[OT 104] Lec. 4: Brain Stem and Spinal Cord
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the brainstem like?
stalk-like
Where is the brainstem located?
at the posterior fossa of the skull
What does the brainstem connect?
the brain, cerebellum, and spinal cord
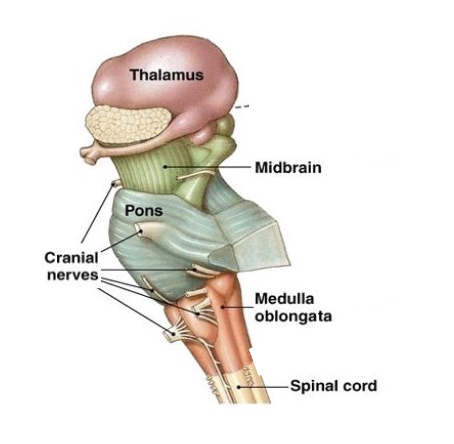
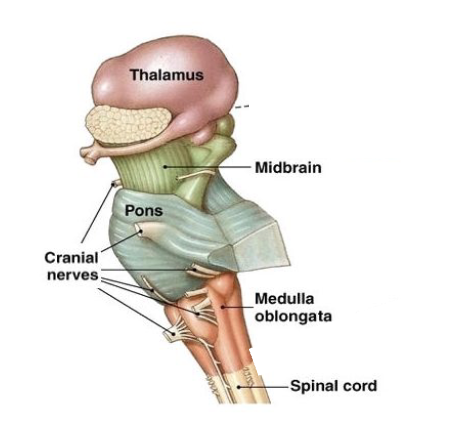
Subdivisions of the brain stem
midbrain
pons
medulla oblongata (deglutition and respiratory center)
Functions of the brainstem
pathway of tracts
regulatory functions - autonomic nervous system (swallowing, breathing, blood pressure, heart rate, consciousness, and sleep)
reflexes
origin of cranial nerves
Carotid body
baroreceptors that regulate blood pressure
important for distension (vasoconstriction and vasodilation)
reticular active system (RAS): for consciousness and sleep-wake cycle system
What originates from the midbrain?
CN 3 and CN 4
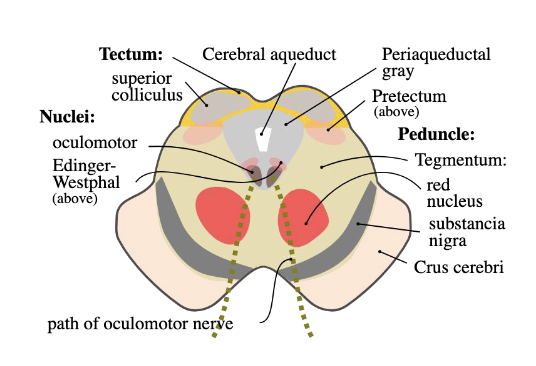
What is the anatomy/divisions of the midbrain?
crus cerebri
cerebral aqueduct
tectum (roof)
tegmentum
Crus cerebri
cerebral peduncle for sensorimotor integration from corticospinal fibers
where interpeduncular fossa is found between the cerebral crura
Cerebral aqueduct of sylvian fissure
where cerebrospinal fluid passes
channel connecting 3rd (superiorly) and 4th (inferiorly) ventricle
Tectum
roof of midbrain
contains 4 round swellings called colliculi called corpora quadrigemina (eyes over ears)
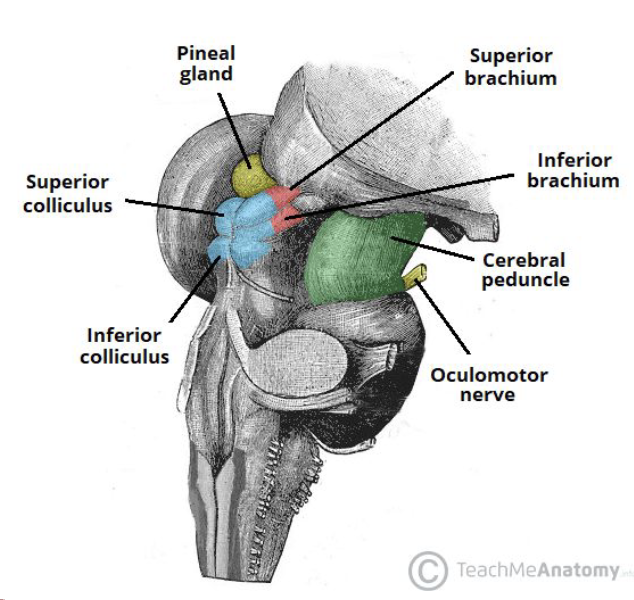
