Anatomy Quiz #2- Liver+GB
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lectures 4-5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
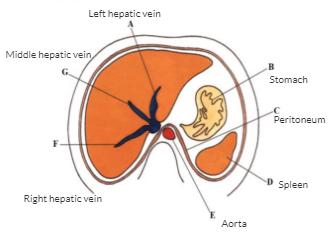
Transverse view of liver
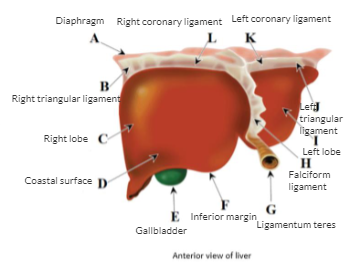
Anterior view of liver
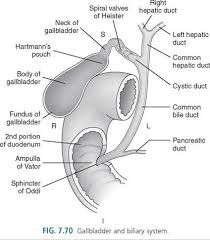
GI and Billiary system
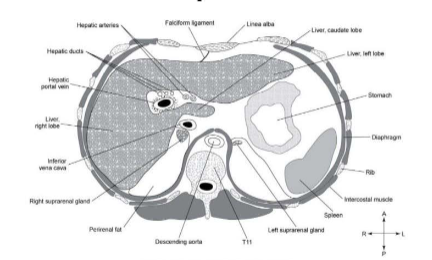
The liver overview
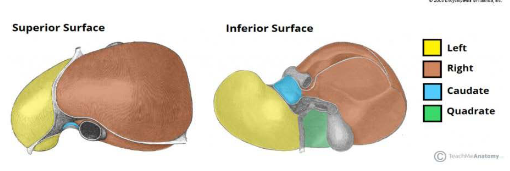
Largest internal organ
Occupies right hypochondriac epigastric region and part of the left hypochondrium
Lies inferior to the diaphragm
Lies in contact with diaphragm, esophagus, duodenum, right kidney, right adrenal, gallbladder right and the colic flexure
Glisson’s capsule
The fibrous layer covering entire liver
Reidels lobe
A tongue/finger like projection of right lobe more common in women
Appearance
Contour and shape of liver vary according to patient’s body habitus
Most of the liver is covered by the peritoneum except Bare area
The margins of the bare area of the liver are formed by the coronary ligaments
Area that rests directly on the diaphragm
IVC fossae
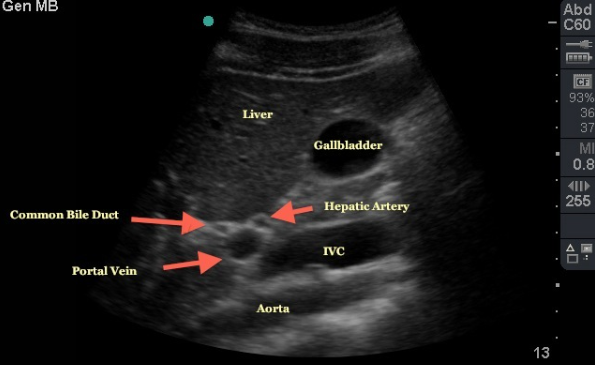
Porta Hepatis
Gallbladder fossae
Porta Hepatis
Hilum of liver where different structures enter/exit
On posterior inferior surface of organ
Portal Triad
Portal vein
bile duct
hepatic artery
Liver lobes LABELED
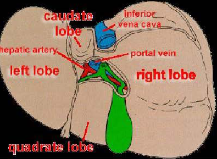
Right lobe
Exceeds left lobe by ratio of 6:1
Occupies right hypochondrial region
Inferior surface marked by three fossae (porta hepatis, gallbladder, IVC)
Left lobe
Smaller than RLL and varies considerably in size and shape
Caudate lobe
Small lobe on posteroSUPERIOR surface of LEFT lobe
Bounded by porta hepatitis, fossa for IVC, and ligamentum venosum.
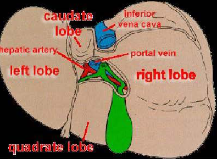
Quadrate lobe-known as medium segment of left lobe
Small lobe on posterior INFERIOR surface of LEFT lobe
Lies between gallbladder and fossa by ligamentum teres
Microscopic
Under microscope, the functional cells of the liver are known as hepatocytes
Liver fissures
Main lobar fissure
Separates right and left lobes
Right intersegmental fissure
Divides right lobe into anterior and posterior segments
left intersegmental fissure
Divides left lobe into medial and lateral segments
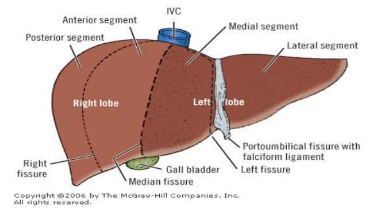
Cauinaud’s liver anatomy
Claude couinad- a french surgeon and anatomist was the first to describe segmental liver anatomy
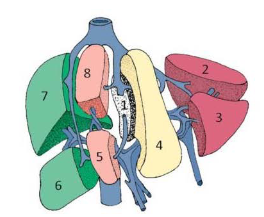
Liver ligaments
Connected to the diaphragm and abdominal wall by falciform ligament, ligamentum teres, coronary ligament (left/right), and triangular ligament (left/right)
Falciform ligament
Attaches anterior surface of liver to anterior abdominal wall
Divides right/left lobes as a peritoneal fold
Free margin of the ligament contains ligamentum teres
Ligamentum teres
Obliterated fetal remnant of the umbilical vein in the fissure
Divides left lobe into medial and lateral segments
Coronary ligament
Attach superior surface of the liver to the diaphragm
Triangular ligament
Attach superior sides of surface of liver sides to diapham
Ligamentum venosum
Fibrous remnant of ductus venosus of fetal circulation
Sits between caudate lobe and main parts of left lobe
Hepatic Recesses
Spaces between liver and surrounding structure
Clinical importance due to infected fluids that can collect in three areas forming an abscess
Subphrenic spaces
Subhepatic space
Morrisons pouch
Subphrenic spaces (left right)
Located between diaphragm and liver on either side of the falciform ligament
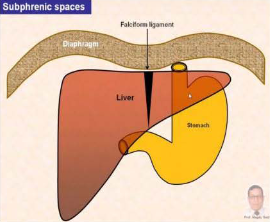
Subhepatic space
Between inferior surface of liver and stomach
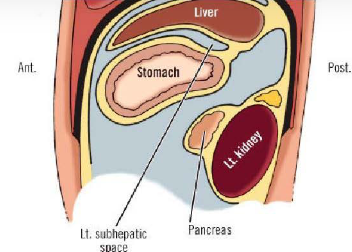
Morrisons pouch
