MT 4 Senescence and Hallucinations
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
inability to see two or more objects presented at the same time, although they can be identified individually
simultagnosia= ____________
Balint syndrome
TRIAD
1. simultagnosia
2. oculomotor ataxia egclumsy eye movements)
3. oculomotor apraxia eg.trouble initiating saccades:
TRIAD
1. simultagnosia
2. oculomotor ataxia eg clumsy eye movements
3. oculomotor apraxia eg.trouble initiating saccades
describe Balint Syndrome
bilateral parietal lobe lesions
what causes balint syndrome?
unable to reach and grab things based on visual stimulus. Therefor, accommodation, convergence, binocular and oculomotor skills can be affected -> will have issues with motion perception
describe oculomotor ataxia in Balint syndrome
problems with fixation, saccade initiation and accuracy and pursuits. -> this causes chaotic eye movements
describe Oculomotor Apraxia in Balint syndrome
neurogenerative diseases eg. Alzheimer disease
most common way to get bilateral damage to the parietal lobe causing Balint syndrome?
Balint syndrome: argued that is bilateral hemispatial visual neglect. neglect both sides of view but they can see a single object, and do not neglect a portion of the object which can occur in unilateral neglect
unilateral neglect: damage to right hemisphere parietal lobe
Balint syndrome vs neglect
Balint patients
Alzheimer dementia patients
both have simultagnosia
which patients fail the cookie theft picture?
lost ability to recognize faces including their own, also called face blindness
what is prosopagnosia?
looking at the 2 eyes, nose then mouth
adults seem to all perform the same facial scan paths
damage to the fusiform gyrus near IT or V4, usually bilateral damage occasionally right hemisphere. recent evidence has shown a reduced volume in the inferior longitudinal fasiculus.
what damage in the brain causes prosopagnosia?
fusiform gyrus
V4 is known as the end of the parvo stream where objects and faces are recognized however they are not in the same location. where are faces recognized?
role in biological motion
what is the role of the superior temporal sulcus (STS)?
superior temporal sulcus (STS)
where does biological motion occur?
Emotion recognition and facial memory
inferior longitudinal fasciculus is thought to connect ________
get face blindness (prosopagnosia) as well as emotion blindness
if there is a lesion in the inferior longitudinal fasciculus what can occur?
they are inverted compared to healthy patients easier to match faces when right side up
prosopagnosia patients actually can identify faces easier if __________
inverted images like healthy patients are
patients with prosopagnosia's are not fooled by ___________
started as a joke saying there is a single neuron that is for your grandmother. now it is thought it might a network of cells that are grandmother cells, these are combination of cells for faces we know really well -> these may overlap in facial processing
describe prosopagnosia and grandmother cells
- patients with Asperger syndrome (AS)
- Williams Syndrome (rare genetic disorder have intellectual disability, overly trusting, star like pattern in iris)
who can get prosopagnosia?
congenital, acquired
________ prosopagnosia is relatively common
_________ prosopagnosia is relatively rare
opposite of prosopagnosia, remember ever face they have ever seen
describe super recognizers
a. dark adaptation
b. colour vision
c. contrast sensitivity
d. stereopsis
e. flicker perception
f. motion perception
A shortage of gaba mediated inhibition in the visual cortex might underlie age- related visual deficits including:
showing worsening dark adaptation as we age starting at 60yo.
