CHEM 41 DNA TRANSLATION
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Translation
Process of translating mRNA to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis
Peptide bonds
Link amino acids in a polypeptide chain
5’ to 3’
Genetic code is written in a typical convention of _____ to _____
Codon
Triple of bases
Reading frame
Established by AUG
Frame shift mutation
Reading frame shifts due to mutation (deletion or addition of DNA bases)
AUG
Initiation codon
Commaless
Genetic code is _____, meaning bases are not skipped
Non-overlapping
Genetic code is _____, which means no single base can take part in the formation of more than one codon
Degeneracy
Also known as redundancy of genetic code
several
Degeneracy of genetic code allows for _____ codons to code for the same amino acids
Stop codons
UGA, UAA, UAG
Met (AUG) and Trp (UGG)
Only _____ and _____ have a single codon
resistance against DNA mutations
Degeneracy of genetic code provides _____ against ______
Conservative substitution
Amino acid with different base but similar properties is caused by ______
Quasi-universal
Genetic code features and translation applies to prokaryotes and eukaryotes across all species
anticodon, H-bonding
Codon in mRNA is complementary to _____ sequence in tRNA via _____
parallel
Alignment of RNA sequences (mRNA and tRNA) is _____
cloverleaf or cruciform
Secondary structure of tRNA achieved by complementary base pairing
T arm (loop)
tethers tRNA to ribosome
D arm (loop)
identification of tRNA by aminoacyl synthethase
aminoacyl-tRNA synthethase
Enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid on tRNA to the 3’-OH end
Acceptor stem
Amino acid binding site via ester bond
3’-OH
The amino acid binds to the ____ of the acceptor stem
Wobble base pair
Noncanonical (non-Watson and Crick) base pairing of third codon base with its anticodon
inosinate (I)
Some tRNAs contain _____ which is flexible and can H-bond with U, C, and A
Aminoacylation or charging of tRNA
Cleavage of a triphopshate group
aminoacyl-tRNA synthethases
Enzyme that catalyzes amino acid activation and linkage
Structural basis of genetic code
amino acid recognition and tRNA loading by aminoacyl-tRNA transferase is the _____
ribosomes
Molecular machines responsible for protein synthesis
rRNA and protein
Comprise ribosomes
larger and more complex
Eukaryotic ribosomes are _____ and _____ than prokaryotic ribosomes
80S
Prokaryotic ribosome : 70S :: Eukaryotic ribosome : _____
E (exit site), P (peptidyl site), A (aminoacyl site)
Three sites in the ribosome
Exit site (E)
Accomodates deactylated/”spent” tRNA
Peptidyl site (P)
Accomodates tRNA attached to growing peptide chain
Aminoacyl site (A)
Accomodates aminoacyl-tRNA
Initiation factors (IFs)
Proteins that initiate translation
Shine-Dalgarno site
Short, purine-rich initiation sequence upstream of AUG in prokaryotic mRNA (-7 to -4)
initiation complex
Large prokaryotic ribosomal subunit (50S) associates to form _____
transcription
Translation can occur simultaneously with _____ in prokaryotes
5’ cap
In eukaryotes, the small ribosomal subunit binds to the _____
5’ cap
Prokaryotes : Shine-Dalgarno site :: Eukaryotes : ____
one amino acid
Polypeptide chain extends by _____ residue per cycle
fMet (formylmethionine)
Eukaryotes : Met :: Prokaryotes : _____
