Immune attack on tissues
What is tissue damage in immunology
Hypersensitivity
What is an allergy
A disorder in which the immune system is overly sensitive to a foreign substance
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is tissue damage in immunology
Hypersensitivity
What is an allergy
A disorder in which the immune system is overly sensitive to a foreign substance
What is autoimmunity?
When body attacks its own cells
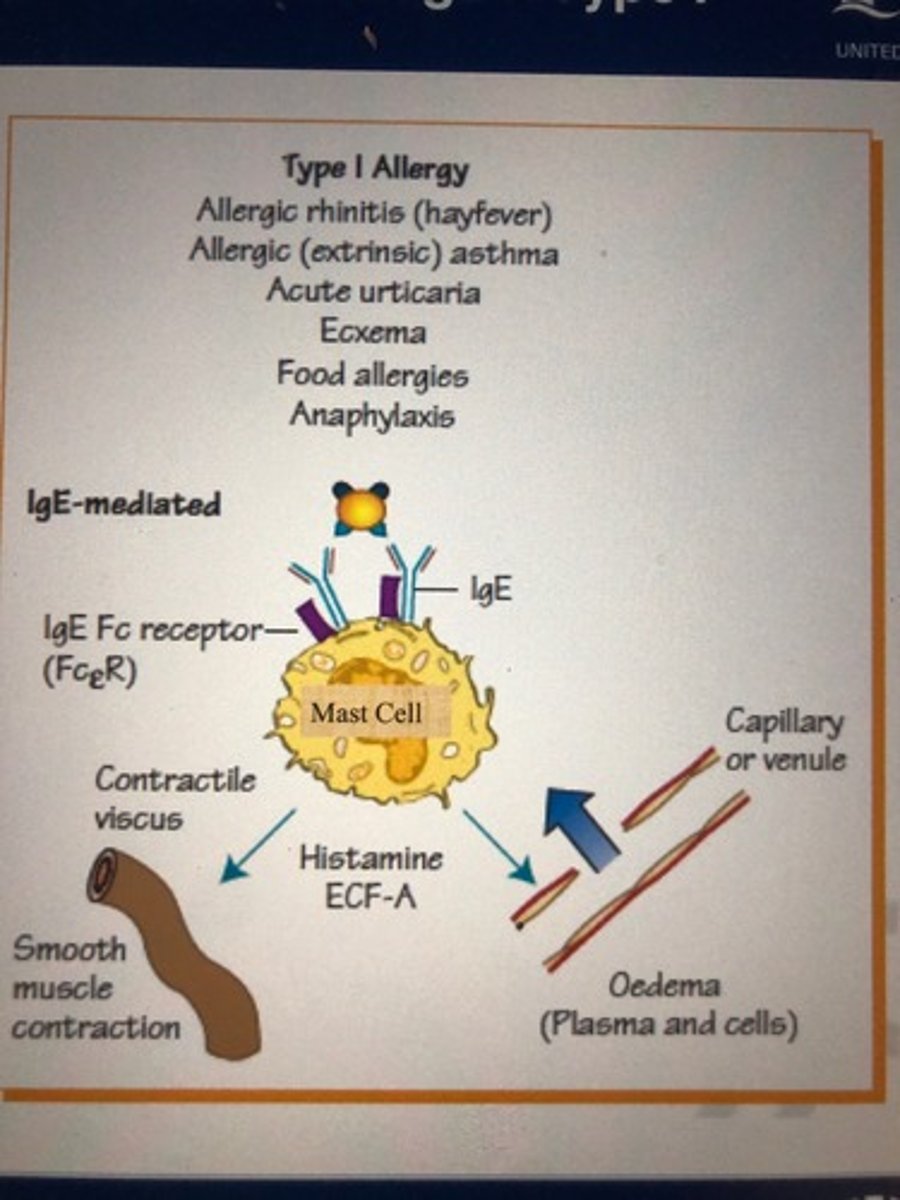
What is type 1 hypersensitivity?
-Antigen binds to IgE found on mast cells or basophils
-triggers release of histamine
-occurs in allergies
What is type II hypersensitivity?
