Practice Comprehensive Final
1/530
Earn XP
Description and Tags
vestibule
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
531 Terms
What are clusters of neuronal cell bodies in the central nervous system called?
nuclei
What is the functional classification for neurons that carry information from peripheral receptors to the central nervous system?
sensory
What type of glial cell is responsible for supporting neurons and maintaining the blood/brain barrier?
astrocyte
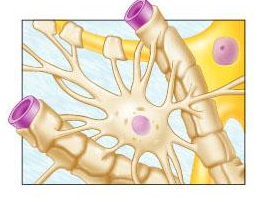
identify the type of glial cell shown.
astrocyte
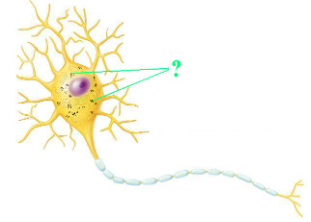
Identify the indicated part of a neuron.
nissl bodies
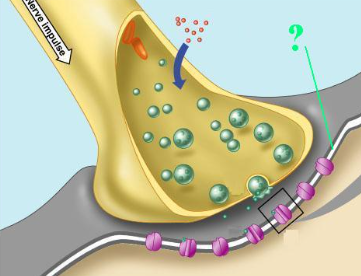
Identify the indicated part of a synapse.
postsynaptic membrane
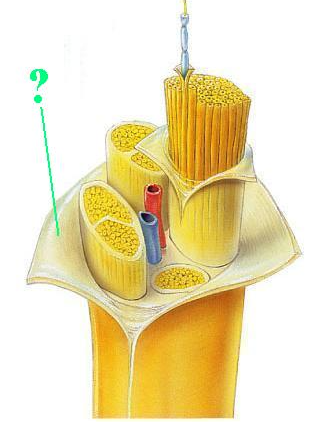
Identify the indicated connective layer of a nerve.
epineurium
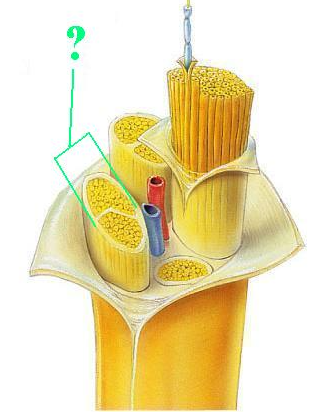
Identify the indicated part of a nerve.
fascicle
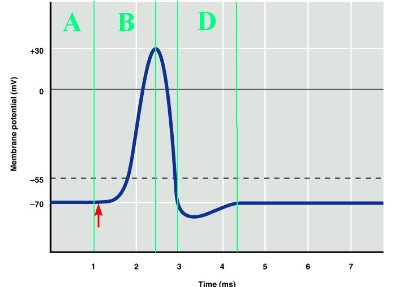
Which labeled portion of the diagram corresponds to the resting potential of the axon?
A
What do we call the period during which initiation of an action potential requires a higher than normal threshold stimulus?
relative refractory period
Hyperpolarization is the result of the excessive exit of which ion from the cell?
potassium
In the PhysioEx exercise, what was the effect of curare on the nerve?
inhibition
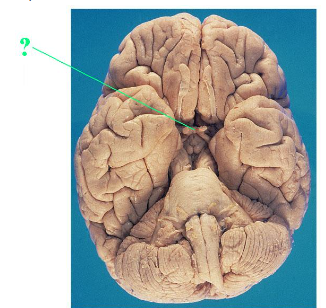
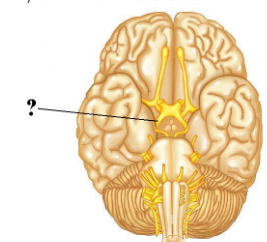
Identify the indicated structure of the brain.
optic chiasm
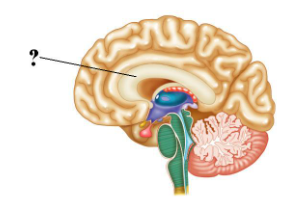
Identify the indicated structure of the brain.