describe this graph
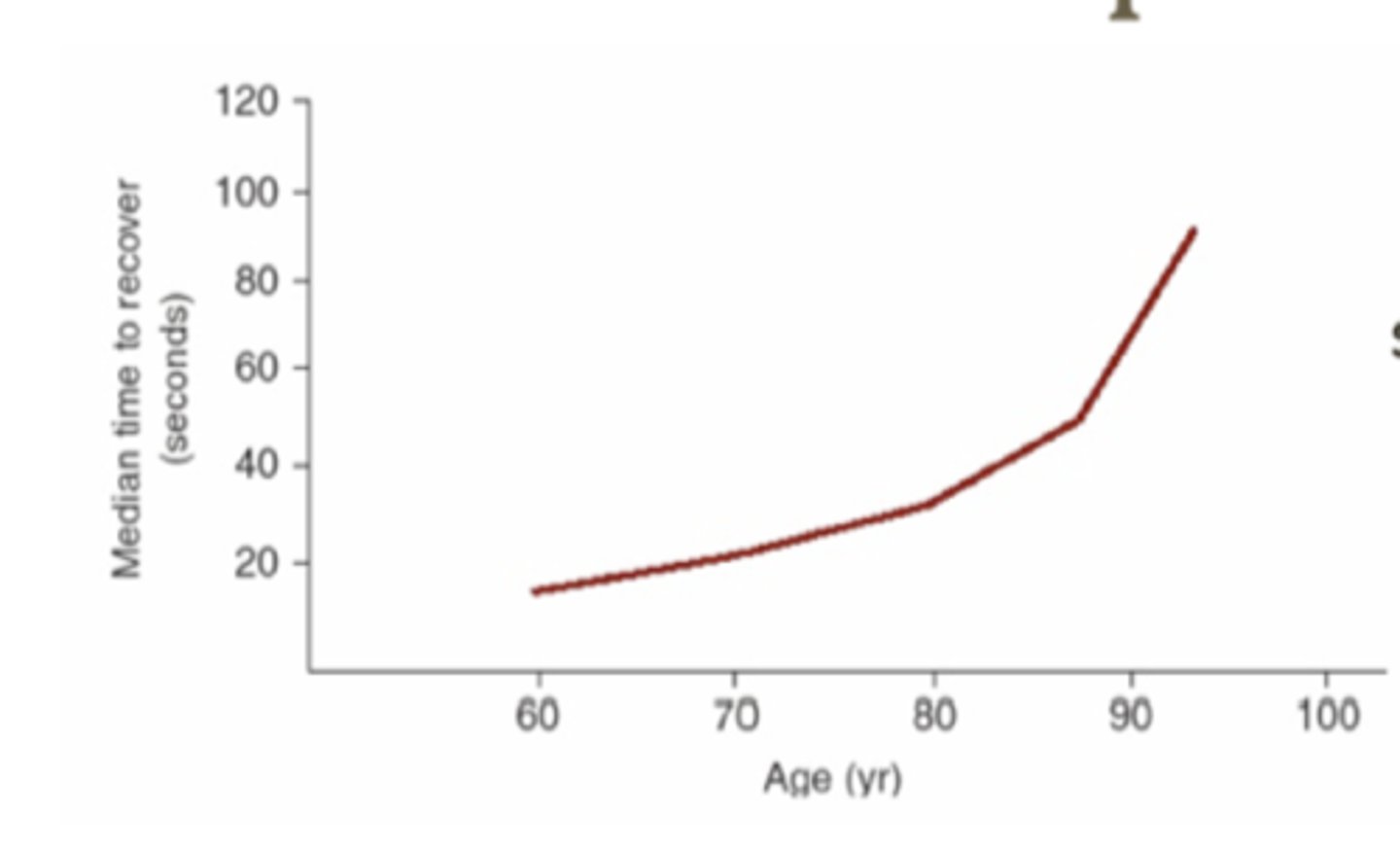
under 60yo= 10 seconds
at 60yo= becomes 20 seconds
by 90yo= up to 60 seconds
describe dark adaptation as we age
due to photostress recovery time. not necessarily due to poor acuity due to lack of dark adapation because of lack of gaba in brain
major reason elderly people stop driving?
decrease in pupil size with age, known to decrease by 0.5mm every 10 years
what is senile miosis?
20yo = 7mm
70yo= 7*0.5=3.5mm
estimated pupil size at 20yo? 70yo?
narcotics, hallucinogens
what causes extremely small pupils? extremely large pupils?
blue-yellow and red-green can be acquired
after 65yo 10% have colour vision defects
at 90 yo 75% have colour vision defects
issue is lack of gaba causing issues with blobs and inter blobs in cortex
what is the best argument for testing colour vision on all new patients and periodically on established ones?
there is too much noise in the cortex
- either need higher contrast to see it at 20/150 or need larger target eg. 20/300 to see 4 CPD
- contrast threshold now may be with 20/30 instead of 20/20
how does a lack of gaba cause decrease in contrast sensitivity as we age?
