AE2001 Fundamentals of ecology / 3 Genetic diversity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Genetic diversity
Variety of genetic traits within a species or population.
Essential for adaptation and survival.

Alleles
Different versions of a gene within a population.
Contributes to genetic diversity.
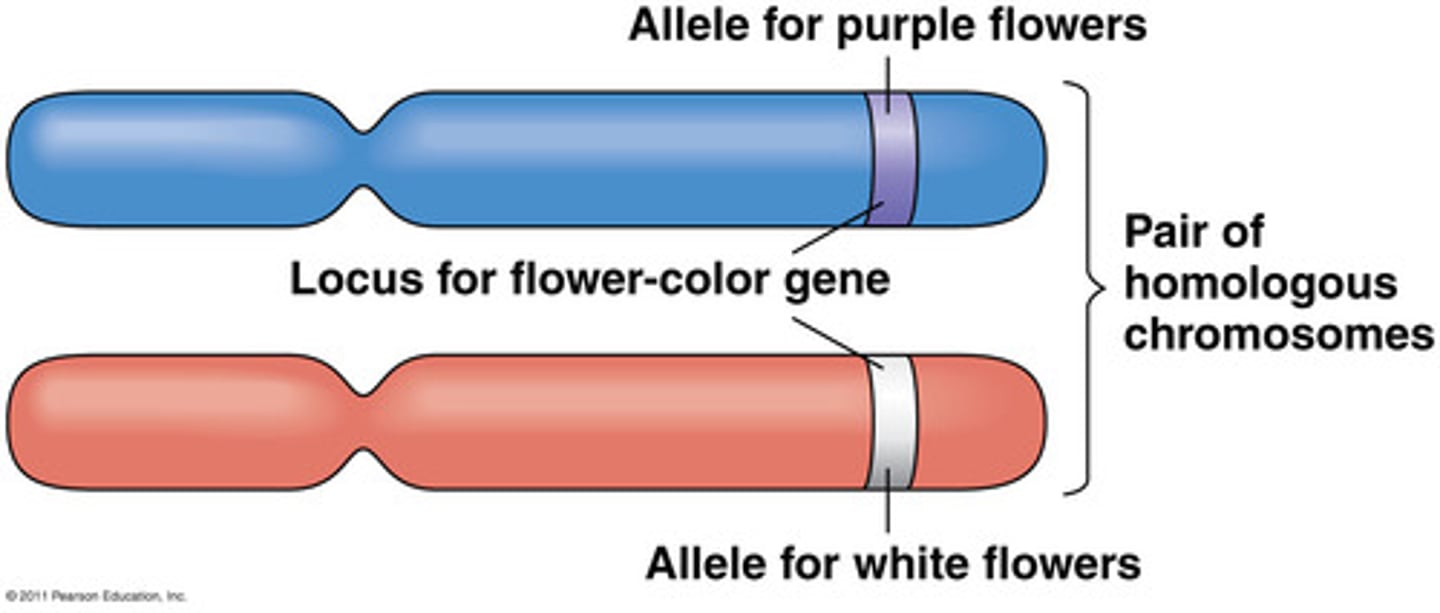
Homozygous
Two identical alleles for a specific gene.
Influences trait expression.