corpus callosum
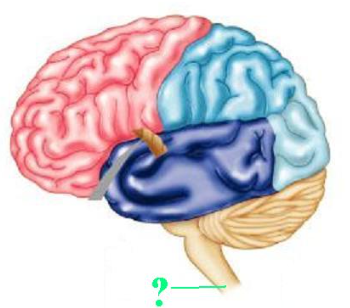
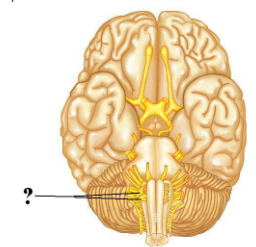
Identify the indicated structure of the central nervous system.
spinal cord
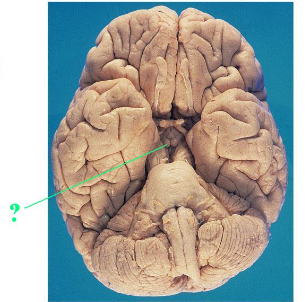
Identify the indicated structure of the brain.
mammilary bodies
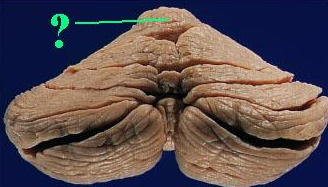
Identify the indicated lobe of the cerebellum.
anterior lobe
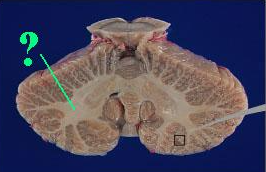
Identify the indicated portion of the cerebellum.
white matter
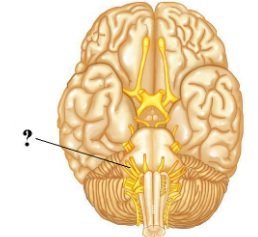
Identify the indicated structure.
optic tract
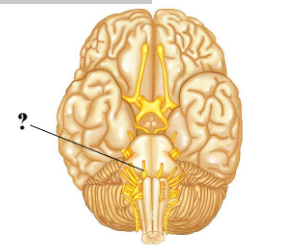
Identify the indicated cranial nerve.
hypoglossal
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?
sensory
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?
motor
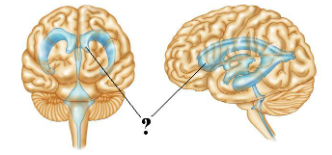
Identify the indicated portion of this space.
anterior horn of lateral ventricle
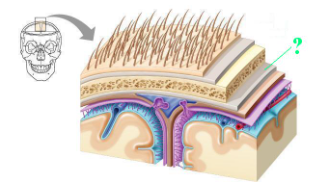
Identify the indicated part of the coverings of the brain.
periosteal dura mater
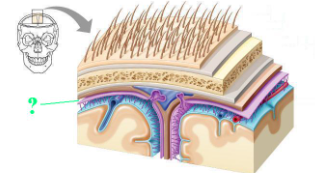
Identify the indicated space.
subdural space
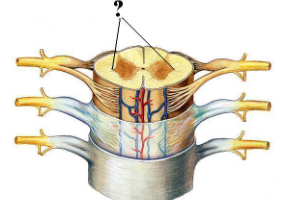
Identify the indicated structure (be specific).
lateral horn
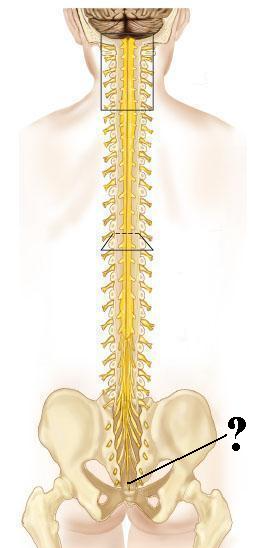
Identify the indicated structure.