Space posterior to right liver lobe and anterior to right kidney
Right subhepatic space
Liver blood supply
Recieves dual blood supply from the portal vein and the hepatic arteries
Portal vein supplies 75% of blood to liver while hepatic arties supply 25%
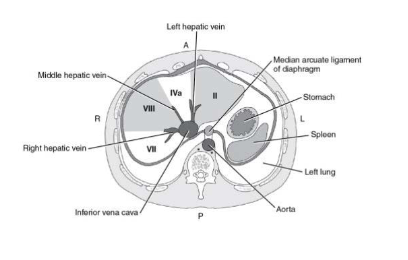
Transverse view of liver segments (slide 43)
Biliary system
The biliary system is composed of the gallbloadder and bile ducts (intra/extrahepatic)
Serves to drain the liver of bile and store it until it is transported to the duodenum to aid in digestion
Together with the liver and pancreas the biliary system plays a role in the digestive process
Bile ducts
The intrahepatic ductal system begins at a microscopic level in the liver lobule
The intrahepatic ducts merge into larger ducts as they follow a course from the periphery to the central portion of the liver eventually forming the RIGHT and LEFT hepatic duct
The ducts run beside the hepatic arteries and protal veins throughout the liver parenchyma
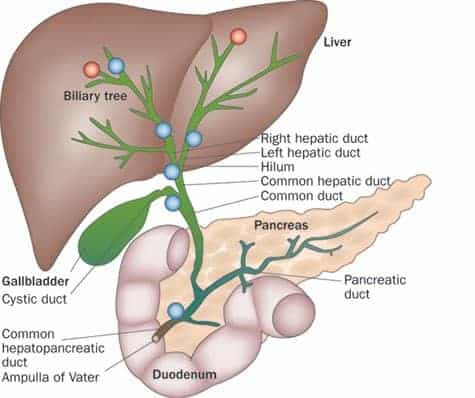
The RIGHT and LEFT hepatic duct into the COMMON hepatic duct
unite at approximately the level of the porta hepatis and together they form the COMMON HEPATIC DUCT which marks the beginning of the EXTRAherpatic biliary system
the COMMON hepatic duct is located anterior to the portal vein and lateral to the hepatic artery in its caudal descent from the porta hepatis
the COMMON hepatic duct runs PARALLEL with the PORTAL VEIN, travels medially in the body and is joined by the CYSTIC DUCT to form the COMMON BILE DUCT
Common Bile Duct
role is to transport bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum
continues caudal descent along hepatic artery and portal vein
curves slightly to the right away from the portal vein and then posterior and medium to the first part of the duodenum behind pancreas head
distal portion lies in a groove on the posterior surface of the head of the pancreas where it joins the main PANCREATIC duct
ampulla of vater
common bile duct and main pancreatic duct form the apmulla of vater which empties its contents through the major papilla (opening of duodenum)
the opening of the duodenum is controlled by the SPHINCTER OF ODDI
cystic duct
4cm in length
connects gallbladder to biliary tree by joining the common hepatic duct
cystic duct+common hepatic duct= common bile duct
contains tiny projections (spiral valves) which serve to keep lumen of the duct open
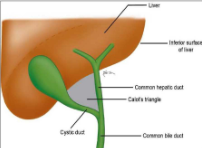
gallbladder
reservoir for storign and concentrating bile before going to duodenum
intraperitoneal organ
pear shaped
fundus/body/neck
fundus
common for gallstones to collect
body
lies to the right of the porta hepatis and continues as the cystic duct before meeting with the hepatic to the COMMON BILE DUCT
Gallbladder layers
serosal (OUTER)
fibromuscular (middle) controls contractions
stimulated by cholecystokinin to force bile into the duodenum in response to fat/protein ingestion
mucosal (inner) ruage is found
bile
alkaline fluid formed in the liver
stored in gallbladder
discharged into duodenum
used to assist digestion and absorption of fat and eliminate cholesterol/bilirubin
rugae
folds of the wall in an expandable organ
gb blood supply
cystic artery supplies from the right hepatic artery
drainage is via cystic vein into the portal vein
major impression in the right lobe
right kidney and COLONIC FLEXURE
what separates the right and left lobe of the liver?
middle hepatic vein (falciform cannot be seen in scan)
in coronal view what would you see first from the right to left?
you would see the gallbladder first (coronal u get a slice of tje back half of body)
the bare area of the liver is formed by the?
coronary ligaments