6.2.3 Polyesters and Polyamides
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
list the two types of polymers
addition
condensation
how do addition polymers form
when unsaturated alkene monomers react to form long saturated alkane chains.
conditions required to make addition polymers
high temperature
high pressure
catalyst
give the balanced equation for formation of a poly(alkene)
monomer, no brackets
bond sticking out of brackets in polymer
n to the right in the polymer
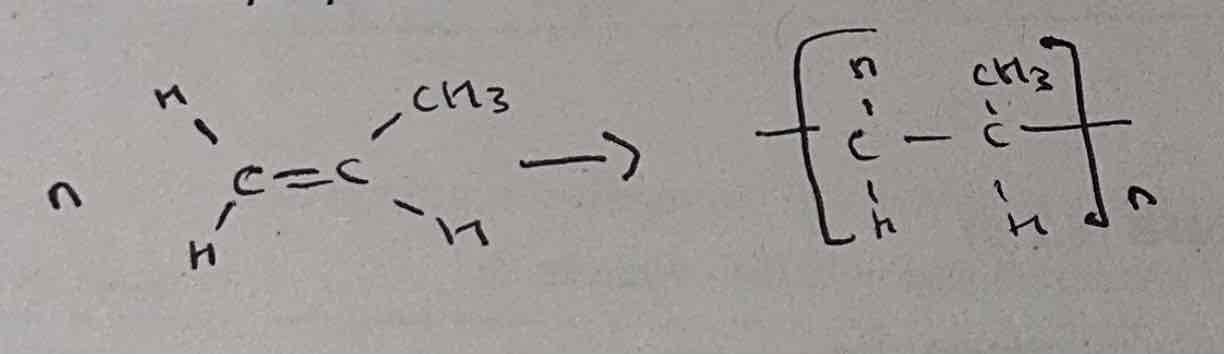
draw a Poly(alkene) with 3 monomers
always draw bonds going out of brackets
always have 2 carbons in one monomer (other carbons go on top/bottom)
3 monomers = 6 carbons in polymer
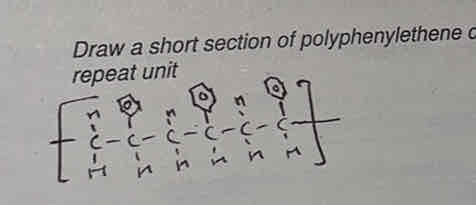
how many carbons in one monomer