filum terminale
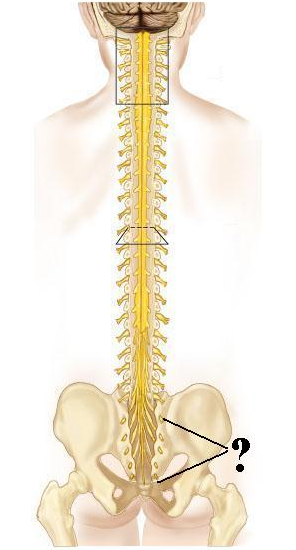
Identify the indicated structures.orbicularis occuli muscle
sacral spinal nerves
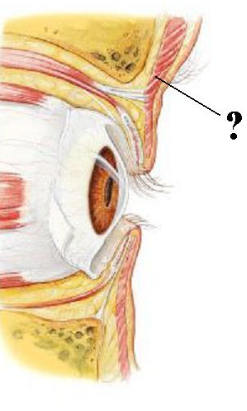
Identify the indicated structure.
orbicularis occuli muscle
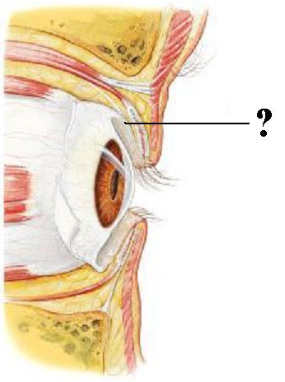
Identify the indicated layer.
palpebral conjunctiva
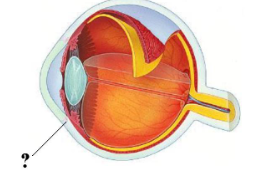
Identify the indicated opening.
canal of schlemm
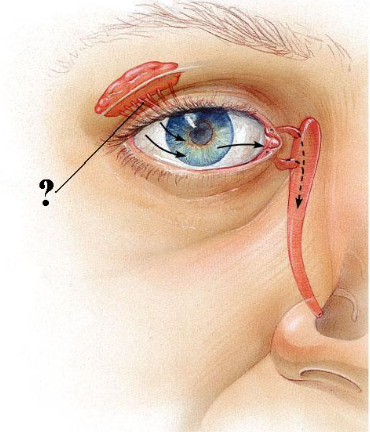
Identify the indicated structures.
excretory ducts of lacrimal glands
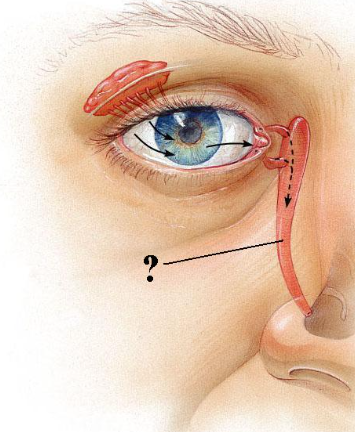
Identify the indicated structure.
nasolacrimal duct
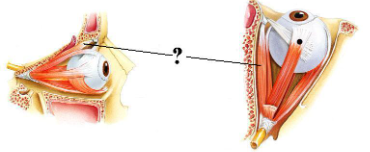
Identify the indicated structure.
superior oblique muscle
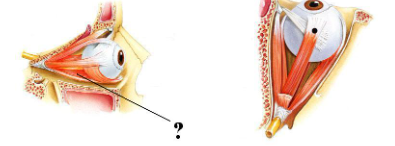
Identify the indicated structure.
inferior rectus muscle
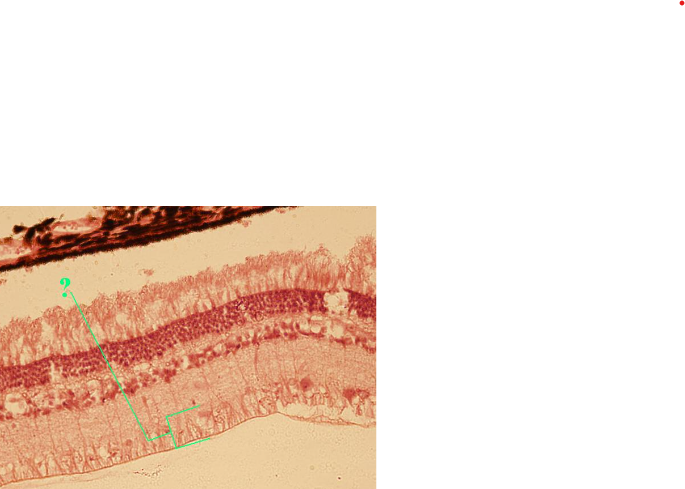
Identify the indicated layer of the retina.
