Soils Final Exam
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
The red, brown, and tan colors found in soils are caused by…
a. Reduced iron which has a charge of +2
b. Oxidized iron which has a charge of +2
c. Reduced iron which has a charge of +3
d. Oxidized iron which has a charge of +3
e. Silica and organic matter what has no net charge
d. d. Oxidized iron which has a charge of +3
Soil “A” has color by the Munsell code of 10YR 3/3 while soil “B” is 10YR 4/2. Thus soil “B” has…
a. a higher Hue
b. a higher chroma
c. a higher value
d. higher value and chroma
e. higher chroma and hue
c. a higher value
A soil very high in organic matter is likely to have a soil color that is…
a. low in value
b. high in value
c. high in chroma
d. 2.5YR hue
e. 5YR hue
a. low in value
Sand is _____ in diameter.
a. 2mm-.05mm
b. 2mm-.5mm
c. 1mm-.05mm
d. 2mm-.02mm
e. 1mm.005mm
a. 2mm-.05mm
Very sandy soils usually have…
a. Rapid water infiltration rates and a low bulk density
b. Rapid water infiltration rates, high bulk density, and low water storage capacity
c. low water percolation rates and low water storage capacity
d. Low water infiltration rates, high bulk density, and moderate water storage
e. none of the above
b. Rapid water infiltration rates, high bulk density, and low water storage capacity
In a typical loam surface soil, which occupies the smallest volume?
a. Minerals
b. Organic material
c. water
d. air
e. none of the above
b. Organic material
The zone of maximum clay accumulation in a soil profile is the ___ horizon.
a. A
b. E
c. BE
d. B
e. BC
d. B
The horizon of maximum leaching would be …
a. Oi
b. AB
c. E
d. C
e. B
c. E
The hydrometer readings in a textural analysis are 35g/l at 40 seconds, and 15g/l at 2 hours. if no temperature correction is needed the 50g sample contained…
a. 20% silt and15% clay
b. 30% clay and 40% silt
c. 30% sand and 70% clay
d. 40% silt and 15% sand
e. none of the above
b. 30% clay and 40% silt
The translocation of iron and clay into a soil horizon is referred to as..
a. Addition
b. Eluviation
c. illuviation
d. transformations
e. Losses
c. illuviation
Which of the following is the least compacted soils?
a. 1.62g/cm³
b. 1.23g/cm³
c. 1.55g/cm³
d. 1.65g/cm³
e. 1.20g/cm³
e. 1.20g/cm³
A soil sample from the intramural fields has a wet weight of 900g, an oven dry weight of 800g, and occupies a volume of 500 cubic cm. If the particle size is 2.6g/cm³, what is the bulk density and % pore space of this sample?
a. BD= 1.4g/cm³ %PS=42%
b. BD= 1.6g/cm³ %PS=38%
c. BD= 1.6g/cm³ %PS=62%
d. BD= 1.8g/cm³ %PS=69%
e. BD=1.8g/cm³ %PS=31%
b. BD= 1.6g/cm³ %PS=38%
Of the following soil properties, which one is not affected by tillage?
a. Structure
b. Bulk density
c. Texture
d. Porosity
e. All of the above
c. Texture
A soil “E” horizon has many peds that are developed predominantly along the horizontal axis (flaky). This is typical of a structural form called…
a. Platy
b. Prismatic
c. Massive
d. Angular blocky
e. Columnar
a. Platy
Which structure(s) are commonly found in B horizons?
a. Granular
b. Massive
c. Sub-angular blocky
d. Prismatic
e. C and D
e. C and D
Native vegetation, topography, and climate are three of the soil forming factors. The other two are…
a. leaching and biologic factors
b. Oxidation and organic matter
c. Time and parent material
d. Eluviation and translocation
e. Physiology and rainfall
c. Time and parent material
The parent material on a river flood plain would be considered..