3x more contrast to see the same target
someone 3x our age needs __________
at 55yo most people have under 85 local arc seconds stereo
by 66yo down to only 85% have under 85 arc seconds stereo
by 90 only 20% have under 85 arc seconds stereo
this is due to lack of gaba in V2 causing loss in stereo
how does a lack of gaba cause decrease in stereopsis as we age?
20/200 arc seconds stereo
monovision results in __________
use heidelberg edge with flicker defined form but if don't have that run humphrey matrix
how can you test if flicker perception is decreased when aging due to lack of gaba?
intermediate and high spatial frequencies
older adults have reduced CFFs particularly at ______________
have too much neurotransmitters causing you not able to see motion
how can epilepsy cause akinetopsia?
positive spontaneous visual phenomena (PSVP)
hallucination including migraine aura, basically anything that we think is there but is not
hallucination including migraine aura, basically anything that we think is there but is not
visual field loss or AION
describe positive spontaneous visual phenomena (PSVP). what does it not include?
timing is different,
how do hallucinations and real images differ with VEP?
1. Allesthesia
2. Distortions
3. Kinetopsia
4. Palinopsia and polyopia
5. phosphenes and photopsias
6. formed hallucinations
what are the 6 types of positive spontaneous visual phenomena (PSVP)
6 types of positive spontaneous visual phenomena (PSVP)
1. Allesthesia
2. Distortions
3. Kinetopsia
4. Palinopsia and polyopia
5. phosphenes and photopsias
6. formed hallucinations
can be somatosensory, association, visual, auditory
sensory referral eg. a patient touched on the left side feels touch on the right
visual allesthesia: transfer of visual images from one half of visual field to the other. often co- occurs with unilateral neglect so often arises from damage to right parietal lobe
what is Allesthesia?
metamorphopsia
micropsia
macropsia
what are visual distortions (dysmetropsias)?
apparent reduction in size and can lead to teleopsia, the perception that objects are further away
enlargement of objects seen and can lead to pelopsia, perceiving things closer than they are
what is micropsia? what is macropsia?
teleopsia
micropsia can lead to=
pelopsia
macropsia can lead to=
1. Ambien (sleep aid)
2. Seizure disorder eg. epilepsy
3. any viral infection (micro) and viral encephalitis (macro)
what causes micropsia AND macropsia?
1. AMD
2. cerebral infarction (stroke)
3. macular hole
4. migraine HA
what ONLY causes micropsia?
1. celexa (anti-depressant)
2. cocaine use
3. epiretinal membrane and cystoid macular edema
4. hypoglycemia
what ONLY causes macropsia?
kinetopsia
perception of movement when there is none
perception of movement when there is none
what is kinetopsia?
MT/ V5
akinetopsia is caused by lesion in __________
kinetopsia
________ happens with epileptic seizures
excitation of the MT (V5) as well as possibly at the retina
where does kinetopsia occur?
Palinopsia
the recurrent appearance of a visual image after the stimulus has long since disappeared
the recurrent appearance of a visual image after the stimulus has long since disappeared
Palinopsia
cerebral polyopia
seeing the same object multiple times, side by side or in a cirlce
seeing the same object multiple times, side by side or in a circle
describe cerebral polyopia
palinopsia, polyopia
both ________ and _________ can occur together resulting in apparently floating multiple objects
Trazodone an anti-depressant drug
palinopsia and polyopia can be a side effect of ___________
pressure phosphenes, migraine aura
spontaneous phosphenes are NOT __________ eg. ________
structured images, such as geometric figures often recurring in a repetitive pattern
what are photopsias?
trigeminal neuralgia
what causes photopsias?
formed= electrical stimulation of grandmother cells or some such visual association areas
unformed= like phosphenes and photopsias
what are FORMED visual hallucinations? UNFORMED?
