AE302.6 Engine Cooling and Lubrication System
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
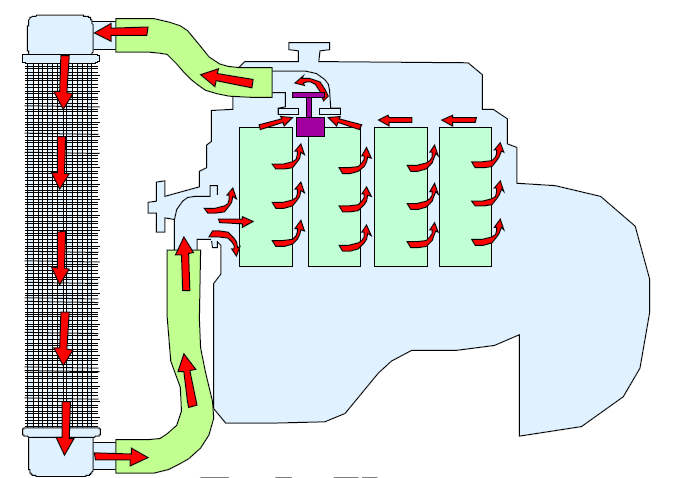
Indirect (water) cooling
Indirect cooled engines uses another medium to transfer heat from the engines to the cooling air. The medium used in this case is water, this method is used in most modern vehicles. Coolant is used to remove the heat from the engine and transfer the heat into the radiator where it is evaporated into the air. The image shown shows the correct airflow of coolant travelling through the indirect cooled engine.
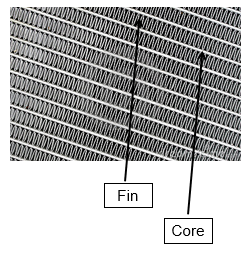
Radiator fins and cores
Heat transfers from various hot parts of the engine to the coolant, which then moves to the radiator where it dissipates heat into the surrounding air. The image shown is the air cooling fins and core, the heat transferred from the hot engine components, the air is released into the radiator fins passing into the radiator core fins.
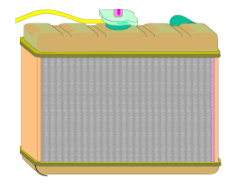
Down Flow Radiator
The top and bottom tanks are North/South, the coolant flows from the top to the bottom of the radiator.
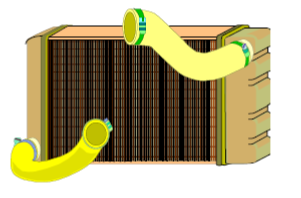
Cross Flow Radiator
Cross Flow Radiator. The tank is West/East, the coolant flows from side to side in the cross flow radiator.
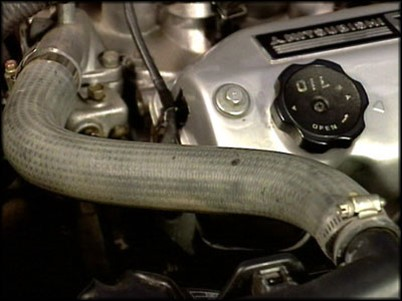
Radiator Hoses
The radiator hose connects allows the radiator to connect to the engine, it allows the engine to move and vibrate. It allows expansion and contraction as the engine heats up and cools down, overall the hose allows these vibrations and movements so that it can maintain proper functionality.
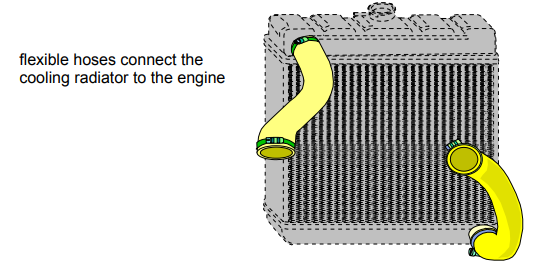
Coolant hoses
Coolant hoses are made of either silicone or rubber, the fabric used to design the coolant hose is designed to withstand the pressure of the cooling system.
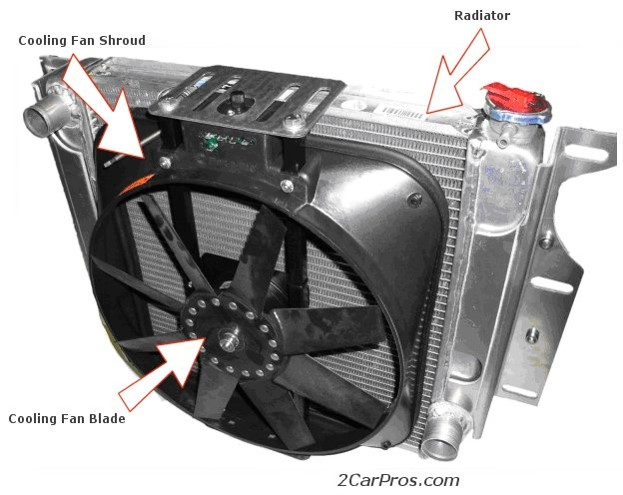
Cooling Fans
The purpose of the cooling fan is to pull air through the radiator fins when the vehicle speed is slow. Radiator fans can be driven by either an electric motor or drive belt.