Corpora Quadrigemina: Superior Colliculi (2)
SUPERIOR COLLICULI (2)
for visual and ocular reflexes
gaze and vergence centers (divergence: eyes outwards, convergence: eyes inwards)
connected to lateral geniculate body
Corpora Quadrigemina: Inferior Colliculi (2)
INFERIOR COLLICULI (2)
auditory reflexes
sound localization: knowing where the sound comes from
connected to medial geniculate body
Tegmentum
floor of the midbrain
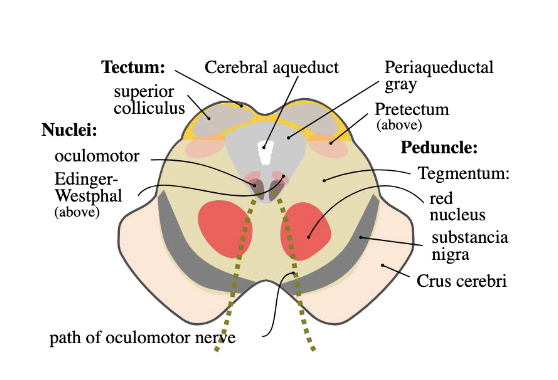
Tegmentum: Nuclei
oculomotor
edinger westphal nucleus
red nucleus: passage of ascending tract fibers that connect to the primary motor cortex (BA 4)
for fine tuning and coordination of motor movements
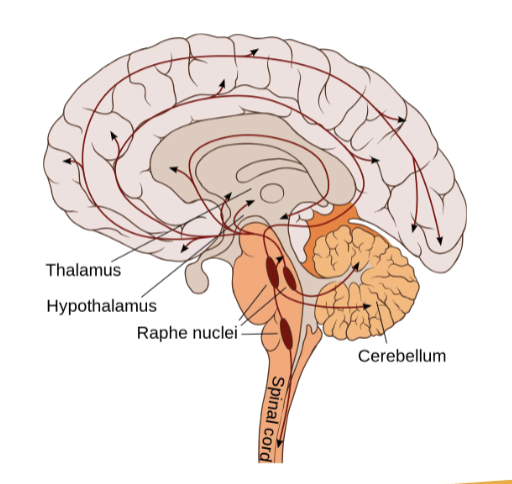
Raphe Nuclei
extend from midbrain to spinal cord
part of the RAS
major serotonin-producing neurons in the CNS
serotonin: happy hormone
modulates sleep-wake cycle, level of arousal, sensory input
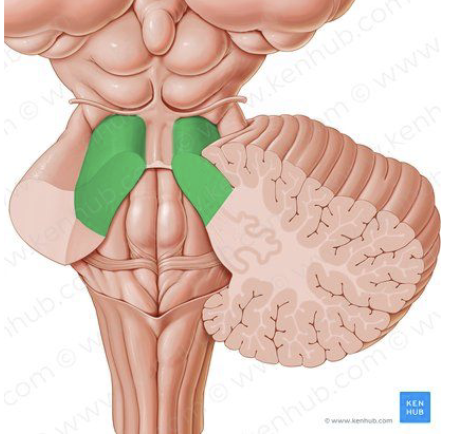
Superior Cerebellar Peduncle
connect the brainstem to the cerebellum
main OUTPUT pathway of the cerebellum
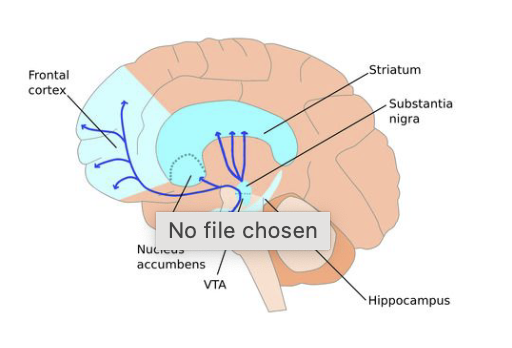
Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) and Substantia Nigra
main producer of dopamine in the CNS
low dopamine levels = less initiation from muscle groups = balance difficulties (parkinson’s)
Substantia Nigra
pars reticulata: contains GABA
pars compacta: contains dopamine and projects to the striatum , putamen, and the caudate nuclei.