amino group, carbonyl group
_____ of next AA attacks _____ of previous AA, forming a peptide bond
release factor
Protein that binds at A-site which releases the completed polypeptide and dissociates the ribosome into subunits
sites of regulation
Amino acids containing N, O, or S act as _____
formyl group, methyl, or additional residues
Enzymatic removal acts on _____, _____, or _____
Acetylation
addition of an acetyl group (-COCH3)
Glycosylation
Sugars added to specific amino acids
N-linked
Sugar added to Asn
O-linked
Sugar added to Ser or Thr
Kinases
Enzyme that transfers phosphates
isoprenyl group
Addition of _____ from intermediates of cholesterol synthesis pathway
farsenyl group
3 isoprenyl groups attached together
disulfide linkage
Two Cys residues form a _____
pre in preproenzyme
signal sequences within enzyme’s AA sequence that direct it to its proper cellular location
pro in preproenzyme
enzyme is inactive and requires cleavage or other modifications to be activated
also called zymogen
Virus
Small collection of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat (capsid); exceptions to the central dogma
RNA
Majority of virsues contain _____ except adenoviruses
replicate by themselves
Viruses cannot ______
proofreading activity
Known viral RNA replicases lack _____
synthesis of RNA strand
RNA replicase catalyzes _____ of _____ strand
mutation and evolution
RNA viruses undergo very rapid _____ and _____
Retrovirus
Type of virus that creates a DNA copy of its RNA genome
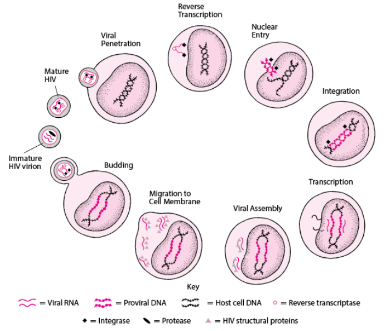
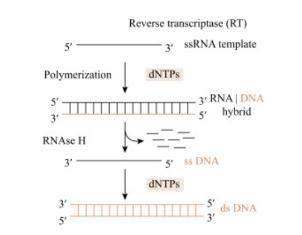
Reverse transcription
The process of synthesizing DNA from an RNA template
dsDNA
Reverse transcriptase catalyzes synthesis of _____from the ssRNA genome
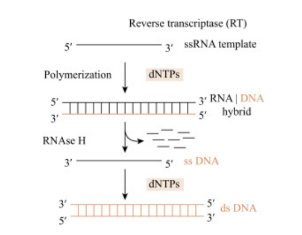
RNA-dependent DNA synthesis
Reverse transcriptase first makes the DNA strand complementary to the viral RNA template
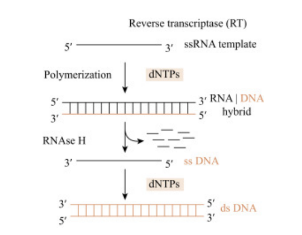
RNA degradation
Reverse transcriptase degrades viral RNA in the DNA-RNA hybrid
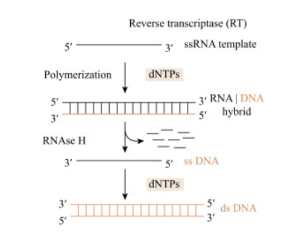
DNA-dependent DNA synthesis
Reverse transcriptase completes the synthesis of the other DNA strand, forming the dsDNA copy
tRNA primer, high error rate, and high mutation/evolution rate
Reverse transcriptase uses _____ and lacks 3’ to 5’ proofreading like RNA pol; leading to _____ and _____
integrase
Enzyme that integrates the dsDNA copy into the host cell’s genome
proviral DNA
passed onto succeeding generations and can be transcribed upon meeting certain conditions
Coronavirus
Virus with spike proteins that have a crown-like appearance
positive-sense ssRNA genome, RNA-dependent RNA synthesis
Coronavirus contains a _____ genome and utilize _____ synthesis
Ribosomal frameshifts
Involves altering the reading frame by shifting one nucleotide to the left and enables the coronavirus to encode more proteins
Lytic and lysogenic cycles
Two cycles observed in bacteriophages
Lytic cycle
New copies of the virus are actively made and causes lysis of the host sell after replication
Lysogenic cycle
Integration of viral genome into host cell’s genome and replicated alongside it
dormant
In the lysogenic cycle, the virus remains _____ until certain conditions are met in the lytic cycle
Zoonotic disease
Infectious disease that jumps from an infected animal to a human