3- Nomenclature
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
the longest chain of atoms (mostly carbon) that contain the molecule's highest-priority functional group
parent chain
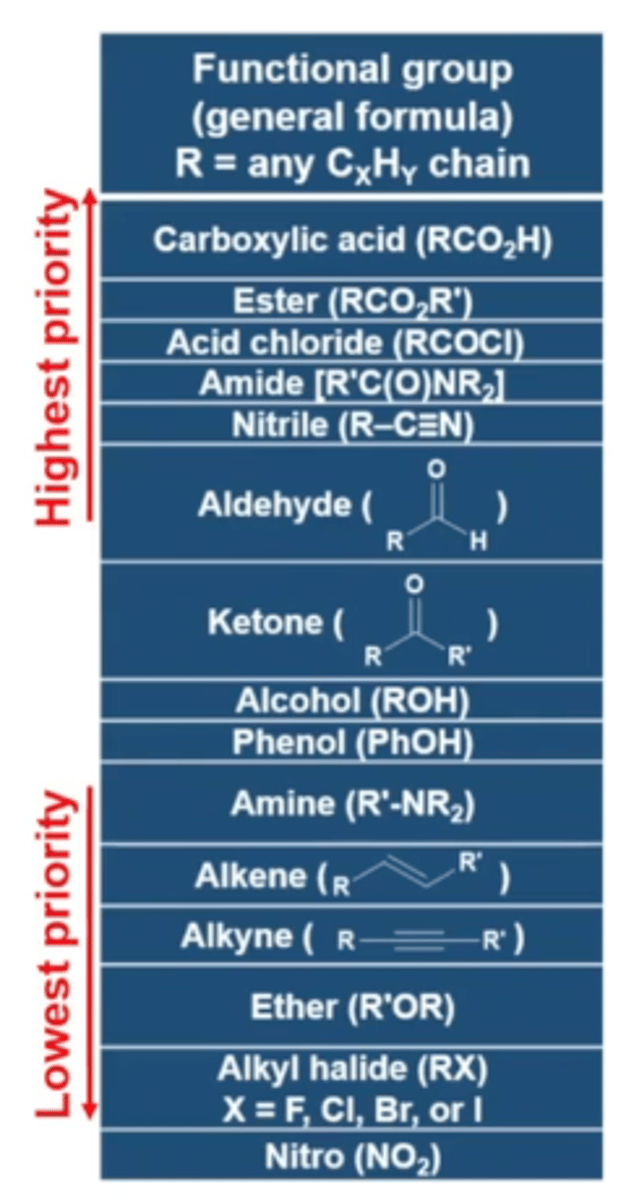
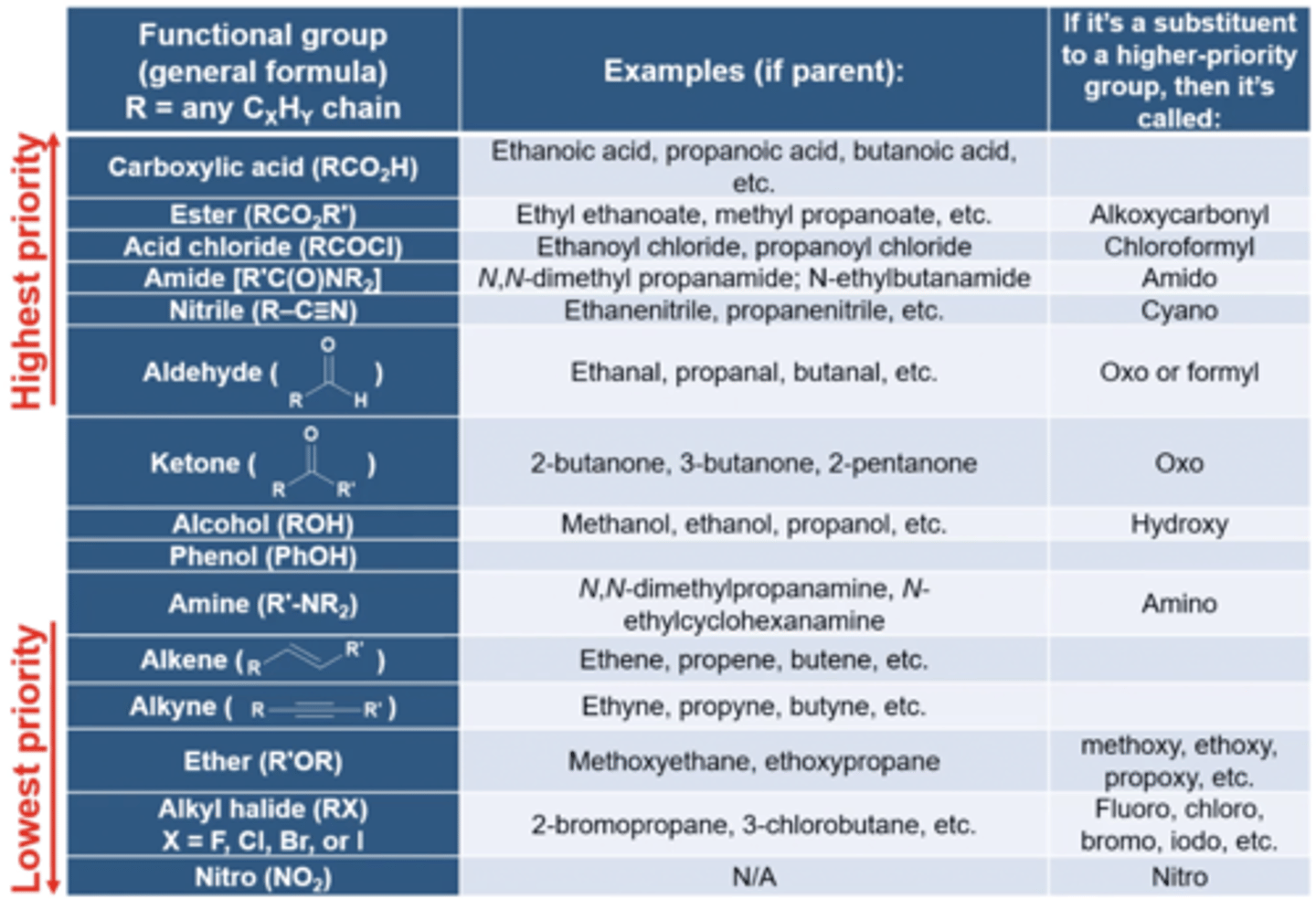
what are the functional groups in order of highest to lowest priority?
carboxylic acid
ester
acid chloride
amide
nitrile
aldehyde
ketone
alcohol
phenol
amine
alkene
alkyne
ether
alkyl halide
nitro
what are the iupac names for the simple hydrocarbon parent chains?
methane (1 C)
ethane (2 C)
propane (3 C)
butane (4 C)
pentane (5 C)
hexane (6 C)
heptane (7 C)
octane (8 C)
nonane (9 C)
decane (10 C)
what does an isopropyl group look like?
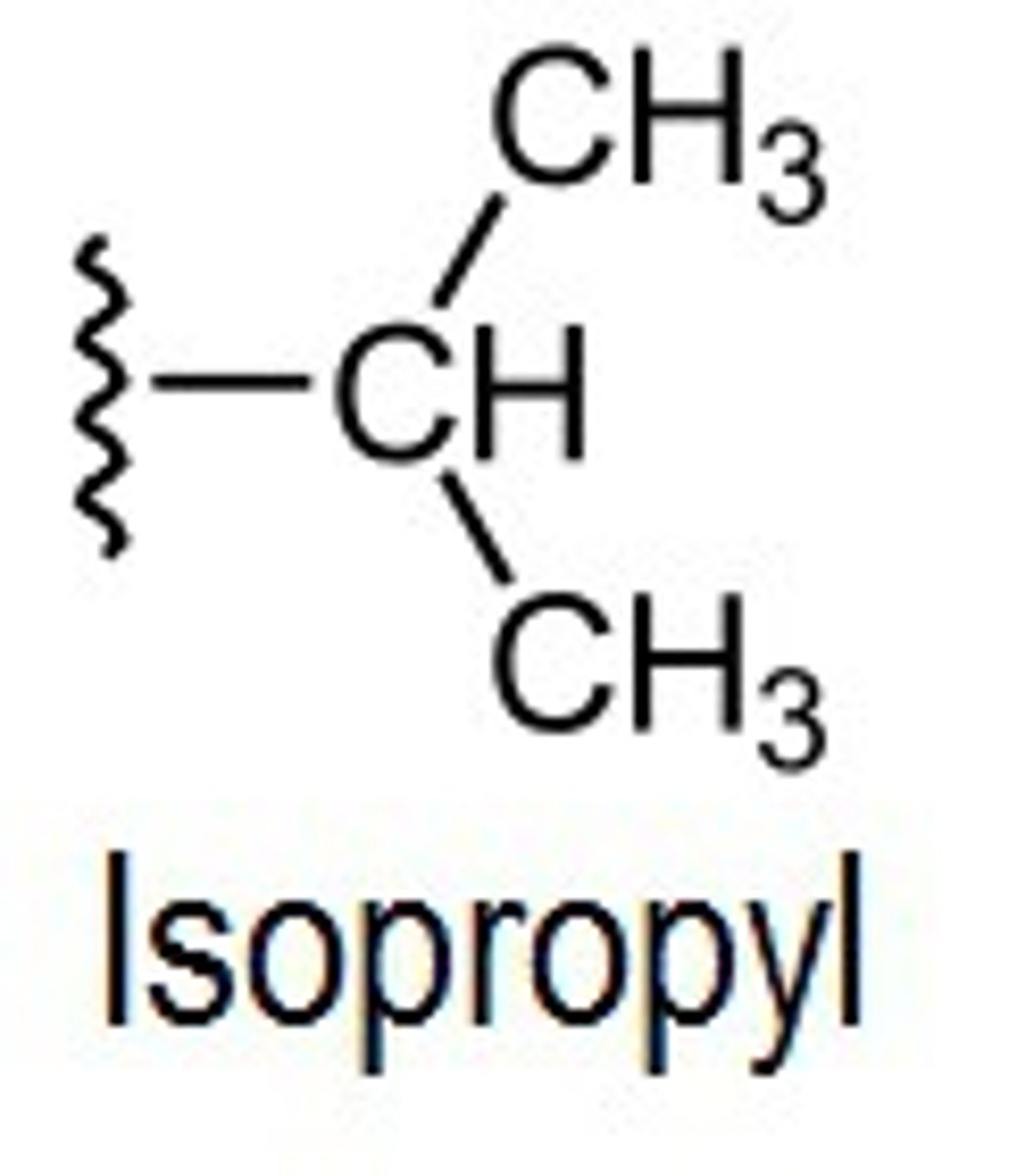
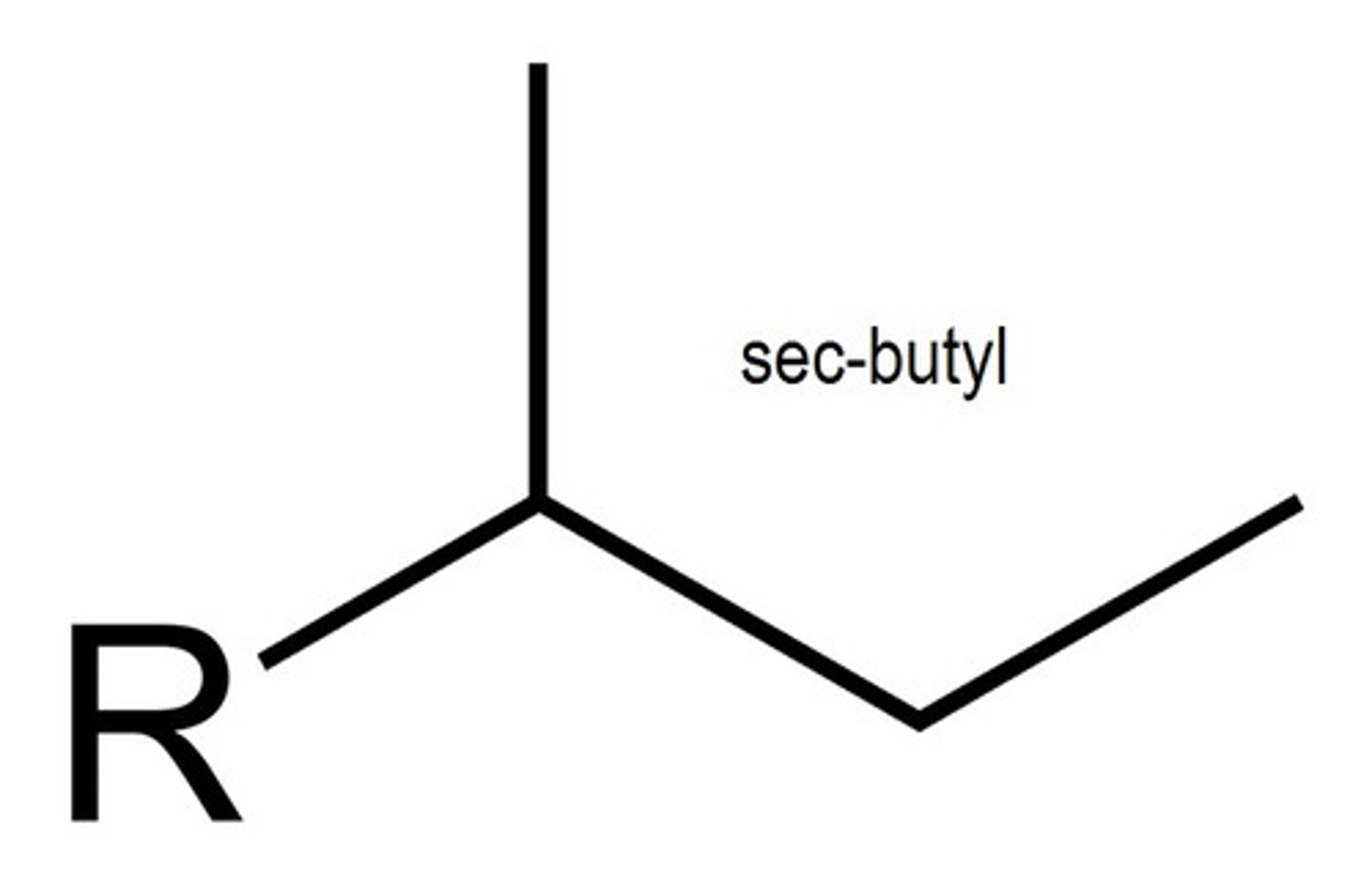
what does a sec-butyl group look like?
what does an isobutyl group look like?
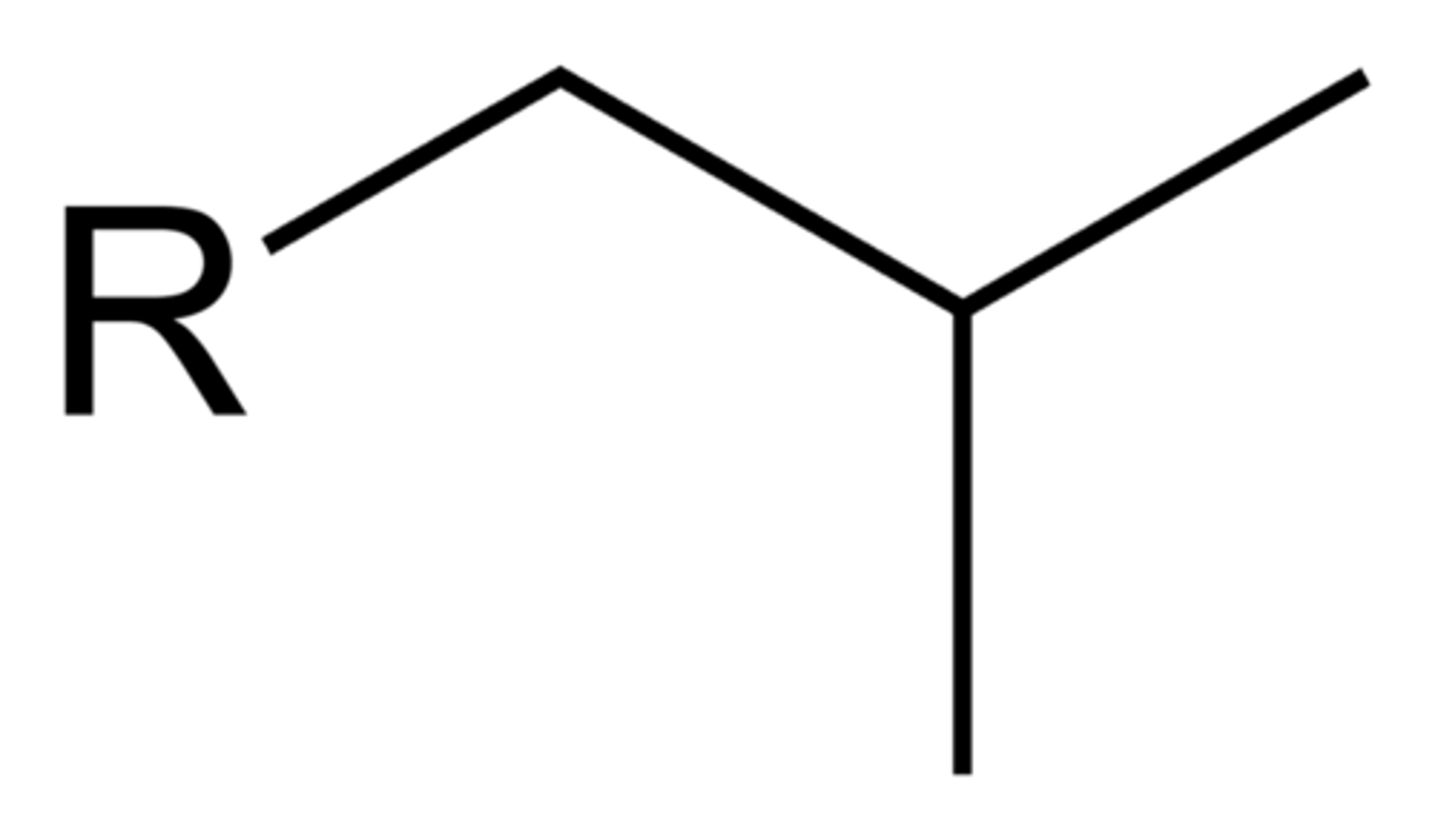
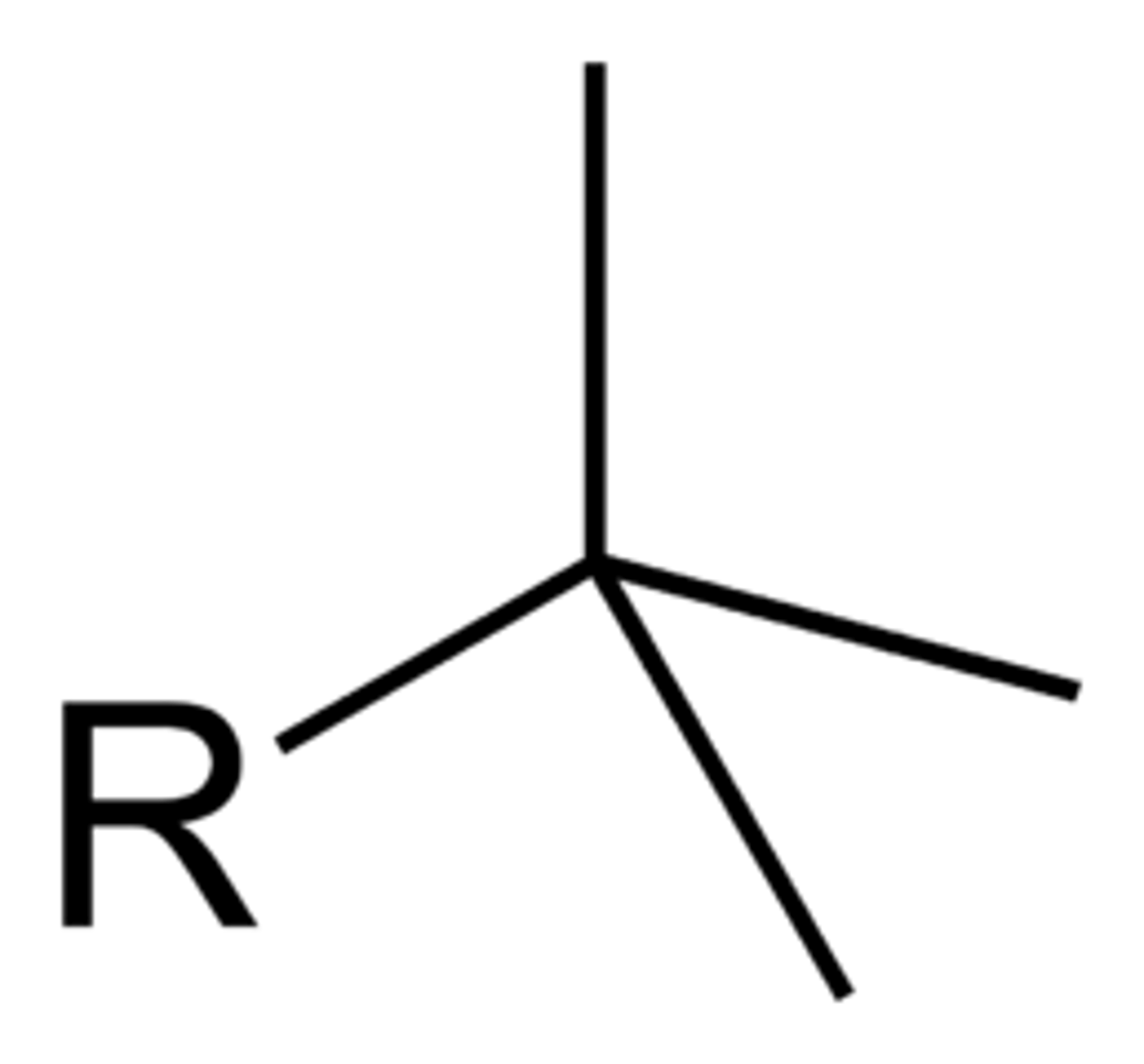
what does a tert-butyl group look like?