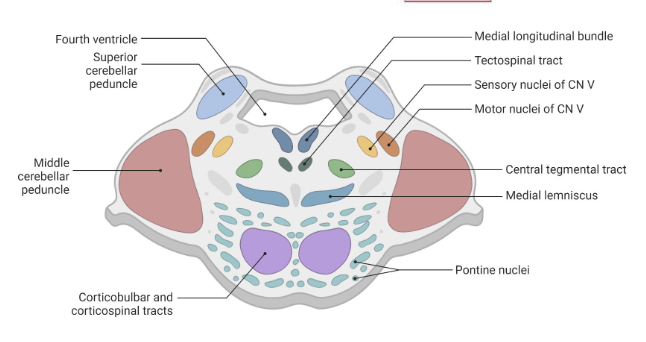
Pons
anterior to the cerebellum
connects midbrain and medulla oblongata
origin of CN 5 to 8
has the basilar groove at midline and middle cerebellar peduncle
Pons: Seat of ?
seat of consciousness
What is ARAS?
Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS)
responsible for overall level of consciousness and the wakeful-sleep states.
Comatose can be associated to problems in the ARAS
What is the Reticulospinal tract?
originates from the pons and spinal cord
“reticulo” = reticular activating system in pons
“spinal” = spinal cord
for locomotion and postural control
Medulla oblongata
connects pons and spinal cord at the level of the foramen magnum
foramen magnum: large opening in base of skull
conical in shape, superior part is broader
origin of C7-12
C7 and 8 are under pons and MO
respiratory and deglutition center
Cranial nerves in the Midbrain
CN 3
CN 4
Cranial nerves in the Pons
CN 5
CN 6
CN 7
CN 8
Cranial nerves in the medulla oblongata
CN 7
CN 8
CN 9
CN 10
CN 11
CN 12
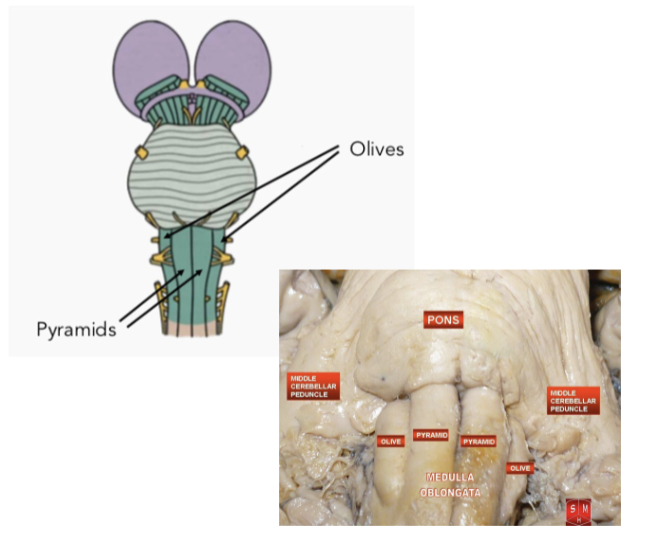
Anatomy of MO: Pyramids
paired bundles of motor nerve tracts
decussation of the pyramids
crossing of motor nerve fibers to other side