ganglion cell layer
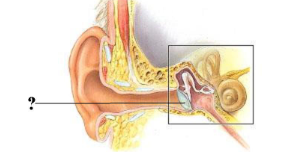
Identify the indicated structure.
tympanic membrane
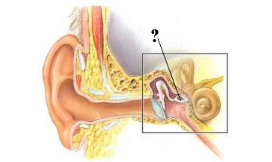
Identify the indicated structure.
stapes
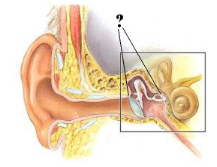
Identify the indicated region of the ear.
middle ear
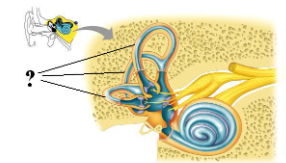
Identify the indicated structures.
semicircular canals
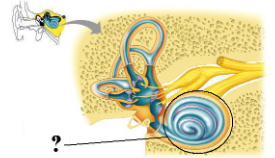
Identify the indicated structure.
cochlea
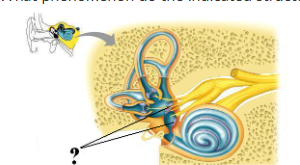
What phenomenon do the indicated structures sense?
static equilibrium
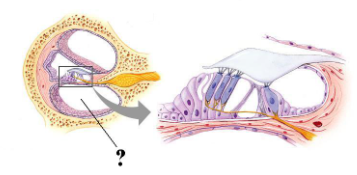
Identify the indicated space.
scala tympani
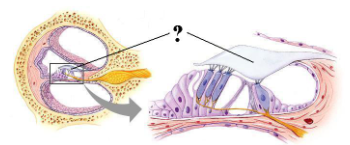
Identify the indicated structure.
tectorial membrane
What fluid fills the scala tympani?
perilymph
The bending of light as is passes from a material of one density to a material of a different density is called:
refraction
Which cranial nerve supplies the medial rectus muscle of the eye?
occulomotor
Which of the three tunics (layers) does the iris belong to?
vascular
To which portion of the ear (outer, middle, inner) does the acoustic meatus belong?
outer ear
With which sense (hearing, static equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium) is the utricle associated?
static
The term "axillary" refers to which region of the body?
armpit
The shoulder is __________ to the elbow.
proximal
The ears are __________ to the nose.
lateral
ventral
medial
You are examining a microscope slide under the 4X objective lens and you switch to the 10X objective lens. The height of the focal point will:
a) increase
b) stay the same
c) decrease
b)stay the same
Which objective lens has the greater depth of field: 100X or 40X?
40X
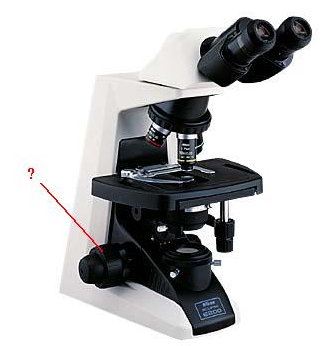
Identify the indicated part of the microscope.
coarse adjustment knob
Given the following physiological requirements at a particular location within the body, name the specific tissue type that would most likely be found there:
This surface must stretch to accommodate the stretching of a hollow organ.
transitional epithelium
Name the criteria by which connective tissues are classified? (check all that apply)
protein fiber type
cell type
matrix composition
arrangement of protein fibers
What do we call an epithelial tissue that is one cell layer thick and is composed of cells that are as high as they are wide?
simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
What primary type of tissue is both excitable and contractile?
muscular
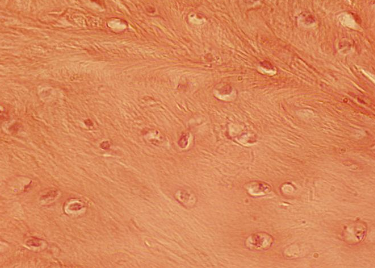
Identify the indicated tissue.
