Semester 1 Review 2024
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Levels of organization
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Functions of the skeletal system
shape and support, protection, production of blood cells, storage of minerals, movement
Functions of the integumentary system
protection, production of vitamin D, regulation of body temperature, elimination of wastes, sensory response
parts of the integumentary system
skin, hair, nails
Functions of the Muscular System
Movement and Stability
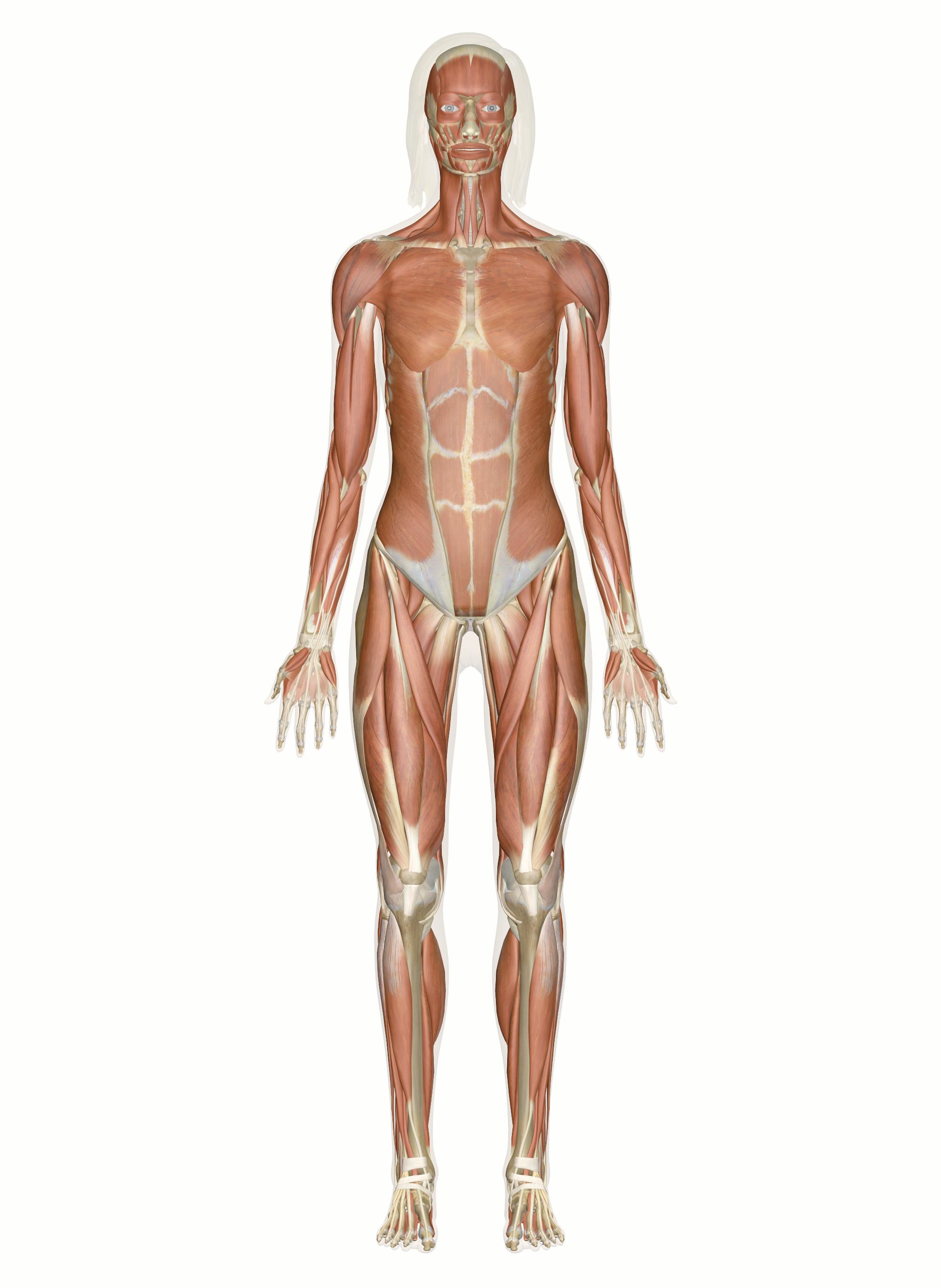