why motor areas affect C/L side of body
location of decussation depends on the tract, but lots of motor nerve tracts decussate at the MO
pyramidal tracts: corticospinal tract (CST) and corticobulbar tract (CBT) which pass through the pyramids unlike the extrapyramidal tracts
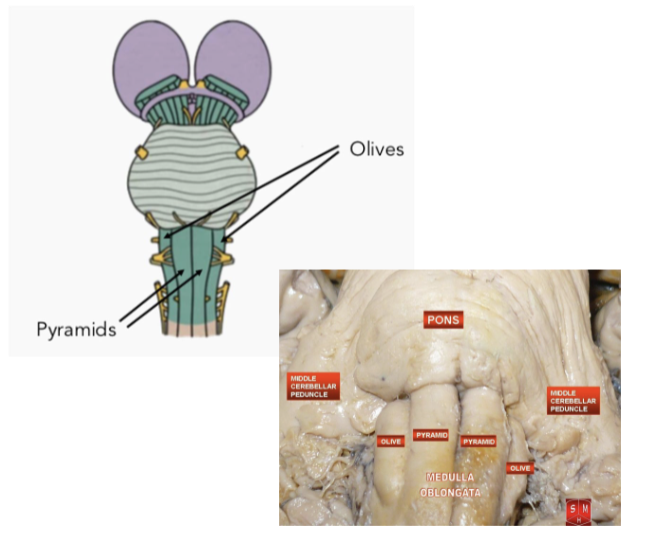
Anatomy of MO: Olives
posterolateral to pyramids
produced by inferior olivary nuclei
important for control of movement
inferior cerebellar peduncle is located behind the olives
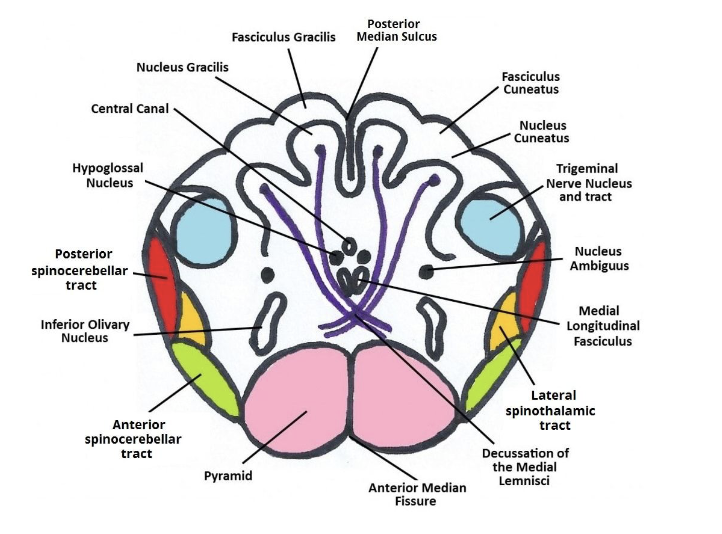
Anatomy of MO: Nucleus Gracilis
found on each side of the posterior median sulcus
forms the gracile tubercles

Anatomy of MO: Nucleus Cuneatus
found laterally to the nucleus gracilis
forms the cunate tubercles
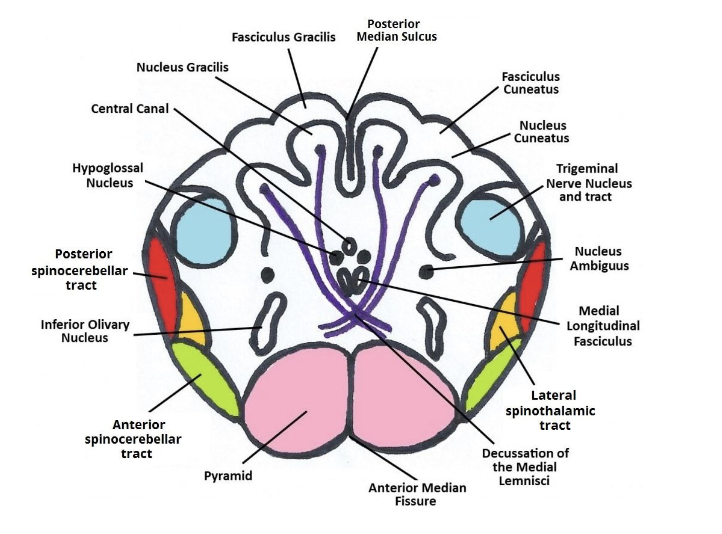
Anatomy of MO: Nucleus Ambiguus
mainly for swallowing and speaking
contains motor nerves that innervate the ipsilateral muscles of the soft palate, pharynx, larynx, and upper esophagus
contains vagal (CN 10) efferent neurons which inhibit the heart rate
Anatomy of MO: Nucleus Solitarius
purely sensory
receive taste, chemoreceptor, baroreceoptor inputs in the aortic arch and carotid body.