IgG or IgM attack antigens on body's own cells
triggers activation of complement ,NK cells and macrophages
Type III hypersensitivity
soluble antigen forms complex with IgG/IgM and accumulate in tissues causing damage
Type I II and III hypersensitivity are
Antibody mediated
Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
T-cell mediated disorders
T H1 activate macrophages to clear foreign material
Leads to Tissue damage
What are the 4 hypersensitivity reactions
Normal immune reactions but activated inappropriately or excessively
Another rename for type 1 hypersensitivity
Atopic allergy
3 components of atopic allergy
Mast cells
Allergens
IgE
What do mast cells usually do
Generate rapid inflammatory response
What happens in atopic allergy
IgE get cross linked
Because it's bound to an allergen
Activated mast cell to degranulate
To release inflammatory mediators
And cause smooth muscle contraction and oedema
What does degranulate mean
Release of contents of granules
From mast cells
Like inflammatory mediators
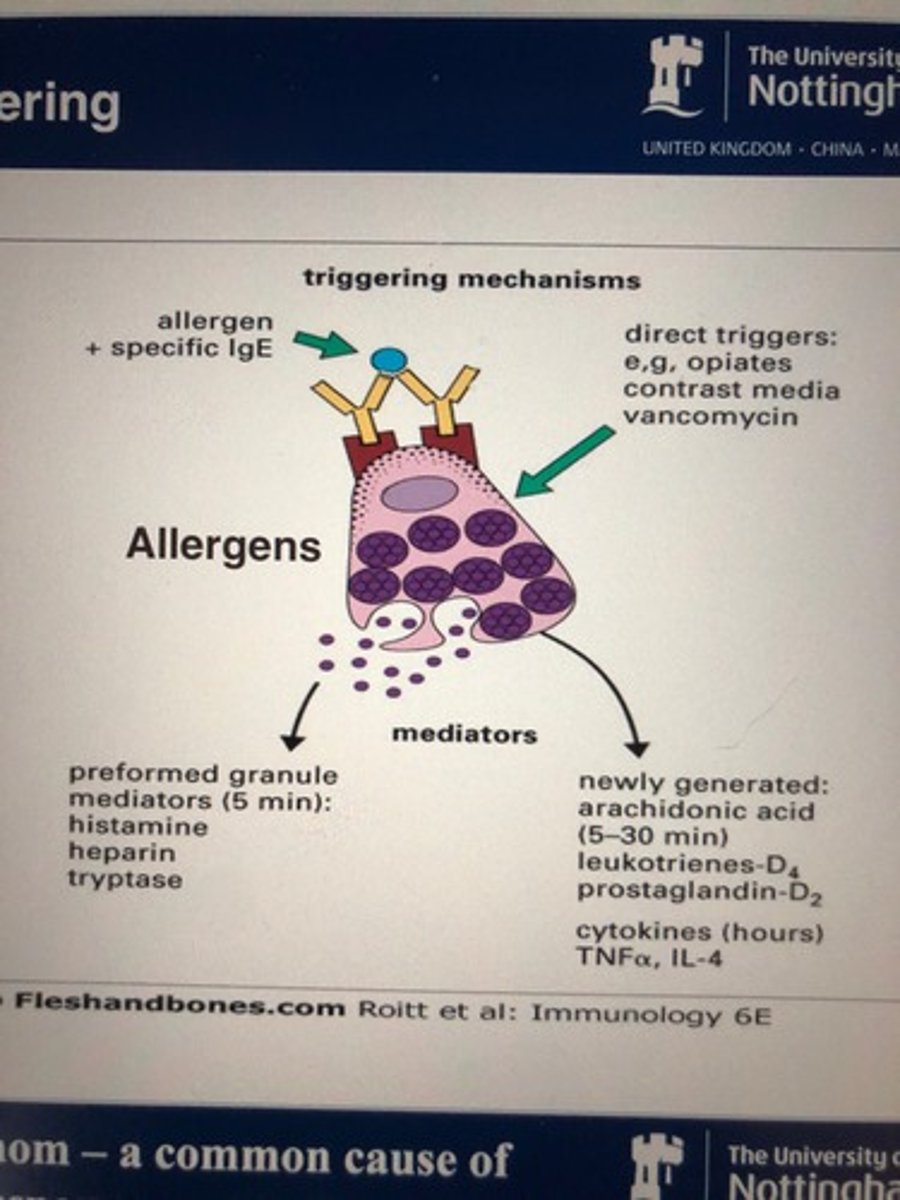
Mechanism of tissue damage 1
Antigen up by APC
Presented on MHC 2 (not a virus)
Interact with CD4 T helper 2 cell
Produce cytokines (IL4)
Helps B cell change surface IgM to Class switch to produce IgE
Specific to the allergen
Bind to mast cell Receptor
Allergen returns binds to surface IgE on mast cell
releases hisramines
Performed and newly performed mediators
Inflammation
What is first exposure to allergen
Sensitisation
Is presented by MHC 2
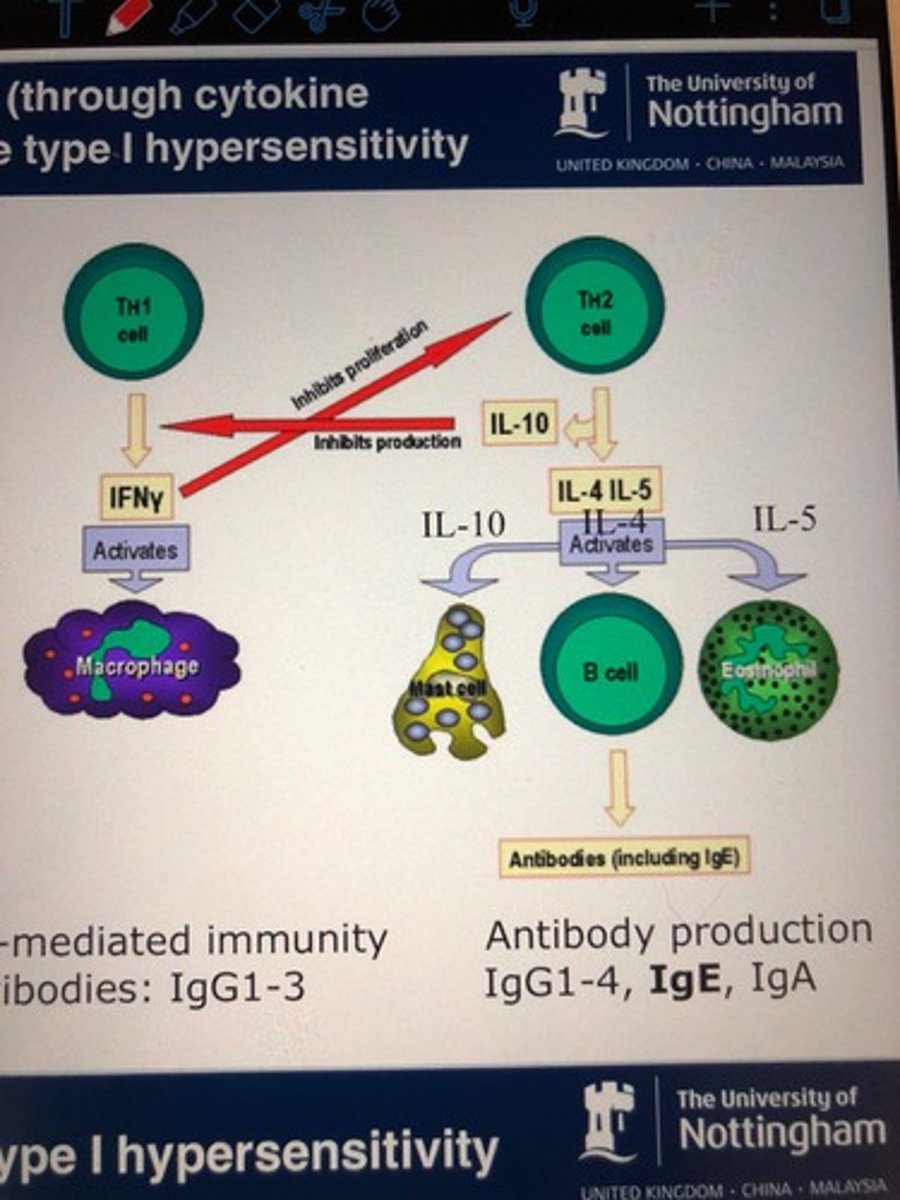
What do Th2 cells do?
