Unit 6: The Nervous System
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
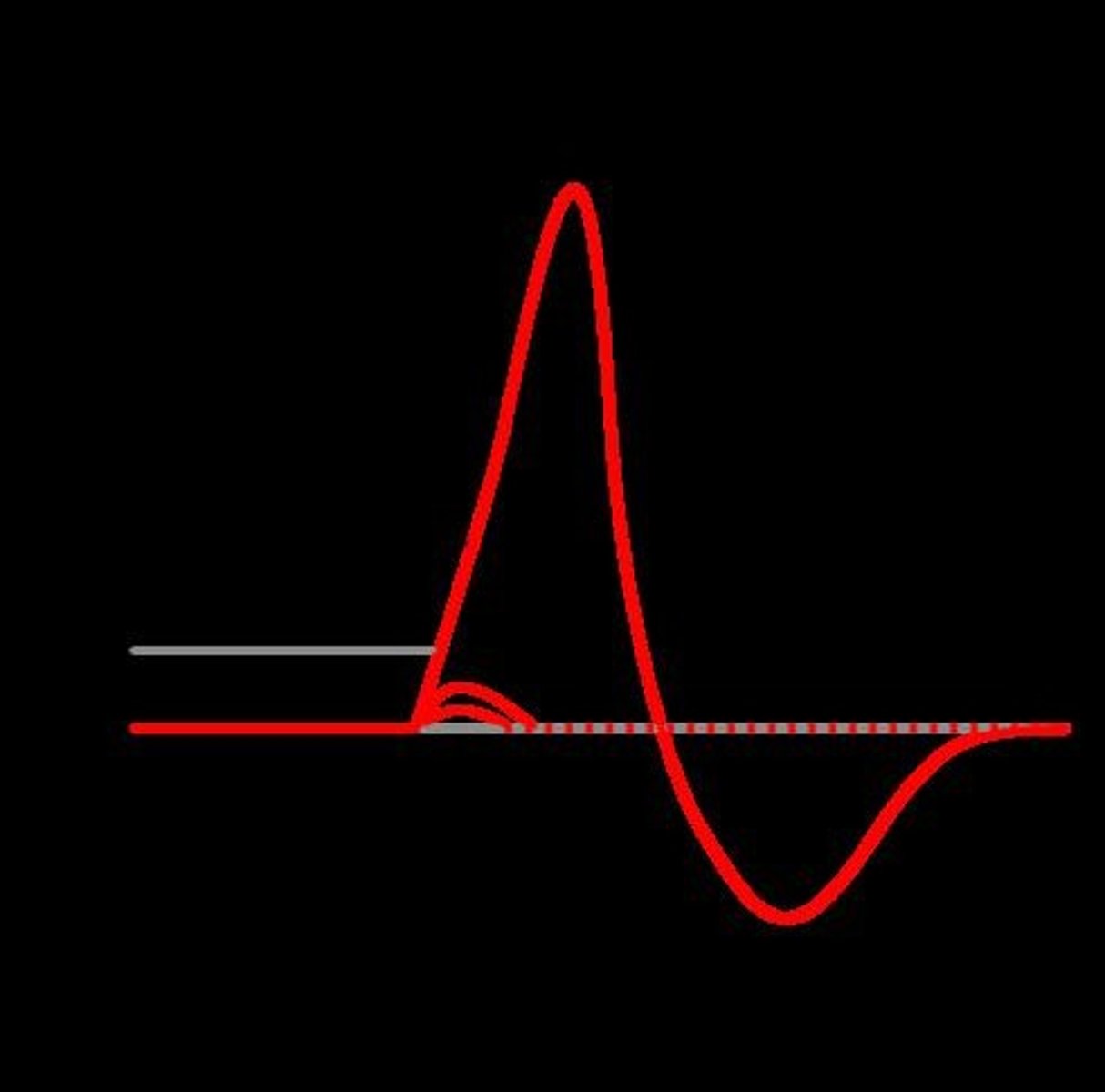
Action potential
The change in electrical potential along the membrane of a neuron associated with the passage of an impulse.
Afferent (sensory) nerves
Responsible for relaying sensation from the body to the central nervous system (CNS).