ex. When heart rate is too fast, the nucleus solitarius receives input from the baroreceptors and relays information to the brain to reduce heart rate and cause vasodilation
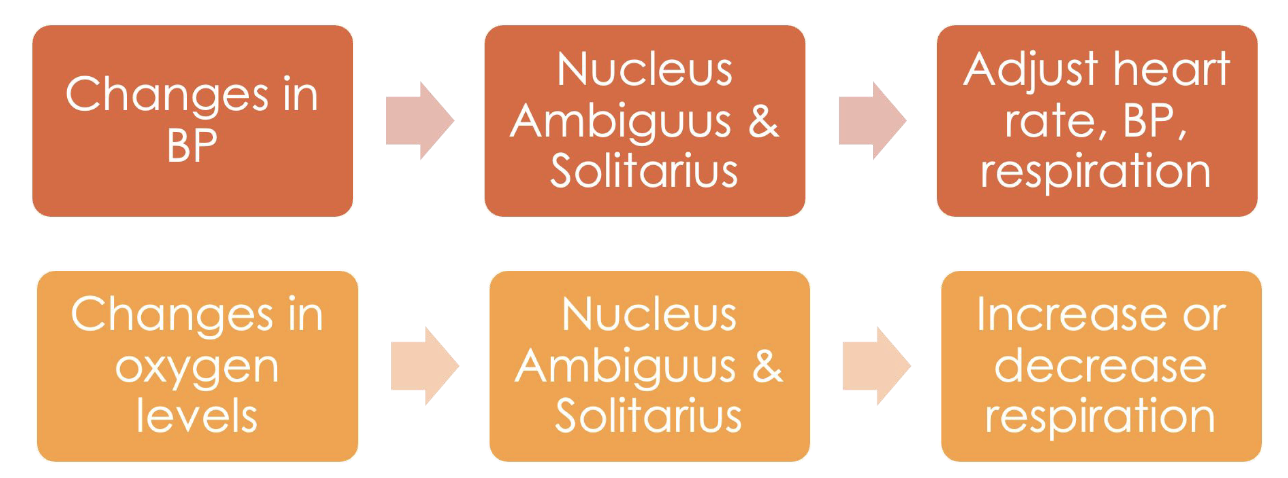
Functions of Nucleus Ambiguus and Solitarius
changes in BP > nucleus ambiguus and solitarius > adjust heart rate, BP, respiration
changes in oxygen levels > nuc. a and s. > increase or decrease respiration
Changes in BP and oxygen levels are received by the nucleus ambiguus and solitarius, which process and relay this information within the brainstem, leading to necessary adjustments
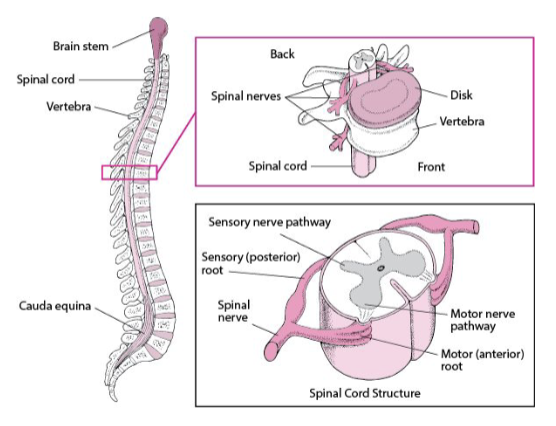
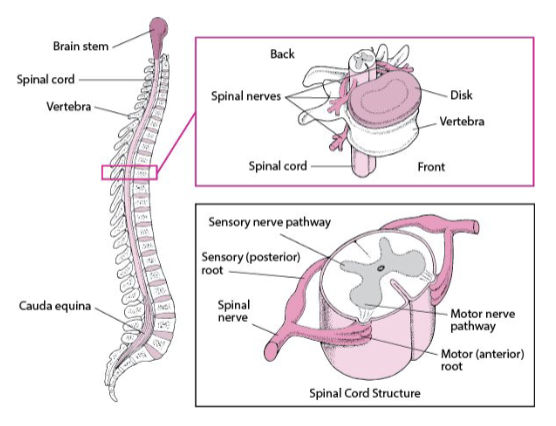
Spinal cord
information highway
located in the spinal canal
occupied 2/3 of the spinal canal
length: 42-45 cm in adults
diameter: 10 mm
expands laterally in the cervical enlargement and the lumbosacral enlargement
SC: Conus medullaris
conical distal end
at the level of L1 or L2 in adults
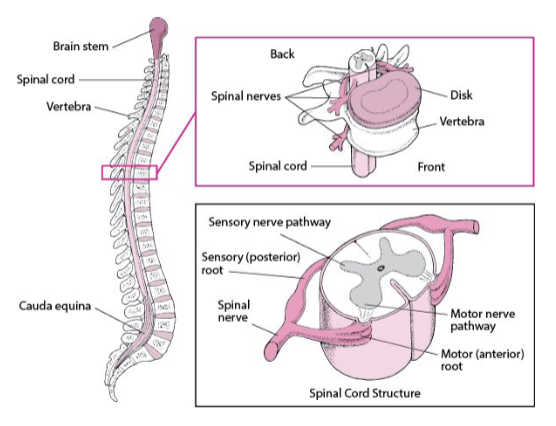
SC: Cauda equina
“Horsetail”
bundle of spinal nerves and rootlets that start at L2 and extend towards the lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal levels
SC: Filum terminale
pia mater within equina that extends from the conus to the distal dural sac
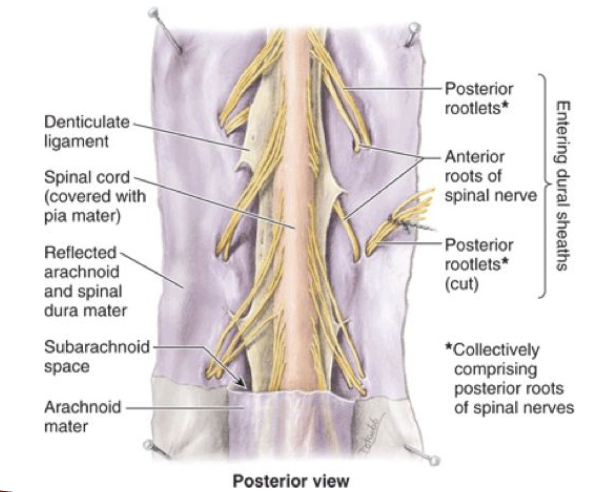
SC: Denticulate ligament
band of fibrous pia mater extending along spinal cord on each side
found between the dorsal and ventral roots
keeps the spinal cord attached to the arachnoid and dura mater to stabilize it
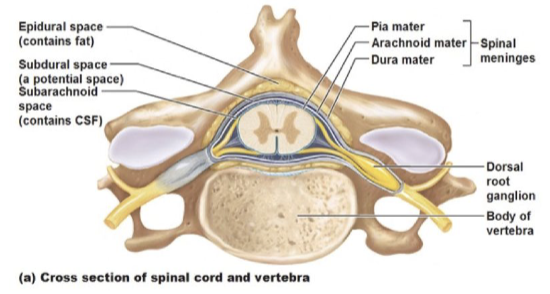
SC: Meningeal Layers
dura, arachnoid, pia mater'
protect the CNS as a shock barrier or cushion
contain CSF which nourishes the brain and SC
SC: Cross section
ventral median fissure
dorsal median sulcus
central/ependymal canal - where CSF passes through
ventral roots (2) - motor nerves, outflow
dorsal roots (2) - sensory nerves
SC: Cross section (Gray and White Matter)
Gray:
Ventral Gray Column/Horn