stimulate humoral (antibody) response
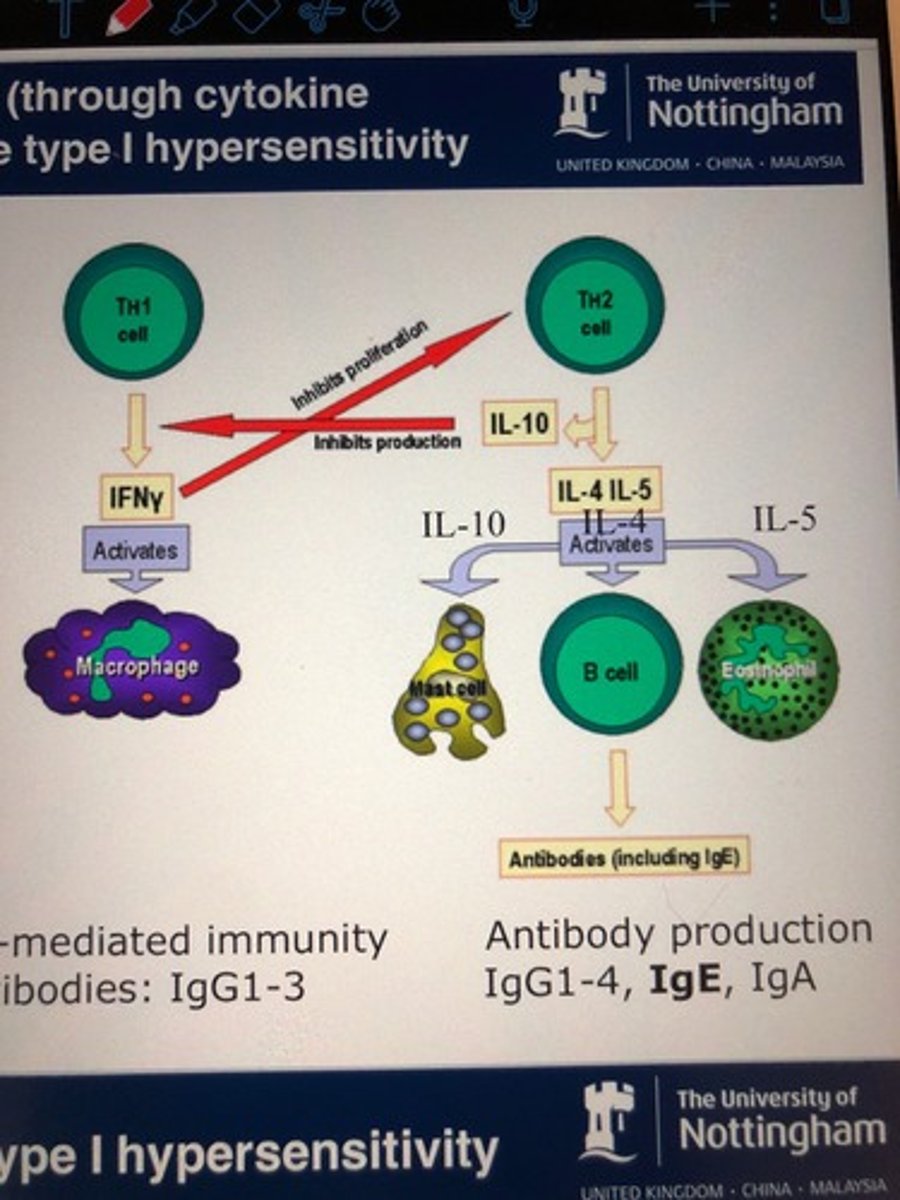
What interleukins are released by TH2 (EEM)
IL4 - class switch to IgE
IL5 - stimulate eosinophils
IL 10 - mast cell activation
What is second exposure to same allergen called
Elicitation
What happens in the elicitation phase
IgE bind to allergen
Cross linked
Mast cell produce pre formed and newly formed mediators
Inflammation
What are in preformed granules (made and released quickly )