a. Alluvial
b. Aeolian
c. Colluvial
d. Eluvial
e. illuvial
a. Alluvial
Lacustrine parent material was deposited…
a. By wind
b. At the bottom of old lakes
c. By glaciers
d. by streams
e. none of the above
b. At the bottom of old lakes
Glacial till is transported and deposited by…
a. High winds associated with retreated glaciers
b. Glacial ice
c. Glacial meltwater
d. Colluvial action
e. None of the above
b. Glacial ice
Many soils in old landscapes are forms from weathering and breakdown of the bedrock. The parent material would be considered…
a. Aeolian
b. Alluvial
c. Eluvial
d. Colluvial
e. Residual
e. Residual
A soil with a significant accumulation of soluble salts in the lower horizons is probably in the order…
a. Alfisol
b. Aridisol
c. Entisol
d. Oxisol
e. Spodosol
b. Aridisol
Most soil with deep (>10”), dark (10YR 3/2) surface horizons Which remain friable are…
a. Aridisols
b. Entisols
c. Mollisols
d. Oxisols
e. Ultisols
c. Mollisols
If the soils are to be used for crop production, for which soil order would land drainage be most critical?
a. Mollisol
b. Inceptisol
c. Aridisol
d. Oxisol
e. Histosol
e. Histosol
Which of the following would you least expect to find in MN?
a. Argiudoll
b.Udipsamment
c. Dystrochrept
d. Haplorthox
e. Hapludalf
d. Haplorthox
Which of the following is considered the oldest soil?
a. Ultisol
b. Spodisol
c. Oxisol
d. Entisol
e. Mollisol
c. Oxisol
Which of the following is considered a young soil?
a. Spodosol
b. Alfisol
c. Inceptisol
d. Entisol
e. Ultisol
d. Entisol
A spodosol would most likely have the following sequence of horizons…
a. Ap, AB, Bt1, Bt2, C
b. A, E Bhs, Bs, BC, C
c. Oi, A, Bt, C
d. A, AB, B, Bx, C
e. A, E, BE, B, C
b. A, E Bhs, Bs, BC, C
What is the soil order of this soil: Loamy, mixed, euic Terric Borosaprists
a. Entisol
b. Inceptisol
c. spodosol
d. Mollisol
e. Histosol
e. Histosol
What is the soil order of this soil: Fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, calcareous, frigid Mollic Udifluvents
a. Entisol
b. Gelisol
c. Afisol
d. Mollisol
e. Histosol
a. Entisol
A soil with the following soil horizons Ap>Bssg1>Bssg2>Cg1>Cg2 is classified as a:
a. Mollisol
b. Entisol
c. Inceptisol
d. Vertisol
e. Histosol
d. Vertisol
A soil witht hefollowing soil horizons Ap>Bw1>Bw2>Cg1>Cg2 is classified as a:
a. Mollisol
b. entisol
c. Inceptisol
d. Vertisol
e. Histosol
c. Inceptisol
A soil witht he following soil horizons A>E>Bt1>Bt2>C is classified as a:
a. Mollisol
b. Spodosol
c. Alfisol
d. Vertisol
e. Histosol
c. Alfisol
Soil properties change markedly across small distances due to small changed in
a. Climate
b. Topography
c. Living Organisms
d. Parent material
e. Both b and d
e. Both b and d
The weakest step in the soil testing procedure is most frequently…
a. Sample collection
b. Extraction of sample
c. Determination of concentration in extract
d. Interpretation of results
e. none of the above
a. Sample collection

Determine the drainage classification for the following soil Pedon description
a. well drained
b. moderately well drained
c. somewhat poorly drained
d. poorly drained
e. none of the above
b. moderately well drained
What is Lacustrine (Parent material) mode of transportation?
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Glacial Ice
d. Residual
e. Gravity
f. Glacial Meltwater
b. Water
What is Tills (parent material) mode of transportation
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Glacial Ice
d. Residual
e. Gravity
f. Glacial Meltwater
c. Glacial Ice
What is vegetations (parent material) mode of transportation.
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Glacial Ice
d. Residual
e. Gravity
f. Glacial Meltwater
d. Residual
What is Colluvium (parent material) mode of transportation.
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Glacial Ice
d. Residual
e. Gravity
f. Glacial Meltwater
e. Gravity
What is Outwash (parent material) mode of transportation.