Autonomic nervous system
A part of the vertebrate nervous system that innervates smooth and cardiac muscle and glandular tissues and governs involuntary actions (as secretion and peristalsis). Consists of the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
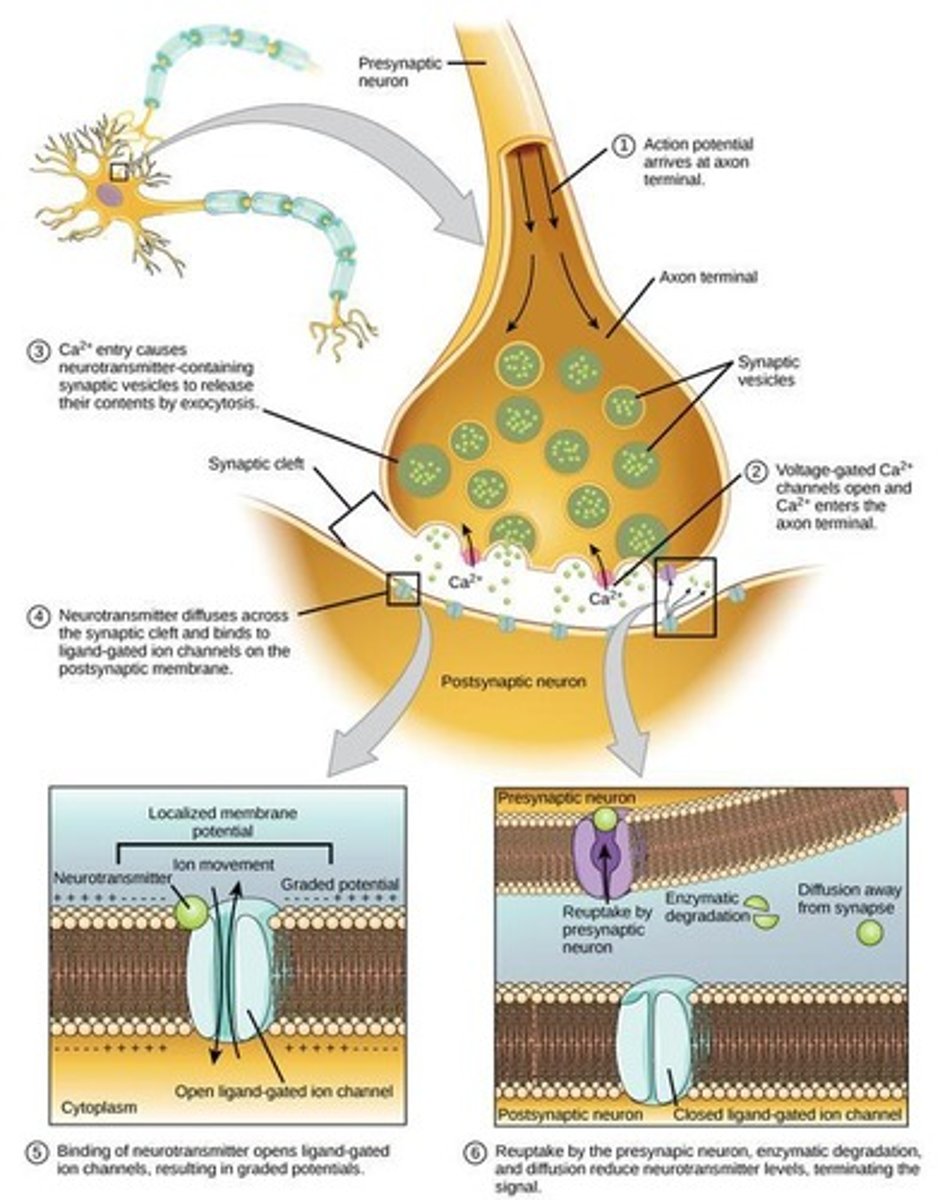
Chemical synapse
Synapse that uses neurotransmitters to transfer signals from one neuron to another.
Central nervous system
The part of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord.
Cerebellum
The back part of the brain that controls balance and the use of muscles.
Cerebrospinal fluid
A colorless liquid, comparable to serum, that is secreted from the blood into the lateral ventricles of the brain. It serves chiefly to maintain uniform pressure within the brain and spinal cord.
Cerebrum
The front part of the brain that is believed to be where thoughts occur.
Depolarization
The return of a cell's electrical potential to its resting state.
Diencephalon
The posterior subdivision of the forebrain.
