Structure of DNA double helix
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What did X-ray diffraction of DNA show
DNA is helical
Strands are anti-parallel
Describe the B-form of DNA
Right-handed double helix
Hydrophobic bases = inside
Perpendicular
10 bases per turn
Hydrophilic backbone = outside
Complementary base pairs = hydrogen bonds
3’-5’ phosphodiester links
Describe other structures of nucleic acids
A-form DNA = dehydrated DNA
A-form RNA = double helical
Z-form DNA = left handed helix
Distinguish between major and minor grooves of DNA
Major = wider + deeper
Sugar phosphate backbone are close together
Most proteins bind here
Minor = smaller
Sugar phosphate backbone are further apart
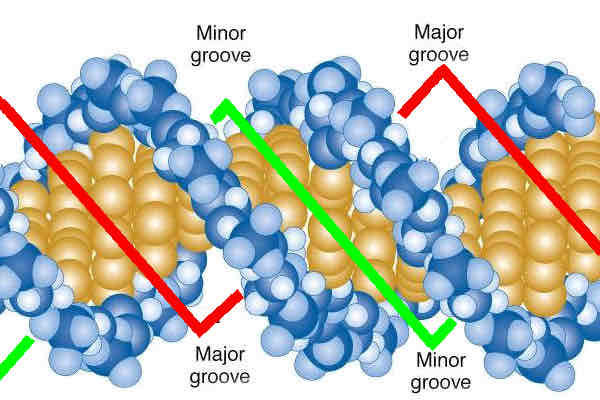
What are major and minor grooves of DNA
Make it easy for bases to be accessed
Have atoms that can for hydrogen bonds with proteins = can regulate transcription/translation or alter structure
What happens when you heat dna
Desaturation - strand seperates
What happens when you cool down dna
Cool quickly = strands stay apart
Cool slowly = strands rejoin
Nucleuses
Cut DNA
Ligase
Join 2 molecules together
Polymerases
Make DNA
Kinases
Add phosphate group
Phosphatases
Re love phosphate groups
Topoisomerases
Type 1 = single-stranded cuts in DNA
Type 2 = double strand breaks in DNA