Chapter 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Alfred Wegener
German meteorologist and polar explorer
Wrote The Origins of Oceans and Continents
He suggested land masses slowly move (continental
drift)
He hypothesized a former supercontinent, Pangaea
He produced 5 Evidences to support this
Wegener’s Evidence for Continental Drift
The continents seem to fit together
Glacial evidence of past glaciers found on four continents
Climate Belts Follow a specific order
Identical fossils found on widely separated landmasses
Mountain belts connect across the Atlantic
Mid-Ocean Ridges (MORs)
Elevated areas of ocean floor, usually in the middle of an
ocean
Deep Sea Trenches
Deep areas of the ocean that tend to boarder one side of a volcanic arc
Volcanic Arcs
Islands in an arc shape created by volcanism
Fracture Zones
Areas where fractured rock breaks up and moves, or offsets, the MORs
Seamount Chains
Linear islands that can erode away and be below seal level
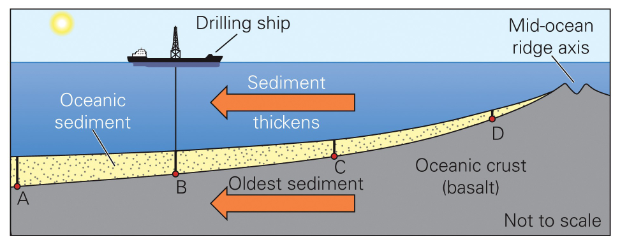
Observation on seafloor sediment
It is thinner near MORs and thicker away from MORs
Composition of Continental crust
Mostly made of granites (felsic)
Composition of Oceanic crust
Mostly made of Basalt (mafic)
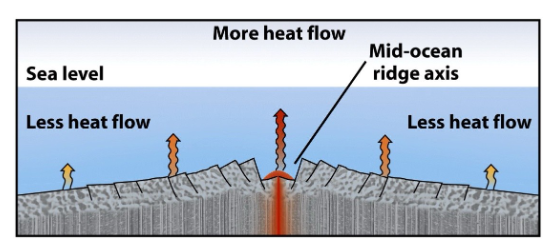
Observation on heat
Heat flow is greater near MORs
There must be a sorce of heat near MORs
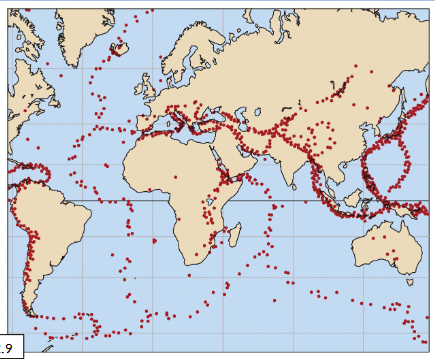
Observation on Earthquakes
Earthquakes in the
Oceans occur in patterns
Seismic Belts, follow bathymetric features like MORs, Trenches and fracture zones
Observations on ridge axis
MORs have a ridge axis that is lower elevation
Seafloor Spreading
Magma rises under MORs pushing each side of the ridge axis away from each other, magma then cools to form new crust
Marie Tharp
Bruce Heezen
Harry Hess
Paleomagnetism
The study of the Earths ancient magnetic field
Magnetic Declination
Angle of the needle and a given line of longitude (reading a
compass)
Magnetic Inclination
The angle of a needle and the surface of the earth
Apparent Polar Wander
Every time a rock forms, it will “Capture” the Earth’s magnetic field in that moment
When we plot the pole based on these layers, and assume the continent is fixed, then we get an ___________ path
Two interpretations of Apparent Polar Wander
1) The pole moves relative to the continent
2) The continent moves relative to the pole
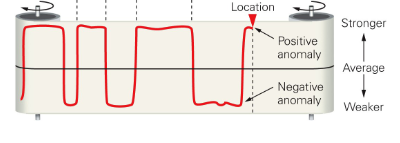
A Proof of Seafloor Spreading