fibrocartilage
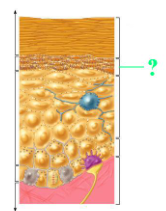
Identify the indicated region of the epidermis.
stratum granulosum
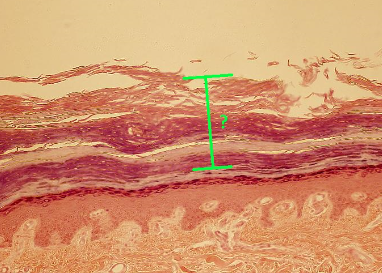
Identify the indicated layer of thick skin.
stratum corneum
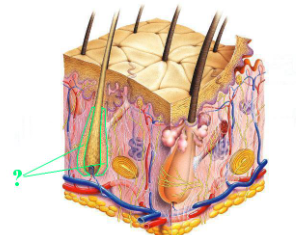
Identify the indicated structure of the integument.
hair follicle
What double walled organelle contains enzymes that oxidize foodstuffs to produce cellular energy?
mitochondrion
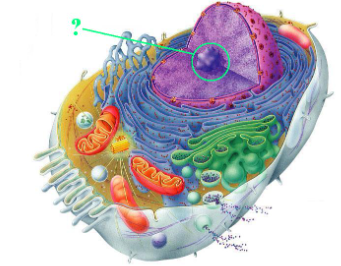
Identify the indicated cellular organelle.
nucleolus
The nuclear membrane disappears during which phase of mitosis?
late prophase
The two main divisions of the skeleton are the appendicular skeleton and the:
axial
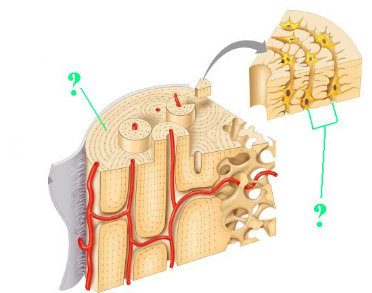
Identify the indicated structure (layer) within compact bone.
lamella

What type (shape) of bone is indicated?
sesamoid
Each osteon is composed of several layers of concentric material. Each layer is called a:
lamella
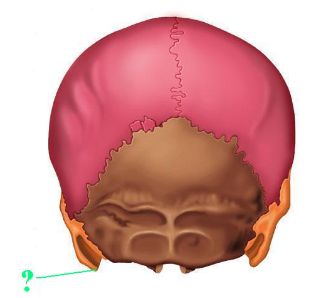
Identify the indicated bone marking (projection).
mastoid process
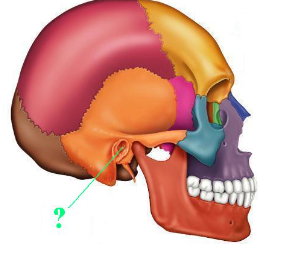
Identify the indicated bone marking (opening).
external acoustic meatus
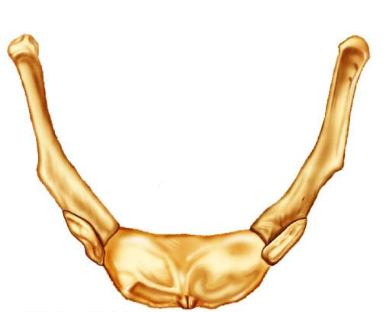
Identify the indicated bone.
hyoid
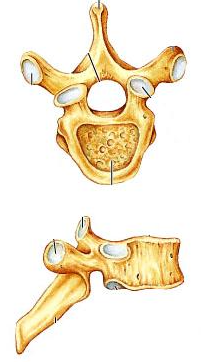
Identify the indicated type of vertebra.
thoracic
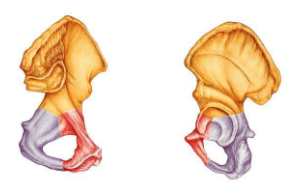
Identify the indicated bone.
