into virulent S-strain. Their work provided strong evidence that the “transforming material” was DNA, not protein, and is the genetic material responsible for heredity.
outline the steps of Avery, MacLeod, and McCarthy’s experiment:
Heat-killed S-cells in a test tube were added to a culture of R-cells; isolating both S and R cell colonies on an agar medium. This proved that the transforming material was not degraded by heat.
Protease and RNAse (enzymes) were added to a test tube of heat killed S cells, then added to a culture of R cells. Colonies of R and S cells were both isolated proving that the transforming material was not destroyed by protease or RNAse, meaning that it was not likely to be protein or RNA.
Step 2 was repeated but with DNAse. When the cells were plated, only R colonies grew—proving that the transforming material was destroyed by DNAse, and thus was likely DNA.
describe the findings of Hershey and Chase’s experiment in 1952:
Hershey and Chase used bacteriophages to prove that DNA material was transferred to progeny while protein material was not. They labeled DNA with phosphorus-32 and protein with sulfur-35. After infection, only phosphorus-32 was found in the bacterial cells, indicating that DNA, not protein, was the genetic material.
outline the steps of Hershey & Chase’s experiment:
Part 1 (DNA):
Infect E. coli with nonradioactive T2 phage (virus).
E. coli cells grown on a medium containing 32-P (labels DNA).
Phages reproduce inside E. coli cells; progeny are labeled with 32-P.
DNA-labeled progeny phage is used to infect nonlabelled E. coli cell.
After infection, kitchen blender is used to remove attached phage capsule (head).
Phages reproduce, E. coli lysis; released progeny contain some 32-P labeled DNA from parental phage.
Part 2 (Protein):
Same steps for Part 1, but this time use 35-S (labels protein). Progeny phages contain almost no 35-S labeled protein, proving that DNA is the transferring material and not protein.
explain what Chargaff’s rule is and how it contributed to the structure of DNA:
Chargaff found that A=T and G=C, contributing to Watson and Crick’s proposal that DNA is in a double helix in which the 4 bases are paired accordingly: adenine (A) with thymine (T), and guanine (G) with cytosine (C).
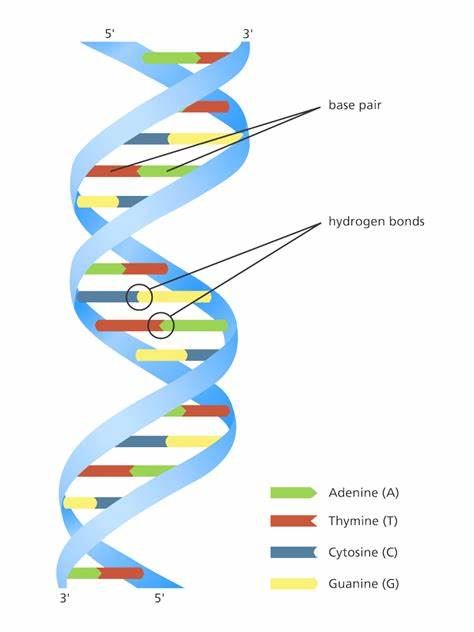
DNA has repeating distances of ____, ____, and ____.
0.34nm, 2nm, and 3.4nm (Wilkins & Franklin)
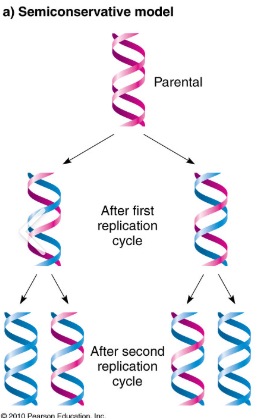
semi-conservative DNA model
each new DNA ladder has one old side (the original) and one new side with a mixture of DNA (what actually happens)
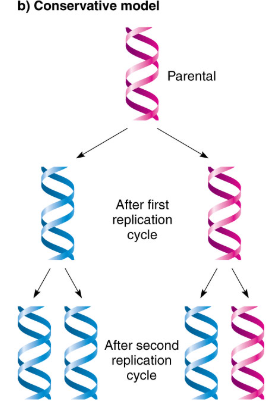
conservative DNA model
one all-old ladder and one all-new ladder (proven wrong)
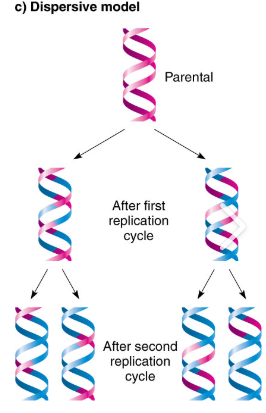
dispersive DNA model
each new ladder is a mix of old and new pieces (proven wrong)
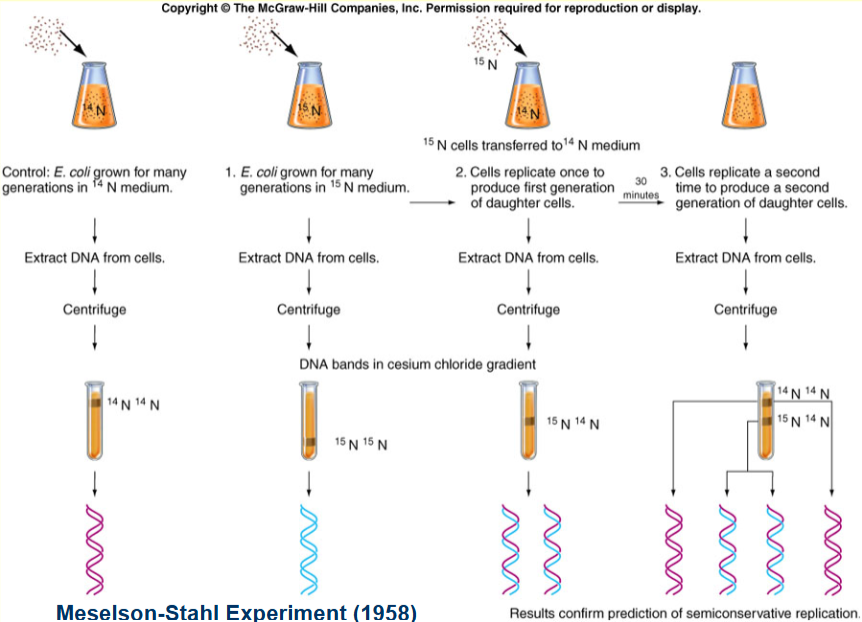
what did the Meselson-Stahl experiment prove?
their experiment proved that DNA replicated semi-conservatively
outline the steps of the Meselson-Stahl experiment:
Control: E. coli grown for many generations in a 14N medium. DNA was then extracted from the cells and centrifuged. The result was one thick band at the top of the test tube. Each strand of DNA contained 14N (14N14N).