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Glacial Ice
d. Residual
e. Gravity
f. Glacial Meltwater
f. Glacial Meltwater
What is Loess (parent material) mode of transportation.
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Glacial Ice
d. Residual
e. Gravity
f. Glacial Meltwater
a. Wind
Which soil order is this:
SLight B horizon development; young soil; usually found on older flood plains or steep slopes.
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
k. Inceptisols
Which soil order is this:
Frost mixing, permafrost, within 200cm of the soil surface
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
a. Gelisols
Which soil order is this:
Large cracks when dry. Swells and churns when wet, has slicken sides within 100cm of surface
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
e. Vertisols
Which soil order is this:
Light colored surface soils, gray to brown subsoils, often some iron oxide accumulation; high (>35%) base saturation
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
g. Alfisols
Which soil order is this:
Accumulation of calcium carbonate and calcium sulfate, or other salts as concentrations or white spots in the sub soil
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
L. Aridisols
Which soil order is this:
A-C profile (no B horizon); may have an Ap horizon. Commonly found on river flood plains or in very sandy soils
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
j. Entisols
Which soil order is this:
Found in old landscapes, especially in tropics. profiles develop very deep. Silicate minerals have been weathered away except for some kaolinite clay.
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
I. Oxisols
Which soil order is this:
organic Profile, >20%
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
c. Histosols
Which soil order is this:
Profile is mostly mineral, <20% organic matter
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
d. Mollisols
Which soil order is this:
High illuvial iron-humus accumulation, Bhs; directly under very light colored E, Usually sandy
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
f. Spodosols
Which soil order is this:
Dark mineralic surface, high in iron, aluminum and organic matter, slightly weathered, low bulk density
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
b. Andisols
Which soil order is this:
Light-colored surface soils, usually yellowish to redish subsoils. Low (<35%) base saturation in argillic horizon. Silicate mineral still present
a. Gelisols
b. andisols
c. Histosols
d. Mollisols
e. Veritsols
f. Spodosols
g. Alfisols
h Ultisols
I Oxisols
j Entisols
k. Inceptisols
L Aridisols
H. Ultisols
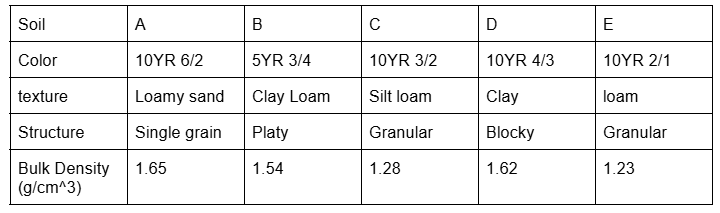
which soil will absorb the most water. based on texture
D
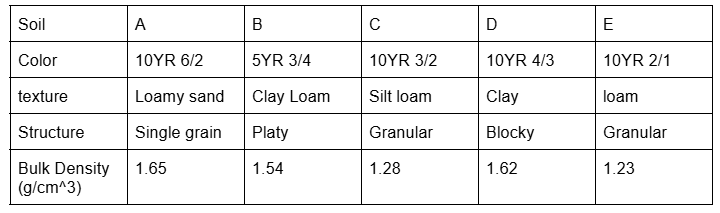
Which soil is the least porous
A
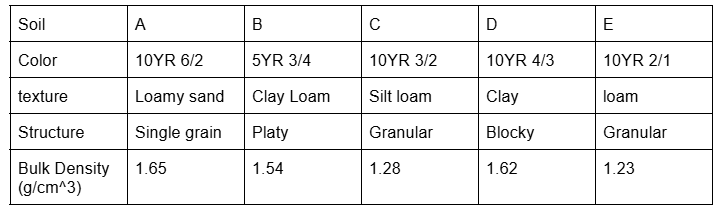
Which soil is the least compacted
E
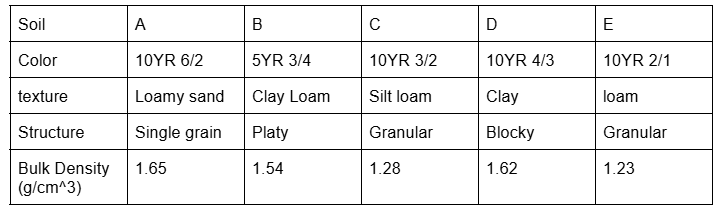
Which soil has the lightest color
A
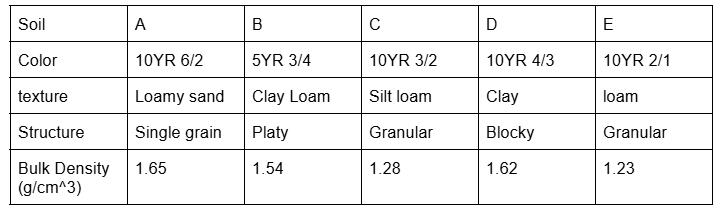
Which soil has the slowest water movement based on structure
B
Two steps recognized in the mechanics of accelerated erosion are…
a. adsorption and exchange
b. Crusting and splash
c. splash and puddling
d. Detachment and transport
d. Detachment and transport
of the following types of erosion, which one interfers with tractor operations in the field?