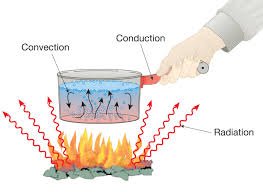
Heat Transfer
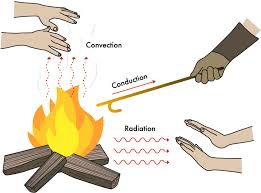
Heat transfer is created by combustion, it is that the engine maintains constant temperature, so that there is no damage that will affect the engines components, caused by overheating. Two things to note, heat transfers in the engine from one hot place to another cold place. Secondly, heat moves by three different modes, these are known as conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction
Conduction is the heat transfer that occurs when an object becomes warm or hot by direct contact. The heat will transfer from one side to the other end, creating an evenly warm/hot object. An example of this in car is the piston rings through to cylinder liners or when the combustion heat moves to the cooler water jacket side of the combustion chamber.
Convection
Convection is the heat transfer through movements of liquid and gases. At the bottom of a warm container/pot there are warmer particles, whereas the colder particles are above are much colder and dense, the cold and dense particles will sink to the bottom whilst the warm particles move up, therefore heating the entire pot. This path is called convection current. Prime example is coolant travelling through water jackets to radiator or when heat from the combustion chamber water jacket causes the water to rise and cooler water flows in to take it’s place.
Radiation
The movement of heat that can be seen or described as heat waves. Every heated object somewhat contains a little bit of heat waves.
Two problems if coolant temperature is exceeded
Lubrication and oil breakdown
Engine components will expand and seize.
Two problems if correct temperature is not reached
Increased engine wear = increased fuel consumption
Poor engine efficiency due to incorrect tolerances.
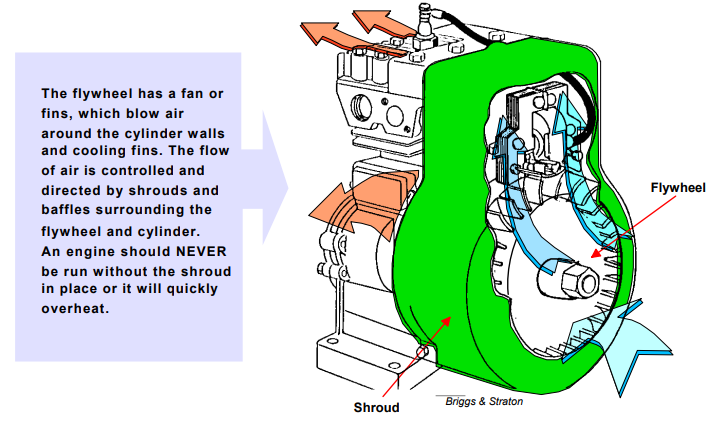
Air Cooled Engines
Air cooled engines or direct cooling engines use no other medium to transfer heat away. A third of the heat is carried away by the exhaust and the remainder is used to power the engine, the average temperature burned gases in the combustion chamber is 1982 degrees Celsius. The life efficiency of a air cooled engine depends on the cooling system efficiency.
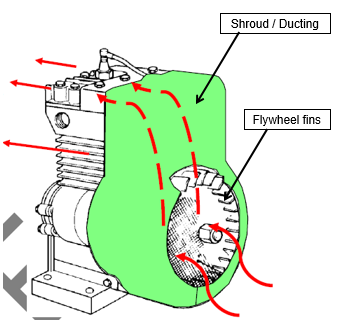
What would be the reason if an engine similar to this had a electrically driven fan fitted?
An electric fan would force air over the engine fins to increase cooling when required.
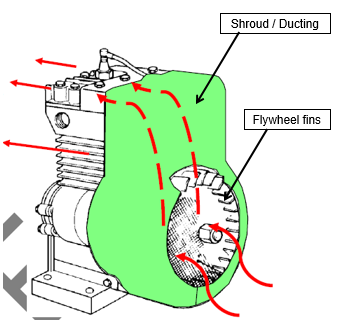
How is the airflow created by the fan and directed to the area of the engine that needs cooling?
The spinning fins on the flywheel create a low pressure in its center. The air is directed across the fins through shrouds and ducting
Service Requirements for Direct (Air) Cooling
Dirt and debris should be removed from the cooling fins to allow good airflow
Ensure there is no damage to the fins on engine and flywheel
Ensure there is no damage to the shrouds or ducting
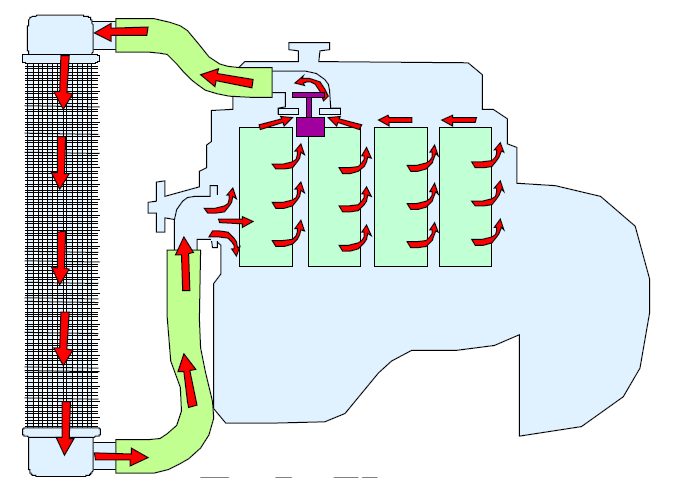
Indirect (Water) Cooling
Indirect cooling engines uses another medium to transfer the heat from the engine components to the cooling air. The medium or method in this case is water, coolant is used to remove the heat away from the engine, back into the radiator which is then dissipated into the air.