1. Dementia
2. Epilepsy and narcolepsy
3. illicit drugs
4. Parkinson disease
5. sleep deprivation
6. psychosis
7. syndromes
what are the 7 causes of FORMED visual hallucinations?
causes of FORMED visual hallucinations
1. Dementia
2. Epilepsy and narcolepsy
3. illicit drugs
4. Parkinson disease
5. sleep deprivation
6. psychosis
7. syndromes
Alzeimer disease
most common type of dementia induced visual hallucinations is due to _______
hypnagogic hallucinations (when falling asleep) and hypnopompic hallucinations (when waking up)
narcolepsy or spontaneous sleeping cause induced hallucinations such as ________ which are seizure induced
1. alcohol
2. cannabis
3. methamphetamine
not just hallucinogen drugs can induce hallucinations ____________ can as well
get intermittent strabismus as well as convergence insufficiency which leads to stereopsis illusions when looking at patterns or flowers
also get audio hallucinations -> women laughing sounds like neighing horse
describe parkinson induced hallucinations
need to replenish neurotransmitters which our brain needs to operate. a lack of sleep can lead to hallucinations and paranoia
why do we sleep?
most scary kind, due to EXCESS neurotransmitter like dopamine or excess blood flow flow to cortex
describe psychotic hallucinations
schizophrenia
example of psychotic hallucinations
higher rates in left-handedness as well as cannabis use before age 30 raises the risk considerably
describe schizophrenia
left superior temporal GYRUS (biological motion occurs in superior temporal sulcus)
the ________ has been suggested to play a key role in auditory and verbal hallucinations in patients with schizophrenia
phantom eye syndrome
for patients with an enucleated eye, visual sensations may still seem to occur in missing eye. probably occur at the terminal end of the optic nerve due to EXCESS neurotransmiter
for patients with an enucleated eye, visual sensations may still seem to occur in missing eye. probably occur at the terminal end of the optic nerve due to EXCESS neurotransmiter
describe phantom eye syndrome
charles bonnet syndrome
syndrome is when visual hallucinations experienced by blind patients
syndrome is when visual hallucinations experienced by blind patients: usually vivid complex visual hallucinations occurring in mentally healthy people
describe charles bonnet syndrome
12-15% of visually impaired patients yet often goes undiagnosed
charles bonnet syndrome affects __________
- have visual impairments due to old age, damage to the eyes or optic pathways
- usually occur during the morning or evening but worse in low lighting
causes of charles bonnet syndrome
retina no longer sends incoming visual sensory impulses back to the brain, but the cortex still sends 80% of the input to the LGN
what is occurring in CBS
- anti-epileptic meds (tegretol)
- blinking rapdily
- vision restoring surgery
treatment of CBS
1. macular diseases
2. retinal diseases
3. optic nerve disease
4. CRAO
5. CRVO
what are 5 things that can cause charles bonnet syndrome?
1. spontaneous nystagmus
2. hallucinations
3. macropsia
4. kinetopsia

ALL caused by depletion in dopamine

parkinsons, sleep induced, and methamphetamine hallucinations
depletion in dopamine can cause __________
- schizophrenia
- phantom eye syndrome
- epilepsy

All take place in right parietal lobe!!

akinetopsia= cannot see motion, destruction in MT/ V5
kinetopsia= can see motion when there is none, excitation of MT/ V5

aura before migraine

zero
what is the numerical value of the expected VEP for a stimulus at the patient's threshold?
visual acuity
what is NOT reduced when we age?
object seems further away
object seems closer
telopsia=
pelopsia=
dementia induced hallucinations and caffeine induced
what hallucinations are due to lack of blood flow?
reduction in dopamine leading to hallucinations, the exact same hallucinations parkinsons can induce
methamphetamine abuse can cause ________ which are _______
80-85yo
at what age will 50% of population fail Ishihara colour vision test?
80yo
at what age will 50% not have 85 arc seconds local stereo?