Efferent (motor) nerves
Responsible for sending out commands from the CNS to effectors in the body, such as muscles and glands.
Electrical potential
Electrostatic potential energy within a membrane.
Ganglia
Nerve cell clusters.
Gap junction
The channel proteins connecting the pre- and postsynaptic neurons in electrical synapses.
Gray matter
Unmyelinated nervous tissue composed mainly of neural cell bodies.
Gyri
Folds in the cerebral cortex (singular: gyrus).
Hyperpolarize
A reduction in the electrical potential of a cell that inhibits the firing of an action potential.
Hypothalamus
A basal part of the diencephalon that lies beneath the thalamus on each side. It forms the floor of the third ventricle and includes vital autonomic regulatory centers (as for the control of food intake).
Medulla oblongata
The somewhat pyramidal last part of the vertebrate brain developed from the posterior portion of the hindbrain and continuous posteriorly with the spinal cord. It encloses the fourth ventricle and contains nuclei associated with most of the cranial nerves, major fiber tracts, and decussations that link the spinal cord with higher centers. It mediates the control of involuntary vital functions, such as respiration.
Meninges
Any of the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. They include the arachnoid, dura mater, and pia mater.
Midbrain
The middle division of the three primary divisions of the developing vertebrate brain, or the corresponding part of the adult brain.
Motor reflexes
Quick, unconscious movements controlled by the spinal cord.
Nerves
Any of the filamentous bands of nervous tissue that connect parts of the nervous system with the other organs and conduct nervous impulses, made up of axons and dendrites together with protective and supportive structures.
Nervous system
The bodily system in vertebrates that is made up of the brain and spinal cord, nerves, ganglia, and parts of the receptor organs, receiving and interpreting stimuli and transmitting impulses to the effector organs.
Neuron
One of the cells that constitute nervous tissue, with the property of transmitting and receiving nervous impulses, composed of somewhat reddish or grayish protoplasm, a large nucleus containing a conspicuous nucleolus, irregular cytoplasmic granules, and highly differentiated cytoplasmic processes.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals used to send signals from one neuron to another.
Parasympathetic nervous system
The part of the autonomic nervous system that contains chiefly cholinergic fibers, inducing secretion, increasing the tone and contractility of smooth muscle, and slowing the heart rate.
Peripheral nervous system
The part of the nervous system that is outside the central nervous system, comprising the cranial nerves, except the optic nerve, the spinal nerves, and the autonomic nervous system.
Pons
A broad mass of chiefly transverse nerve fibers in the mammalian brain stem lying ventral to the cerebellum at the anterior end of the medulla oblongata.