innominate
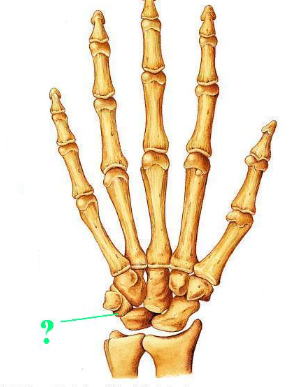
Identify the indicated bone
triquetral
cuneiform
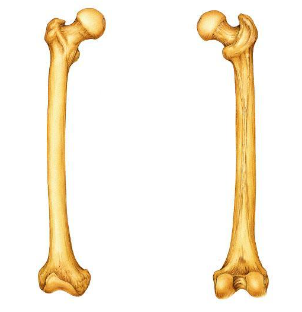
Is the indicated bone from the right of left side of the body?
right
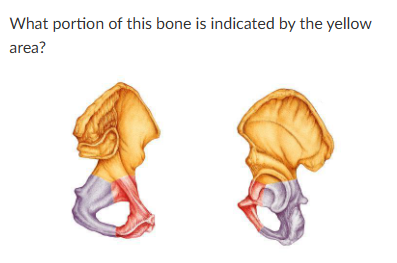
ilium
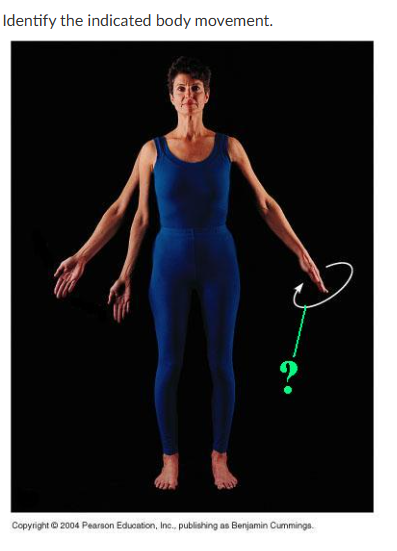
circumduction
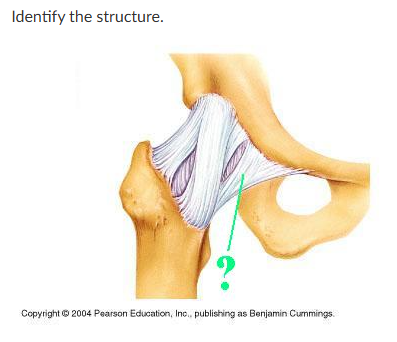
pubofemoral ligament
What structural type of articulation is a syndesmosis?
fibrous
What is the name of the type of synovial joint that has rotational movement around more than two axes where a round head fits into a cup-like depression?
ball and socket
List two of the seven criteria listed in your lab manual that are used to name muscles?

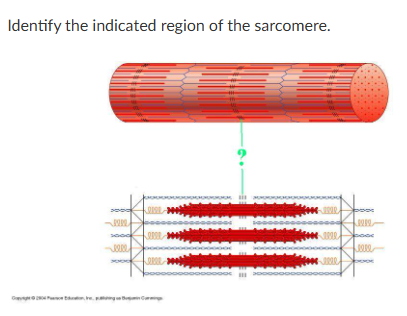
M-line
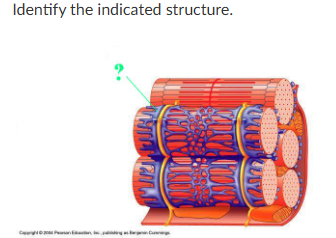
terminal cistern of sarcoplasmic reticulum
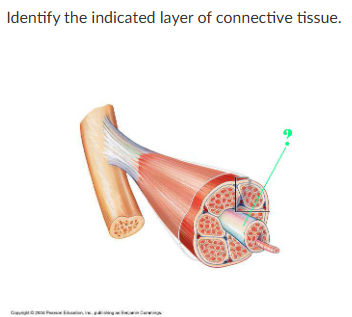
perimysium
A single motor neuron, along with all of the muscle fibers that it innervates, is called:
motor unit
What do we call muscles that are primarily responsible for producing a specific movement?
agonists
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the adductor magnus muscle?
action and relative size
Although no force is generated by a muscle fiber during the latent period, chemical changes, such as the release of ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum do occur. Which ion is released
calcium
Name one action of the supraspinatus muscle.
a)elevation of the mandible
b)abduction of the arm at the shoulder
c)elevation of the scapula
d)rotation of the head
e)lateral rotation of the vertebral column
b)abduction of the arm at the shoulder
Name one insertion of the gracilis muscle.