Muscular System
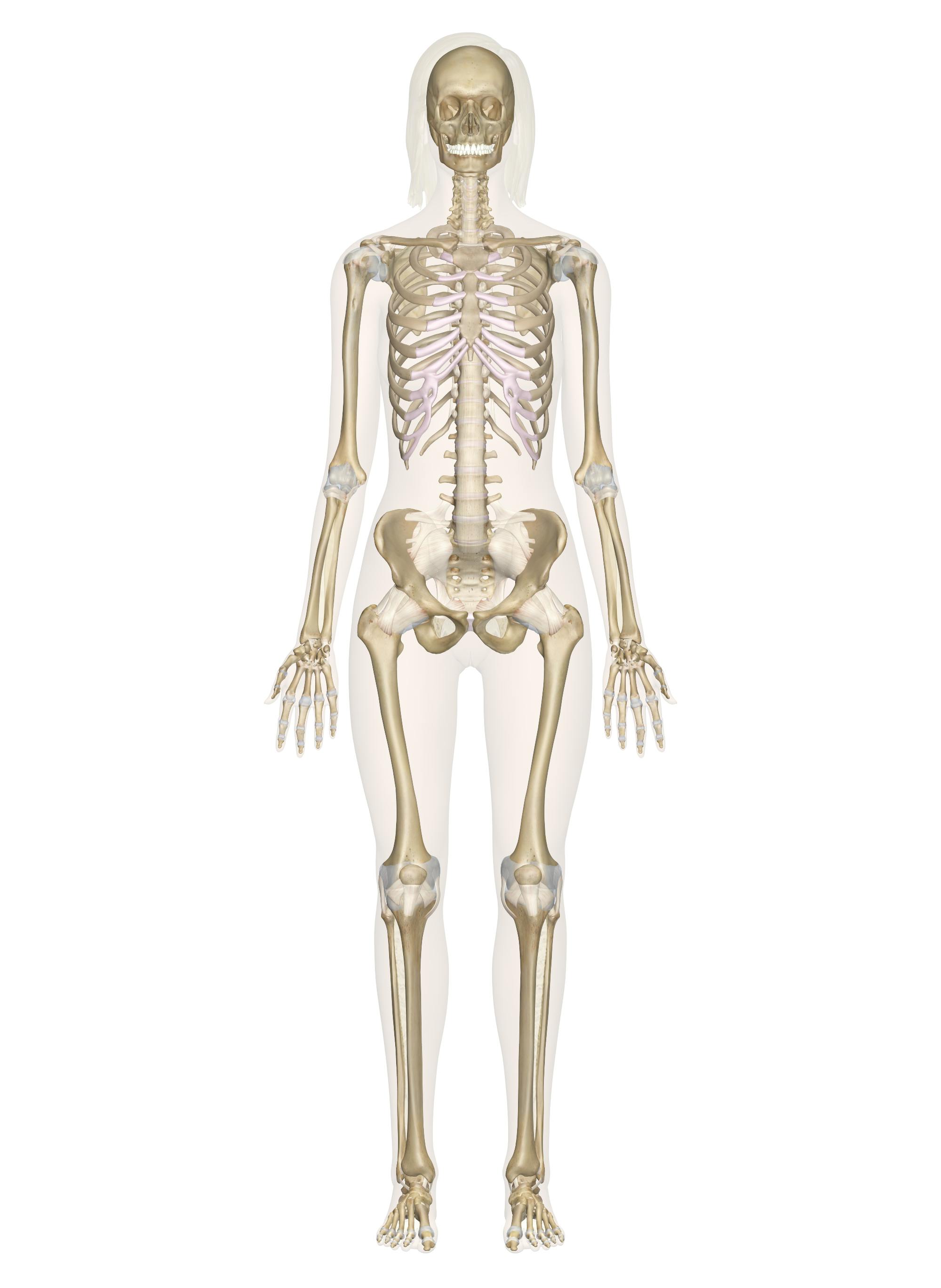
Skeletal System
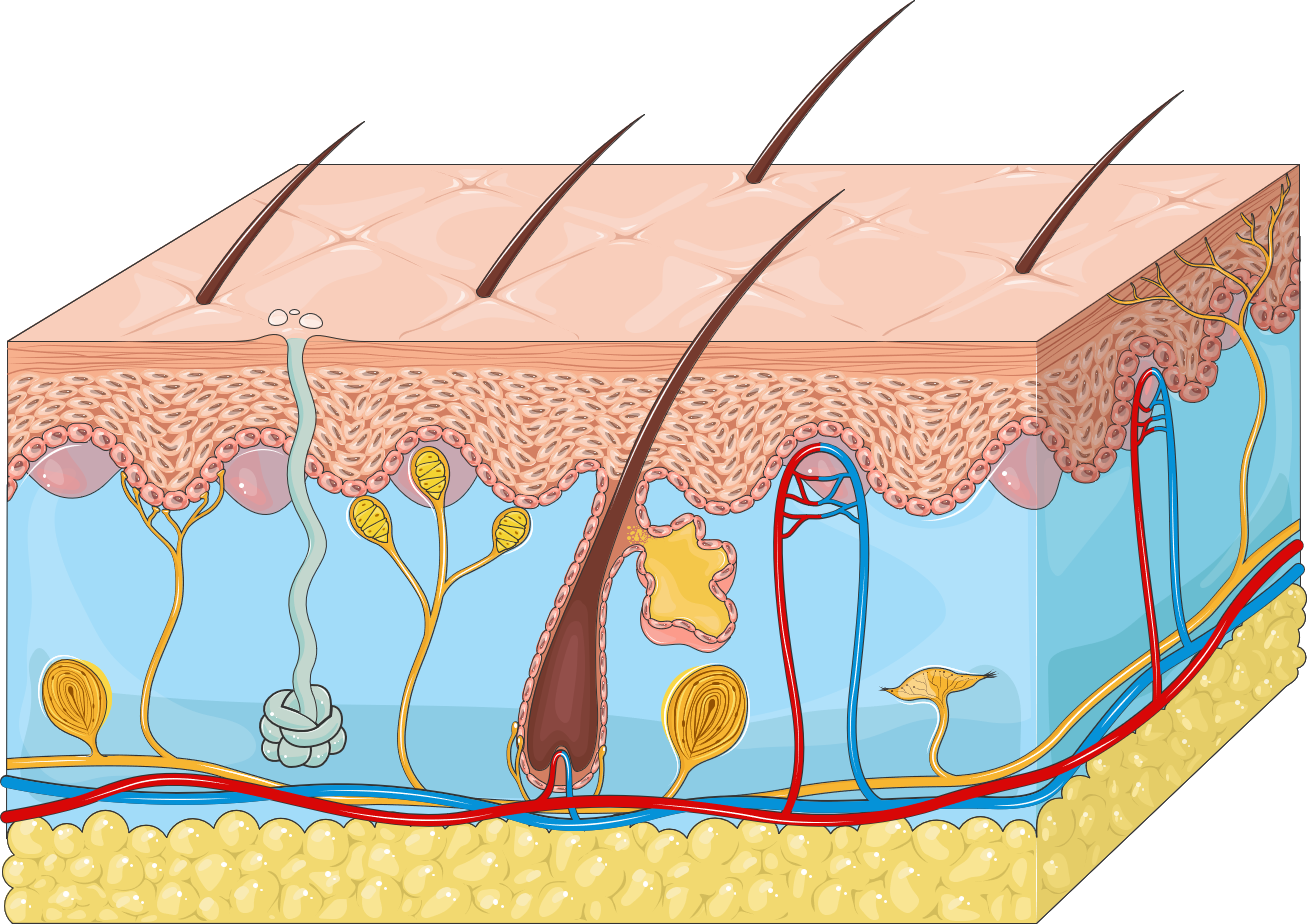
Integumentary System
Endocrine System
System where glands produce chemical hormones that regulate processes such as growth, and reproduction by body cells.