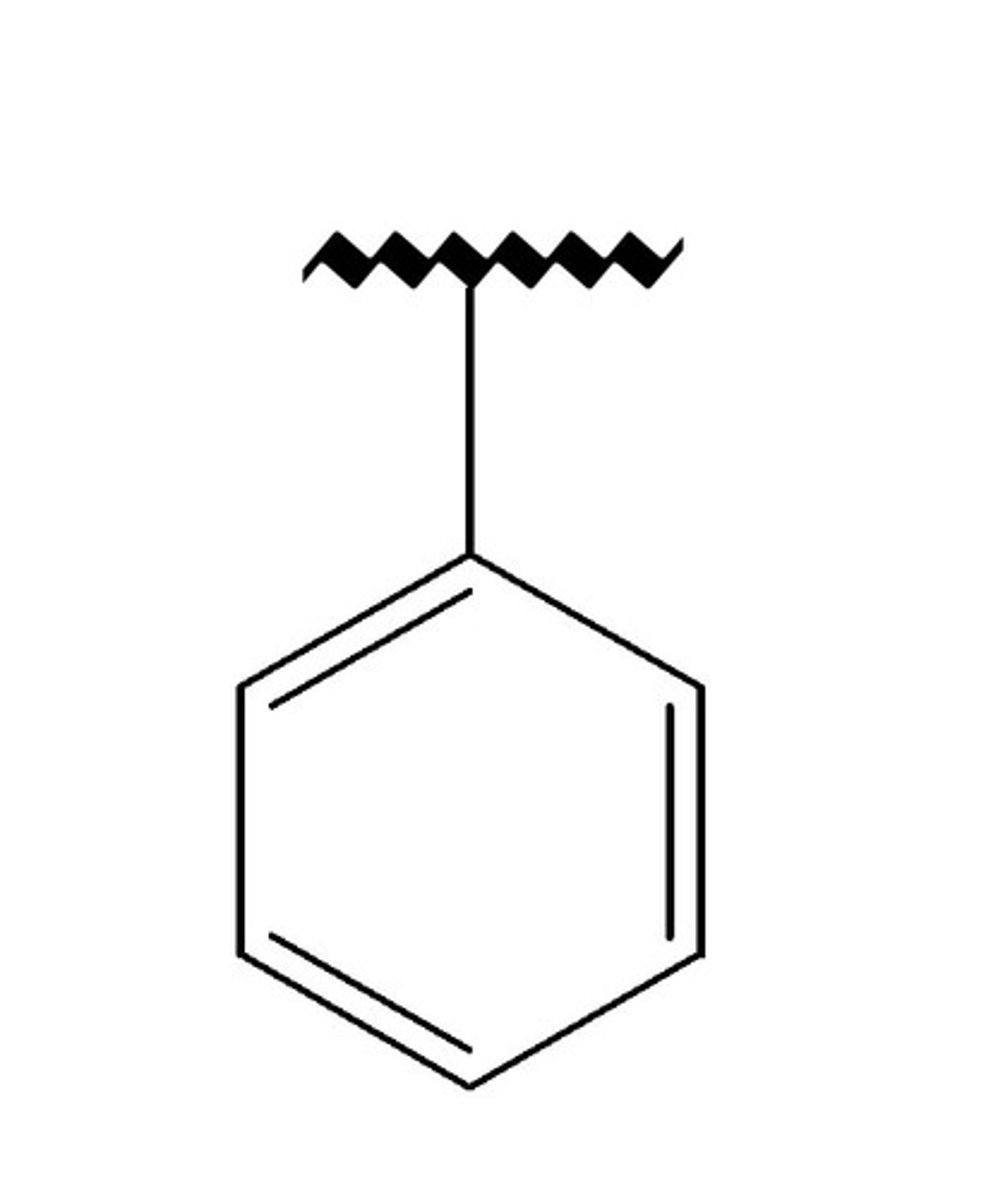
what does a phenyl substituent look like?
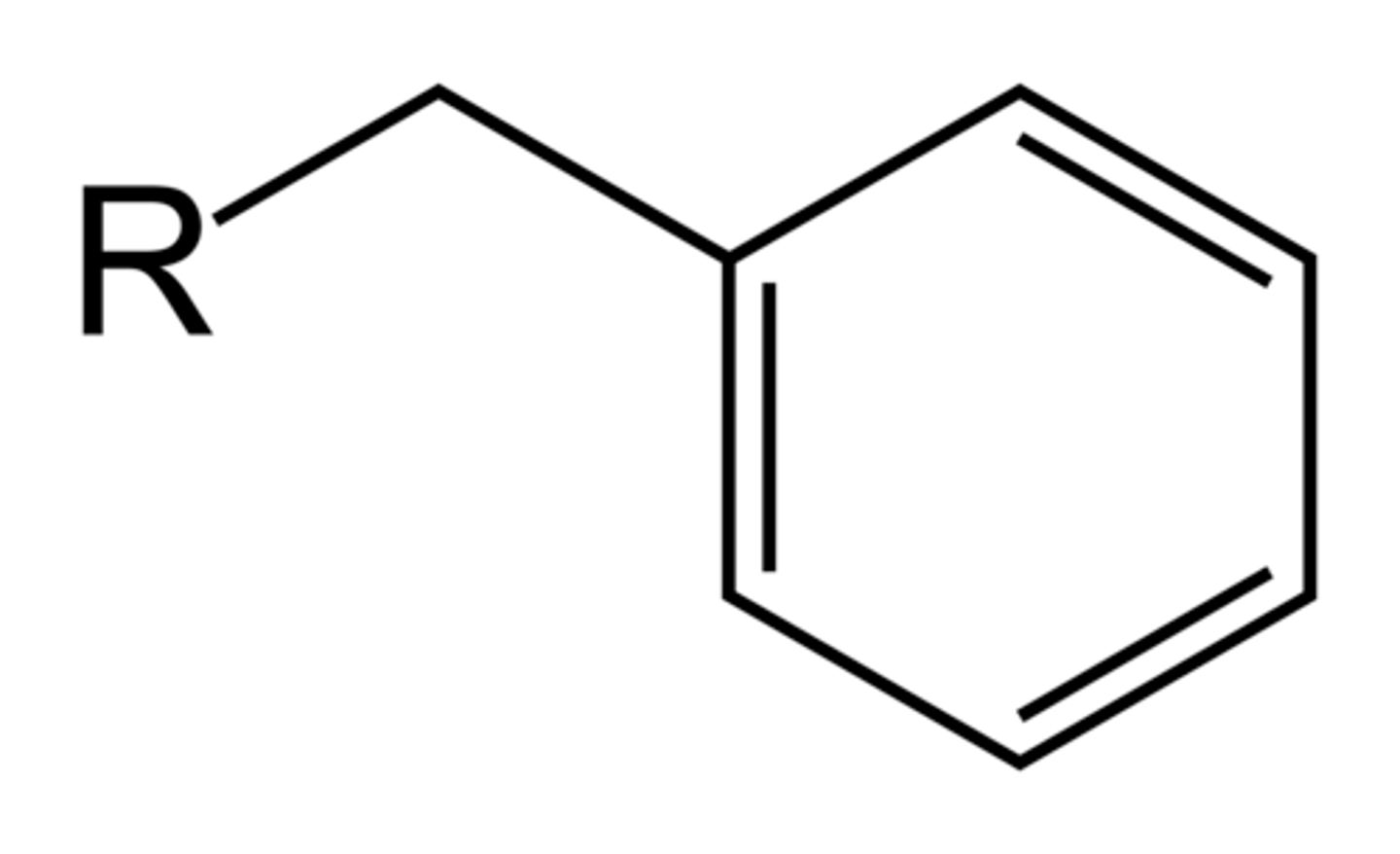
what does a benzyl substituent look like?
what are the steps to naming an alkane?
1. find longest parent chain
2. number the parent chain based on whichever number gives you the smaller number for substituents
3. list substituents first in alphabetical order, replacing -ane with -yl (use di, tri, tetra, etc if substituent shows up more than once)
4. list parent chain afterwards using correct prefix
-di and tri don't count in alphabetics. neither does sec- or -tert
how do you name cycloalkanes?
the same as alkanes but placing cyclo in front of the word
-use cis or trans with 2 substituents (you can also use R/S system)
-use R/S system with 3+ substituents
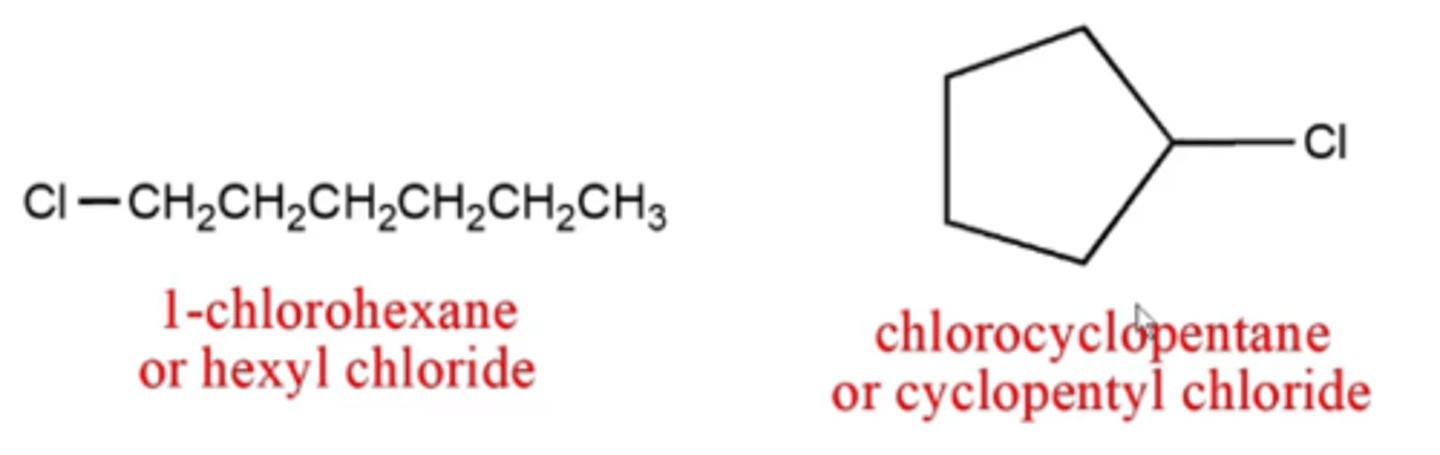
how do you name alkyl halides (carbon molecules that have halogens -F, -Cl, -Br, or -I in them)?
the same as alkanes except:
-use prefixes "fluoro", "chloro", "bromo", or "iodo", with numbers, to identify each halogen substituent and its position
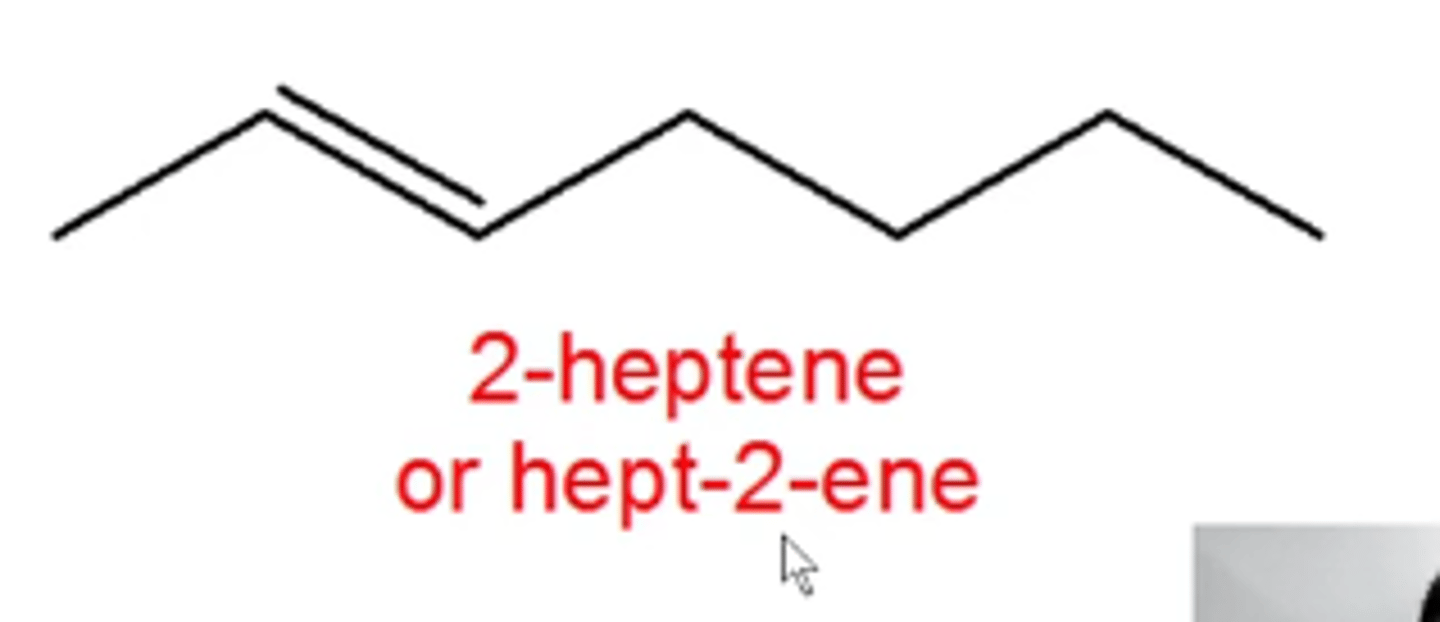
how do you name alkenes?
the same as alkanes except:
-use -ene instead of -ane at the end of the molecule's name
-add a number at the beginning of, or within, the name to indicate where the C=C bond starts (ex. 2-heptene or hept-2-ene)
-add the prefixes cis or trans or E or Z at the beginning of the name to indicate the C=C bond's stereochemistry (Z=Zame Zide)
how do you use the E/Z naming of alkenes?
this applies to molecules that have less than 2 H groups so that they can't be cis or trans
-split the molecules in half and prioritize either group based on atomic number, with double bonds outranking single bonds
-Z is same side priorities
-E is opposite side priorities

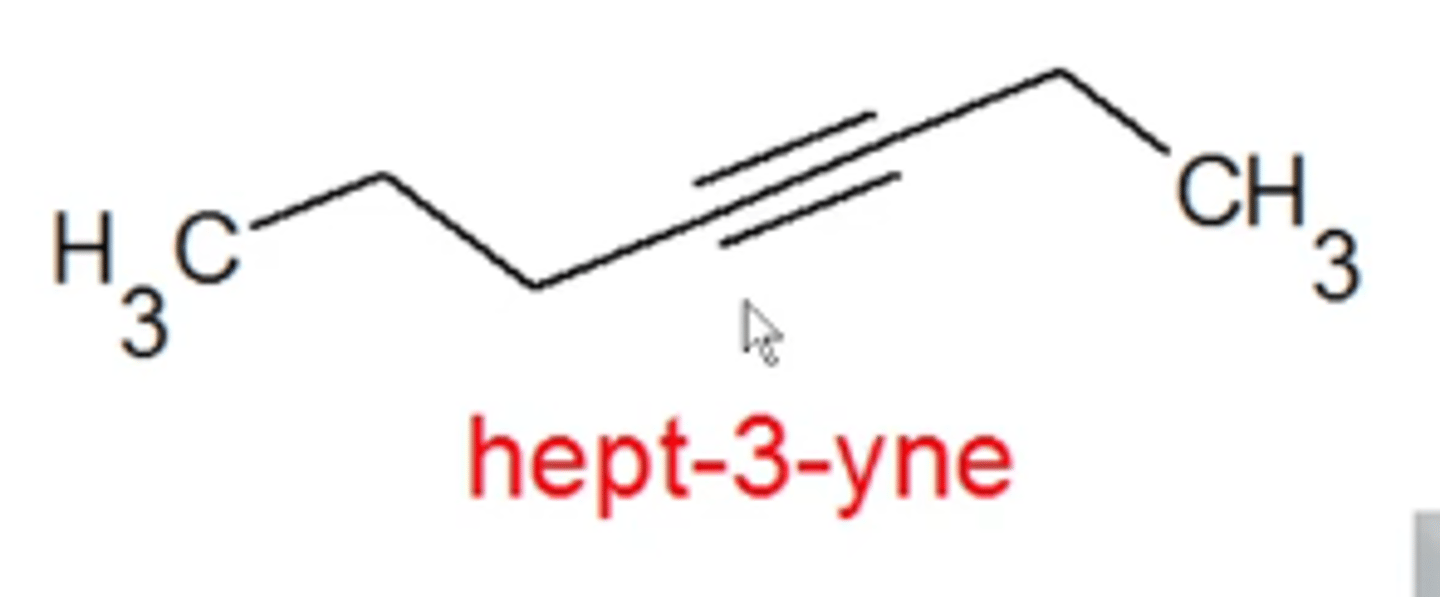
how do you name alkynes?