Lateral Gray Column/Horn
Dorsal Gray Column/Horn
White:
Ventral Gray Column
Lateral Gray Column
Dorsal Gray Column
SC: Dermatomes vs. Myotomes
Dermatomes: skin innervated by single spinal nerve
Myotomes: groups of muscles innervated by single nerve roots
SC: Vertebrae
Cervical: 7
Thoracic: 12
Lumbar: 5
Sacral: 5
Coccygeal: 3-4
Total: 33 bones
SC: Spinal nerves
Cervical: 8 pairs
Thoracic: 12 pairs
Lumbar: 5 pairs
Sacral: 5 pairs
Coccygeal: 1 pair
Total: 31 pairs
SC: Exit points
CerVelow
TaaSic
SC: Gray matter laminas
Rexed’s Laminae
follows a topographic organization
based on the types and functions of the neurons in each laminae
SC: White matter
3 columns
transmits information between brain and body
important for coordination and processing
SC: Reflexes
subconscious stimulus-response
important for diagnosing and localizing neurologic lesions
SC Reflexes: Crossed-extensor reflex
present until two months of age
examiner holds one of the baby’s legs extended and applies firm pressure to the sole of the foot of the same leg.
baby’s free leg flexes, adducts, then extends
grasp reflex
SC Reflexes: Reciprocal innervation
flexor and extensor reflexes of the same limb cannot contract simultaneously
afferent nerve fibers for flexor reflex ms must have branches for extensor motor neurons
SC Lesions: Ant. horn of gray matter downwards are damaged
Affected: striated skeletal ms activity
Cause: trauma, toxins, infections
S/sx:
flaccid paralysis
ms atrophy
diminished or absent DTR
fasciculations and fibrillations
SC Lesions: Damage to lateral white column
S/sx:
spastic paralysis/paresis (tightness/stifness)
disuse atrophy (muscles decrease in size)
hyperactive DTR
diminished or absent superficial reflexes
pathologic reflex (abnormal/primitive reflexes appear in adults)
SC Lesions: Things to consider
what level does abnormality begin (sensory, motor)?
what tracts are affected?
which side are these tracts located?
what sensory modalities are involved?