Postsynaptic neuron
A neuron that receives messages.
Presynaptic neuron
A signaling neuron.
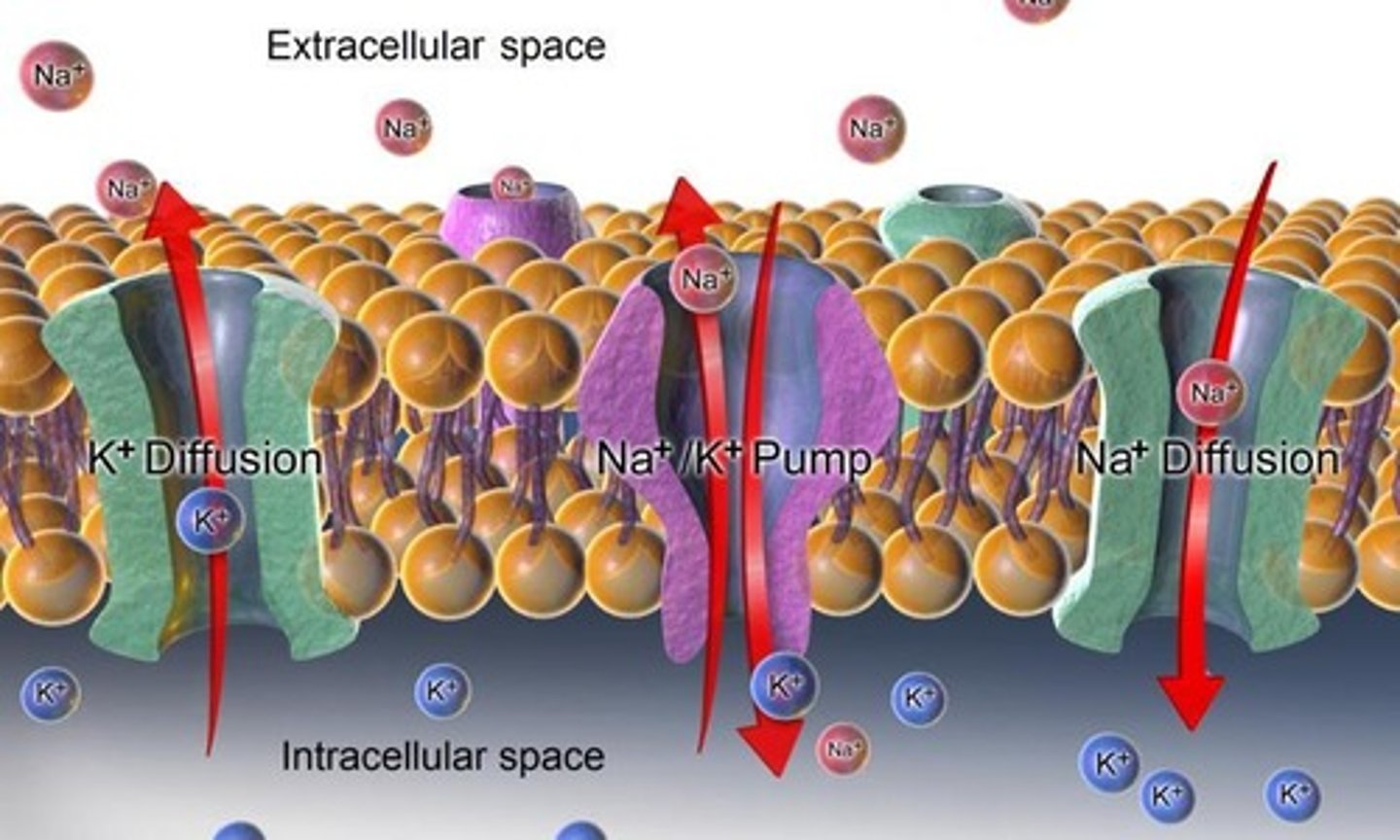
Resting potential
The resting voltage of a neuron (approximately -70 mV).
Somatic nervous system
The part of the peripheral nervous system associated with skeletal muscle voluntary control of body movements.
Spinal cord
The large group of nerves that runs through the center of the spine and carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
Sulci
Valleys in the cerebral cortex (singular is sulcus).
Sympathetic nervous system
The part of the autonomic nervous system that contains chiefly adrenergic fibers and tends to depress secretion, decrease the tone and contractility of smooth muscle, and increase heart rate.
Synaptic vesicle
The vesicle in the axon terminal of a neuron that contains neurotransmitters.
Synapse
A minute gap between messaging neurons.
Synaptic cleft
The extracellular space between pre- and postsynaptic neurons.
Thalamus
The largest subdivision of the diencephalon that consists chiefly of an ovoid mass of nuclei in each lateral wall of the third ventricle and serves chiefly to relay impulses and especially sensory impulses to and from the cerebral cortex.
Voltage-gated ion channels
Ion channels that are activated by changes in the electrical potential of the cell membrane.
Ventricles
The hollow spaces of the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid.
White matter
Myelinated nervous tissue composed mainly of axons.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
One of the two major regions of the nervous system, responsible for processing information and coordinating actions.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The other major region of the nervous system that connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
A subdivision of the PNS that controls involuntary actions and maintains homeostasis.
Homeostasis
The process of maintaining a stable internal environment in the body.
Neurons
The basic functional unit of the nervous system specialized in carrying messages throughout the body.
Neuroglia (Glial Cells)
Support cells in the nervous system that maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons.
Sensory (Afferent) Neuron
Neurons that send information from sensory receptors to the CNS.
Motor (Efferent) Neuron
Neurons that send information from the CNS to muscles or glands.
Interneuron
Neurons that relay information between sensory and motor neurons.
Functions of Glial Cells
1. To surround neurons and hold them in place; 2. To supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons; 3. To insulate one neuron from another; 4. To destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons.
Neuronal Lifespan
Neurons are some of the oldest cells in the body and are typically not replaced when they die.
Neuronal Structure Variation
Not all neurons look alike; their structure depends on their functional need.