same rules as alkanes except:
-use "yne" instead of "ane"
-add a number at the beginning of, or within, the name to indicate where the triple bond starts
-cis/trans and E/Z don't apply here
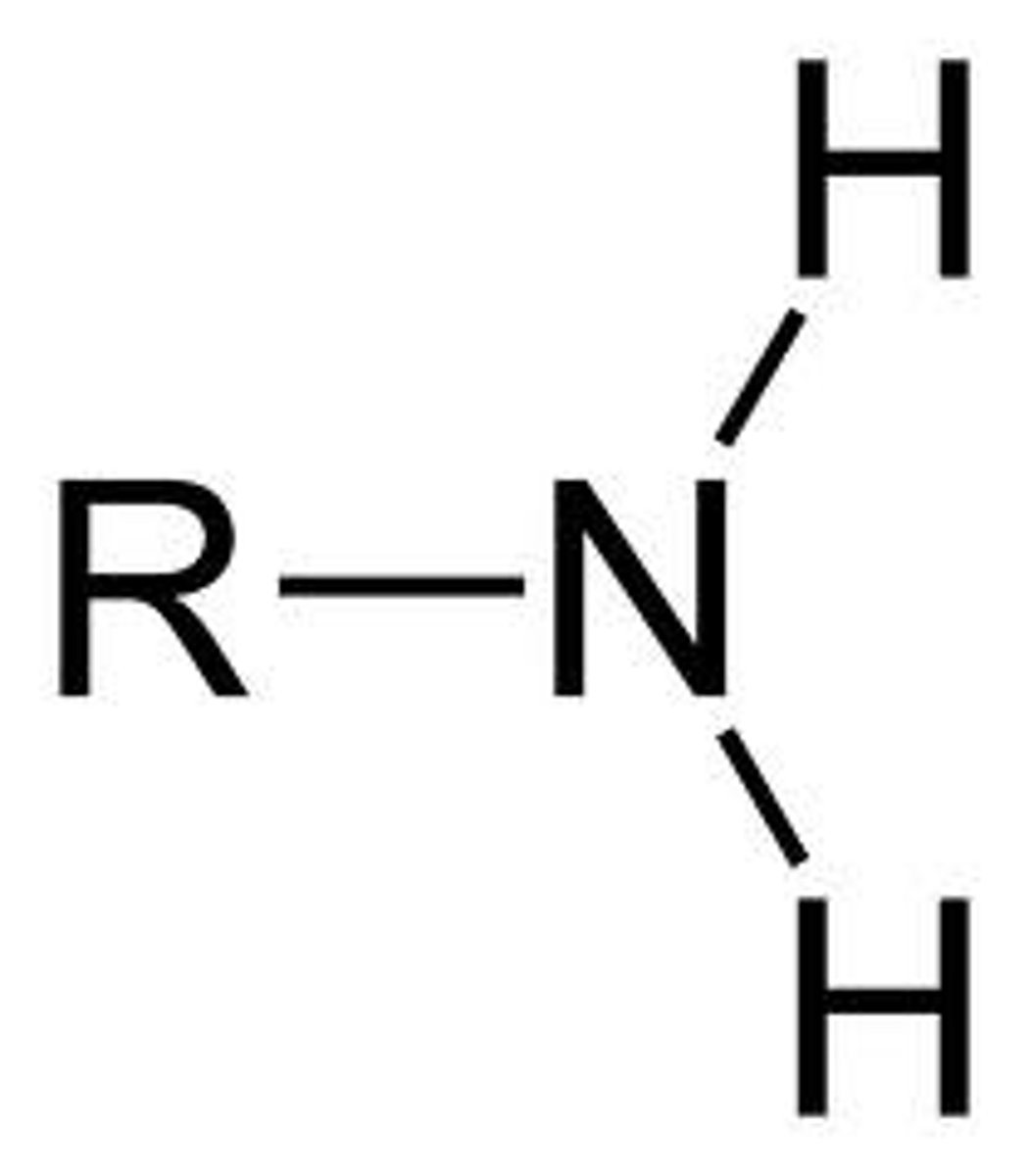
what does an amine look like?
can be primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on how many carbons are bonded to the nitrogen
what happens if you have four carbons bonded to a nitrogen?
the nitrogen gets a formal positive charge and you have a quaternary ammonium salt (except it still has a full octet)
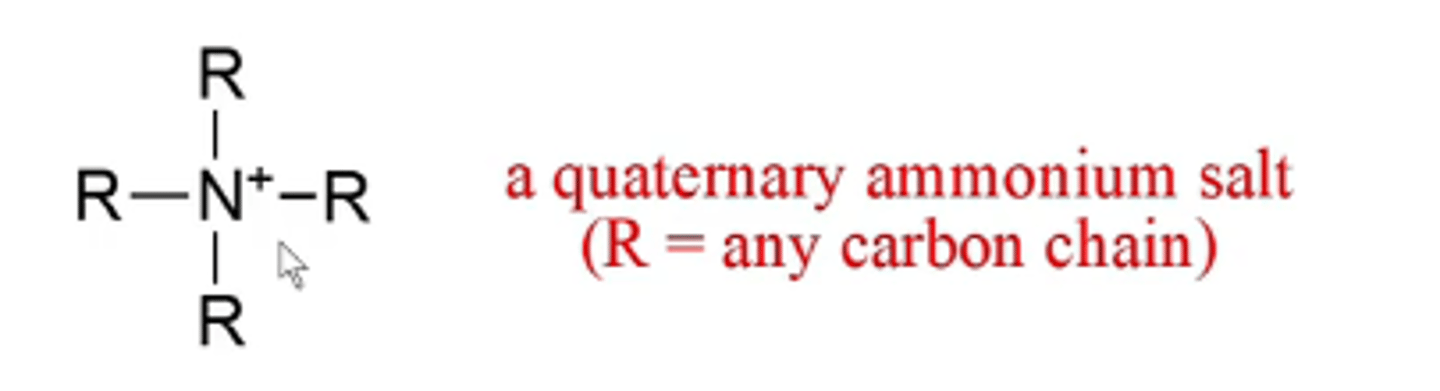
what does an ether look like?
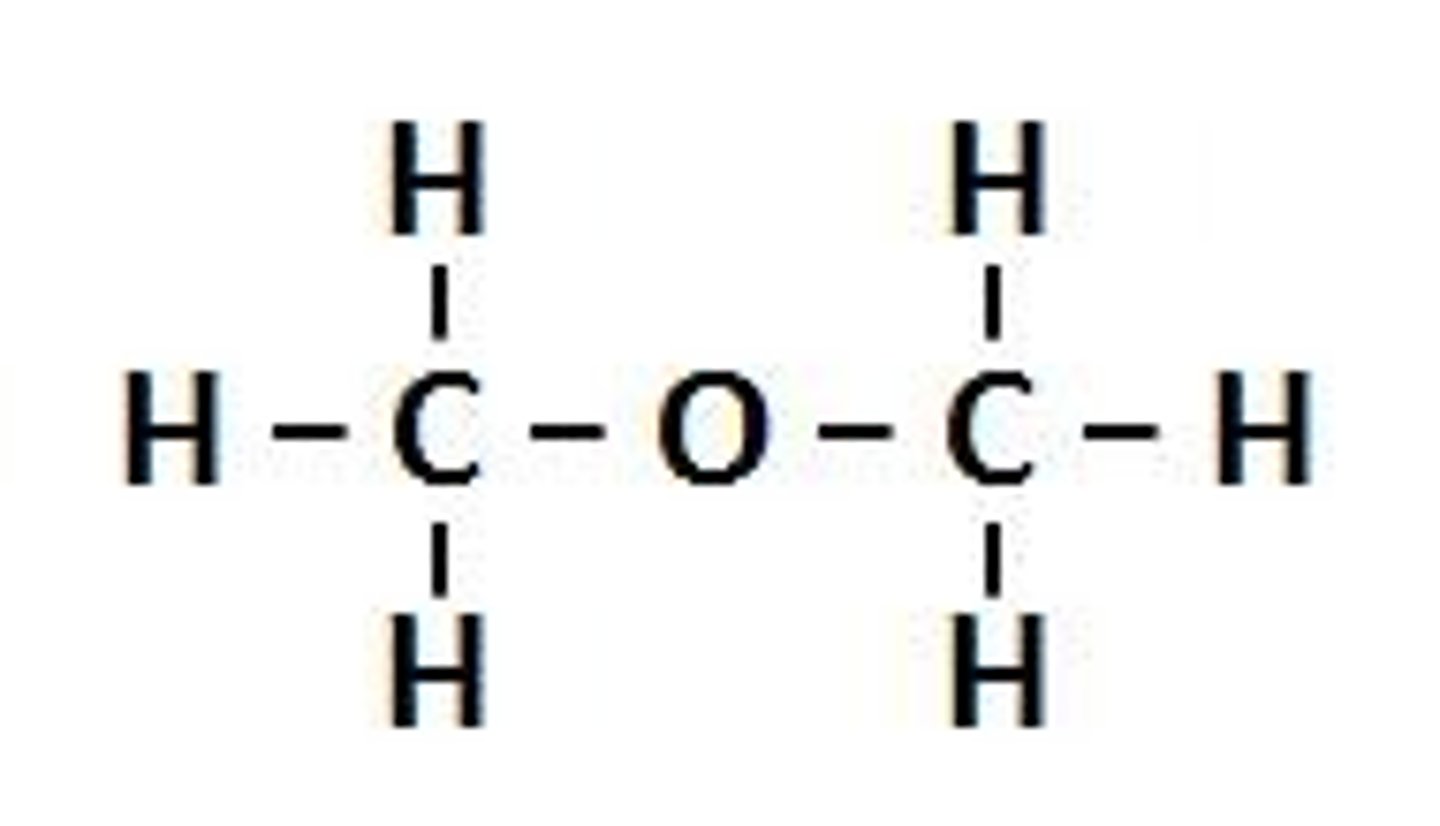
how do you name alcohols?
follow rules for naming alkanes except:
-if the alcohol is the highest priority substituent, the parent chain is the longest carbon chain that has the OH group on it, EVEN IF THERE ARE LONGER carbon chains that DON'T have the OH group on them
-number the carbon chain in the direction that gives the smallest number to the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl (OH) group
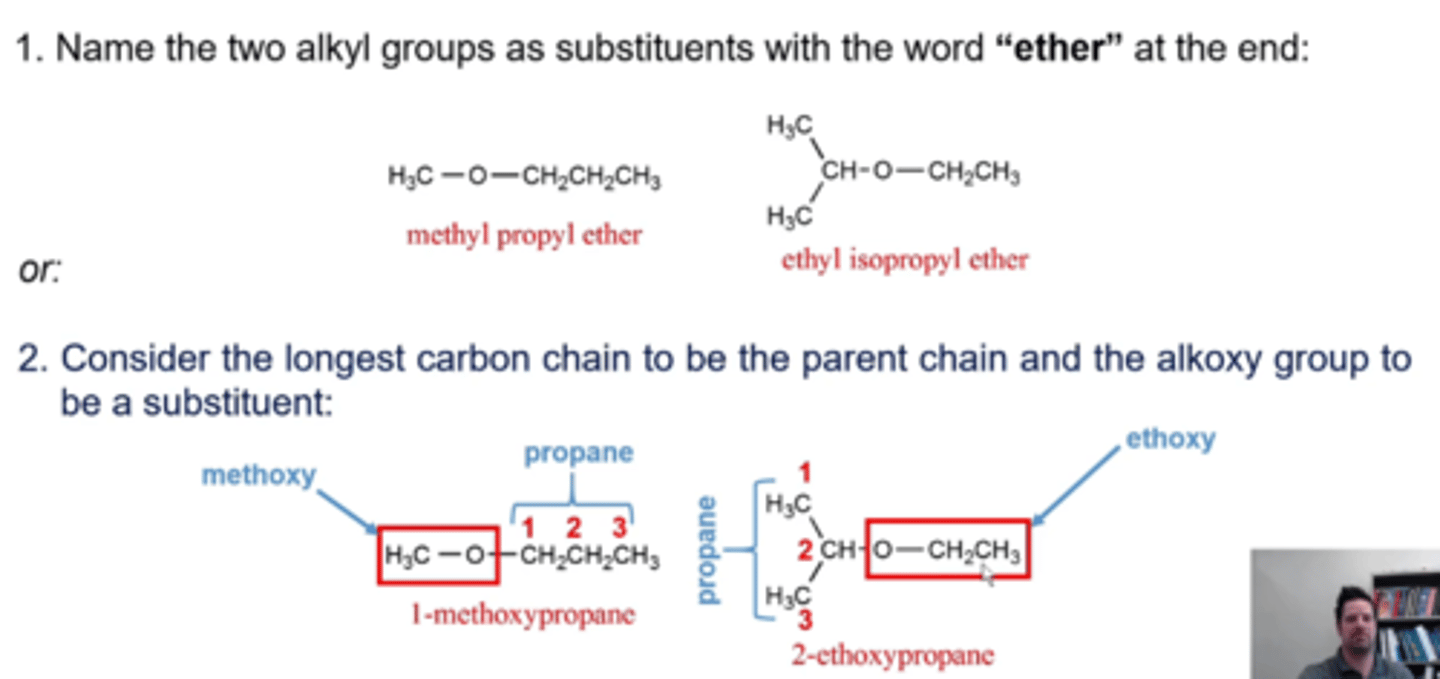
how do you name ethers?
METHOD 1:
-name the two alkyl groups as substituents with the word "ether" at the end, making sure that the substituents are in alphabetical order
METHOD 2
-consider the longest carbon chain to be the parent chain and the alkoxy group to be a substituent
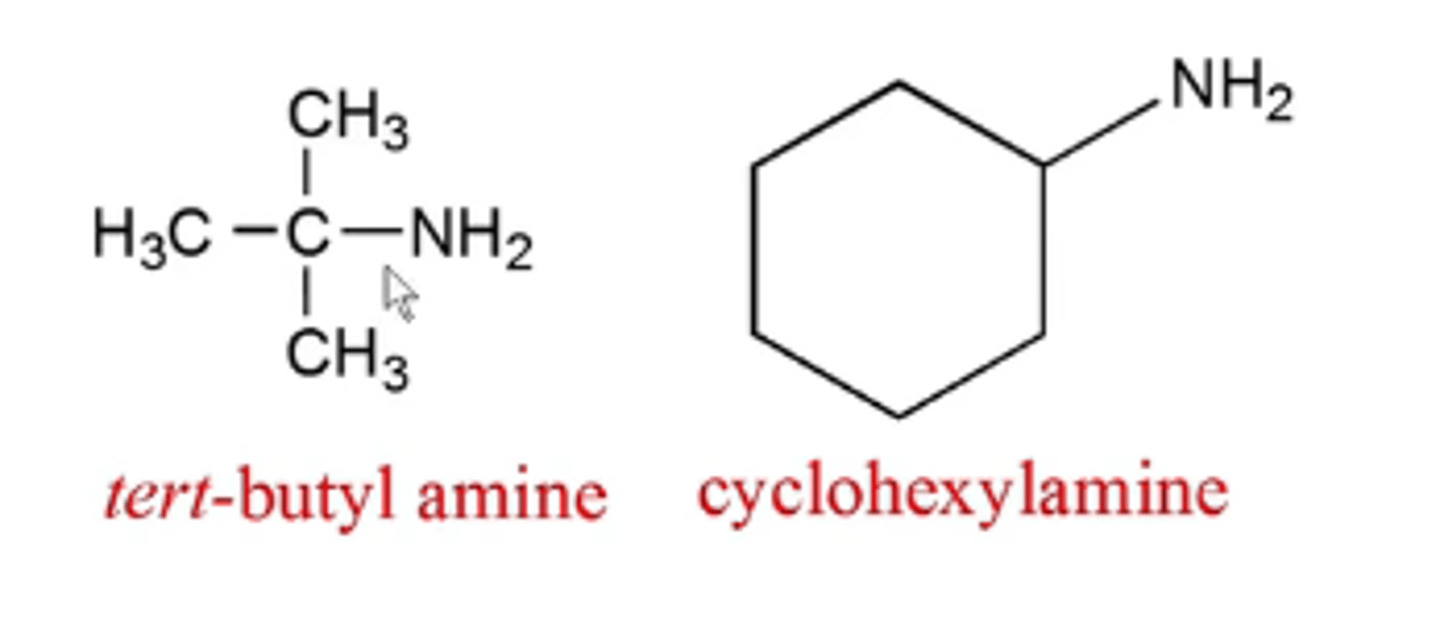
how do you name primary amines?
primary amine:
-add the suffice "amine" to the name of the organic substituent
how do you name symmetrical/secondary amines?
