Biochemistry 415 Exam 1
1/324
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
325 Terms
Which biomolecules are polymers? Which aren’t?
Polymers: Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates
Non-Polymers: Lipids
Proteins are linked by _
Peptide bonds
Carbohydrates are linked by _
Glycosidic bonds
Nucleic acids are linked by _
Phosphodiester bonds
Components of a nucleotide
Base, saccharide (ribose/deoxyribose), phosphate group
The purines are _
The pyrimidines are _
Purines: Adenine, guanine
Pyrimidines: Cytosine, thymine, uracil
The structural difference between ribose and deoxyribose is that _
Deoxyribose is reduced at C2
Central Dogma
DNA makes RNA which makes proteins
Molecules which are _ or _ can traverse the phospholipid bilayer without assistance
Small, nonpolar
Mitochondrion function
Energy extraction reactions
Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex function
Synthesize, process, sort both lipids and proteins
Endosome function
Take material into the cell from the plasma membrane
Lysosome function
Degrade and recycle macromolecules
Order of bond strength
Covalent>ionic>dipole-dipole>London dispersion forces (VDW)
Ionic interactions in proteins are called _
Salt bridges
The energy of electrostatic interactions are _ to distance between ions
Inversely proportional
4 Major Interactions Involving Dipoles
Dipole-dipole, ion-dipole, cation-pi, induced dipole
Ion-dipole reactions are _
The partial attraction of partially charged polar molecules to full ions
Cation-pi interactions are caused by _
The partially negative charge above and below the plane of an aromatic ring
The “face” of aromatic rings are (positive/negatively/un) charged
Negatively
London Dispersion Forces are_
Induced dipole-induced dipole interactions
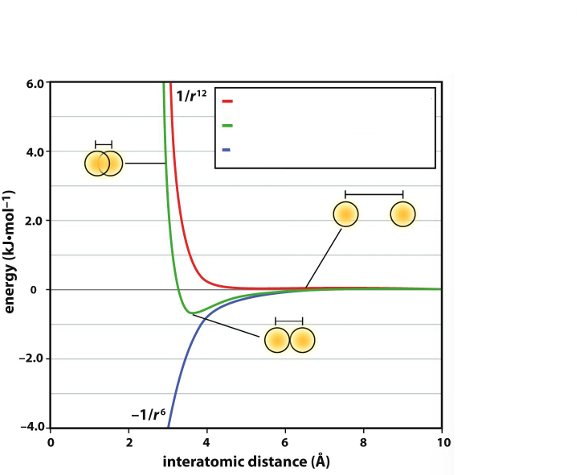
The blue line represents _, the red line represents _, and the green line represents _
London dispersion energy (attractive), electronic repulsion energy, net interaction energy
The hydrogen bond donor donates _, which the acceptor accepts
The hydrogen
The structure of water is classified as _
Tetrahedral (sp3)
Water has _ hydrogen bond donor sites and _ acceptor sites
2, 2
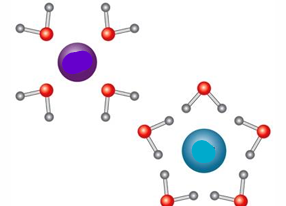
The blue molecule is _ charged and the purple molecule is _ charged
Negatively, positively
Hydrophobic Effect
Nonpolar/hydrophobic species aggregate in solution to minimize surface area
Cause of Hydrophobic Effect
Entropcially-driven; reduce number of water molecules forced into a hydration shell around the solute
Reactions become more spontaneous when enthalpy goes _, entropy goes _, and temperature goes _
Down, up, up
Acid Dissociation Constant (K_a) =
[H+][A-] / [HA]
When pH>pKa, acidic species are _
Deprotonated
When pH<pKa, acidic species are _
Protonated
pH = pKa when _
[HA] and [A-] are present in equal amounts
In amino acids, the carboxylic acid has a pKa in the _ range, whereas ammonium groups have a pKa around _
2-3, 9.6
Function of buffers in biological contexts
Maintain intracellular pH
Buffers are usually comprised of _ and are strongest around _
Weak acid and its conjugate base, The acid’s pKa
Good buffers keep the ratio of weak acid and conjugate base within a factor of _
10
3 Main Biological Buffers
Phosphate, bicarbonate, histidine
The central carbon of an amino acid is called _ or _
C2, alpha carbon
Amino acids found in nature are the _ enantiomer
L
CORN Rule of Amino Acids
With the hydrogen atom pointing back, read rotation of CO, R-group, and N bonds
CCW=L, CW=D
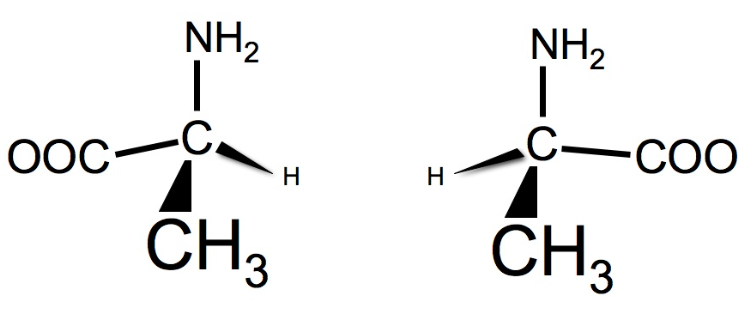
The left structure is _ and the right structure is _
L-alanine, D-alanine