Histamine
Heparin
Tryptase
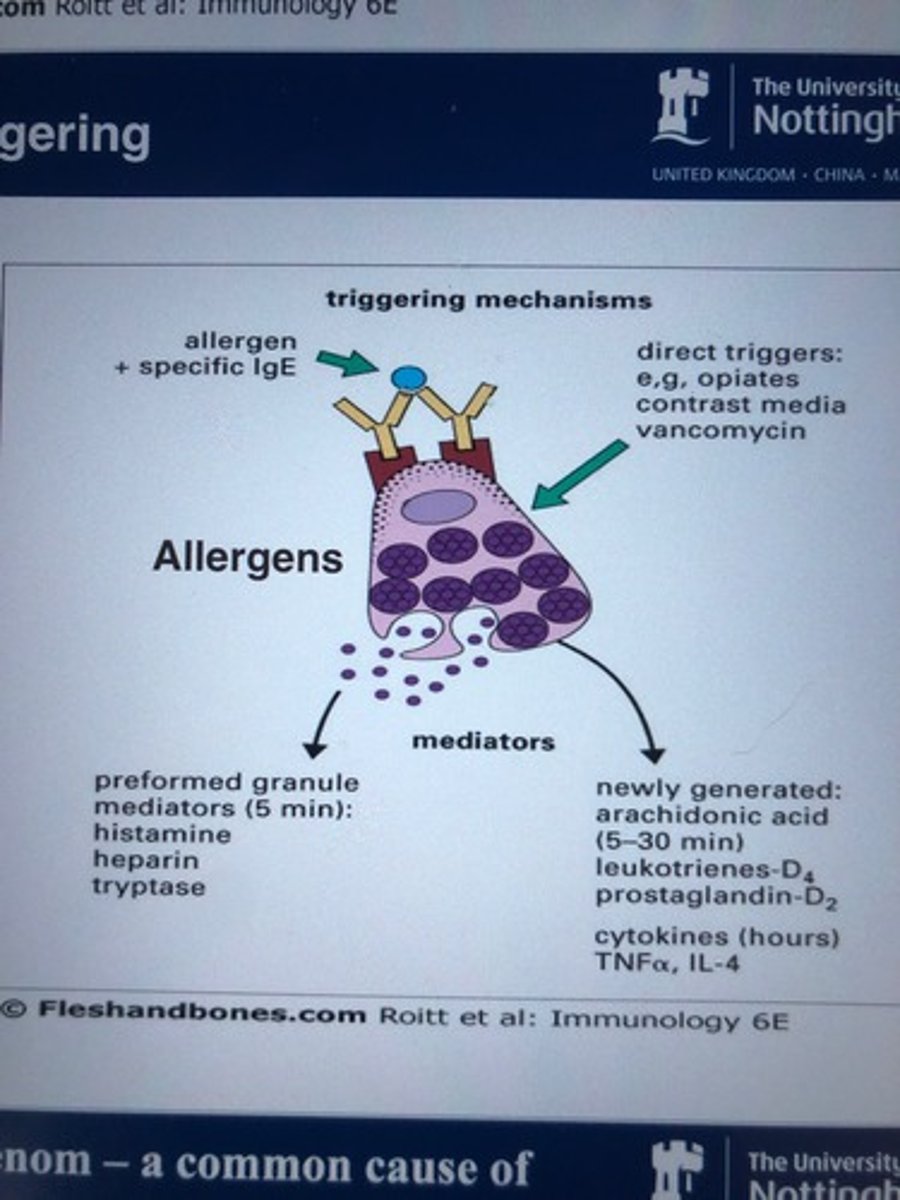
What are in newly generated granules
Arachidonic acid
Leukotrienes
Prostaglandins
Cytokines
How can you get systemic anaphylaxis
IV entry of allergen
Causes oedema tracheal occlusion
Death
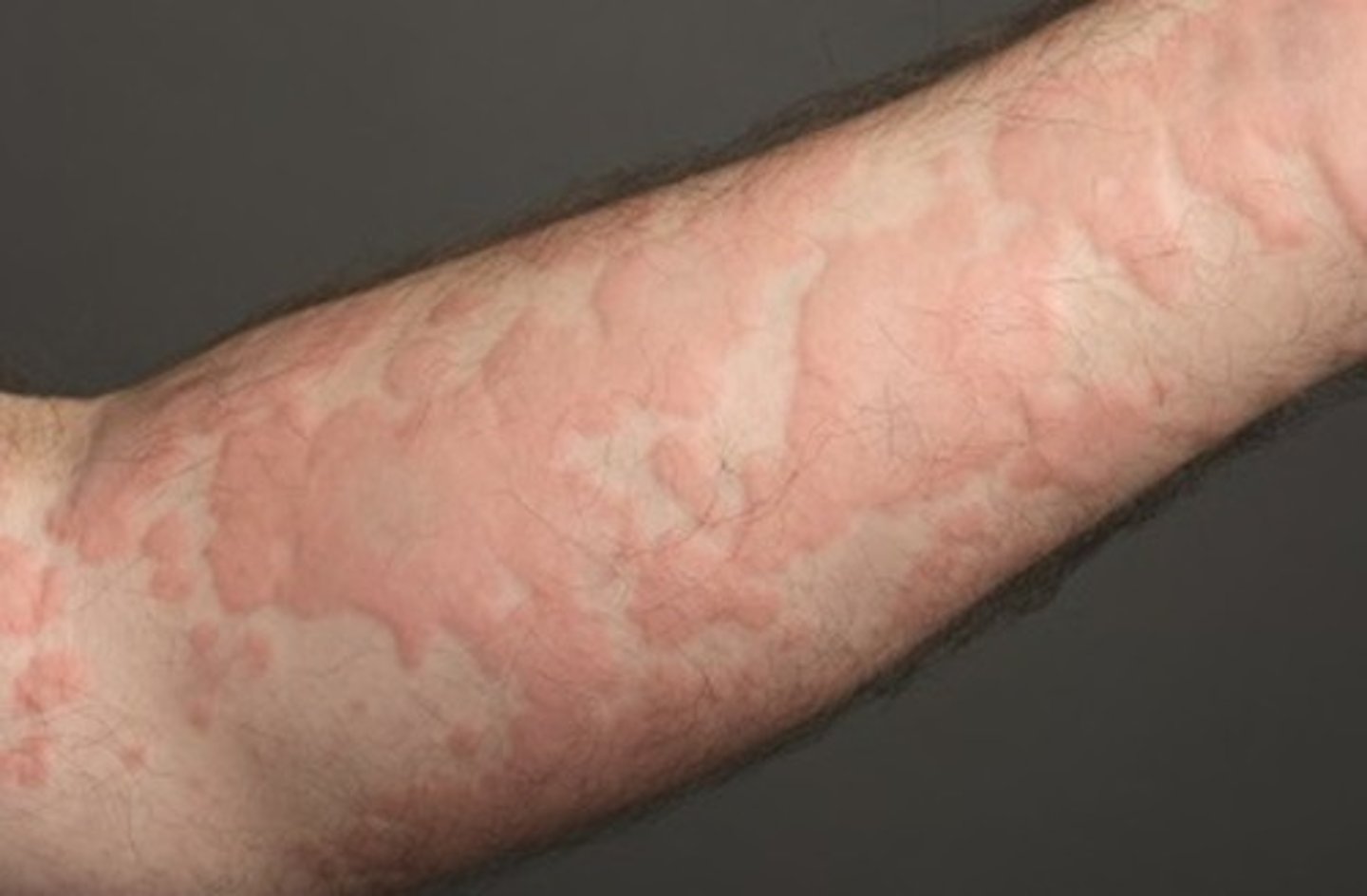
How to get urticaria (wheal and flare)
Subcutaneous entry - under the skin
Local increase in blood flow and permeability
trigger a reaction that causes high levels of histamine and other chemicals to be released in the skin, leading to swelling and itchiness
What causes allergic rhinitis
Inhalation of allergen
Oedema of nasal mucosa
What causes asthma?
Inhalation of allergen into lungs
Bronchial constriction and increased airway inflammation
What causes food allergy reaction
Oral entry
Vomiting
Diarrhoea
Urticaria
Anaphylaxis
What is pruritus?
severe itching
What is urticaria (hives)?