symmetrical/secondary amines:
-add di- or tri- to the alkyl group
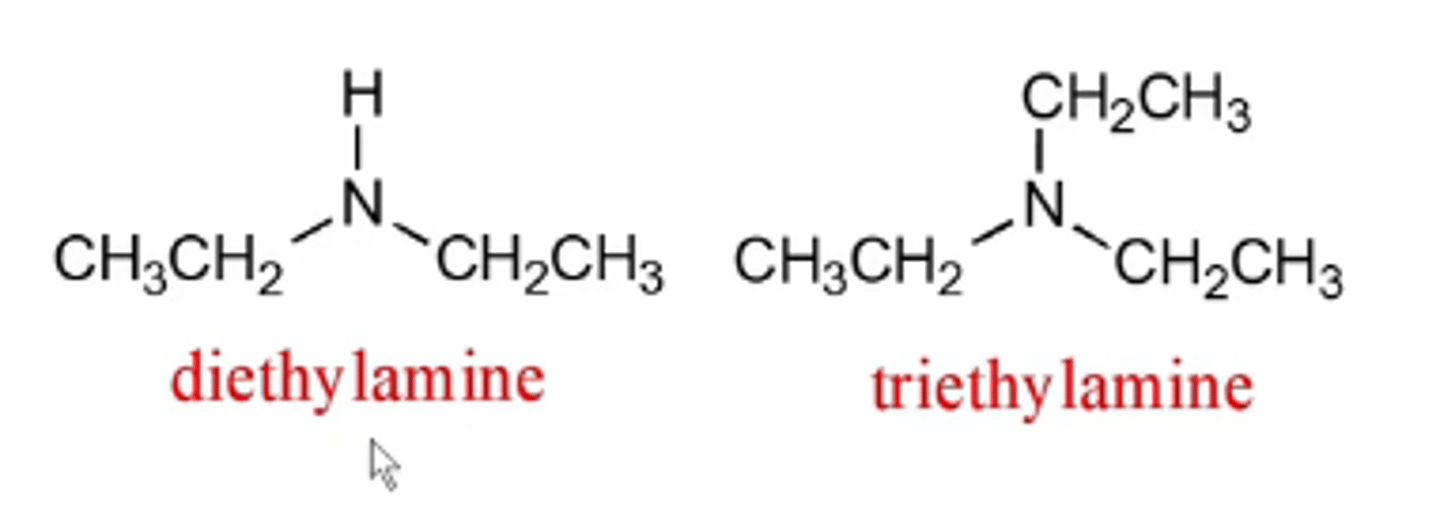
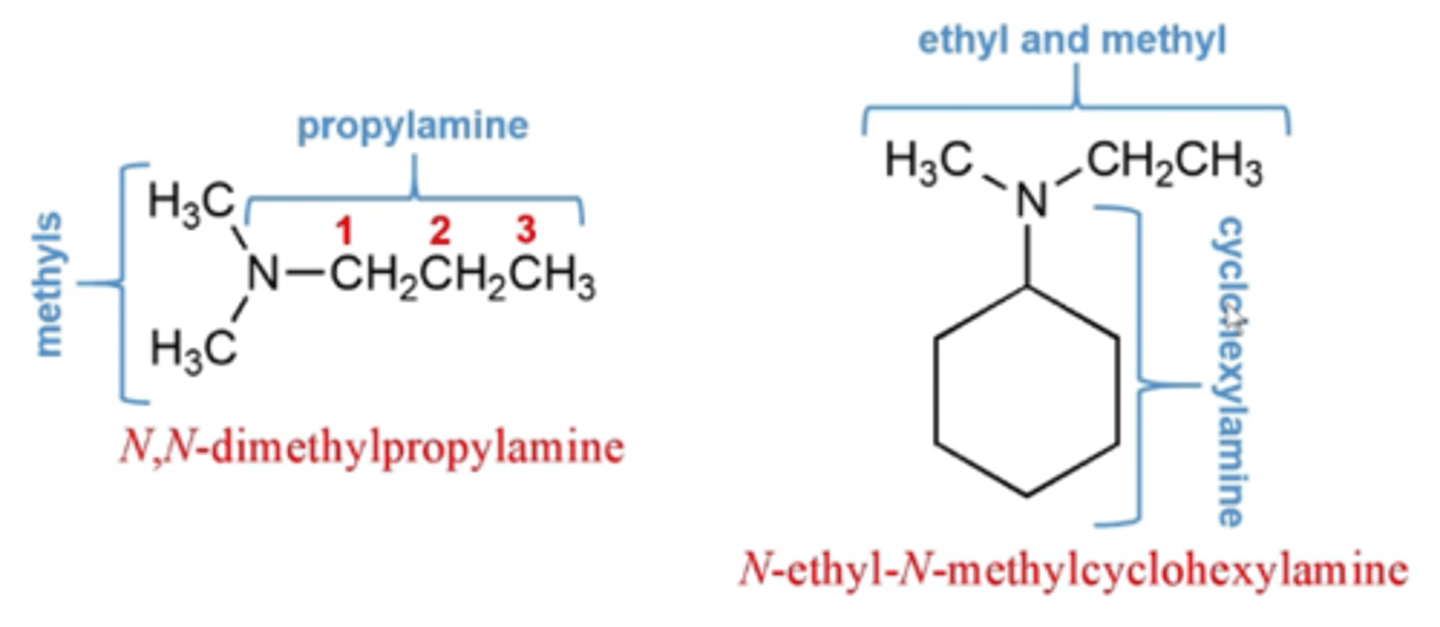
how do you name asymmetrical (tertiary) amines?
asymmetrical (tertiary) amines:
-named as N-substituted primary amines, with the largest alkyl group being named as the parent chain
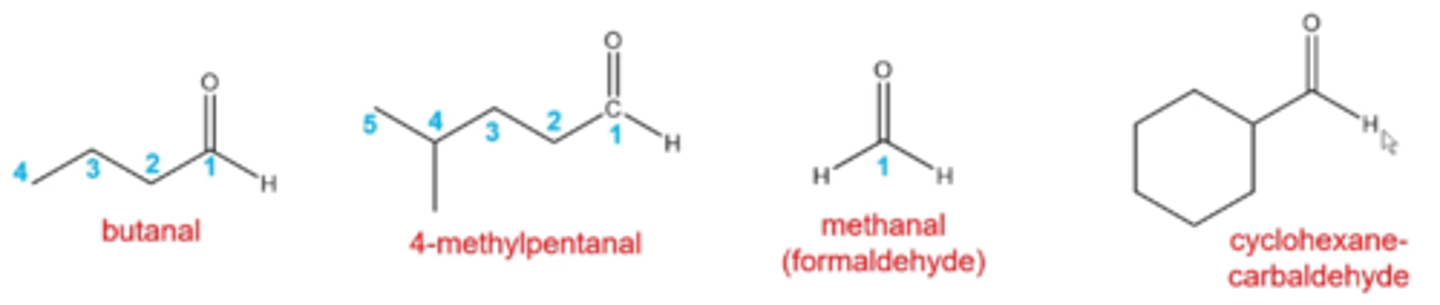
how do you name aldehydes?
follow rules for alkanes except:
-the parent chain is the longest chain that contains the aldehyde
-number the parent chain in the direction that gives the smallest number to the aldehyde carbon
-replace the "e" in the alkane name with the suffix "al"
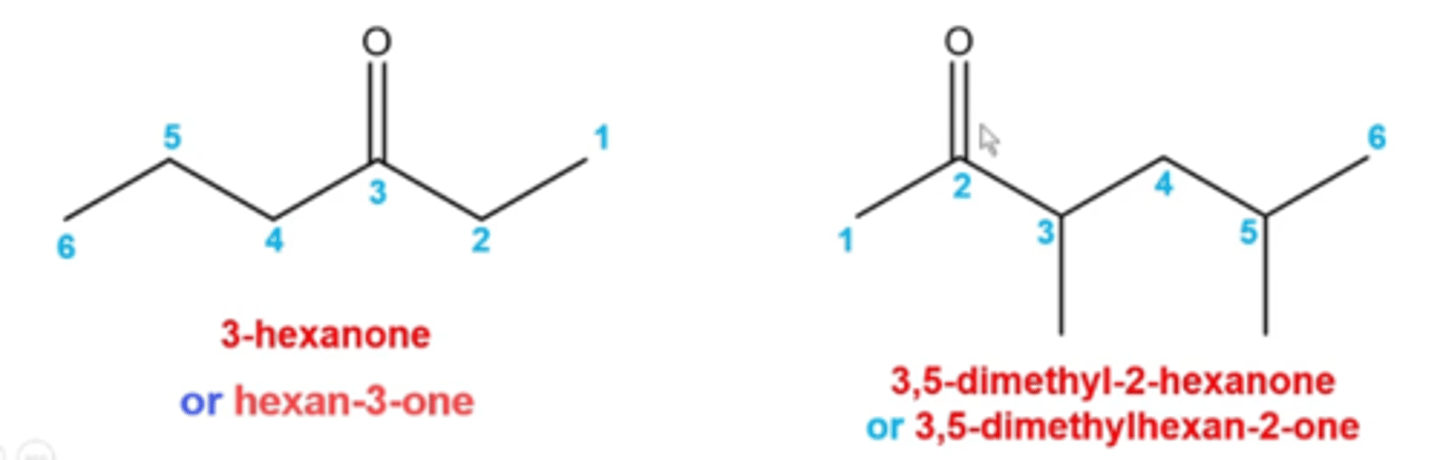
how do you name ketones?
(C=O is called a carbonyl)
METHOD 1
-name the entire parent chain as you would an alkane, but replace the "e" in the alkane name with a number to indicate the position of the C=O bond, followed by the suffix "one" (pic)
METHOD 2
-name each chain on either side of the C=O (carbonyl) and then follow it with the word "ketone" (ex. ethyl propyl ketone or methyl phenyl ketone)
-for any cyclic ketones, just add "cyclo" ex. cyclohexanone
what do carboxylic acids and their derivatives look like?
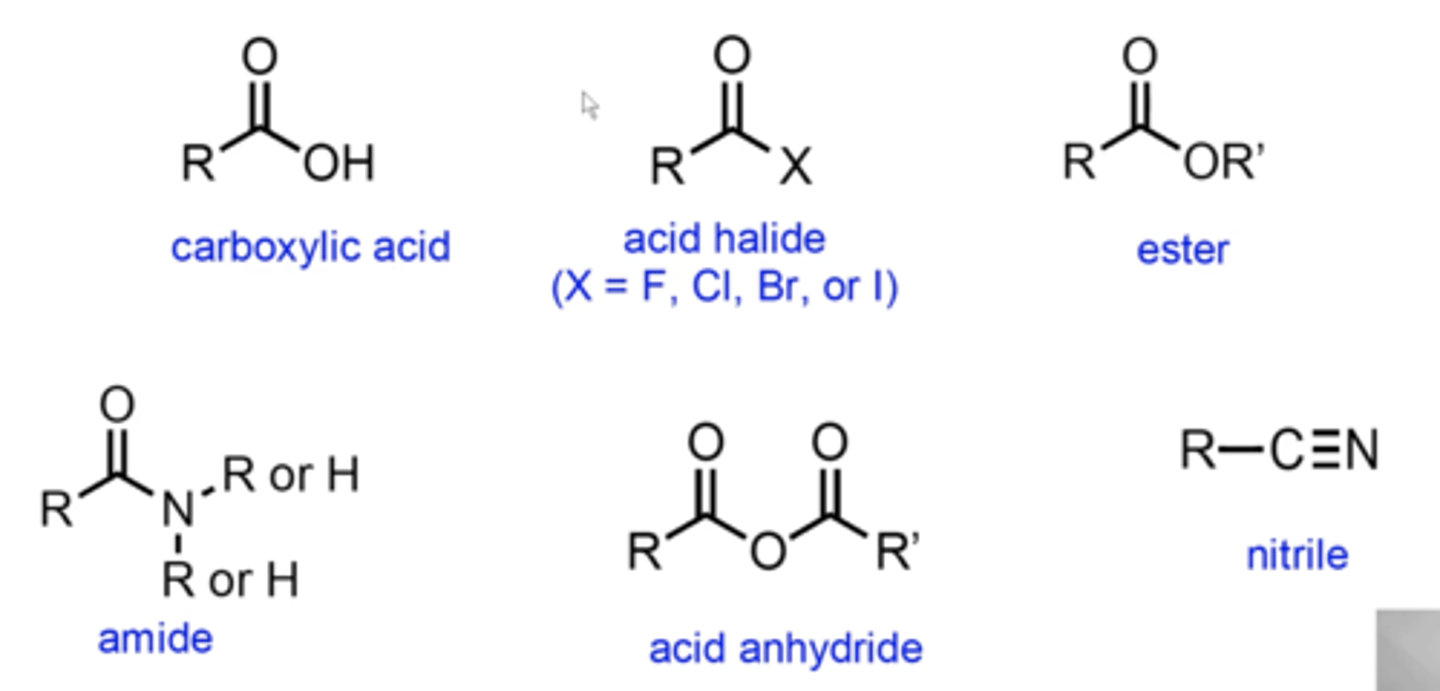
how do you name carboxylic acids?
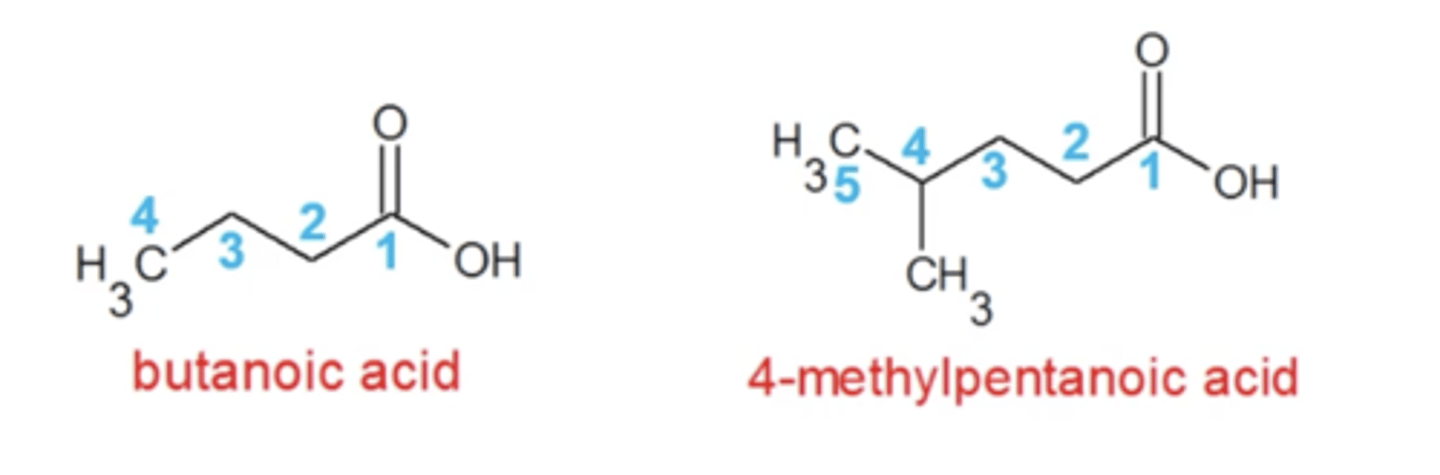
same as alkanes except:
-parent chain is the longest carbon chain that contains the carboxylic acid
-number the parent chain in the direction that gives the C.A. the lowest number
-replace "e" in alkane name with "oic acid"
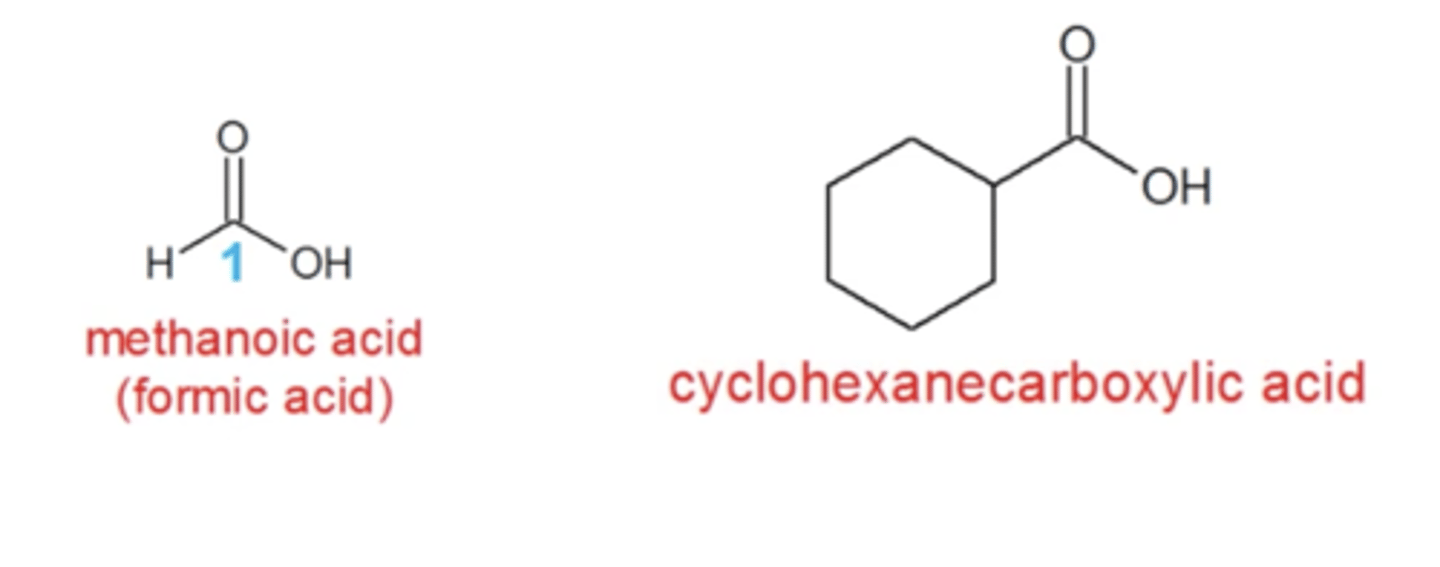
how do you name cyclic carboxylic acids?