2 (the others go on the top or bottom)
Why are poly(alkenes) non-biodegradeable
they are chemically inert:
many strong C-C and C-H bonds
bonds are non polar
list the types of condensation polymers
polyesters
polyamides
difference between condensation and addition polymers
C also forms a small molecule (usually water), A only form the polymer
C have monomers with 2 FG that are both broken; A only have monomers with alkene functional group that are broken
give the FG in polyesters
carboxylic acid
alcohol
give the FG in polyamides
carboxylic acid
amine
why just monomers in condensation polymers have 2 FGs
in order to continue making the polymer chain
two different ways polyesters can be made
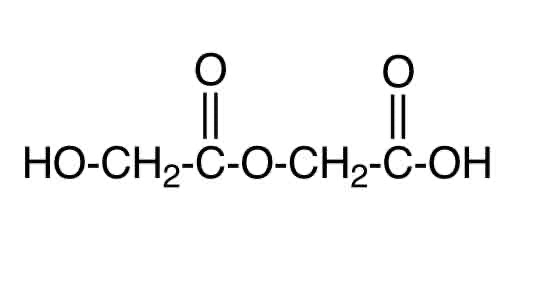
2 monomers containing both COOH and OH functional groups (hydroxycarboxylic acids)
2 monomers, 1 with 2 COOH groups and 1 with 2 OH groups
what’s a hydroxycarboxylic
a compound with both OH and COOH groups
what bond is formed in a polyester
ester bond
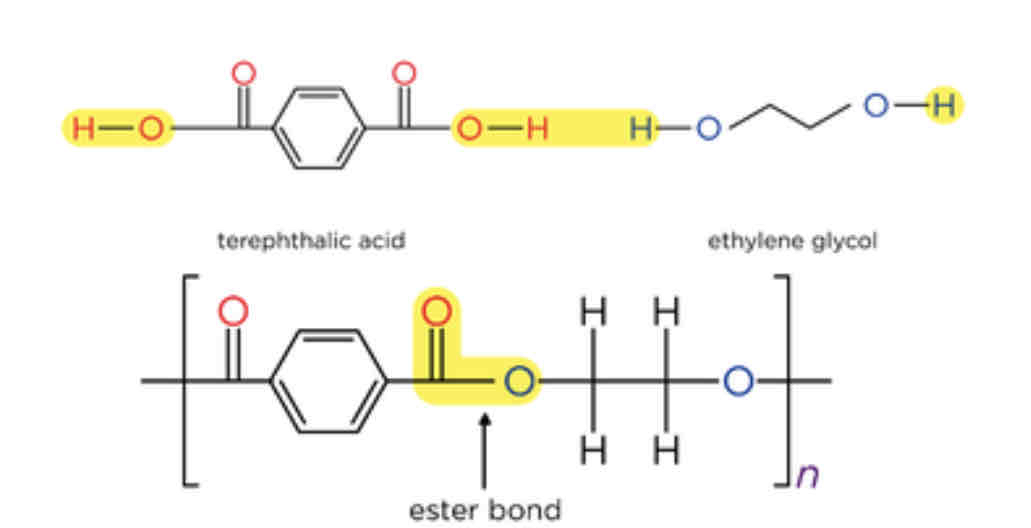
how is an ester bond formed when making polyesters
The COOH group in one monomer reacts with the OH group in another monomer, forming ester bond and water
polymers made from two different monomers
one monomer is a diol
one monomer is a dicarboxylic acid
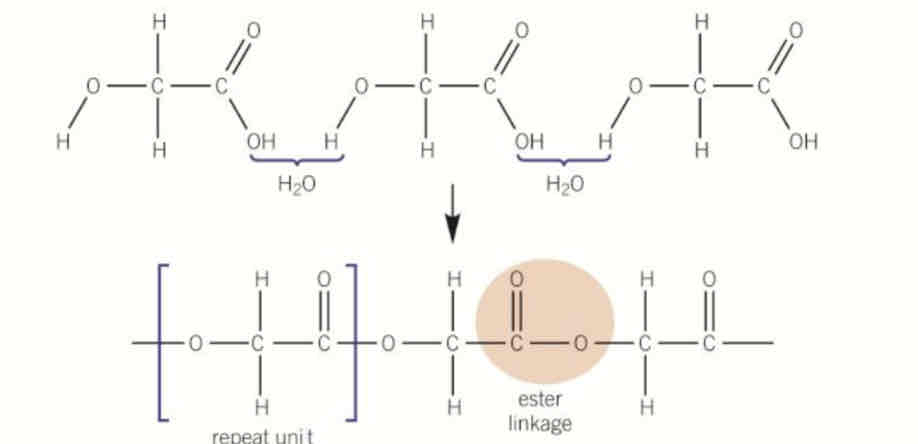
how to draw repeat units of polyesters
amide bonds in middle
remove OH from carboxylic acid end so CO—
remove H from alcohol end so O—
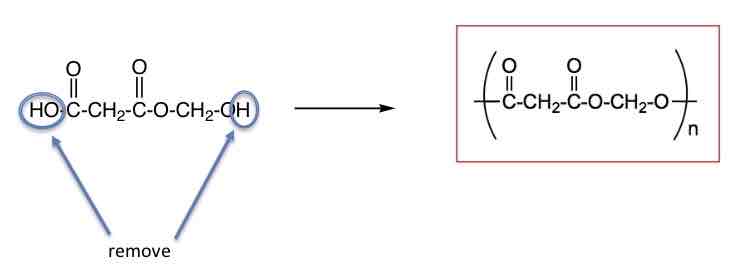
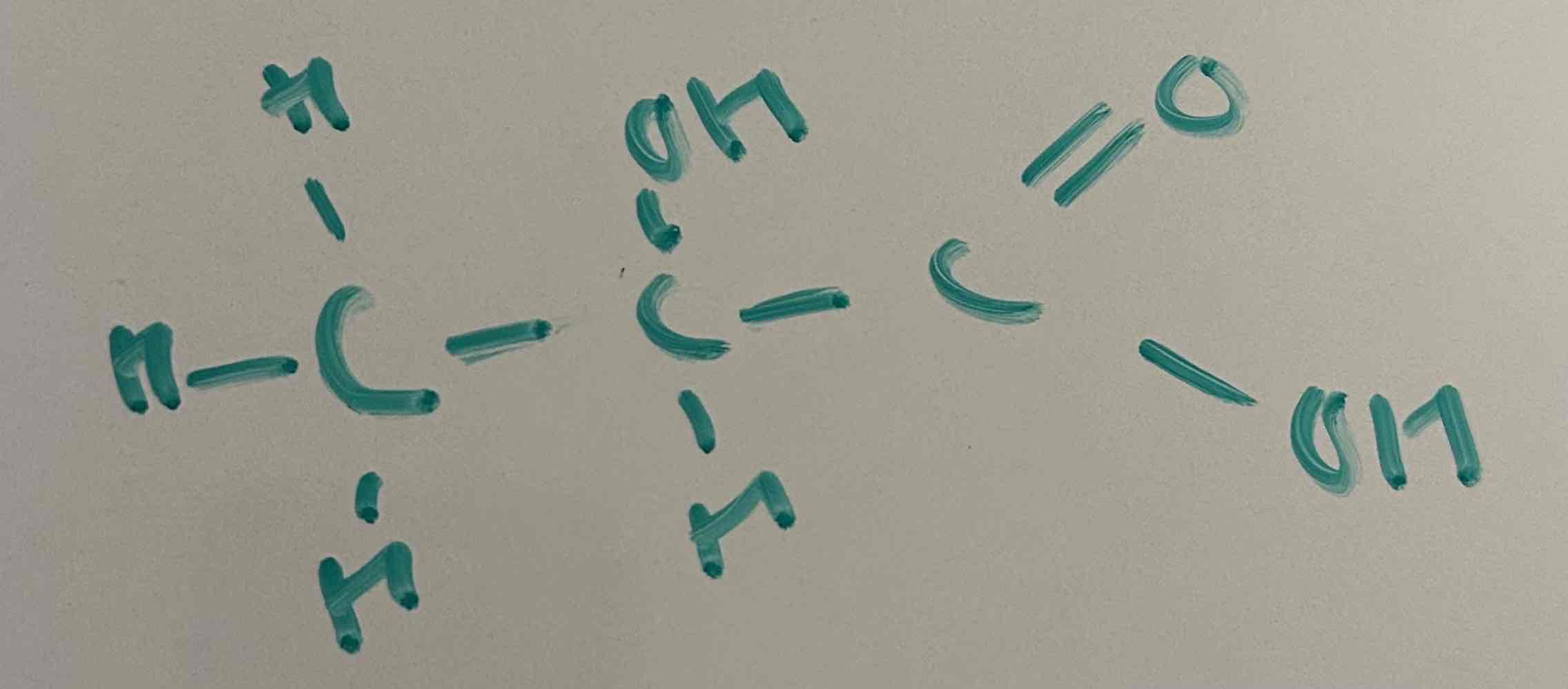
draw a polymer with 3 repeat units or this monomer
