The Circulatory System: Blood Outline Part 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Blood types and transfusion compatibility depends on
plasma proteins & erythrocytes
blood types based on antigens and antibodies
Antigens on RBC surface=
Agglutinogens
Antibodies in plasma=
agglutinins
Agglutination
antibody molecule binding to antigens
causes clumping of RBCs—not good
RBC agglutinogens
antigen A & B
determined by carbohydrate moieties
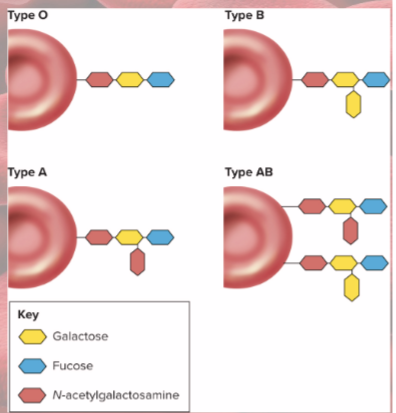
Agglutinins
(antibodies in plasma)
anti-A & anti-B
ABO blood type determined by presence/ absence of..
antigens (agglutinogens) on RBCs
blood type A person has A antigens
blood type B person has B antigens
Blood type AB has both A & B antigens
blood type O person has neither antigen
most common is type O and rarest is type AB
Can a type B dad have a type O child with a type A mom?
Yes!
Can a type O dad and a type AB mom have a type O child?
No!
Antibodies (agglutinins) for every blood type
Type A or O have anti-B agglutinins
Type B or O have anti-A agglutinins
Type AB, have neither
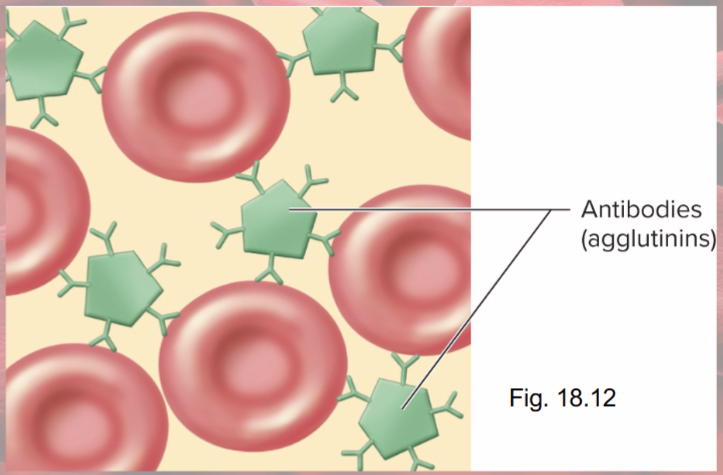
Agglutination problems
agglutinated RBCs block small blood vessels and hemolyze
Hemoglobin blocks kidney tubules, causes renal failure
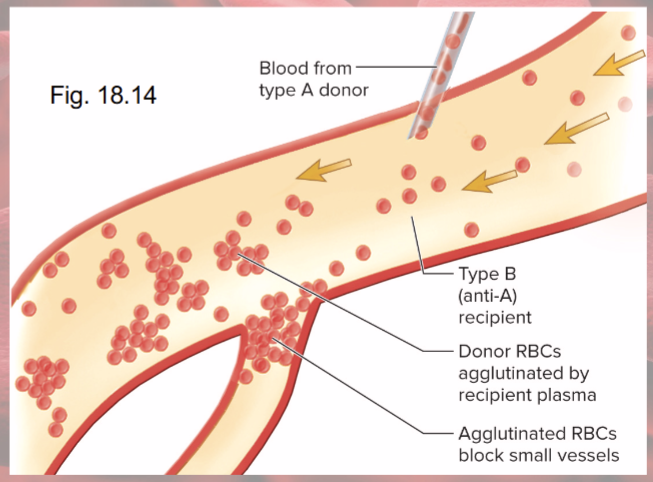
Universal donor is type
O (most common blood type)
Universal recipient is type
AB (rarest blood type)
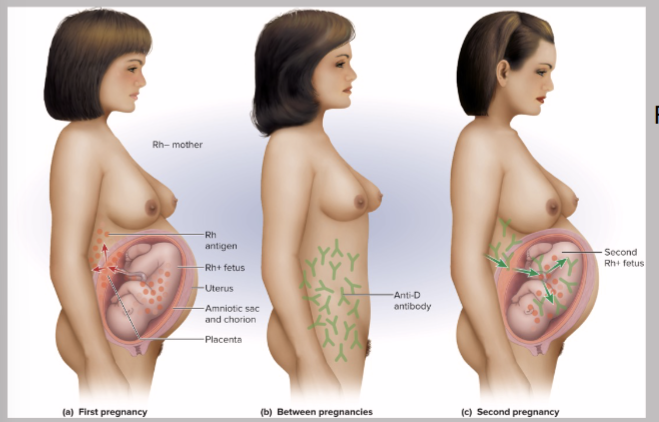
Rh D=
most reactive; patient called Rh+ if D antigen on RBCs
Anti-D agglutinins (antibodies) not normally present form in…
Rh- individuals exposed to Rh+ blood
no problem with first pregnancy
If Rh- mother formed Abs & is pregnant with second Rh+ child——-Anti-D antibodies can cross placenta
RhoGAM does what?