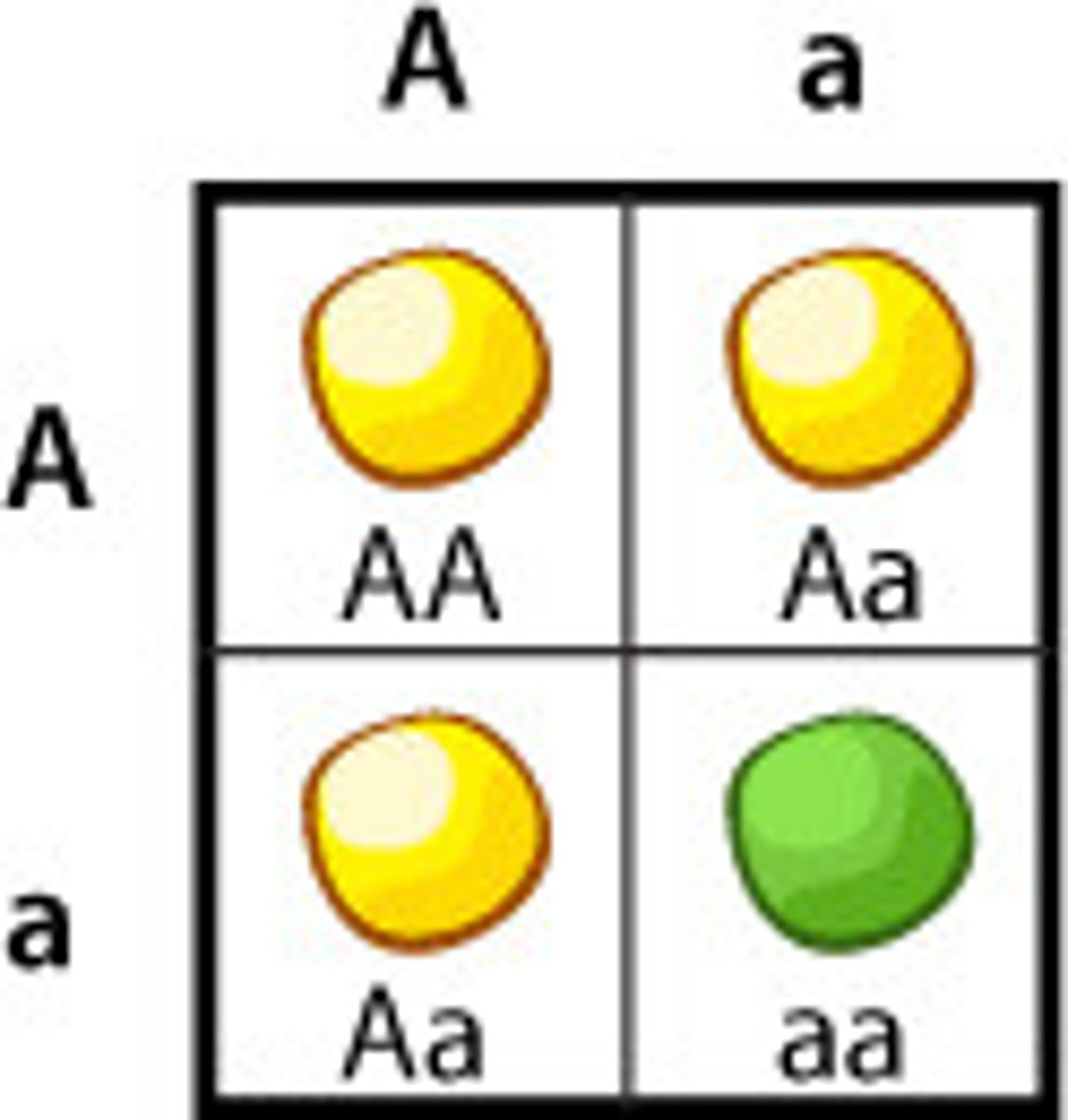
Recessive traits
Traits expressed only when an individual inherits two recessive alleles.
Effective population size
Number of individuals actively reproducing & contributing to next generation’s gene pool.