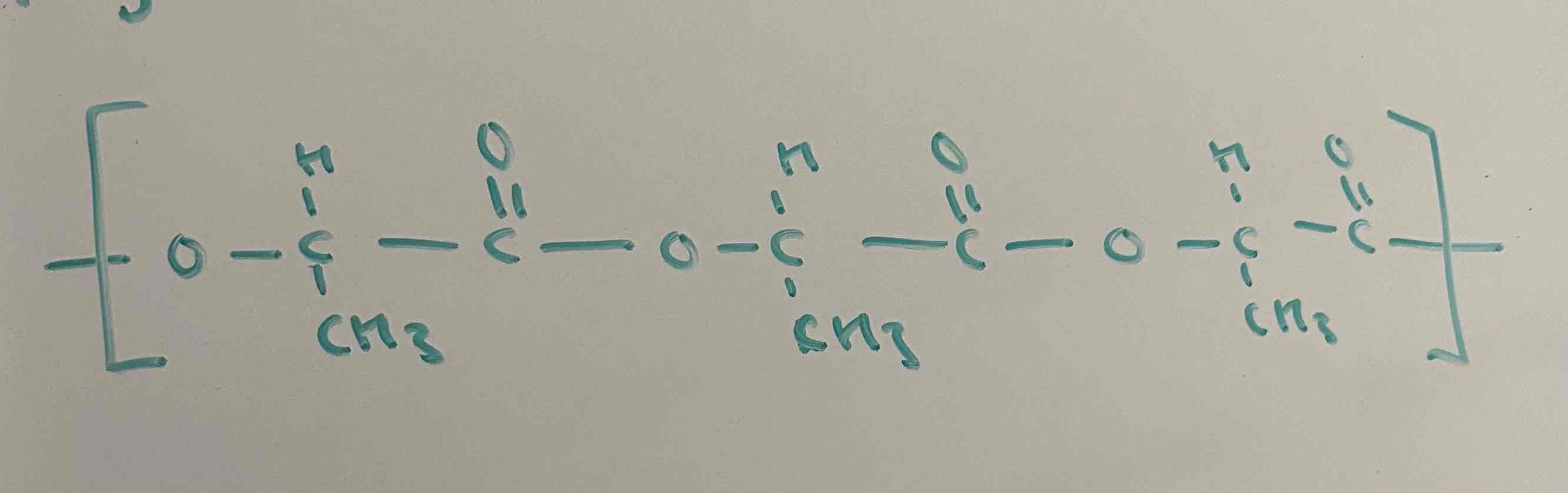
draw 2-hydroxyprooanoic acid in monomer form
put FGs at left and right
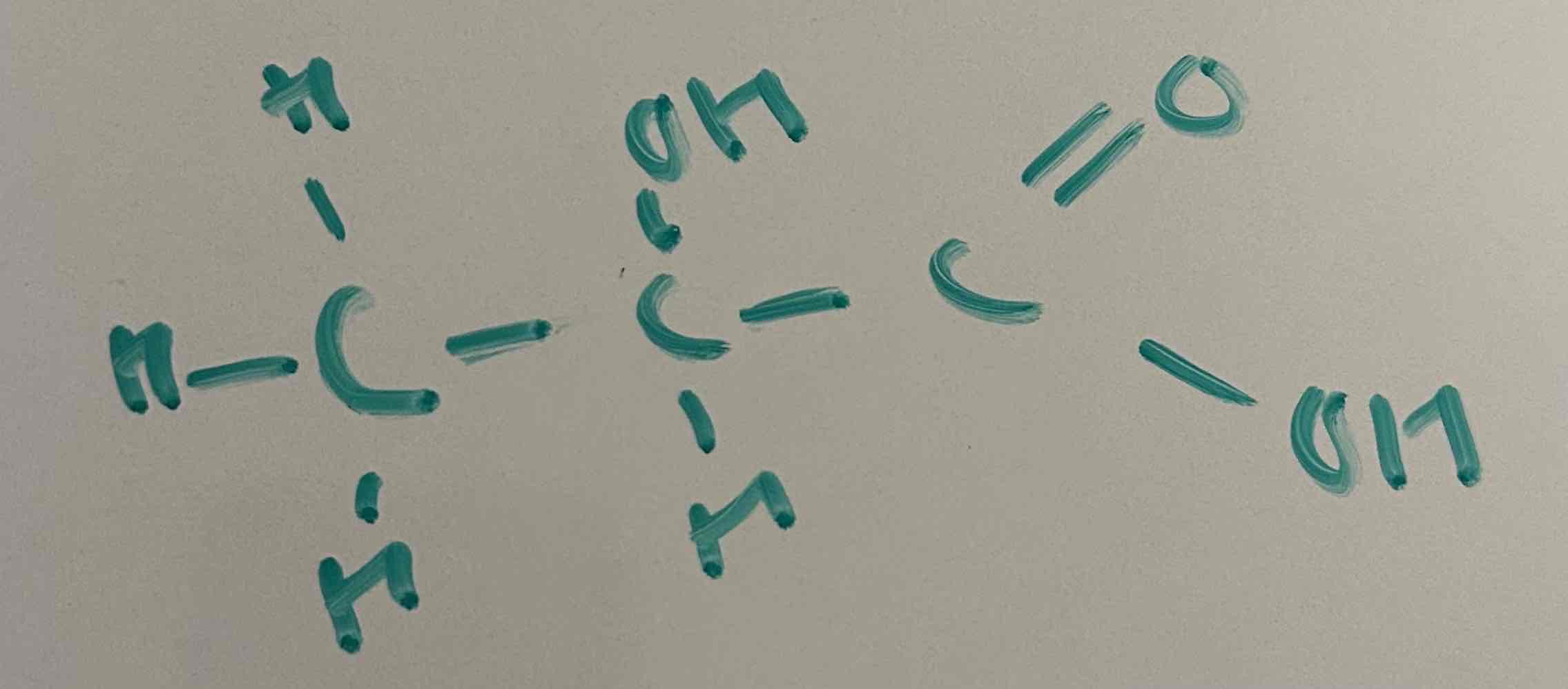
give two ways polyesters can be hydrolysed
acidic conditions
basic conditions
acidic hydrolysis of polyesters
water is the reagent
produces alcohol and carboxylic acid
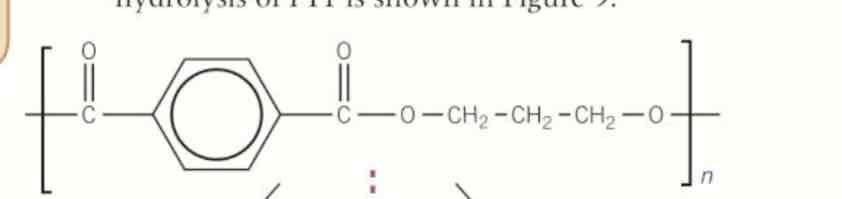
give the acid hydrolysis of this
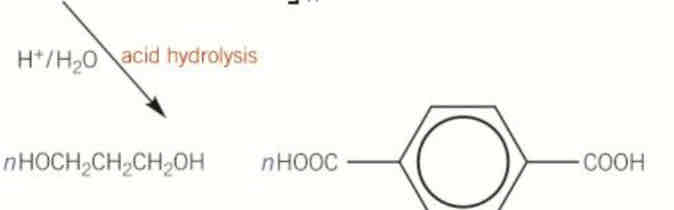
give the repeat unit of this
repeat units don’t have
n
or brackets
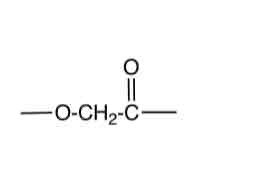
→ n alcohol and n carboxylic
polyester + water →
(water is the reagent in acid hydrolysis)
basic hydrolysis of polyesters
the base is the reagent
produces alcohol and carboxylate
what is the reagent in acid hydrolysis of polyesters