How to determine what a person is allergic to
Introduce 0.2 micro litres of allergen intradermally - wait 20 mins and see where inflammation is because of mast cell IgE cross link
What is type II hypersensitivity
Can be a foreign or self tissue leading to reaction
involved IgG IgM
What is a type III hypersensitivity reaction?
immune complex reaction - found in systemic lupus and rheumatoid arthritis
Immune complexes not cleared and triggers huge systemic response
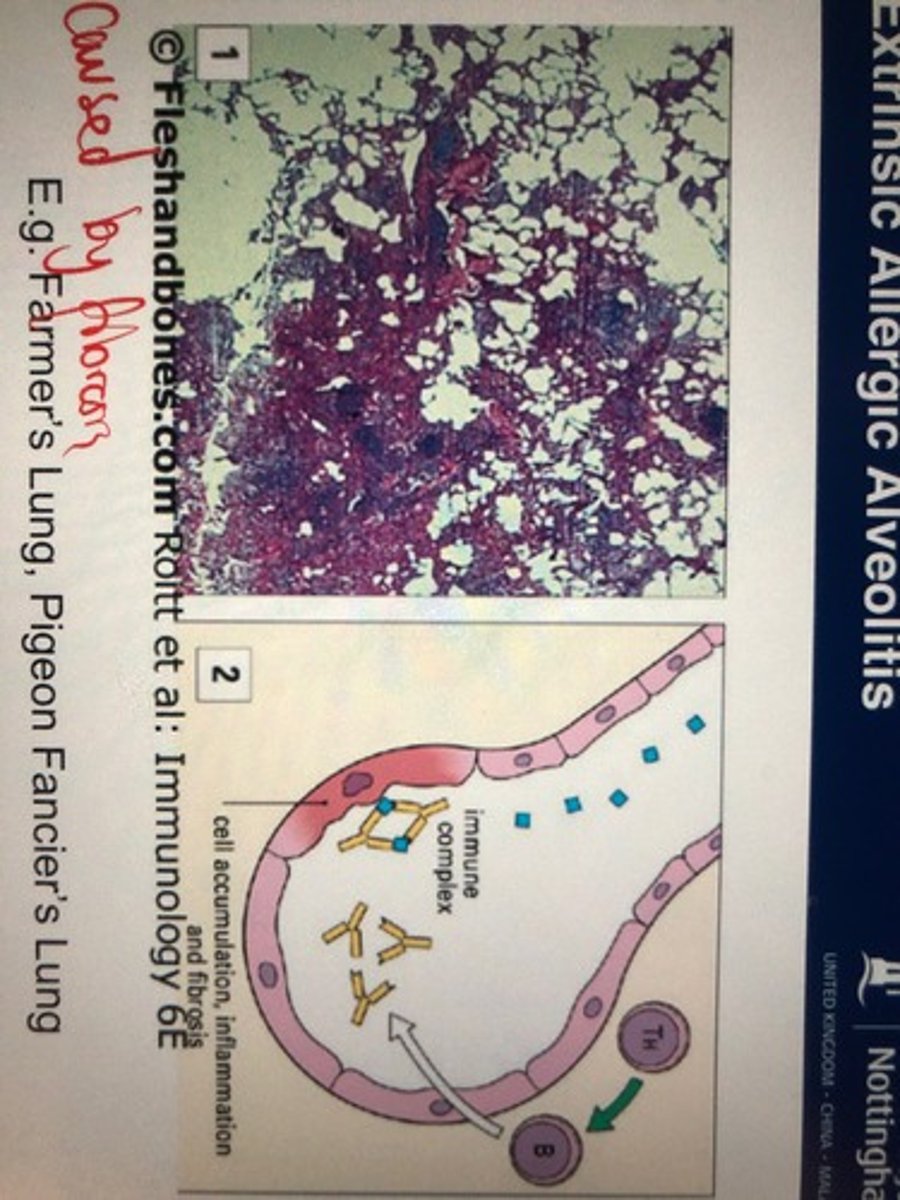
What is extrinsic allergic alveolitis
Caused by organic allergens (Bird poo , mouldy hay , wood dust)
Immune complexes deposit
Lead to fibrosis
Difficulty breathing (can present similar to asthma)
What is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction?
Type IV (D) reactions or cell-mediated delayed hypersensitivity requires sensitized lymphocytes to start the inflammatory reactions. Type IV reactions are seen in contact dermatitis .