"cyclo" in front with "carboxylic acid" at the very end
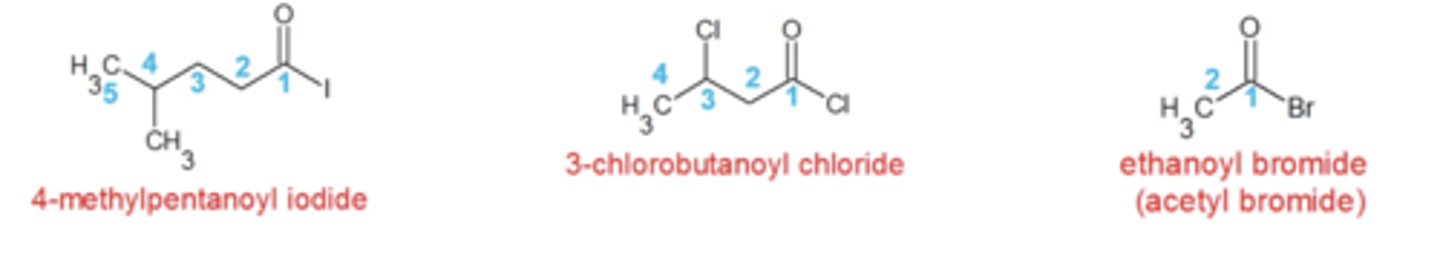
how do you name acid halides?
same as alkanes except:
-parent chain is longest C chain that contains acid halide
-number the parent chain that gives the acid halide the lowest number
-replace "e" in alkane name with "oyl halide"
-put the halogen name at the very end
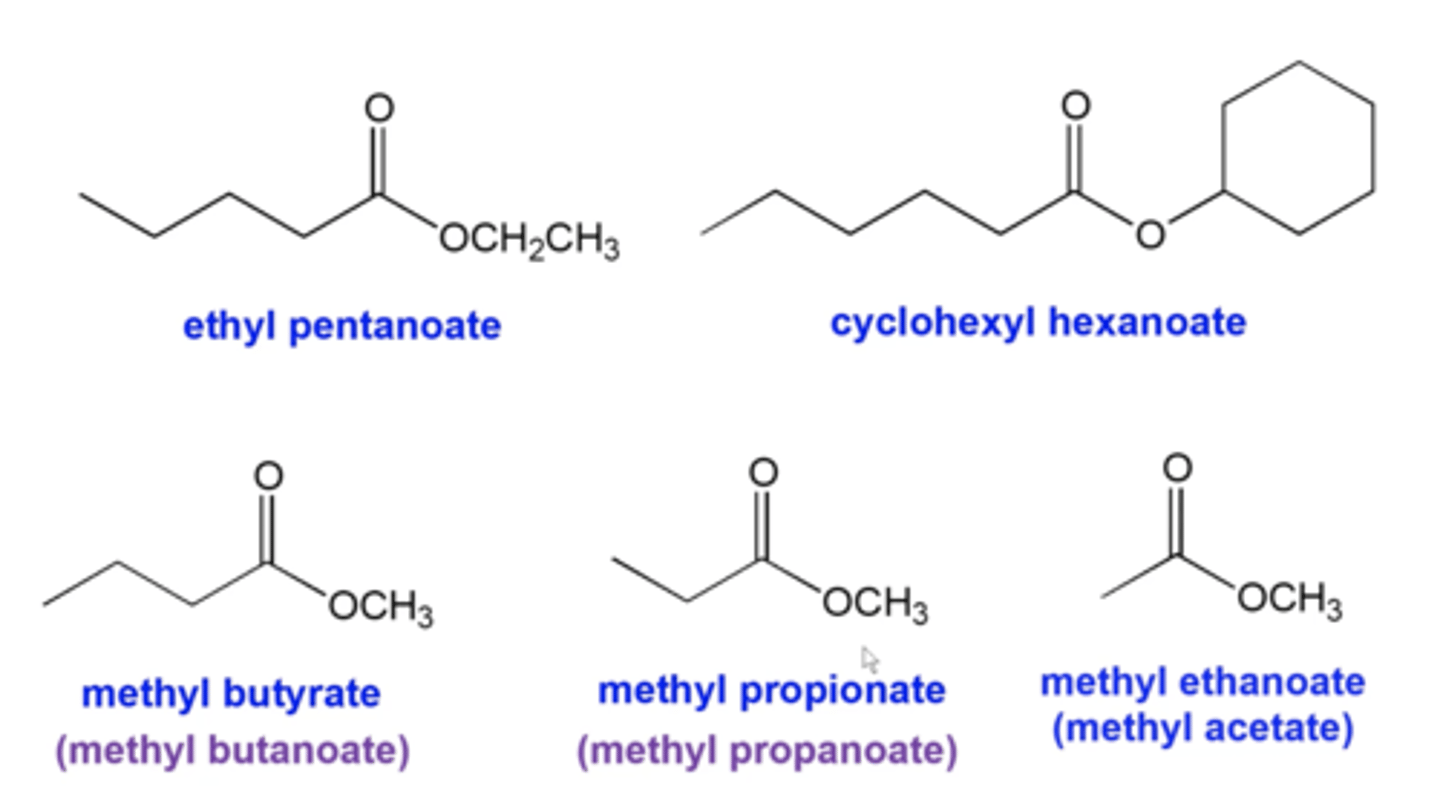
how do you name esters?
same as alkanes except:
-in the name, the alkyl group attached to the ester oxygen gets listed first, as a substituent, with the suffix "yl". The parent chain name then follows
-the parent chain starts at the C=O carbon and is counted moving away from the ester oxygen
-replace "e" in the alkane name with "oate"
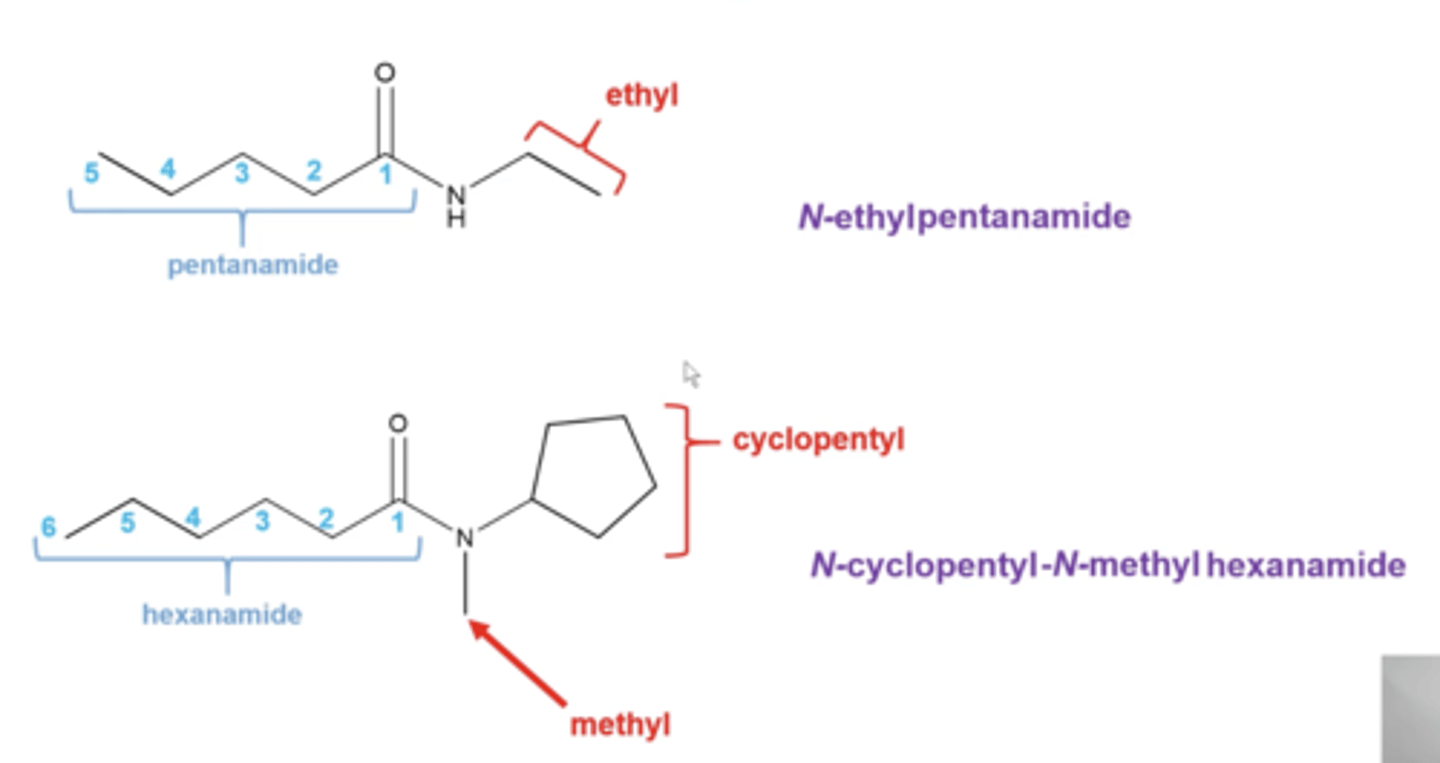
how do you name amides?
follow the same pattern as esters except:
-any alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen gets listed as "N-methyl", "N-ethyl", "N-propyl", etc
-the parent chain starts at the C=O carbon and is counted moving away from the amide nitrogen
-replace "e" in the alkane name with "amide"
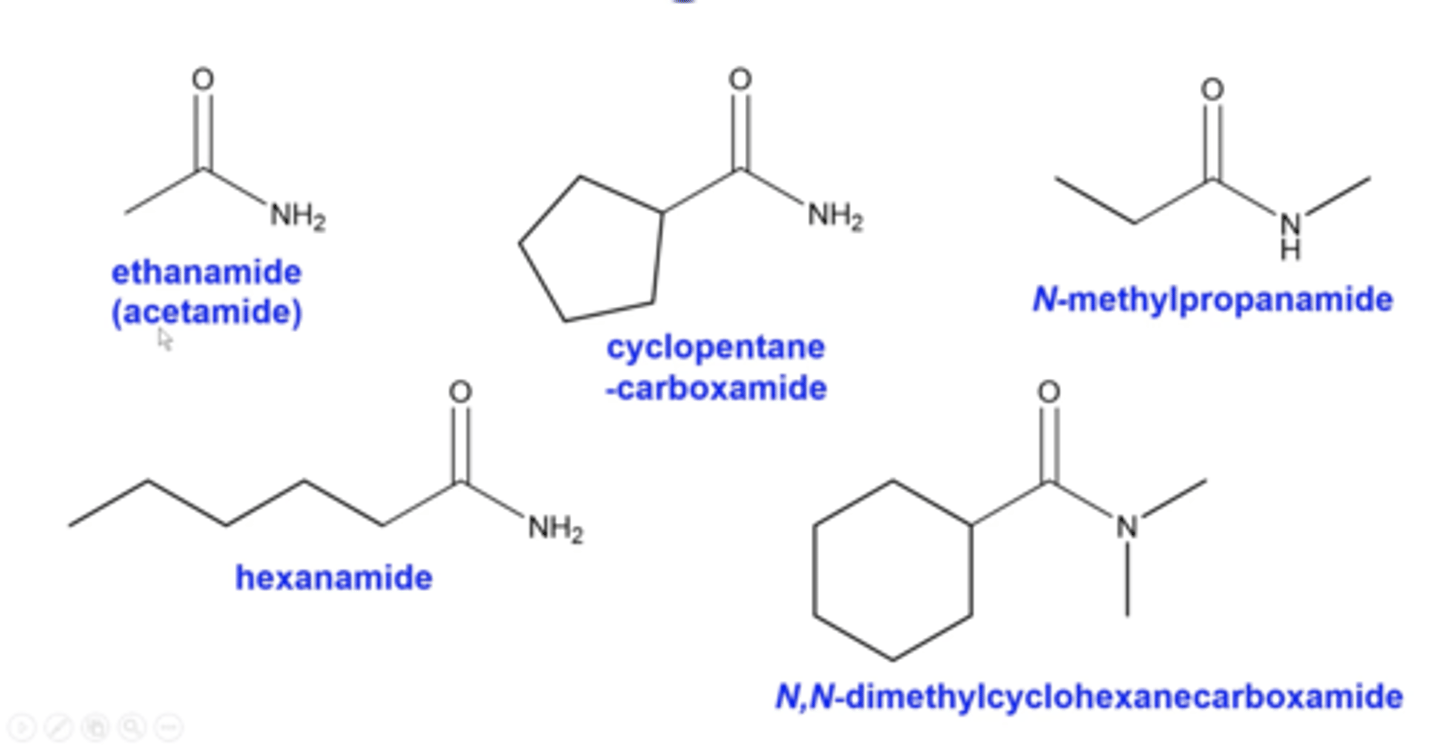
what are some common amides and their names?
-ethanamide is also called acetamide
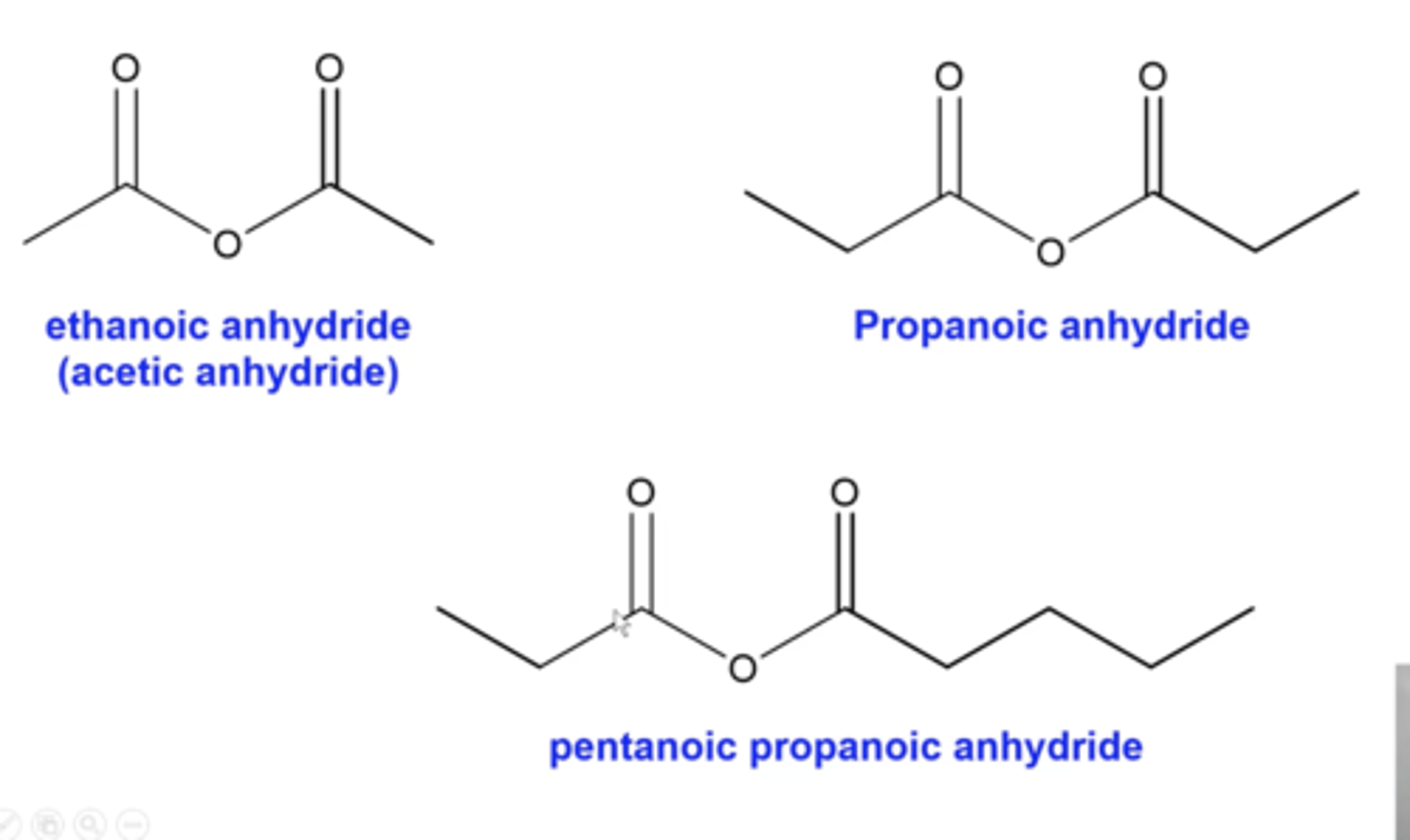
how do you name acid anhydrides?
-determine the length of the chain on either side of the bridging oxygen
-list both lengths alphabetically, replacing their ending "e" with "oic"
-write "anhydride" at the end of the name
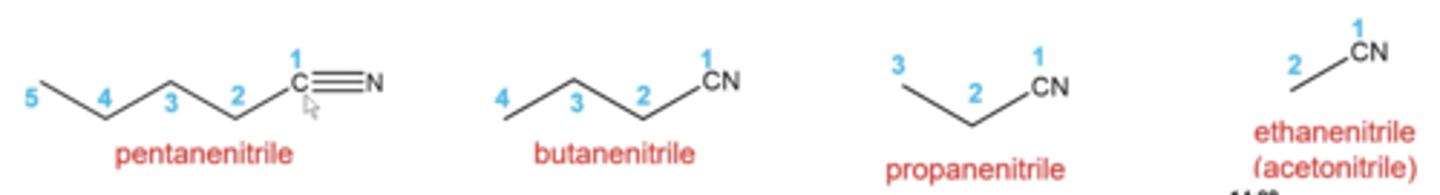
how do you name nitriles?
use same rules as alkanes except:
-parent chain is the longest carbon chain that contains the nitrile carbon
-number the parent chain in the direction that gives you the smallest number to the nitrile carbon
-add suffix "nitrile" to the parent name
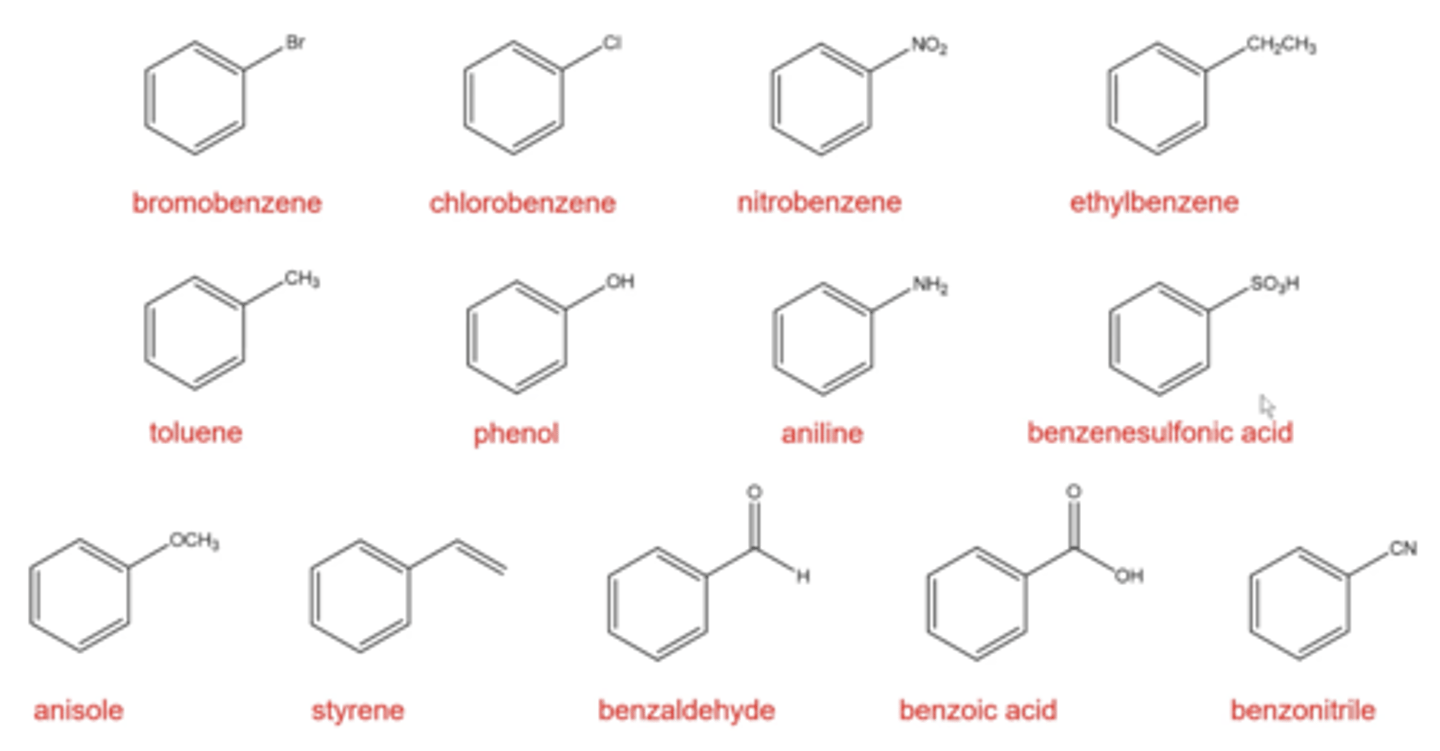
what are the types of monosubstituted benzenes you should memorize?
how do you name substituted benzenes?