water
what is the reagent in basic hydrolysis of polyesters
the base
products of acid hydrolysis of polyesters
carboxylic acid
alcohol
products of basic hydrolysis of polyesters
salts of dicarboxylic acid
diols
polyester + NaOH
→ alcohol + sodium salt of carboxylic acid
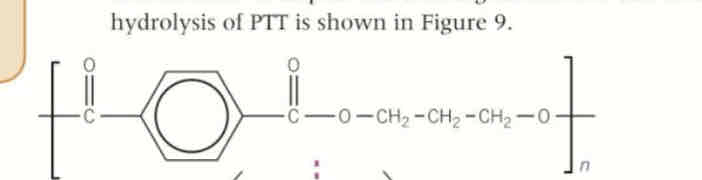
polyester + NaOH
monomers needed to make polyamides
diamines
dicarboxylic acid
diamine + dicarboxylic acid →
→ polyamide + water
what bonds are formed when making polyamides
amide
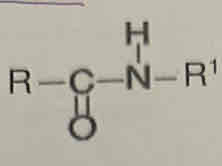
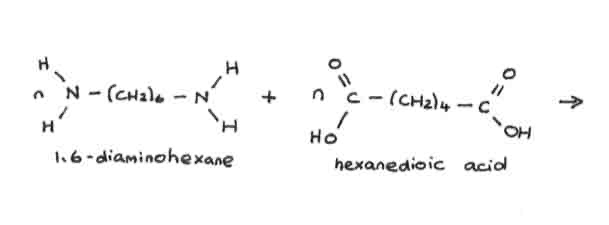
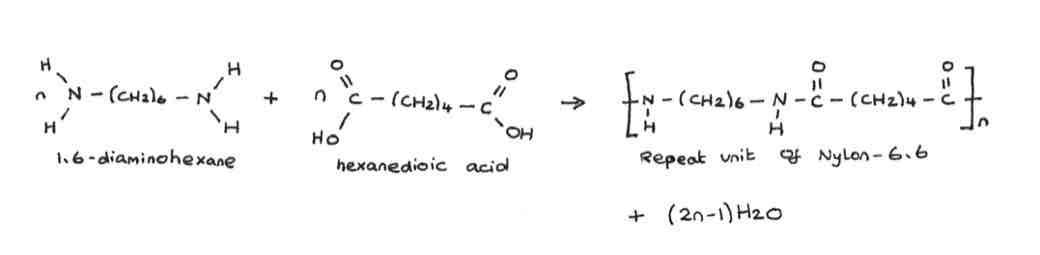
how many water molecules are formed when making polyamides
(n-1) H2O
(number of amide bonds there are = number of water molecules)
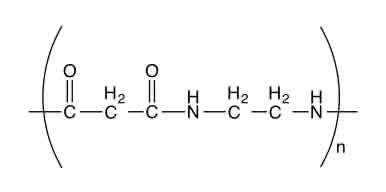