given to pregnant Rh- women
binds fetal agglutinogens in her blood so she will NOT form anti-D antibodies!!!!!!!!!!
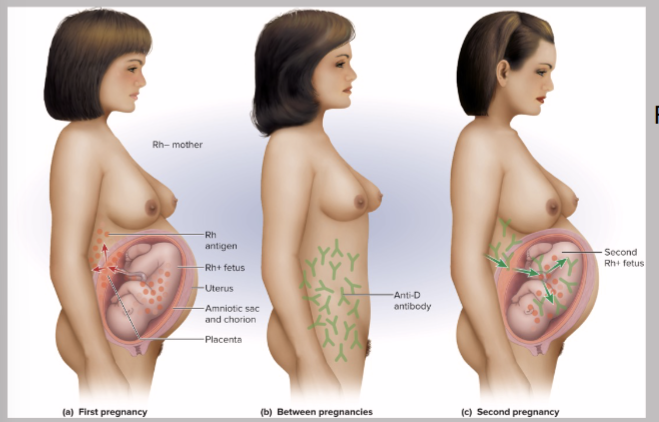
Hemolytic Disease of Newborns (HDN)
Rh antibodies attack fetal blood, causing severe anemia
How many WBCs per microliter?
5,000 to 10,000
Granules:
Granulocytes have SPECIFIC granules: protein-packed lysosomes
(all WBCs have lysosomes=nonspecific granules: cytoplasm looks clear)
Neutrophils anatomy
(granulocyte)
polymorphonuclear
granules barely visible
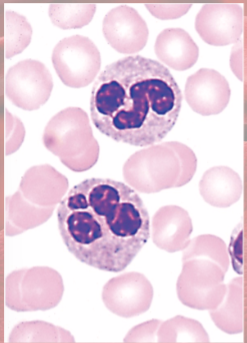
Eosinophils anatomy
(granulocyte)
large red granules; bi-lobed nucleus
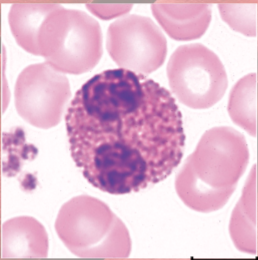
Basophils anatomy
(granulocyte)
large violet granules (obscure S-shaped nucleus)
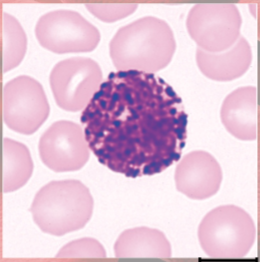
lymphocytes anatomy
(agranulocyte)
BIG round, uniform dark violet nucleus
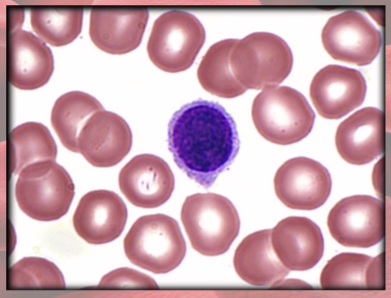
Monocytes anatomy
(agranulocyte)
largest WBC; kidney/horseshoe-shaped nucleus
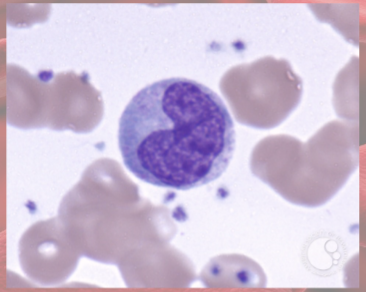
Neutrophils functions
(granulocyte)
increased in bacterial infections
phagocytosis of bacteria
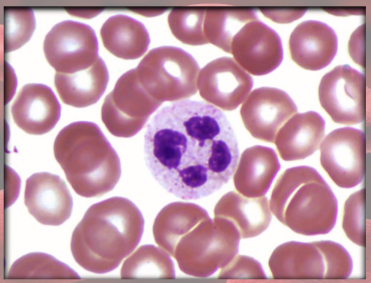
Eosinophils functions
(granulocyte)
increased in parasitic infections, allergies, collagen diseases
release enzymes to destroy large parasites
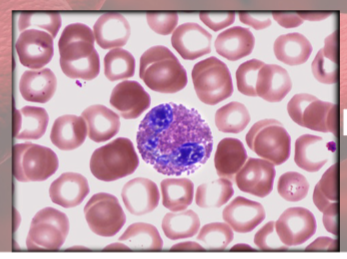
Basophils functions
(granulocyte)
secrete histamine (vasodilator): speeds flow of blood to injured area
secrete heparin (anticoagulant): promotes mobility of other WBCs
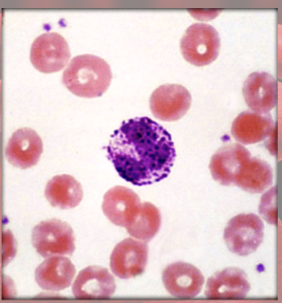
Lymphocytes functions
(agranulocyte)
destroy cells (cancer, foreign, and virally infected cells)
“present” antigens to activate other immune cells
coordinate actions of other immune cells
secrete antibodies and provide immune memory