-identify the parent chain, which is the benzene containing the highest priority functional group (that parent chain is the parent chain name)
-any other lower priority functional groups are named according to their specific substituent names (pic)
-if the numbers are the same in both directions, pick the one that gives the lower number to the substituent that is alphabetically first
carbon/hydrogen molecules that have two or more rings fused together at single carbon points
spiro alkanes
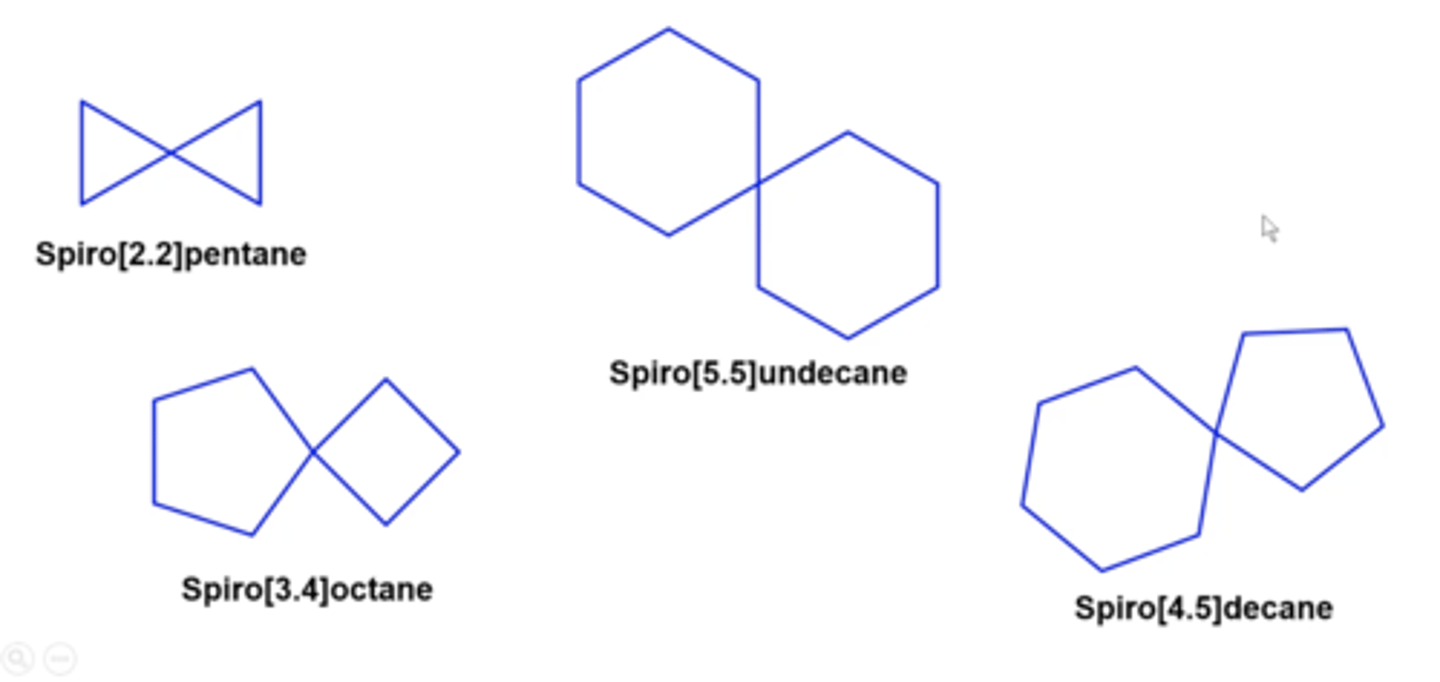
how do you name Spiro alkanes?
spiro [a.b] parent name
-counts total number of carbons across the entire molecule (this is the parent name at the end)
-count the number of carbons to the left and right of the center, that's a.b from LOWEST to highest