Electrochemical Process
The method by which neurons communicate, involving electrical impulses and chemical signals.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty covering that insulates axons and speeds up the transmission of electrical signals.
Nervous Tissue Composition
Nervous tissue is primarily made of neurons and neuroglia.
Neuronal Axon Length
Some axons can stretch over several feet, making them some of the longest cells in the body.
Neuronal Cell Membrane
Neurons, like other cells, are surrounded by cell membranes and contain organelles.
Nervous System Functions
The nervous system coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions and maintains homeostasis.
Neuronal Nuclei
Neurons have nuclei that contain genes, which are essential for cellular processes.
Nervous System Divisions
The nervous system can be divided into the CNS and PNS, each with distinct structural and functional characteristics.
Ions
Electrically charged chemicals in the body, including Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl-, that are crucial for action potentials.
Chemical Synapses
Synapses that use neurotransmitters to transmit signals between neurons.
Electrochemical Gradient
The difference in ion concentration across the cell membrane that creates an electrical potential.
Calcium Ion (Ca2+)
An ion that enters the neuron during an action potential, triggering the release of neurotransmitters.
Sodium Ion (Na+)
An ion that enters the neuron during depolarization, causing the inside of the cell to become positive.
Potassium Ion (K+)
An ion that is pumped out of the neuron to return the electrochemical gradient to the resting state.
Chloride Ion (Cl-)
An ion that contributes to the negative charge of a resting neuron and cannot easily diffuse across the cell membrane.
Threshold Value
The specific level of electrical potential that must be reached for action potentials to occur.
Synaptic Vesicles
Membrane-bound structures that store neurotransmitters at the axon terminal.
Extracellular Space
The area outside the neuron where neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft.
Electromechanical Signaling
The process by which messages are converted from electrical to chemical and then back to electrical in the nervous system.
Selective Permeable Membrane
A type of cell membrane that allows certain ions to pass while restricting others, contributing to the resting potential.
Action Potential Speed
The rate at which action potentials can travel, sometimes reaching speeds of 120 m/s.
Ion Channels
Protein structures that allow specific ions to pass through the cell membrane, crucial for generating action potentials.
Inactivation of Ion Channels
The rapid closure of sodium channels after depolarization, preventing further sodium ion entry.
Excitatory neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter that causes depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, increasing the probability of firing an action potential.
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter that causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, reducing the likelihood of firing an action potential.
Acetylcholine
An excitatory neurotransmitter that causes an influx of positive ions into the membrane at the neuromuscular junction.
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
An inhibitory neurotransmitter that creates an influx of negative ions into a neuron, hyperpolarizing the cell.
Neurotransmission reset methods
The process of removing neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft, which can occur by diffusion, degradation by enzymes, or recycling by the presynaptic neuron.
Acetylcholinesterase
An enzyme that degrades acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft, targeted by some drugs for Alzheimer's patients.
Electrical synapse
A type of synapse where pre- and postsynaptic neurons are physically connected by gap junctions, allowing ions and molecules to flow directly between cells.
Gap junctions
Channel proteins that connect pre- and postsynaptic neurons in an electrical synapse, allowing current to pass directly from one cell to another.
Proximity in electrical synapses
Pre- and postsynaptic neurons are connected by gap junctions.
Proximity in chemical synapses
Pre- and postsynaptic neurons are separated by the synaptic cleft.
Timing in electrical synapses
The transmission of signals is virtually instantaneous.
Timing in chemical synapses
Approximately 1 ms for the message to go from cell to cell.
Directional nature of electrical synapses
Some electrical synapses are bidirectional.
Directional nature of chemical synapses
Chemical synapses are unidirectional.
Reliability of electrical synapses
More reliable and less likely to be blocked.
Reliability of chemical synapses
Less reliable and more likely to be blocked due to the steps required for signal transmission.
Number of neurons involved in electrical synapses
Communication only involves the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons.
Number of neurons involved in chemical synapses
Can synchronize the electrical activity of a group of neurons.
Control in electrical synapses
Less control, as an action potential in one neuron generates an action potential in all connected neurons.
Control in chemical synapses
More control, as the target is more precise.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
A colorless liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, maintaining uniform pressure and providing mechanical and immunological protection.
Foramen Magnum
The opening at the base of the skull where the brain and spinal cord are continuous.