E. coli is grown in a 15N medium (more dense than 14N). The result was one thick band at the bottom of the test tube (15N15N).
Then, 15N cells transferred to 14N medium. Cells replicate once to produce first generation of daughter cells. DNA was extracted from the daughter cells and was centrifuged. The result was one thick band in the center of the test tube (15N14N).
Cells replicate for a second time in the 14N medium. The DNA of their progeny was centrifuged. The result was one thinner band at the top (14N14N) and one thinner band around the middle (15N14N). This confirms the prediction of semi-conservative replication.
first discovered hereditary disease caused by defective genes
alkaptonuria
alkaptonuria is caused by a defective enzyme in the pathway important for the breakdown of ______. this defect leads to an accumulation of ______ that turns the urine black upon oxidation
phenylalanine, homogentisic acid
those with PKU cannot have _____ due to the fact it contains phenylalanine
aspartame
explain how a PKU metabolite can be dangerous to infants and fetuses
Aspartame, a common ingredient in diet soda, is a dipeptide of phenylalanine and aspartic acid. Consumption of aspartame would increase phenylalanine levels, which would increase the buildup of homogentisic acid or other compounds in the chain of phenylalanine breakdown
explain what stop/start codons are
the “go” and “end” signals for protein synthesis, where cells build proteins based on DNA instructions (translating mRNA into proteins)
what are the 3 “stop” codons
UAA, UAG, UGA
what is the “start” codon
AUG
polar uncharged amino acids
Some Times Cats Try A Growl
1. S - Serine
2. T - Threonine
3. C - Cysteine
4. T - Tyrosine
5. A - Asparagine
6. G - Glumatic
polar charged amino acids
A Good Lawyer Aims High
1. A - Aspartic acid
2. G - Glutamic acid
3. L - Lysine
4. A - Arginine
5. H - Histidine
non-polar amino acids
Go And Take Vital Part In Promoting Mother Language
1. G - Glycine
2. A - Alanine
3. T - Tryptophan
4. V - Valine
5. P - Proline
6. I - Isoleucine
7. P - Phenyl alanine
8. M - Methionine
9. L - Leucine
explain why an M1V mutation in the PAH enzyme is so problematic
mutation in the first codon that turned methionine into valine. this changes the AUG to a GUG, which results in no PAH being produced
is an M1V mutation or a R40W mutation worse?
M1V, since no protein can be produced at all. R408W mutation changes arginine to tryptophan in codon 408, the protein translated but looks like a Trp instead of an Arg, so only 3% of the activity of a normal enzyme.
define pleiotropy
a single gene affecting multiple traits
give an example of pleiotropy
i. melanin synthesis and PKU - in the absence of PAH, the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine is blocked. Tyrosine is a precursor to melanin.
ii. 40% of cats with blue eyes are deaf. among cats with white fur and blue eyes, about 40% are born death. the reason is that pigment cells derived from the neural crest migrate to various tissues including hair follicles, the eyes, and the middle ear, where