The magnetic field sometimes “flips”
Magnetism in sea-floor rocks varies farther from MOR
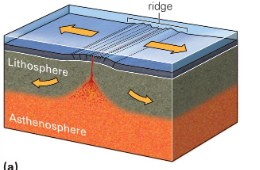
Divergent Boundary
Forms when two plates move apart through the process of seafloor spreading
Spreading crust is filled in with magma from the asthenosphere, which creates MORs
Ocean crust grows wider
Exclusively happens in oceans
Convergent Boundary
Two plates move towards each other. At least one plate MUST be oceanic
The older, colder, more dense oceanic plate will bend down into the asthenosphere in a process called subduction
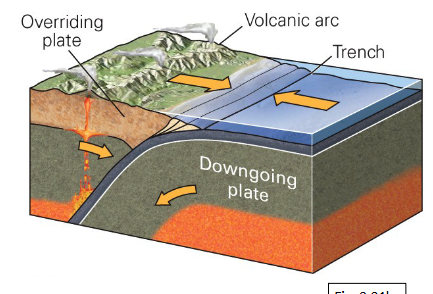
Earthquakes and the Fate of Subducted Plates
Very large earthquakes (EQs) occur where the two plates meet, due to friction
EQs also occur very deep in the subducting plate, known as the Wadati-Benioff Zone
Accretionary Prism
Scraped up sediment off the subducting plate onto
the overriding plate
Found in Convergent Boundaries
Deep Ocean Trench
Area where two plates first meet and one ocean crust is
thrust downward into the mantle
Found in Convergent Boundaries
Continental Volcanic Arc
Present on continental crust when there is O-C convergence
Island Volcanic Arc
Present on the overriding oceanic plate in O-O convergence
Transform Boundary
When two plates slide past one another. No creation and no destruction
MOST occur in Oceanic crust
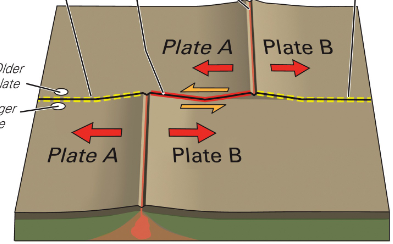
Triple Junction
The meeting of any 3 plates and plate boundaries
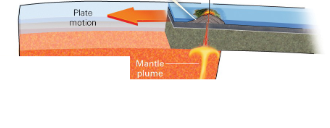
Hot Spots
Anomalously hot mantle material buoyantly rises and melt through the crust to produce volcanoes
The crust moves over the spot to create a chain of volcanoes in time
Continental Rifting
Continental crust moves apart creating a rift
If enough rifting occurs, ocean crust will be
created and the rift will evolve into a divergent boundary
Collision
Convergence will eventually consume all the ocean crust, bringing two continental masses towards one another
Continental crust cannot sink into the mantle, so it builds upwards, creating mountains
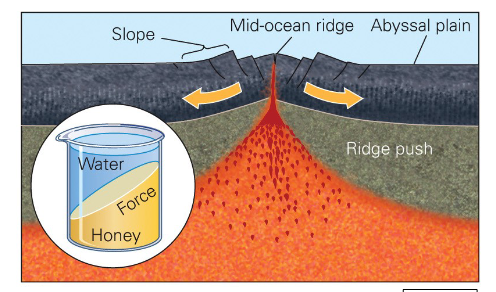
Ridge Push
Gravity pulls down the elevated MOR, causing it to push on
the lower elevated abyssal plains
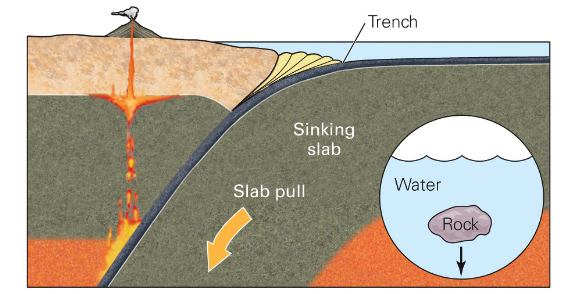
Slab Pull
The subducting slab is cold and dense and sinks into the asthenosphere, pulling all of the attached ocean crust behind it
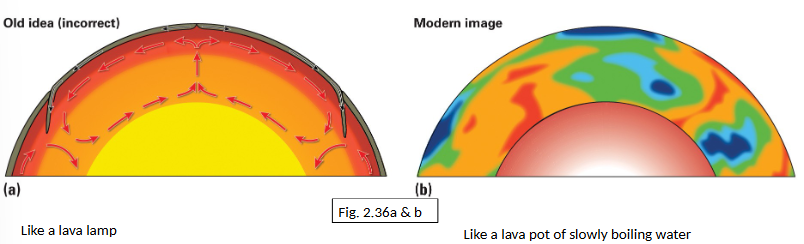
Mantle Convection