draw a repeat unit of a polyamide
O=C— (bond sticking out)
HN— (bond sticking out)
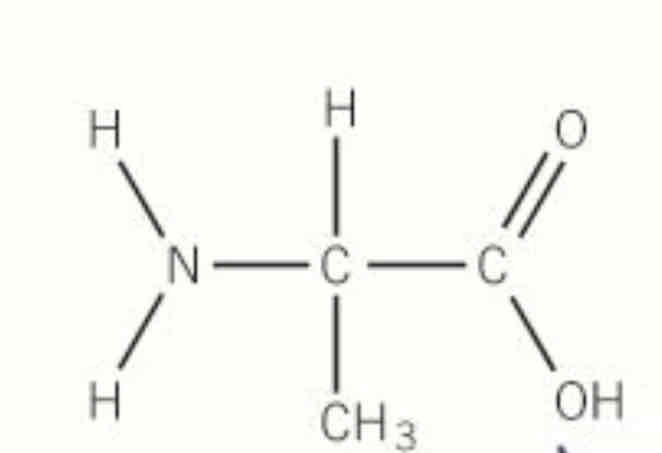
how can we make polyamides from one monomer
by using amino acids (they have both COOH and NH2 group)
when amino acids make polymers what are they called
polypeptide / proteins
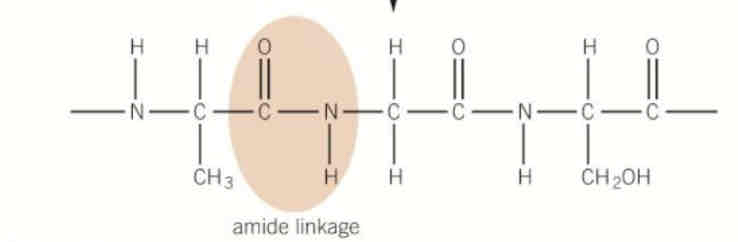
draw the polymer with 3 repeat units made from this monomer
two ways we can hydrolyse polyamides
heating with aqueous acid
heating with aqueous base
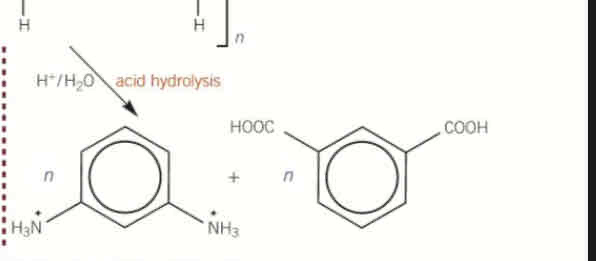
acidic hydrolysis of polyamides
acid is the reagent
produces carboxylic acid and ammonium salts (-NH3+) of the amine group
what is the reagent in acidic hydrolysis of polyamides
acid
(not water since we have a basic group that can react with the acid)