![<p>spiro [a.b] parent name</p><p>-counts total number of carbons across the entire molecule (this is the parent name at the end)</p><p>-count the number of carbons to the left and right of the center, that's a.b from LOWEST to highest</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/596e339b-a3a8-4d9c-8302-db2a2767b348.png)
carbon/hydrogen molecules that have two or more rings fused together across multi-carbon bridges (bridgehead carbons)
bicyclic alkanes
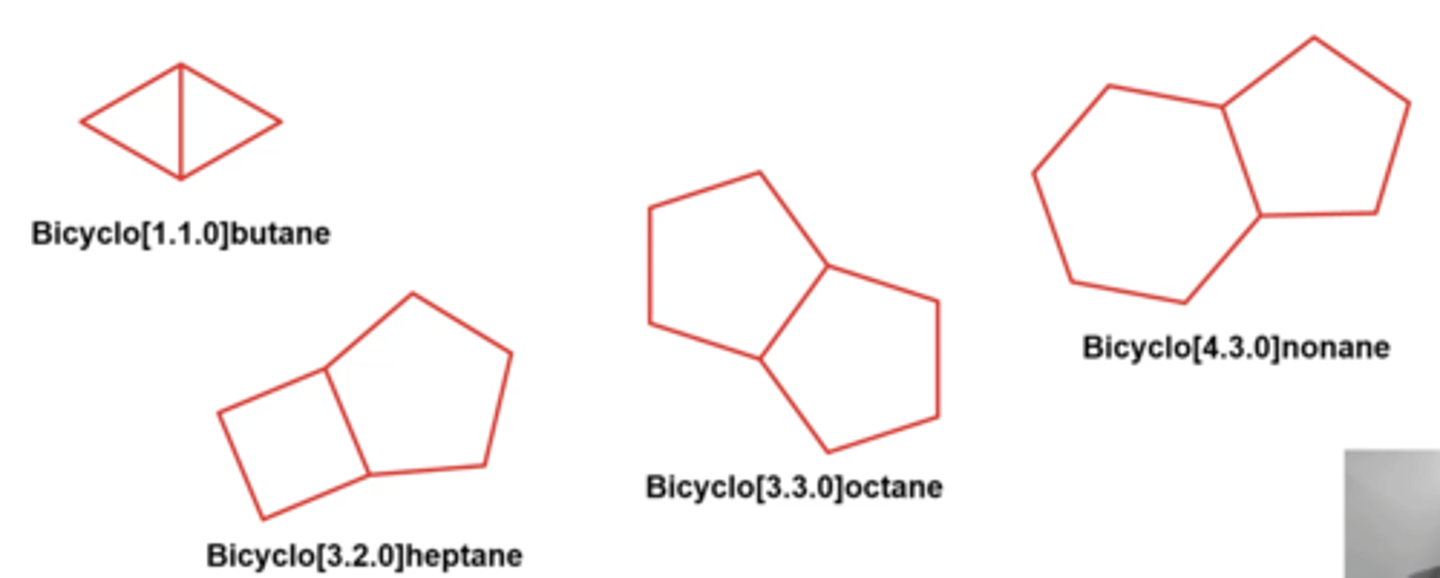
how do you name bicyclic alkanes?
bicyclo [a.b.c] parent name
-count total number of carbons across the entire molecule (this is the parent name)
-count the number of carbons to the left, right, and above bridgehead carbons, and those are [a.b.c] from HIGHEST to lowest
![<p>bicyclo [a.b.c] parent name</p><p>-count total number of carbons across the entire molecule (this is the parent name)</p><p>-count the number of carbons to the