In AA Fischer projections, the amino and hydrogen groups are placed on the _ axis, while the carboxylate and R-group are placed on the _ axis
Horizontal, vertical
In AA Fischer projections, the amino and hydrogen groups are oriented on _ bonds, while the carboxylate and R-group are oriented on _ bonds
Wedged, dashed
If an AA Fischer projection is correctly established, the amino group being on the right side indicates the _ enantiomer, while the amino group being on the left side indicates the _ enantiomer
D, L
Isoelectric Point
pH where net charge of a molecule is zero (pKa-1 + pKa-2 / 2)
Hydrophobic Amino Acids
Glycine, Alanine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Proline, Methionine
Polar Amino Acids
Serine, Cysteine, Tyrosine, Threonine, Asparagine, Glutamine
Negatively Charged Amino Acids
Aspartate, Glutamate
Positively Charged Amino Acids
Histidine, Lysine, Arginine
Cysteine is unique in its ability to _
Form disulfide bonds
Amino Acids Which Can Form Salt Bridges
Aspartate, Glutamate, Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
At biological pH, aspartic acid and glutamate are _, histidine and cysteine are _, and tyrosine, lysine, and arginine are _
Deprotonated, sometimes protonated, protonated
2 Cases of Environment Perturbing pKa
1) Hydrophobic environment makes uncharged form more stable (e.g. lower pKa for lysine, histidine, arginine)
2) Repulsion if AA’s of the same type are present (e.g. raise pKa if two adjacent glutamates)
Amino acid order is read _
N-terminus to C-terminus
Dihedral/Torsion Angle
The relative rotation around a covalent bond
Dihedral Bond Types
φ, ψ, ω
φ angles are determined around the _ bond
Nitrogen-alpha Carbon
ψ angles are determined around the _ bond
Alpha carbon-Carbon
ω angles are determined around the _ bond
C-N (peptide)
In dihedral bonds, clockwise is designated as _ and counterclockwise is designated as _
+, -
Peptide bonds cannot freely rotate because _
This means that peptide bonds exist _
They have double bond character
In plane
The _ conformation of peptide bonds is favored
This corresponds to a ω angle of _
Trans
180 degrees
_ (AA) has unique stereochemistry in that it can sustain the cis form better than other amino acids
Proline
The two major regions of phi and psi bonds are designated _ and _
Alpha and Beta
The alpha region on a Ramachandran plot has dihedral angles of
Phi: -60 degrees
Psi: -50 degrees
The beta region on a Ramachandran plot has dihedral angles of _
Phi: -120 degrees
Psi: 120 degrees
The most flexible AA on Ramachandran plots is _ and the least flexible is _
Glycine, Proline
Secondary protein structures are established by _
Hydrogen bonding patterns between carbonyl and amide groups on nonadjacent amino acids
Alpha Helices, read in the N→C direction are considered _ by orientation
Right-handed
There are _ amino acids per alpha helix turn, with a _ rise per turn
3.6, 5.4 angstrom
Hydrogen bonding occurs in the backbone between numbered residues “i” and “_”
i+4
In alpha helices, carbonyl groups are oriented towards _ and N-H groups are oriented towards _
The C-terminus, the N-terminus
Due to the orientation of charged carbonyl groups, the alpha helix has a _ at the C-terminus and a _ at the N-terminus
Partial negative charge, partial positive charge
Every 3-4 residues usually have _ properties, often creating an _ alpha helix
Similar properties, amphipathic
Beta Strand side chains are oriented so that they are _
Alternating
Two side chains on the same face of a Beta Strand are _ apart, while those on different faces are _ apart
7 angstroms, 3.5 angstroms
Beta Strands form Beta Sheets by _
Backbone hydrogen bonding (carbonyl and amino group)
Are parallel or antiparallel Beta Sheets more stable?