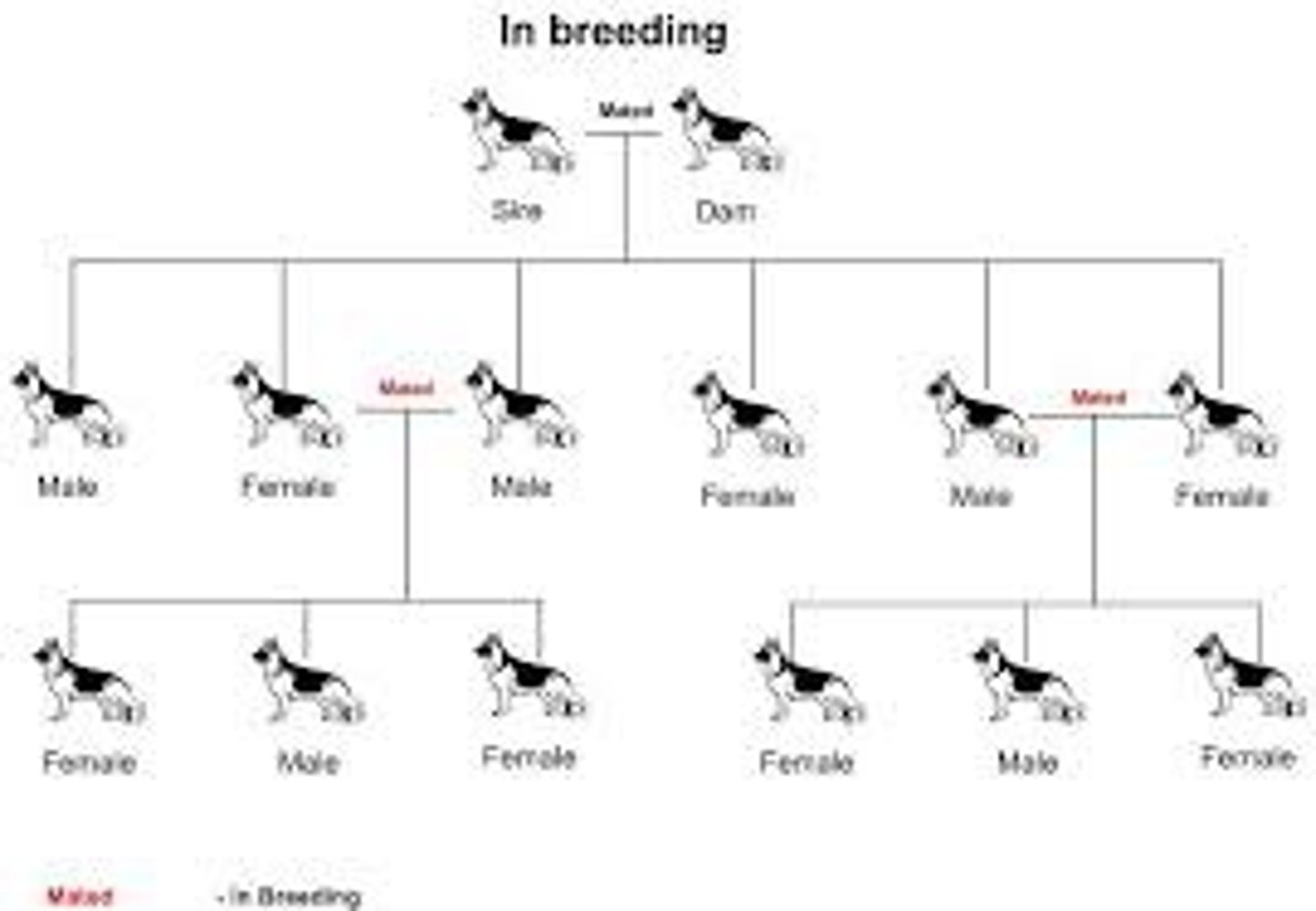
Inbreeding
Mating between closely related individuals
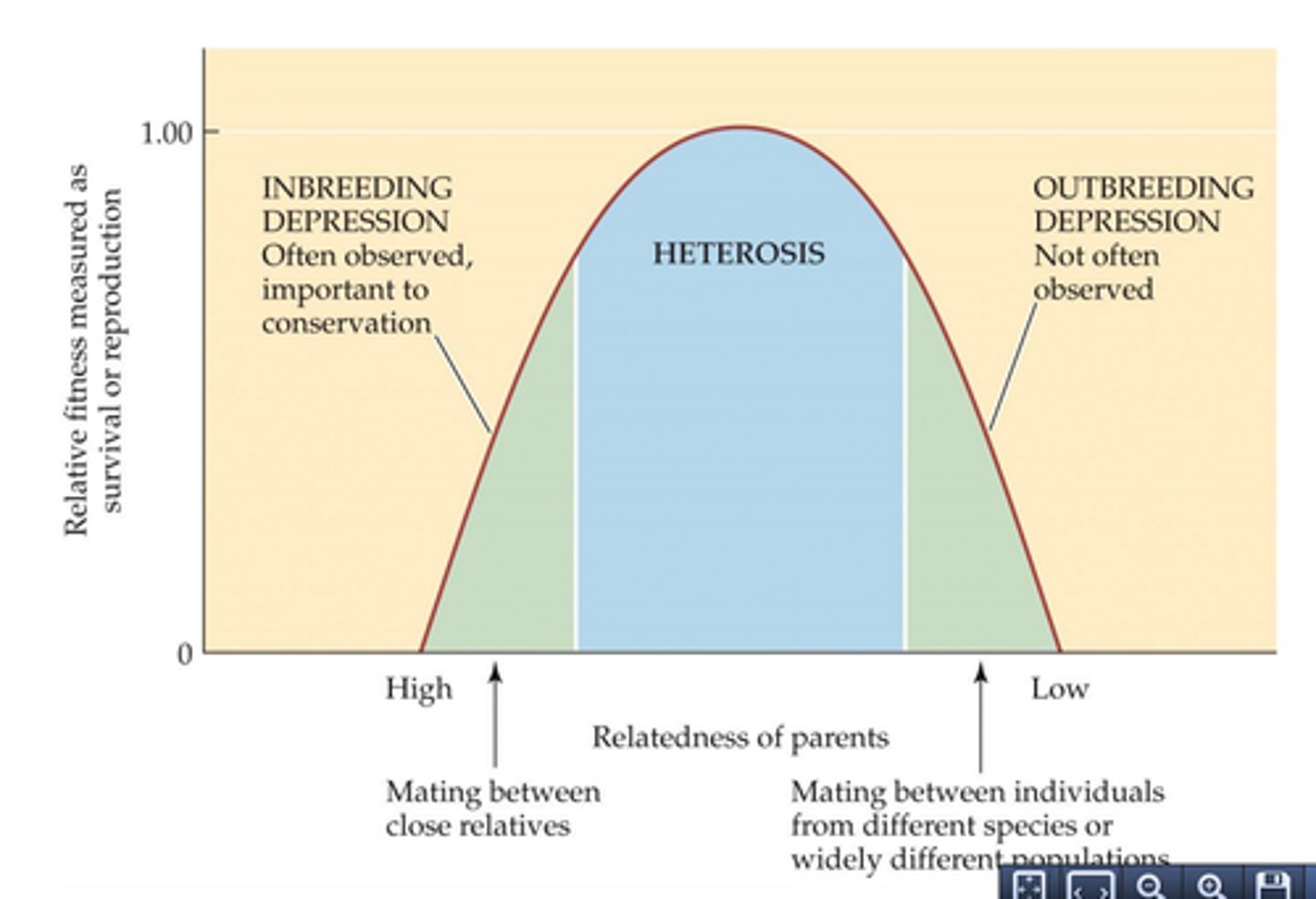
Leads to inbreeding depression: higher expression of harmful recessive traits.
Inbreeding depression