Gland
An organ that produces and releases chemical hormones through the endocrine system into the bloodstream.
Hormone
Chemical messenger produced by the endocrine glands to signal the body
Nervous System
The body's electric communication system, made up of the brain, spinal cord and nerves
Immune System
System that protects against infection and disease
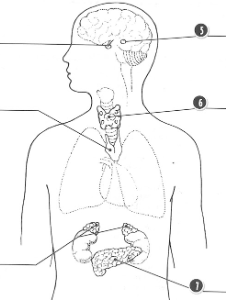
Endocrine System
Immune System
Nervous System
Digestive System
A system that provides nutrients to the body
Respiratory System
A system that removes Carbon Dioxide and takes in Oxygen
Circulatory System
A system that transports oxygen, nutrients and waste products around the body
Urinary System
filters blood and removes waste in the form of urine
Natural Selection
A process in which organisms that have variations that give an advantage then reproduce at higher rates and pass on those adaptations.
Selective Breeding (artificial selection)
The process of humans breeding organisms that results on offspring with desired genetic traits.
asexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent.
sexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents
Energy Pyramid
A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one trophic level to another in a food chain
Trophic Level
the position that an organism occupies in a food chain, food web, or energy pyramid (e.g., producer, primary consumer, etc.)
Consumer
An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms in a food chain/web/pyramid
Producer
An organism that makes its own food in a food chain/web/pyramid
Autotroph
Broad category organisms that make their own food
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.
10% Law
Only 10% of the energy in one trophic level gets passed onto the next trophic level
Decomposer
an organism, especially bacteria, fungus or invertebrate, that decomposes organic material.
Energy lost to the environment in an energy pyramid.
heat
The direction energy moves in an energy pyramid
from bottom to top
Watershed
An area where all groundwater and surface water drains into the same body of water.
Surface Water
Water that collects above the surface of the ground
Groundwater
The water that is beneath Earth's surface
Aquifer
A permeable rock layer that can hold or transport groundwater
Runoff
Water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground
Oil, Fertilizer, Sewage, Pesticides, Chemicals
Types of groundwater contamination
Artificial Reef
A man-made structure placed in the ocean to promote marine life and enhance fishing opportunities.
Overfishing
The practice of catching fish at a rate faster than they can reproduce, leading to a decline in fish populations.
Dead Zones
areas in the ocean with low oxygen levels, often caused by algae and water plant blooms.
Fertilizer Runoff
The flow of extra fertilizers from agricultural land into water bodies.
Fossil Fuels
Release Carbon Dioxide into the atmosphere
Deforestation
The clearing or thinning of forests by humans.
Effects of Fertilizer Runoff
harmful excess water plant growth, oxygen depletion in water, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems.
Effects of Deforestation
Increases Carbon Dioxide in the atmosphere and soil erosion.
Prokaryote
Most basic cell; No nucleus or organelles; (Pro=No)
Kingdoms: Eubacteria & Archaebacteria
Eukaryote
Complex Cell; Do have nucleus & organelles (Eu=Do)
Kingdoms: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Heterotrophic
Motile
Kingdom Animalia
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Autotrophic
Non-motile
Kingdom Plantae
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Heterotrophic
Non-motile
Kingdom Fungi
Dutch Kings Play Cards On Fat Green Stools
Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species