Antiparallel
Why are (parallel/antiparallel) Beta Sheets more stable?
Antiparallel Beta Sheets have linear geometry in their hydrogen bonds, while parallel Beta Sheets have bent geometry
Antiparallel Beta Sheets are connected by _
4-amino acid reverse turns
Parallel Beta Sheets are connected by _
An Alpha Helix or large loop
_ and _ (AA’s) are not commonly found in an Alpha Helix or Beta Sheet
Glycine, Proline
Structural Motifs and Domains are similar in that they are both _, but are different in that _
Regions within a polypeptide chain that have a specific function
Domains can function independently, while structural motifs would unravel if the rest of the protein were cleared away
Why are structural motifs not independent?
They rely on hydrogen bonds from other parts of the polypeptide chain
2 Common Structural Motifs
1) Helix-Turn-Helix (DNA binding motif)
2) Beta Sheet-Alpha Helix-Beta Sheet
4 Determinants of Tertiary Structure
Disulfide bonds, salt bridges, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic packing
Tertiary structure describes _
How secondary structures are oriented towards each other in space
Quaternary structures describes _
Spatial arrangement of and interactions between polypeptide chains
Each polypeptide chain in a protein’s quaternary structure is called a _
Subunit
_ residues are usually found on the surface of folded globular proteins, while _ residues are found in the interior of the protein
Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic
Protein folding is thermodynamically driven to achieve _
The _ often has a substantial impact on achieving this goal
The lowest Gibbs free energy possible
Hydrophobic effect
Protein Chaperones
Protein complexes which can provide a hydrophobic environment for proteins to refold (costs ATP)
Chaotropic Agents (e.g. urea)
Molecules which disrupt solvent H-bonds, reducing the entropy gain from releasing water, and scrambling the folding of proteins which rely on the hydrophobic effect
Causes of Protein Denaturation
Temperature, pH changes, organic solvents, chaotropic agents
Carbohydrate General Formula
Cn(H2O)n
C1 on an aldose is the _, while C1 on a ketose is often part of the _
Carbonyl carbon, R group
In carbohydrate Fischer projections, D-sugars have the _ on the _, while L-sugars have them on the _
Furthest hydroxyl from a carbonyl, right, left
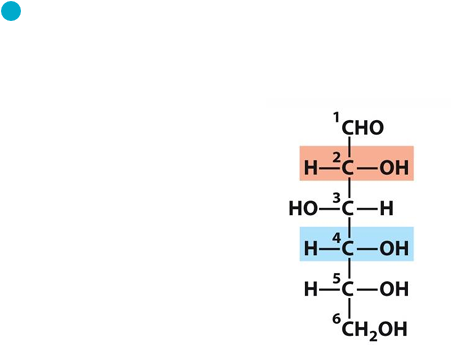
This sugar is _
D-Glucose
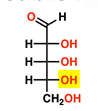
This sugar is _
D-Ribose