Reduced survival and fertility of offspring from closely related parents.
Caused by expression of harmful recessive genes.
Outbreeding depression
Reduced fitness when genetically distant individuals breed, disrupting local adaptations.
Example: Crossbreeding between two deer populations adapted to different climates can lower survival rates.
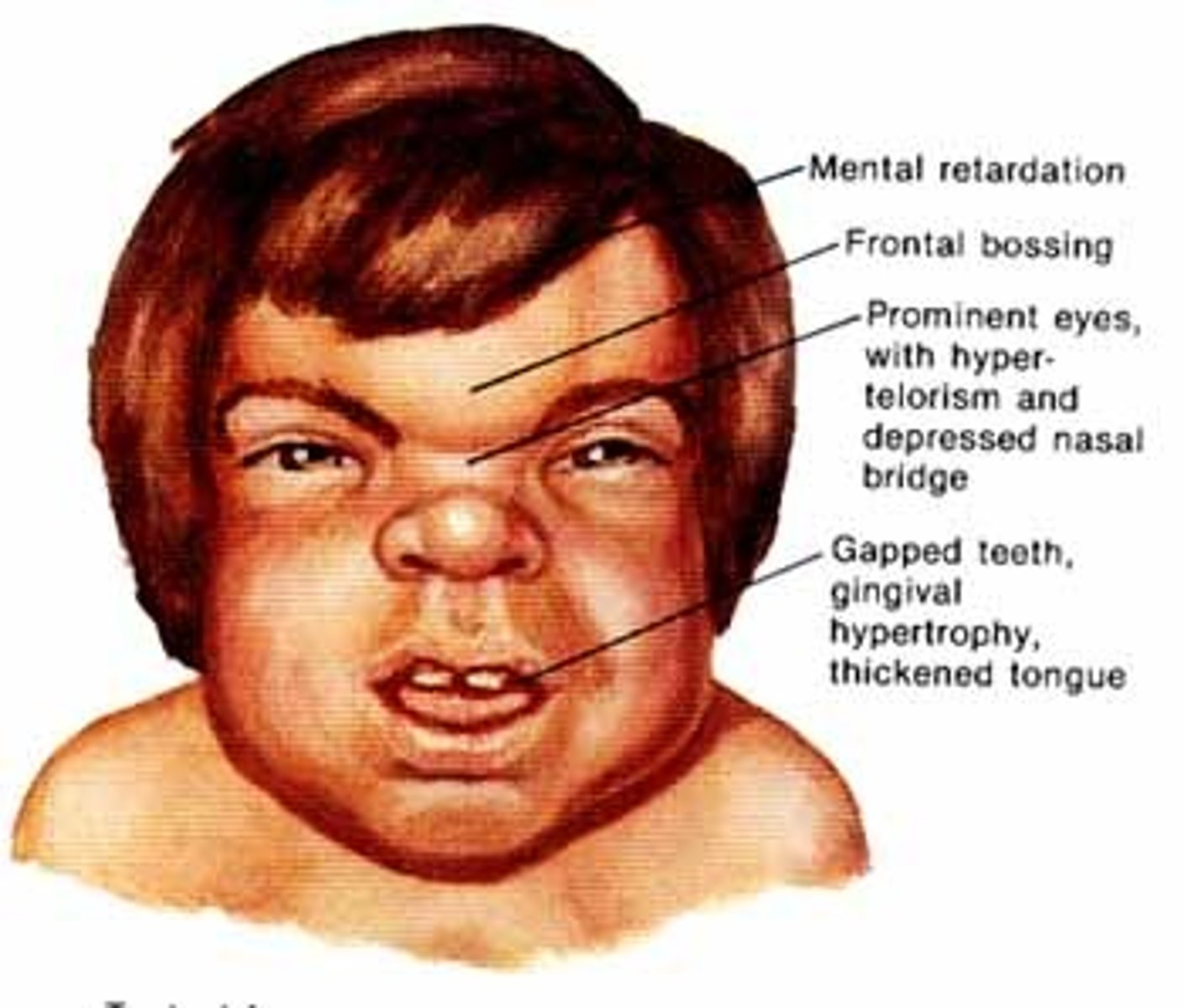
Hurler’s syndrome
Rare genetic disorder, disproportionately found among Irish Travellers due to consanguinity.
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies.