A)linea aspera of the femur
B)medial surface of the fibula
C)body of the pubis
D)medial surface of tibia
E)patella
D)medial surface of tibia
Name one origin of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
A)skin and muscle at the corner of the mouth
B)frontal bone
C)Ramus of the mandible
D)skin of the eyebrow
E)zygomatic arch
B)frontal bone
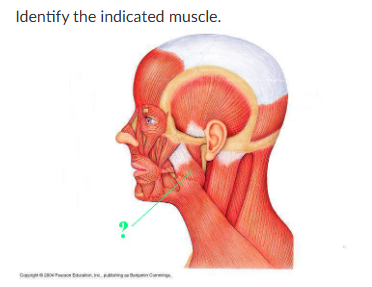
masseter
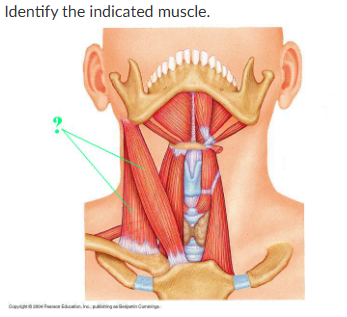
sternocleidomastoid
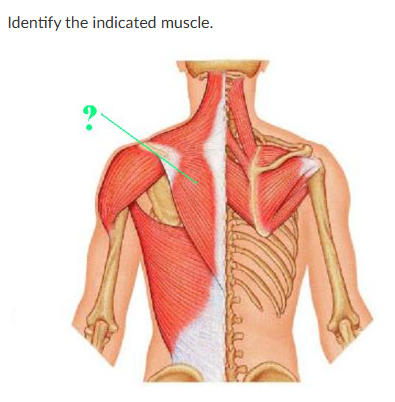
trapezius
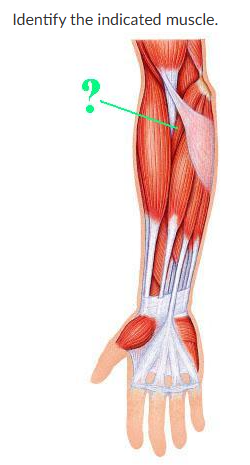
pronator teres
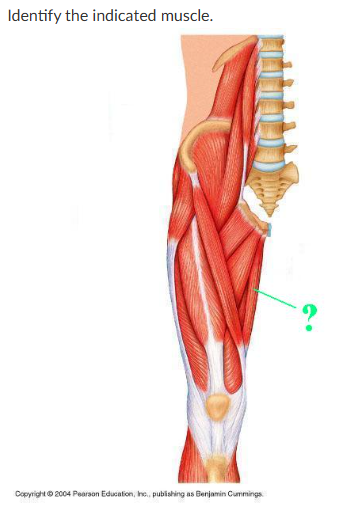
gracilis
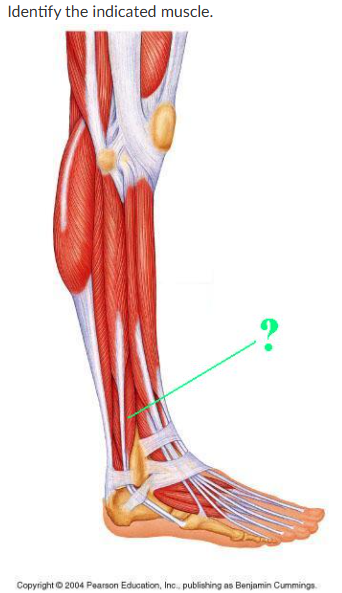
fibularis brevis