a. Gully
b. sheet
c. rill
d. slope
e. none of the above
a. Gully
which of the following will increase the likelihood of soil erosion?
a. Reduced soil cover
b. tillage resulting in a smooth soil surface
c. decreased water infiltration
d. all of the above
e. A and C
d. all of the above
which factor in the soil loss equation is strongly influenced by soil texture?
a. R
b. K
c. LS
d. C
e. P
b. K
Which two factors of the universal soil loss equation could be most easily adjusted by the individual landholder
a. K and R
b. C and LS
c. C and P
d. K and C
e. LS and P
c. C and P
if one did no-till planting rather than conventional tillage with fall plowing then
a. Erosion is greater because tillage controls erosion
b. soil loss should be reduced because of the greater amount of surface plant residues
c. Erosion is reduced because no - till leaves a clean soil surface
d. Soil loss increases since no-till soils allow less water
b. soil loss should be reduced because of the greater amount of surface plant residues
The attraction of two like molecules for one another is termed
a. Evaporation
b. Cohesion
c. adsorption
d. absorption
e. Tension
b. Cohesion
Available soil water is between ______and _______.
a. Saturation-Field Capacity
b. Wilting point-Unavailable water
c. Field Capacity - Wilting point
d. none of the above
c. Field Capacity - Wilting point
Water moving by unsaturated flow in a lateral direction id being moved by the forces of…
a. Adhesion
b. Cohesion
c. Gravity
d. A and B
e. A,B and C
d. A and B
TDR’s (Time Domain Reflectometry) measures soil water
a. Potential
b. Content
c. Evaporation
d. Osmotic Forces
b. Content
The components of the overall soil water potential include all of the following except
a. Matrix potential
b. Osmotic potential
c. gravitational Potential
d. Unsaturated potential
d. Unsaturated potential
Tensiometers measure soil water
a. Content
b. Potential
c. Flow
d. Hygroscopic
e. A and B
b. Potential
The soil collids responsible for the negative charge (CEC) are
a. Sand and silt
b. Kaolinite and lime
c. Clays and organic matter
d. Illite and lime
c. Clays and organic matter
A light colored soil with a CEC of 5 cmol(+)/kg would most likely be in the textural class of
a. silty clay loam
b. silt loam
c. Sandy loam
d. clay
c. Sandy loam
What is the charge of soil?