Impactful in small populations, due to chance loss of alleles.
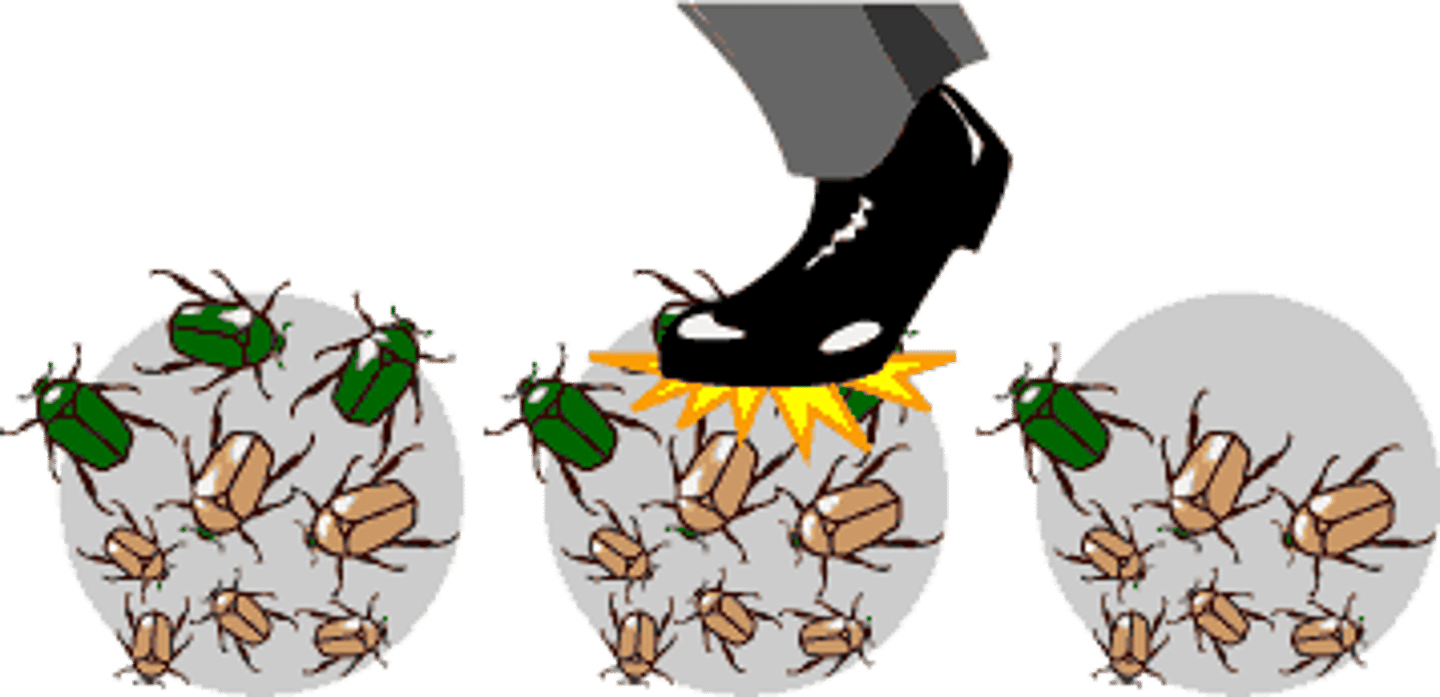

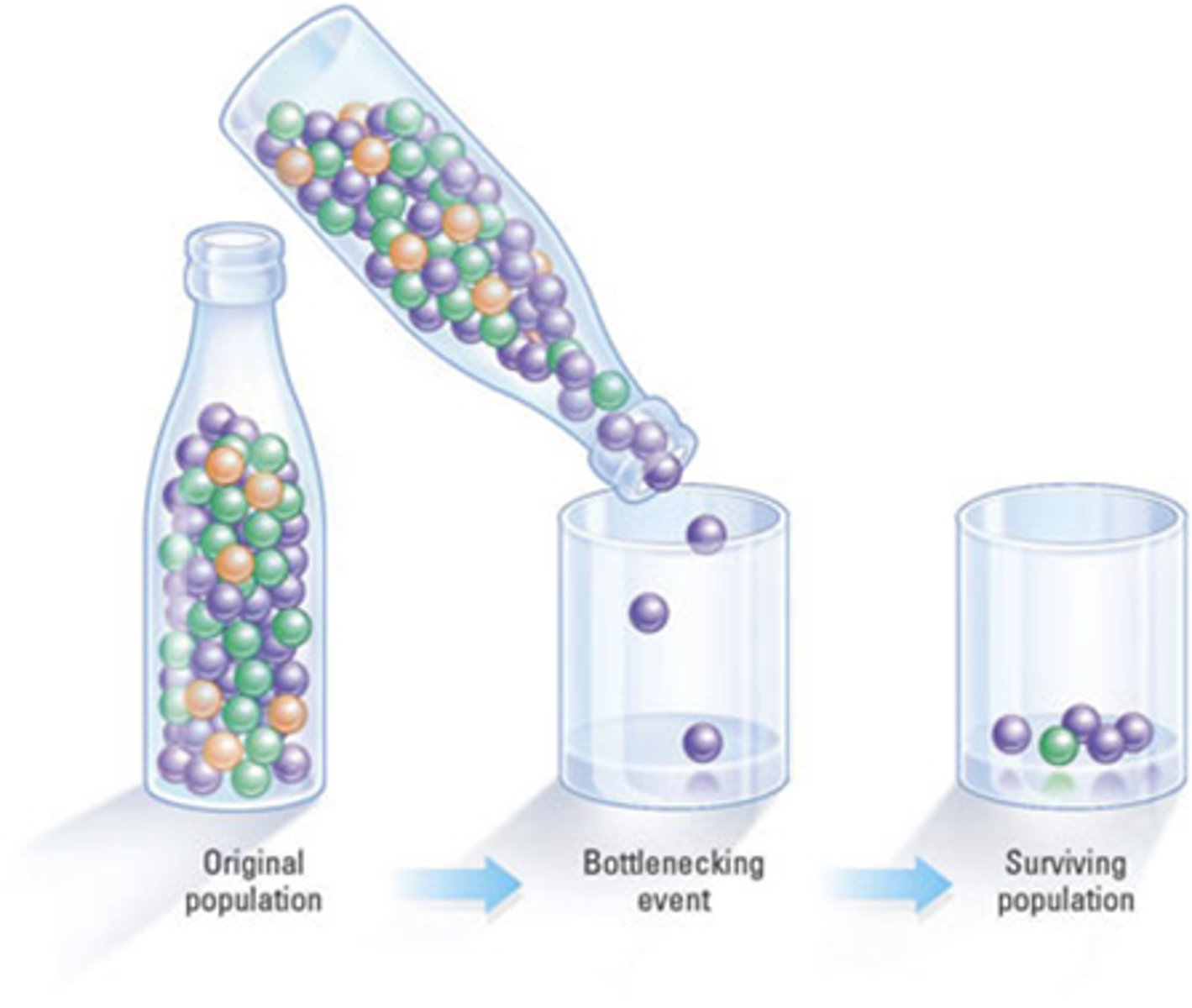
Bottleneck effect
Sharp reduction in population size that causes a significant loss of genetic variation.