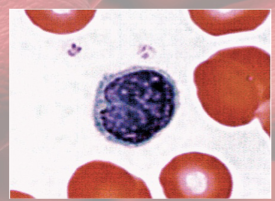
Monocytes functions
(agranulocyte)
increased numbers in viral infections and inflammation
leave blood and transform into macrophages
phagocytize pathogens and debris
“present” antigens to activate other immune cells—antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
Leukopoiesis
production of WBCs
HSCs—CFUs—then…
myeloblasts (form neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), monoblasts (form monocytes), lymphoblasts (form lymphocytes)
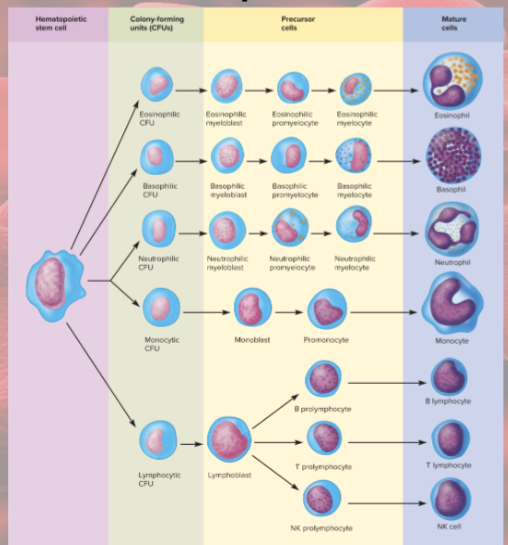
Circulating WBCs do…
NOT stay in blood
granulocytes leave in 8 hrs and live 5 days
monocytes leave in 20 hrs and transform into macrophages and live years
lymphocytes provide long-term immunity (decades) and is recycled
Leukopenia
low WBC count (less than 5,000)
caused by: radiation, poisons, some viral diseases
concern: elevated risk of infection
Leukocytosis
high WBC count (over 10,000)
caused by: infection, allergy, dehydration
Differential WBC count
% of total WBC count for each type of leukocyte
Leukemia
cancer of hemopoietic tissue; extraordinarily high number of circulating leukocytes and their precursors
Myeloid leukemia
uncontrolled granulocyte production
Lymphoid leukemia
uncontrolled lymphocyte or monocyte production
acute vs chronic leukemia
appears suddenly, progresses rapidly
vs
can go undetected for months, survival time 3 yrs (untreated)
Complete Blood Count
Hematocrit (RBC %)
Hemoglobin concentration
total count for cells and platelets
differential WBC count—NLMEB
RBC size and hemoglobin concentration per RBC
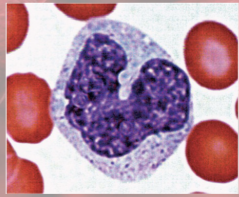
Normal vs leukemic blood
photo
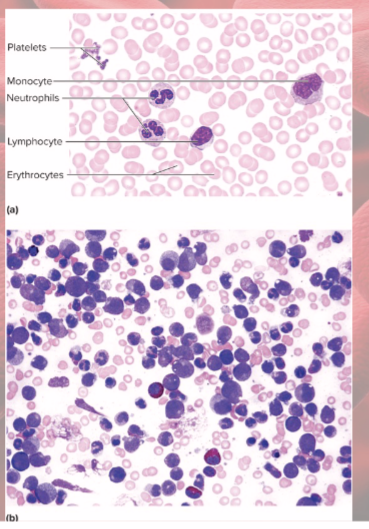
effects of Leukemia
impaired function, therefore opportunistic infections, impaired production of RBCs, platelets