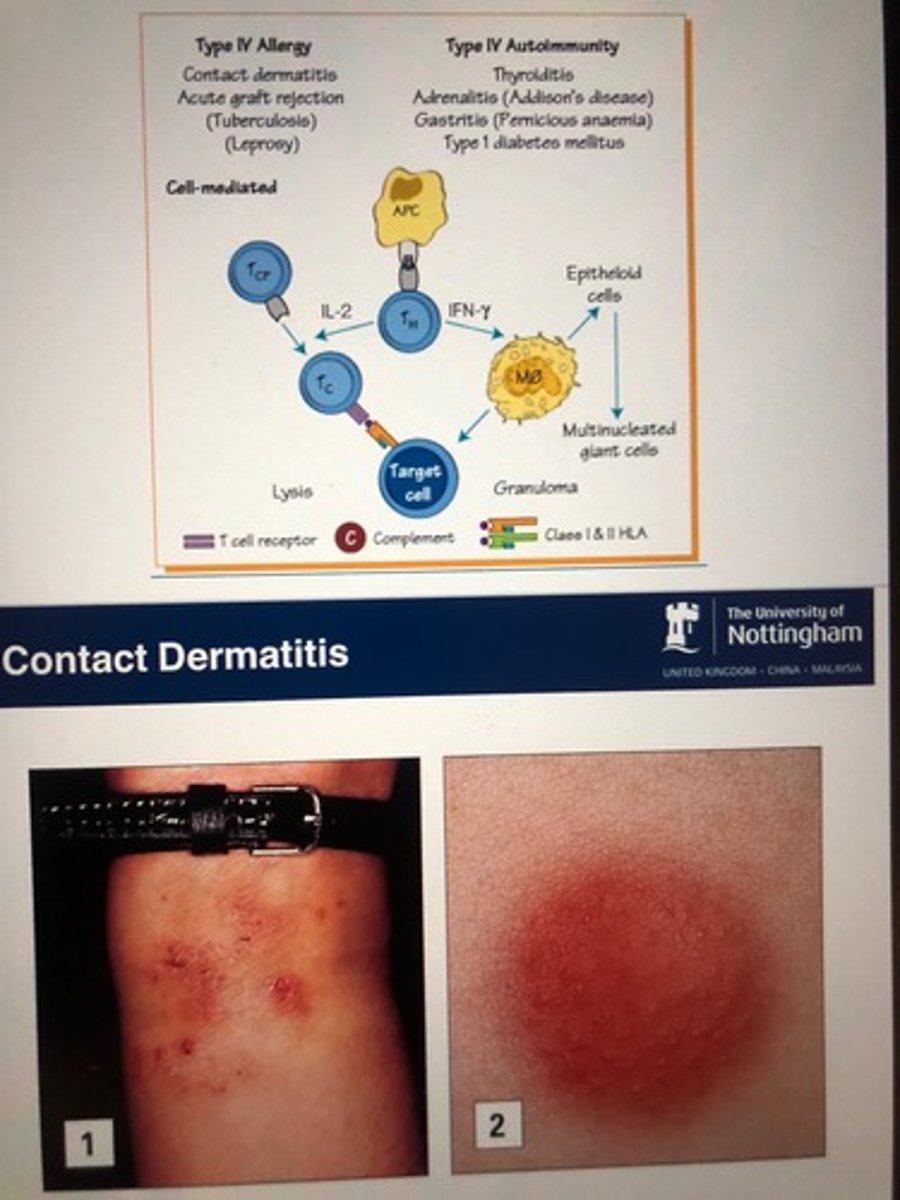
What is Type IV reaction mediated by
T H1 cell and macrophages
Takes 2-4 days for reaction
Examples of Type 1 hypersensitivity
Allergic rhinits
asthma
eczema
food allergies
acute urticaria
Type 2 hypersensitivty
Blood transfusion reactions
Allergic hemolytic anemia
Pemphigoid
Type 3 hypersensitivity
Dermititis
Allergic alveolotis
systempic lupus
rhematoid arthritis
Type 4 hypersensitivity
Contact dermatitis
TB
Type 1 diabetes
Gastritis