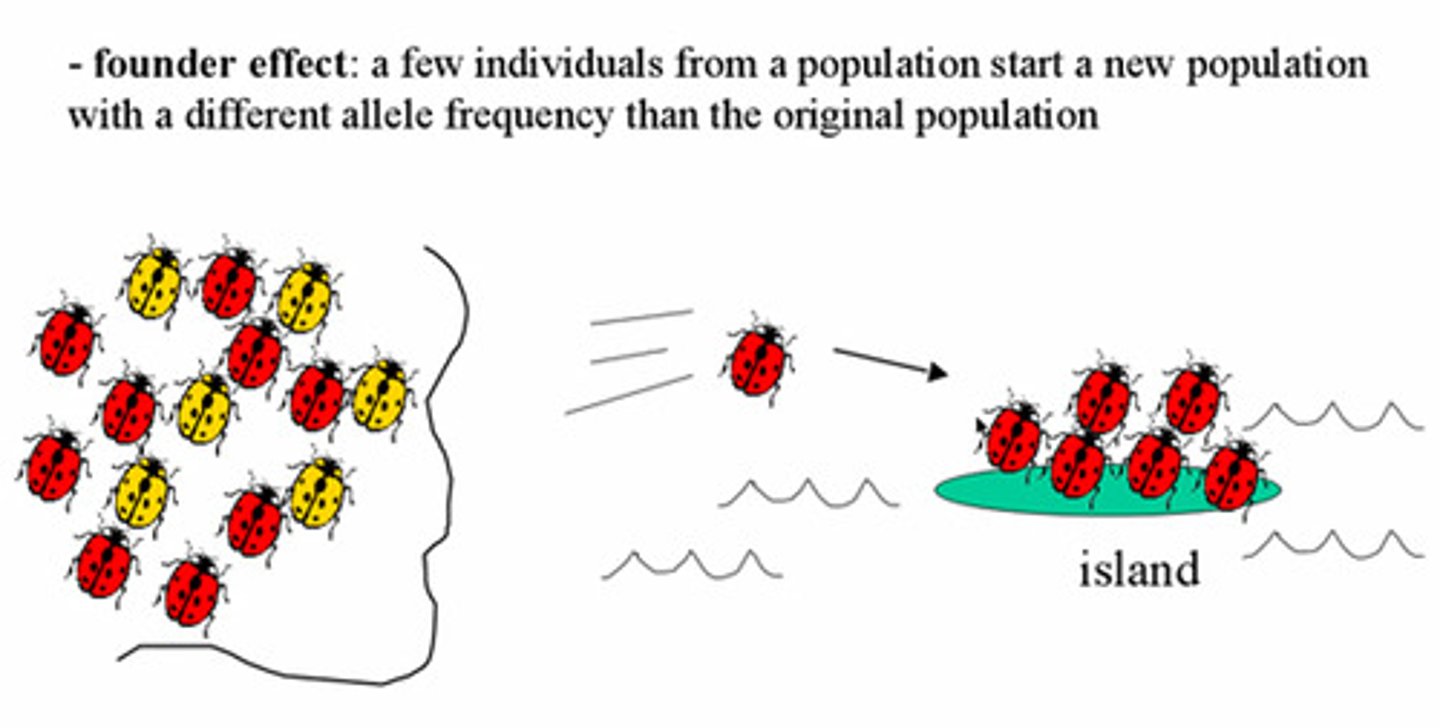
Founder effect
Genetic drift occurring when a small group establishes a new population
Alters allele frequencies due to limited genetic diversity.
Cavendish Banana & Gros Michel Banana
Gros Michel wiped out by fungal disease, lead to reliance on cloned Cavendish banana, susceptible to Panama Disease due to lack of genetic diversity (issue of monoculture)
Mountain gorillas
Adapted to inbreeding through genetic purging,.
Repeated inbreeding exposes harmful recessive alleles, removing them over generations.