left, right, and above bridgehead carbons, and those are [a.b.c] from HIGHEST to lowest</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/845f7a67-3cd4-4fa7-8acd-f8d8b02857ce.png)
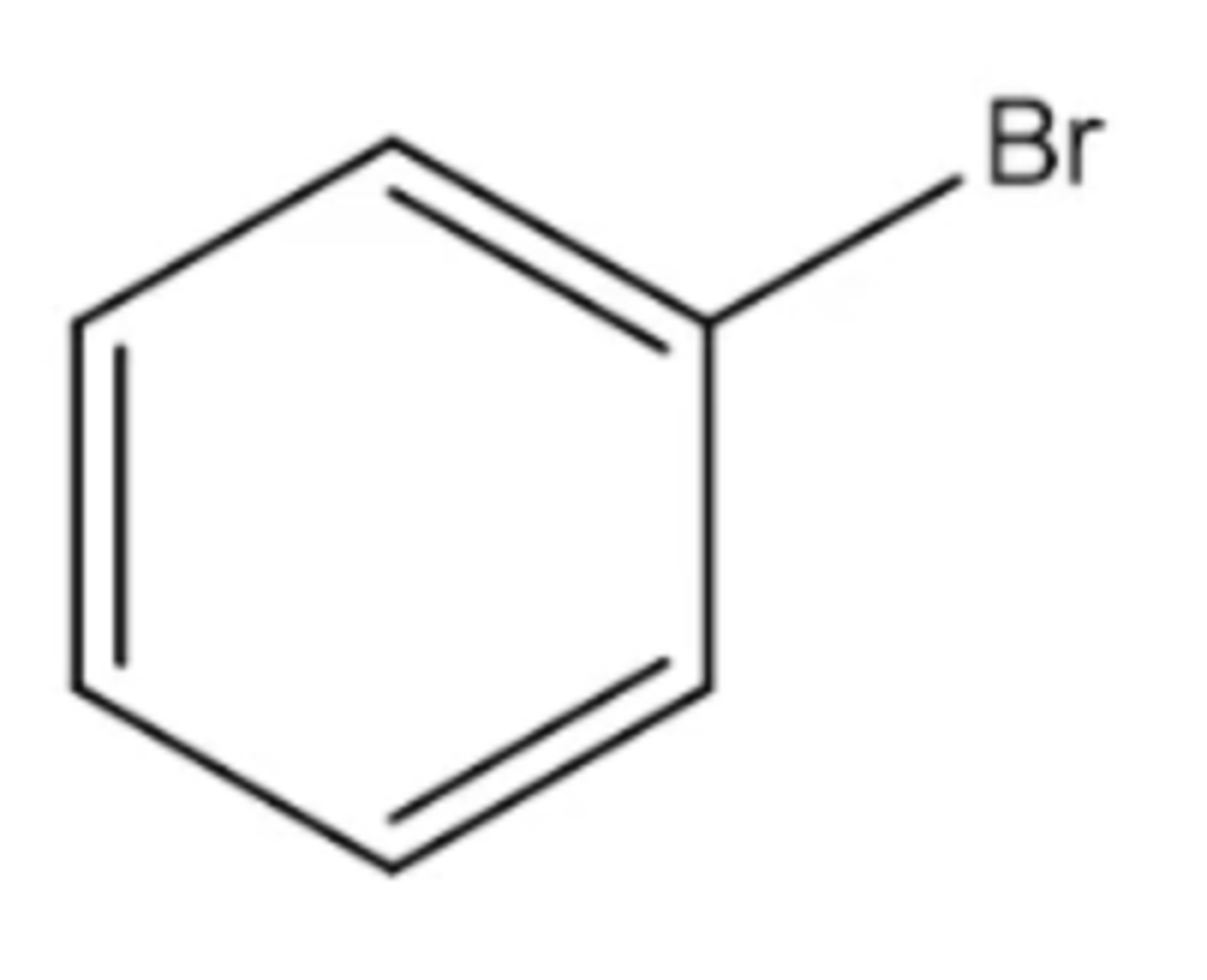
bromobenzine
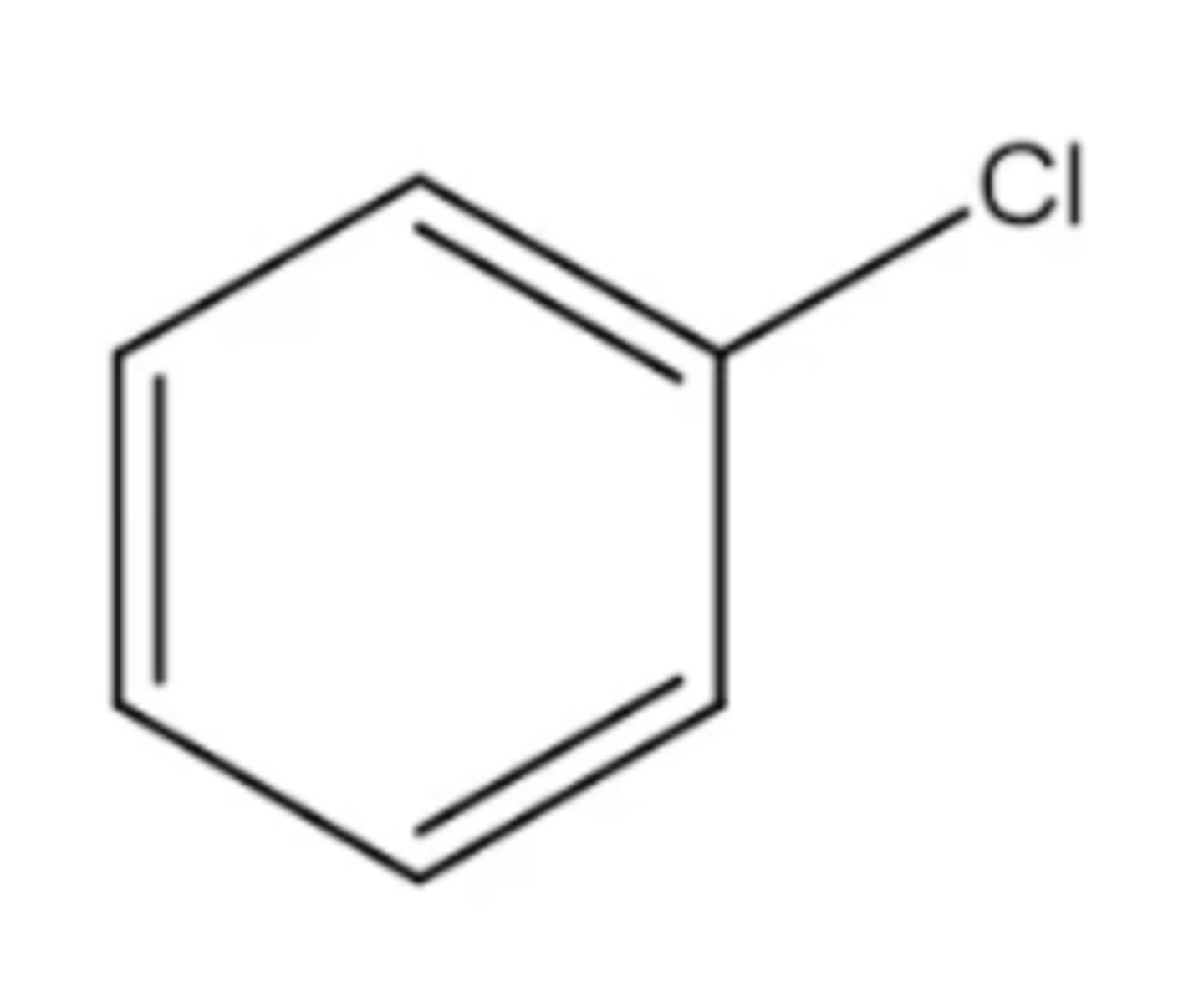
chlorobenzine
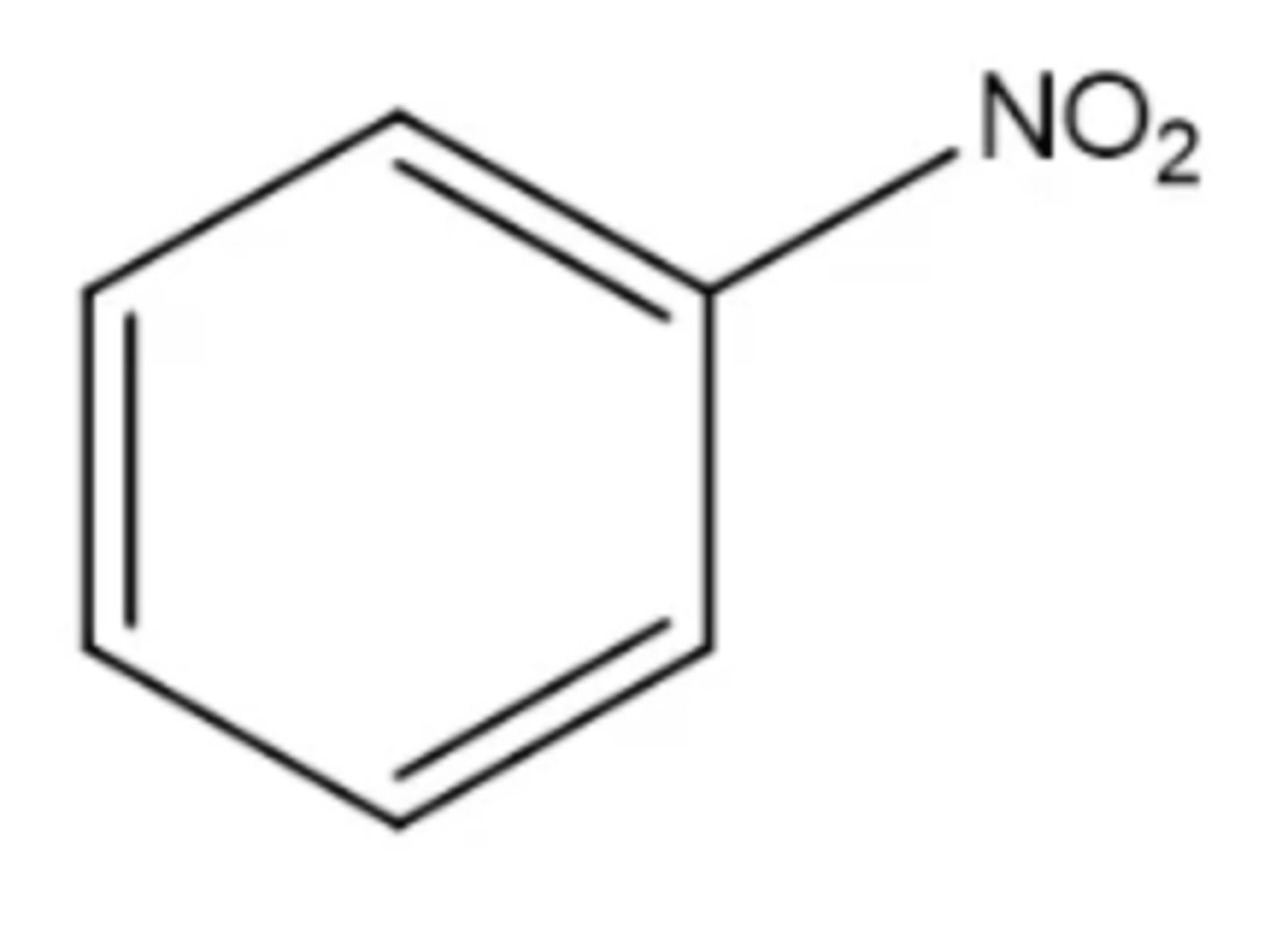
nitrobenzine
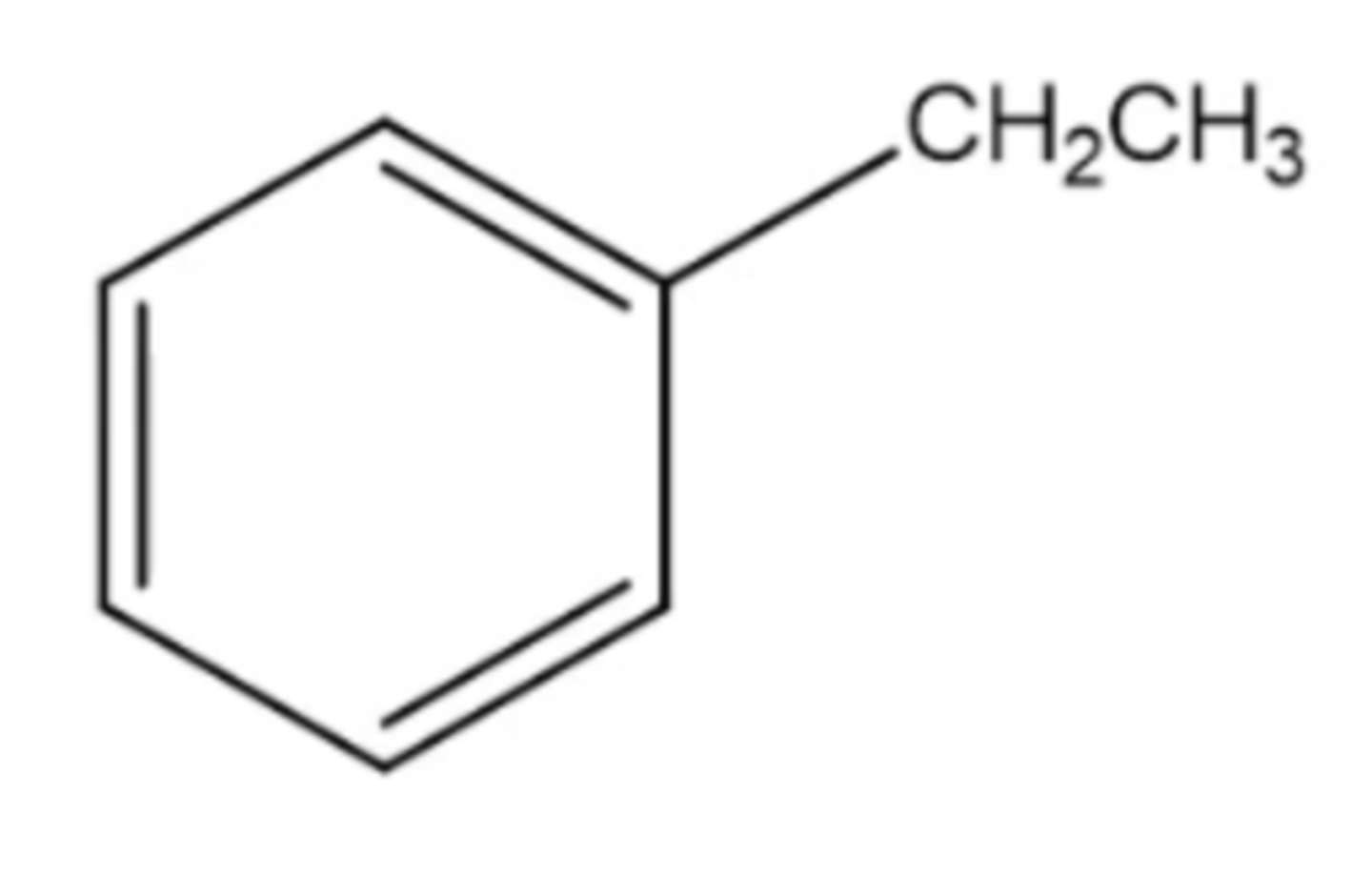
ethylbenzene
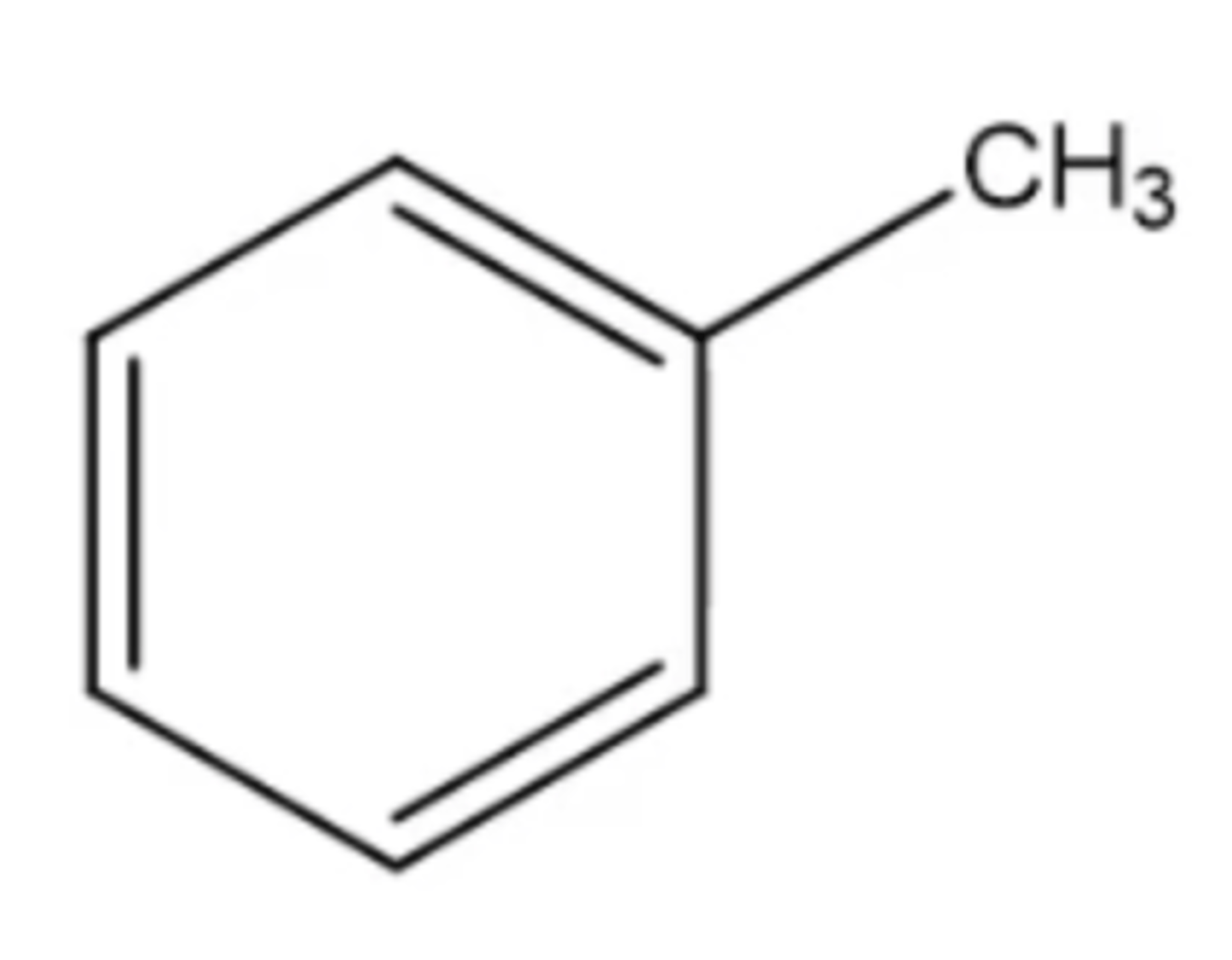
toluene
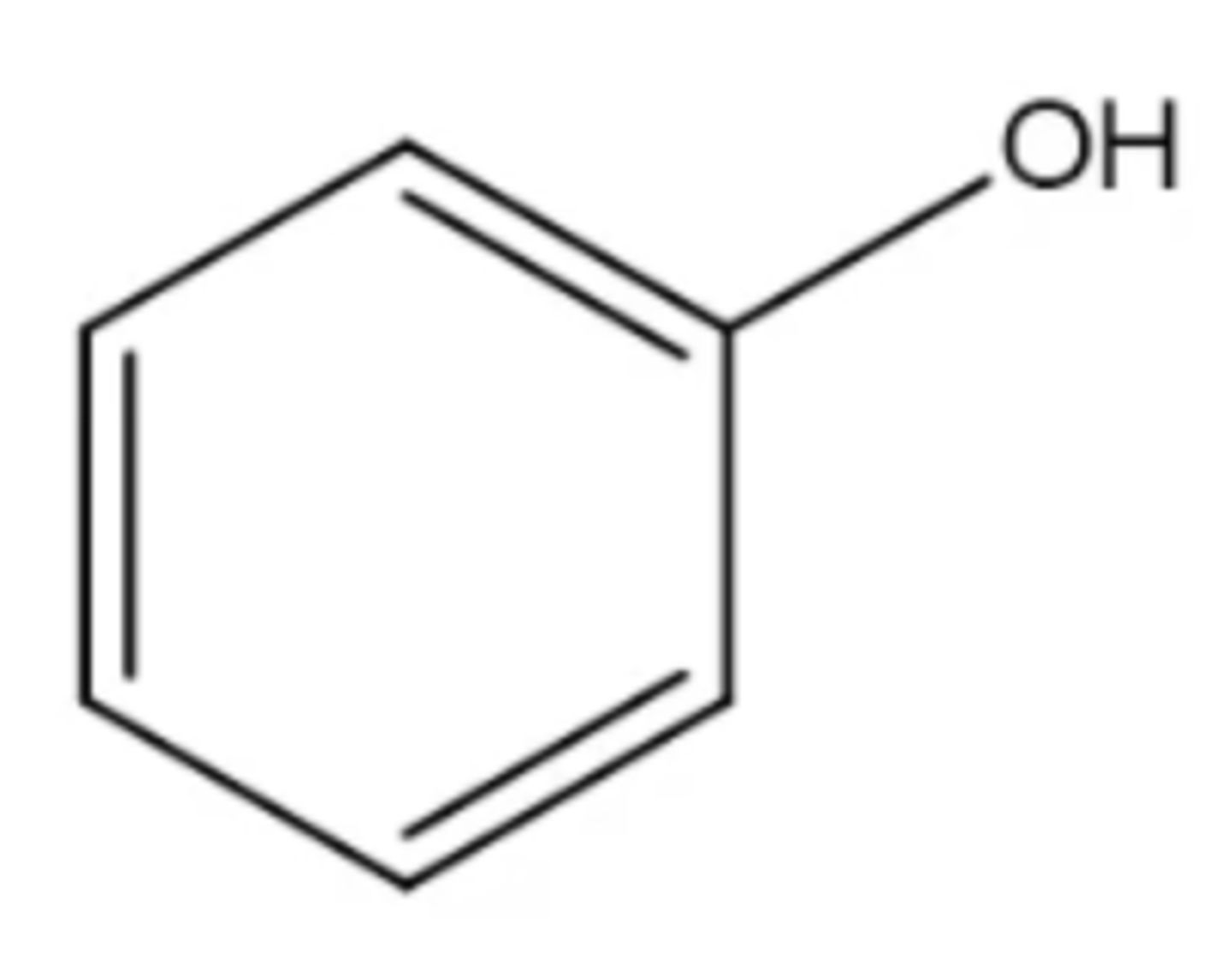
phenol
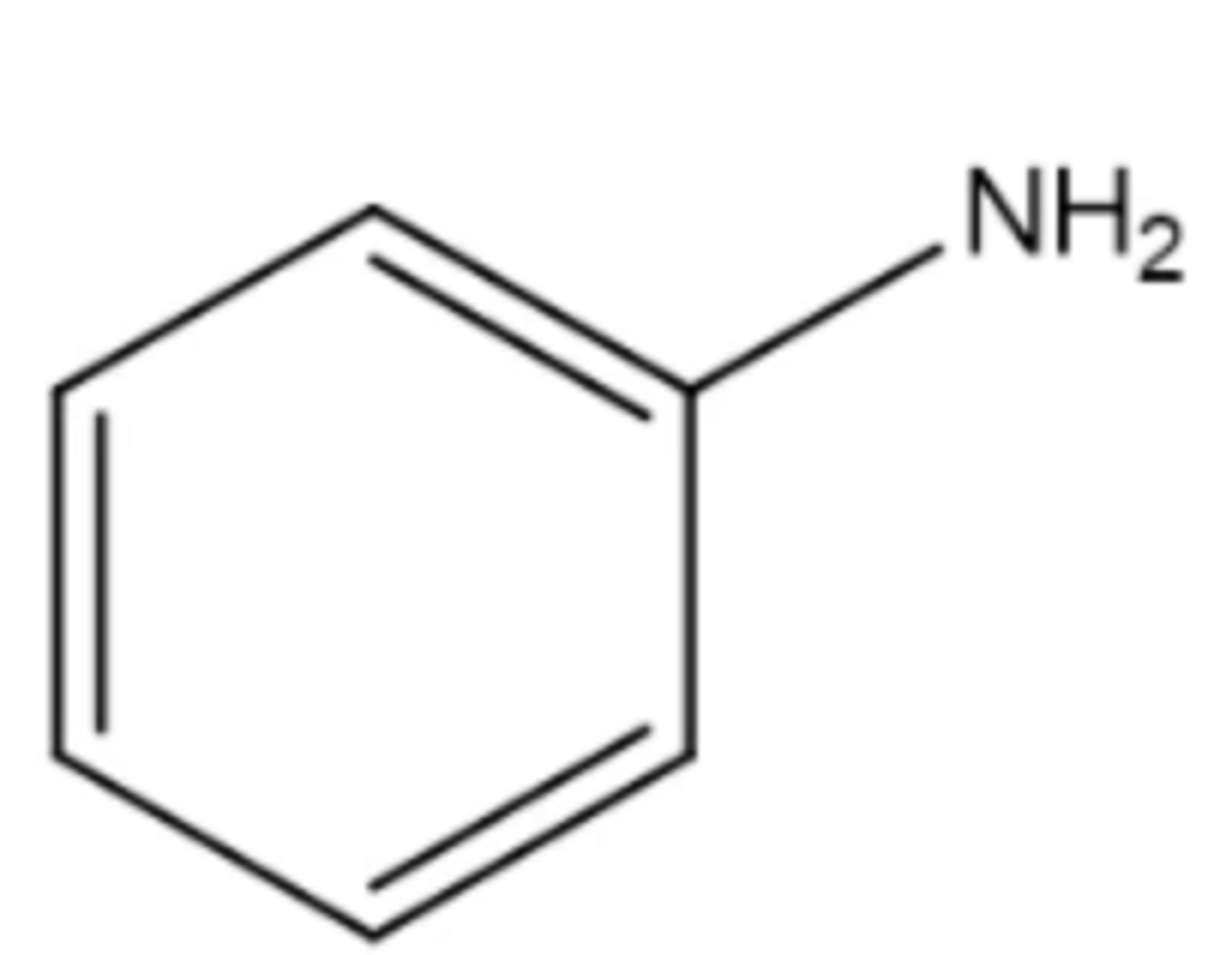
aniline
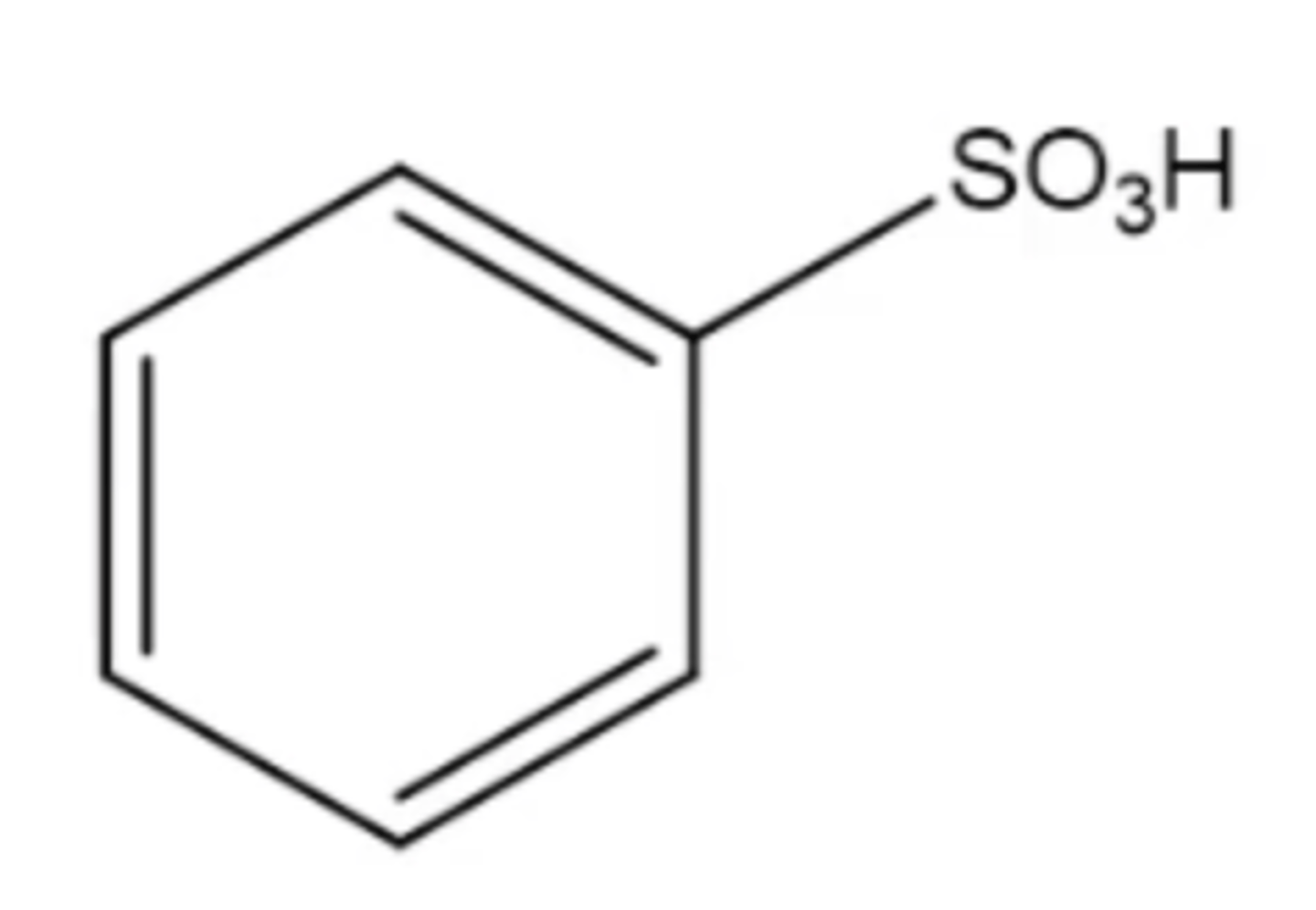
benzenesulfonic acid
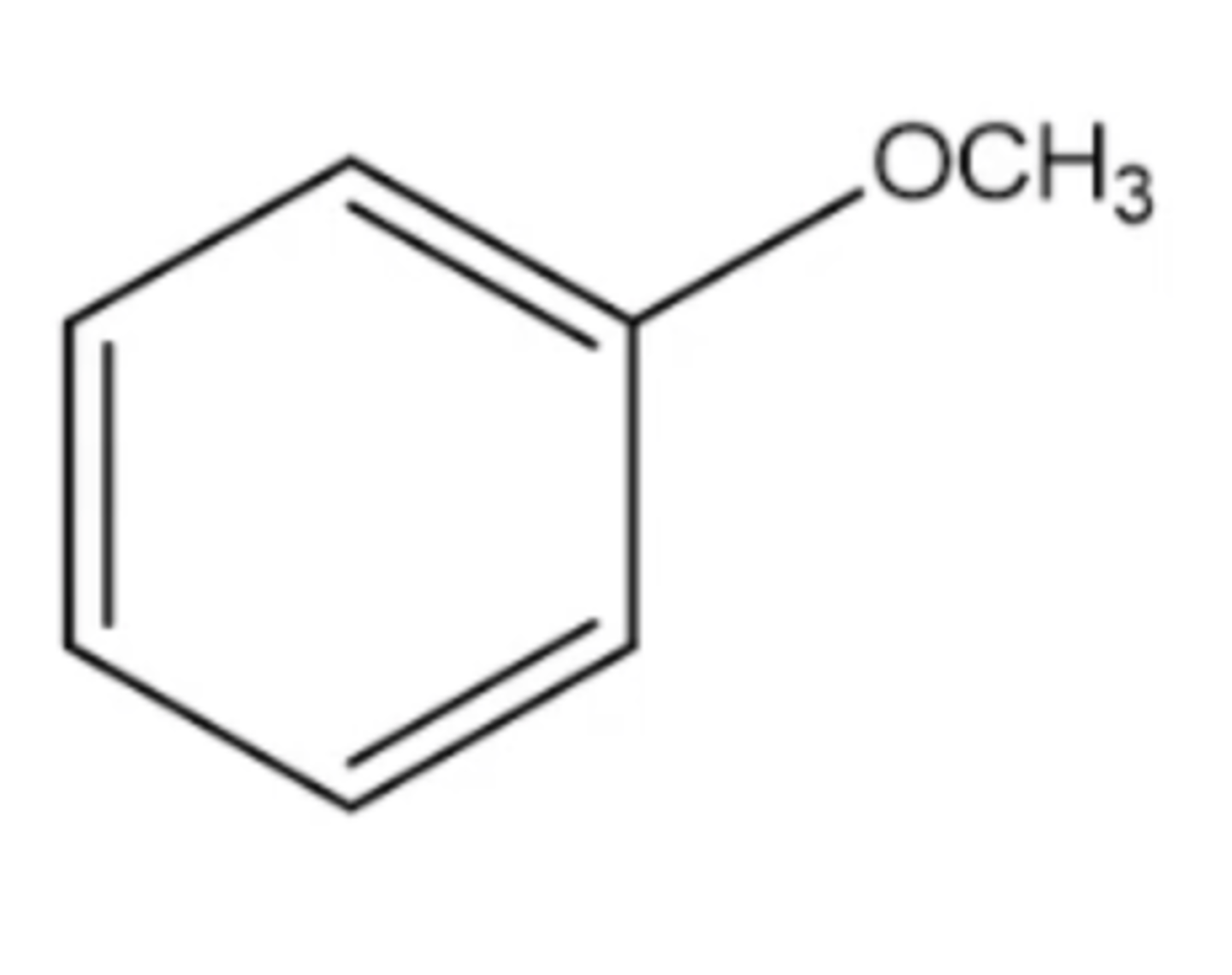
anisole
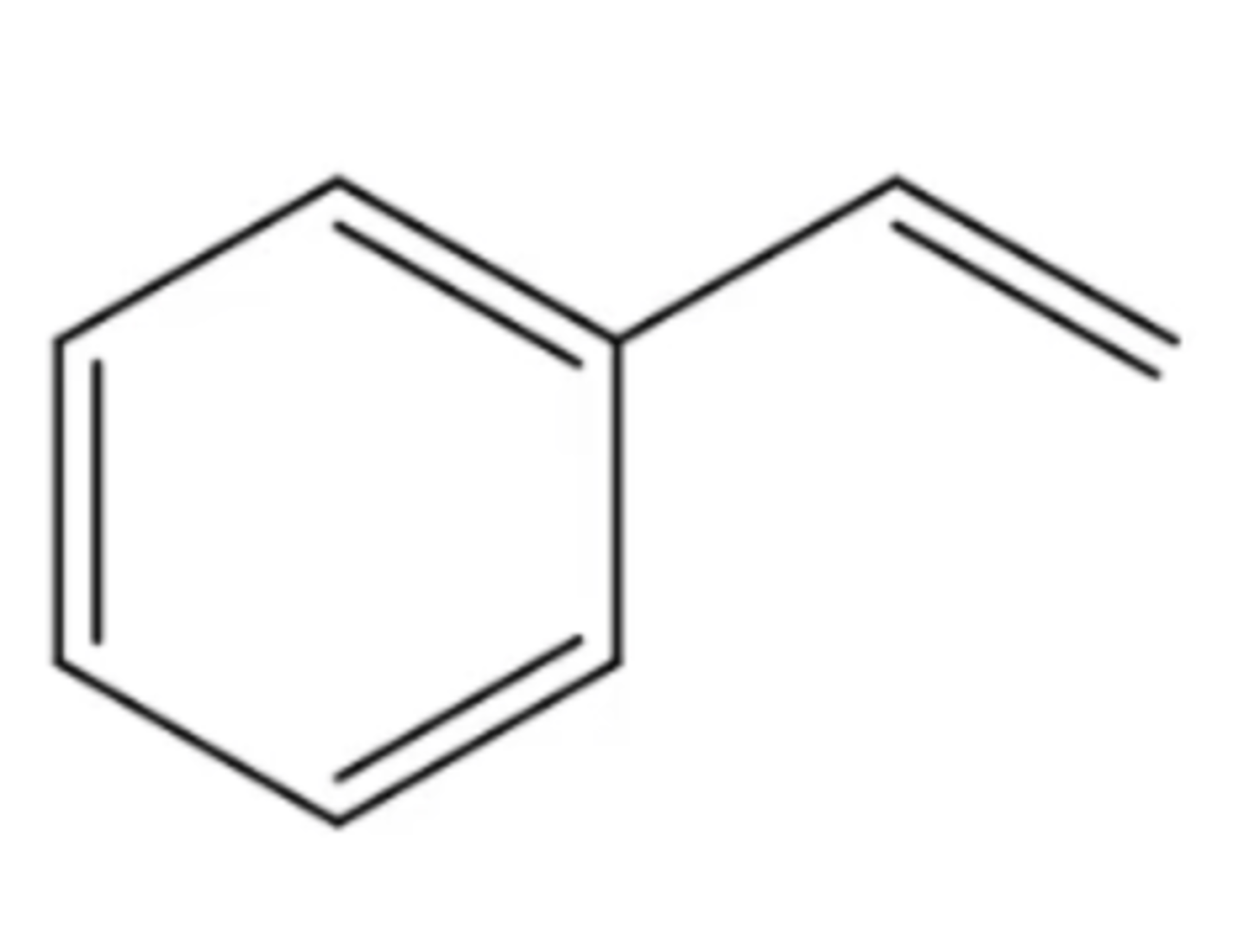
styrene
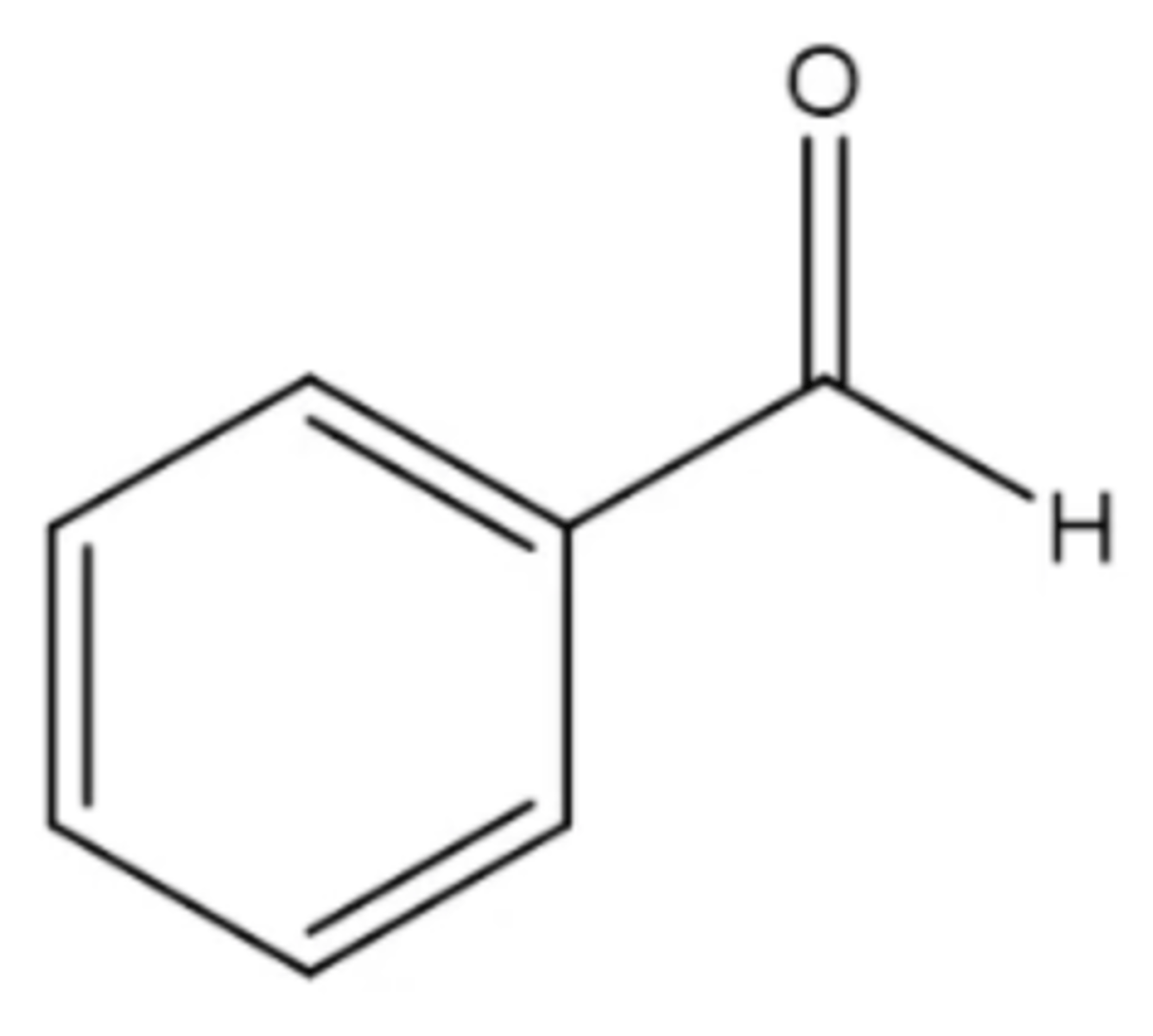
benzaldehyde
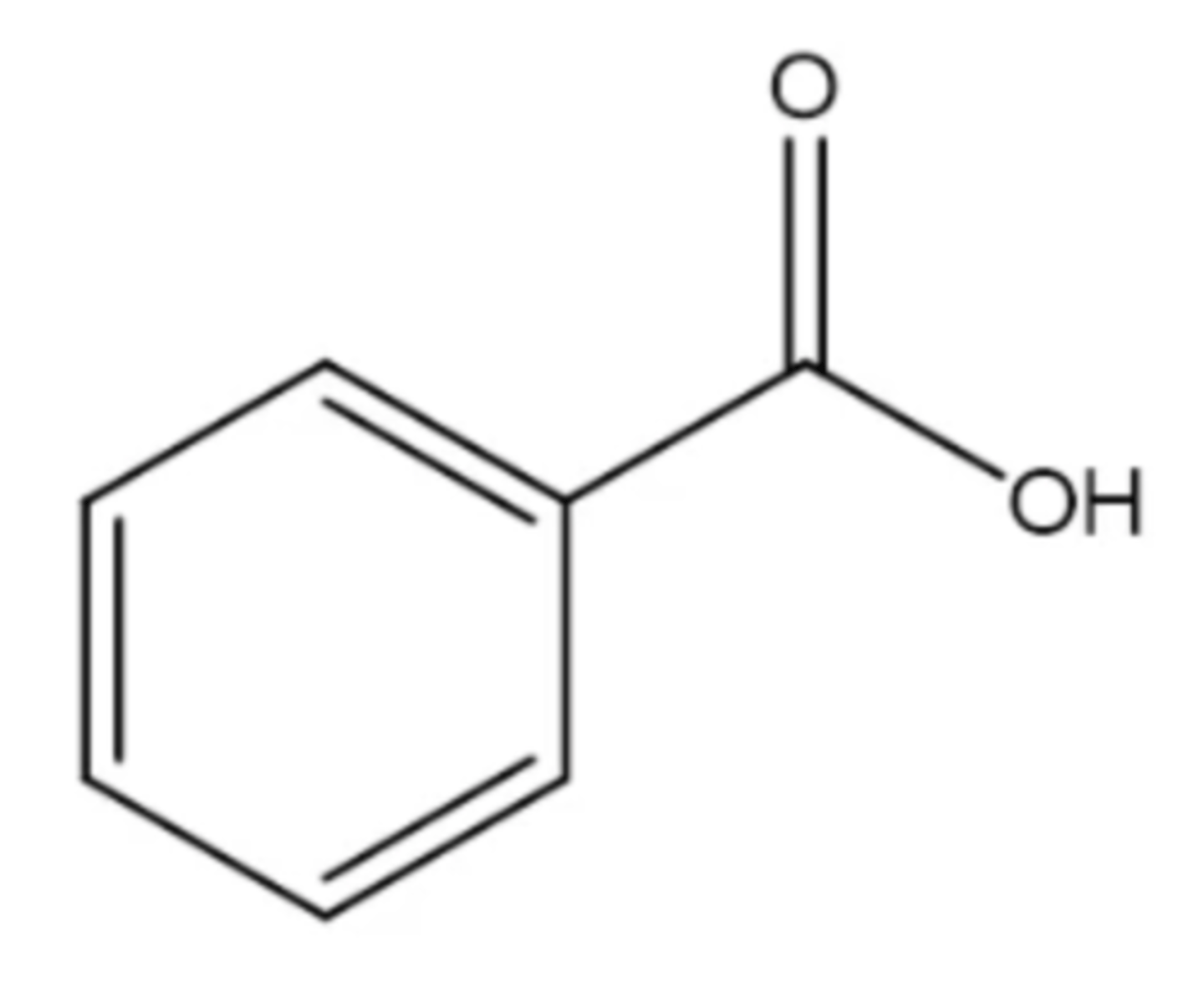
benzoic acid
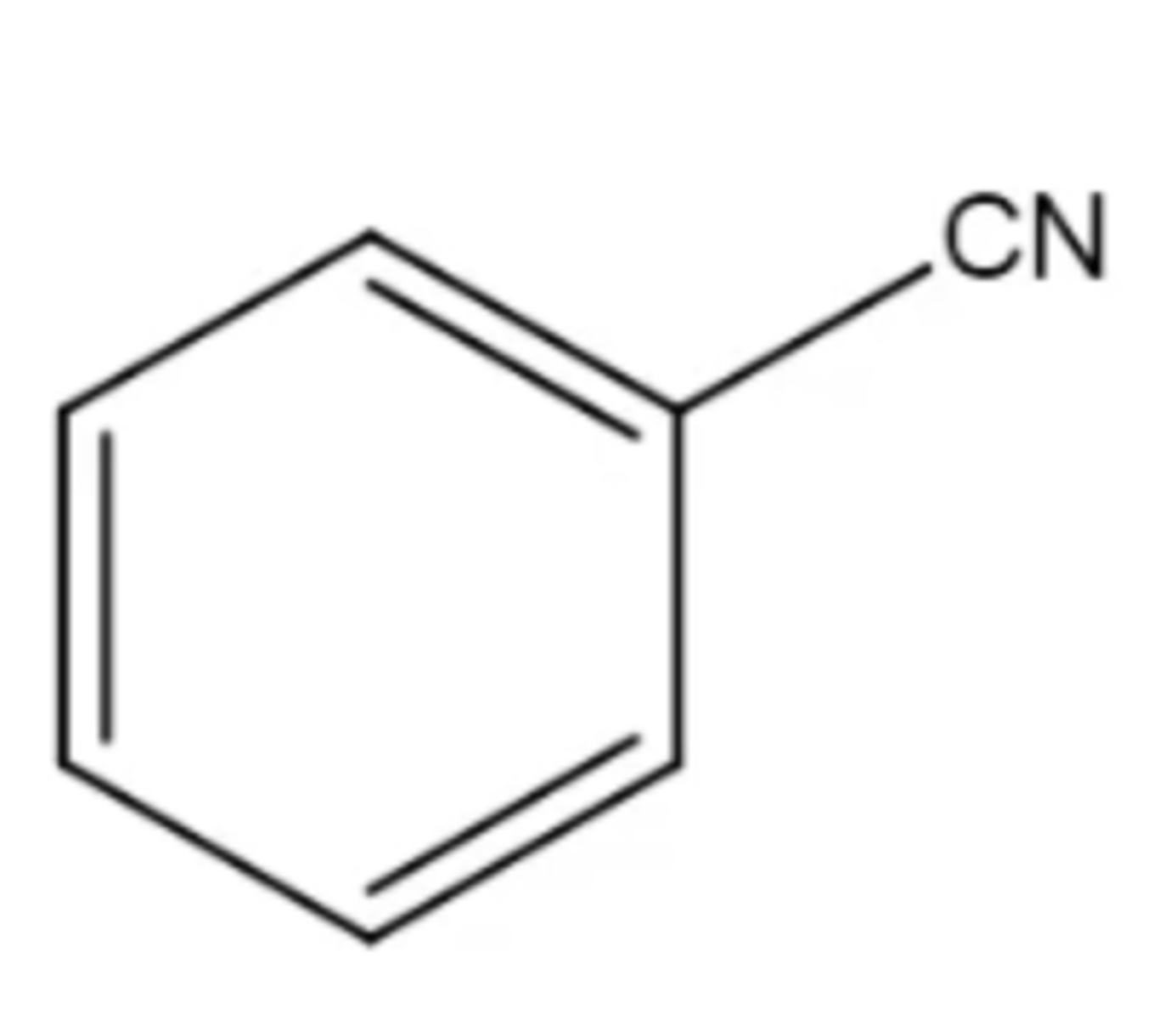
benzonitrile