a. Negative
b. Neutral
c. Positive
d. A and C
e. none of the above
a. negative
The clay minerals montmorillonite and illite have
a. A positive charge coming mostly from isomorphic substitution
b. A negative charge coming mostly from broken edge bonds
c. A positive charge coming mostly from broken edge bonds
d. a negative charge coming mostly from isomorphic substitution
d. a negative charge coming mostly from isomorphic substitution
When liming a soil with a pH of 5.8, the acidity which must be neutralized is found
a. On the soil exchange sites
b. In the soil solution
c. In the center of the silicon tetrahedrons
d. A and B
a. On the soil exchange sites
The ion in soil is considered an “acid” cation because it reacts readily and strongly with hydroxyles and becasue it reacts with water molecules casuing them to lose (or dissociate) hydrogen ions. it is
a. Phosporus
b. Magnesium
c. Calcium
d. Aluminum
e. Potassium
d. Aluminum
A highly buffered soil always
a. Has a higher pH than a poorly buffered soil
b. Has a lower pH than a poorly buffered soil
c. Has a higher CEC than a poorly buffered soil
d. A and C
e. B and C
c. Has a higher CEC than a poorly buffered soil
A pH meter measures
a. Active acidity which is found on the exchange sites
b. Active acidity which is found in the soil solution
c. Reserve which is found on the exchange sites
d. Reserve acidity which is found in the soil solution
e. A and D
b. Active acidity which is found in the soil solution
Soils become acidic due to
a. Prolonged leaching
b. Reduction of ammonium to nitrate
c. Anions released from roots
d. Aluminum released from clay minerals
e. A and D
e. A and D
Soil pH’s commonly range from
a. 2-11
b. 0-14
c. 3-8
d. 1-10
e. 0-8
c. 3-8
Lower soil pH (approx pH=5.0) tends to increase the availability of
a. Fe
b. Zn
c. Al
d. P
e. A, B, and C
e. A, B, and C
A pH of 8 is considered:
a. Neutral
b. Acidic
c. Absorbent
d. Alkaline
e. None of the above
d. Alkaline
A soil pH of 4.8 or less can cause a toxicity to _____?
a. Mg
b. Mn
c. Al
d. H
e. B and C
e. B and C
Does adding one ton Ammonium sulfate Increase or decrease the soils pH?
Decrease
Does adding one ton Potassium nitrate Increase or decrease the soils pH?
Increase
Does adding one ton IBDU (isobutyraldhyde urea) Increase or decrease the soils pH?
Decrease
Does adding one ton CaMg(CO³)² Increase or decrease the soils pH?
Increase
Does adding one ton Elemental sulfur (S) Increase or decrease the soils pH?
Decrease
Which one is commonly found in Ultisols
a. montmorillonite
b. Illite
c. Kaolinite
c. Kaolinite
Which one is a 1:1 clay mineral
a. montmorillonite
b. Illite
c. Kaolinite
c. Kaolinite
Which one contains interlayer potassium
a. montmorillonite
b. Illite
c. Kaolinite
b. Illite
Which one has a CEC of aprox 100 cmol(+)/kg
a. montmorillonite
b. Illite
c. Kaolinite
a. montmorillonite
Which one is commonly found in well-drained Midwestern soils
a. montmorillonite
b. Illite
c. Kaolinite
B. Illite
What are the 5 environmental factors that control the rate of decomposition and mineralization?
Warm Temps
soil moisture
Neutral pH
Drying/rewetting soil
Good aeration
What forms of Nitrogen are taken up by the plant
NH4^+ , NO3^-
What forms of phosphorus are taken up by the plant?
H2PO4^- , HPO4^2-
What forms of potassium are taken up by the plant
K^+
A soil with 10% illite clay, 20% montmorillonite clay, and 2% organic matter would have an approximate CEC of
a. 4 cmol(+)/kg
b. 14 cmol(+)/kg
c. 28 cmol(+)/kg
d. 40 cmol(+)/kg
e. 80 cmol(+)/kg
c. 28 cmol(+)/kg
Most anaerobic organisms are
a. Algae
b. Fungi
c. Bacteria
d. Actinomycetes
c. Bacteria
Of the following types of nitrogen additions, which one is arranged in order from greatest to least in terms of their contribution to most agricultural soils?
a. Legume–Rhizobium symbiosis > lightning > nonsymbiotic nitrogen fixers
b. Legume–Rhizobium symbiosis > nonsymbiotic nitrogen fixers > lightning
c. Lightning > legume–Rhizobium symbiosis > nonsymbiotic nitrogen fixers
d. Nonsymbiotic nitrogen fixers > legume–Rhizobium symbiosis > lightning
b. Legume–Rhizobium symbiosis > nonsymbiotic nitrogen fixers > lightning