products of acidic hydrolysis of polyamides
carboxylic acid
ammonium salts (-NH3+) of the amine group
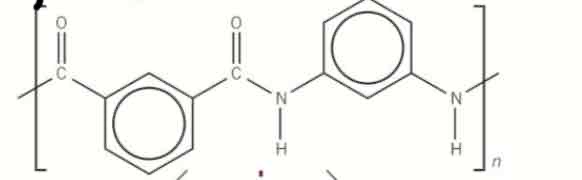
give the acid hydrolysis of this
basic hydrolysis of polyamides
base is the reagent
produces amines + carboxylates (salts of carboxylic acid group)
what is the reagent in basic hydrolysis of polyamides
the base
what are the products of basic hydrolysis of polyamides
amines (NH2)
carboxylates (salts of carboxylic acid group)
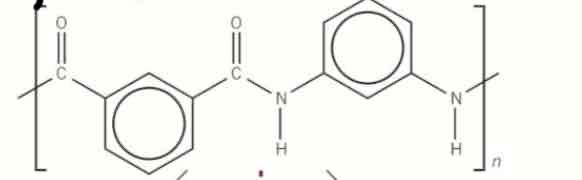
give the basic hydrolysis of this
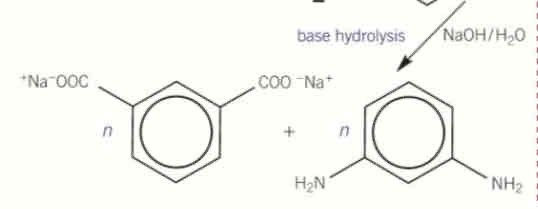
Polyamide + NaOH →
→ amine + carboxylate (Na+COO-)
polyamide + HCl →
→ carboxylic acid + ammonium salt (NH4Cl)
why are condensation polymers biodegradable
ester bonds and amide bonds are able to be hydrolysed