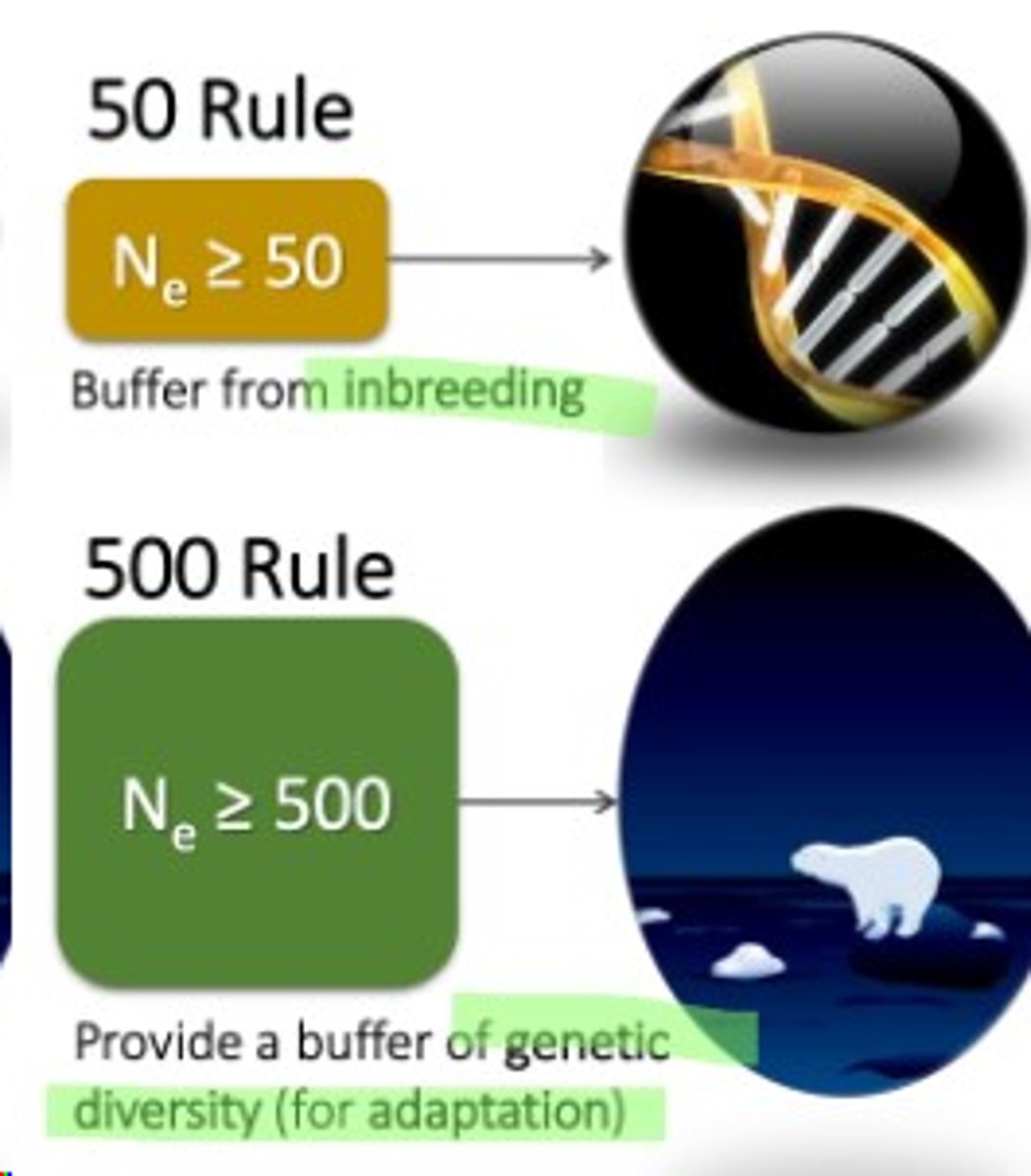
50/500 rule
Populations need at least 50 individuals to prevent inbreeding and 500 to minimise genetic drift over time.
Genetic rescue paradox
Introducing new individuals can reduce inbreeding but may disrupt local adaptations, causing outbreeding depression.
Translocation
Moving individuals from one population to another to increase genetic diversity & prevent inbreeding.
Zoo studbooks
Records tracking captive animal pedigrees to prevent inbreeding in zoos.
Coefficient of inbreeding
Measures genetic similarity between individuals, with higher values indicating greater inbreeding risk.

Inbreeding avoidance
Behaviour preventing mating between close relatives.
Example: African wild dogs rarely mate within their natal pack, avoiding close relatives.

Consanguinity
Marriage / reproduction between close relatives, common in some societies (Middle East, Irish Travellers).
Leads to increased genetic disorders (e.g., Hurler’s syndrome).
Pedigree breeding (agriculture)
Breeding closely-related livestock for desired traits.
but increases harmful recessive traits & reduces genetic diversity.
Example: Holstein dairy cattle

Xenophobia hypothesis
Behavioural avoidance of mating with genetically distant individuals, possibly reducing outbreeding depression risk.