Deviance Key Words
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Deviance
violation of cultural roles
Laws
Norms defined by the government as principles citizens must follow
Formal Law
Laws applied in court
Constitution

Informal Law
Unwritten rules governing behavior in society
Come into the office on time, or you’re fired

Sanction
Regulations of thoughts and behavior based on cultural norms
Formal Sanction
Designated bodies of groups to carry out punishment

Informal Sanction
Non-designated bodies of groups carrying out punishment
taking it into their own hands

Functionalism
Society is a system of interdependent parts working together to maintain stability and equilibrium
Durkheim’s Functions of Deviance
Deviance serves a function in society as it reinforces social norms, promotes social cohesion, and can lead to social change.
Merton’s Strain Theory
There is a discrepancy between societal goals and the available means to achieve them
Conflict
The heart of society, through class and power by maintaining the status quo
steal a bike? JAIL
insider trading? …. no jail
Control Approach Human Nature
Humans are naturally deviant, thus we must actively keep it under control
it is abnormal to engage in deviant behavior
Broken Windows
Sign of disorder lead to greater disorder
If one window is left unrepaired, it is a sign that no one cares, therefore it’s fair game
Social Disorder
about space, not people
no one knows each other, thus no one is going to care if its chaos in the streets
Physical Disorder
litter and graffitti
Surveillance
Supervision of activities of which everyone is somewhat subject to
Direct Survaillance
Actually Watching

Record Survaillance
files
permanent record
transcript
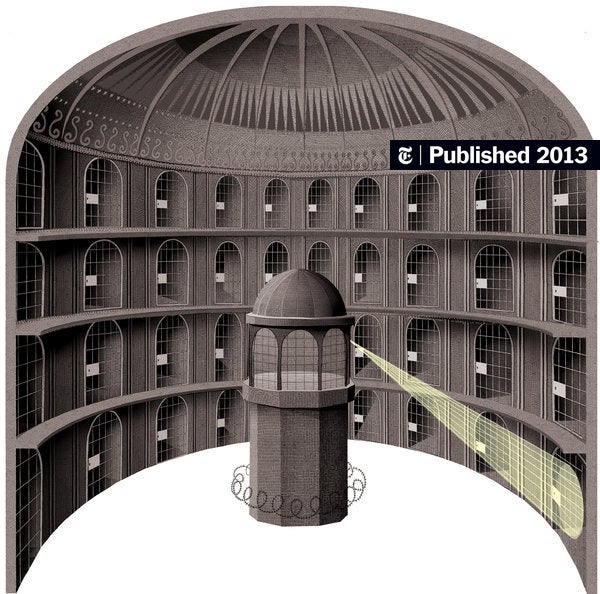
The Panopticon
A theoretical design for a prison where inmates are always visible to a central watchtower, promoting self-regulation among the prisoners.

Interactionalist Labeling Theory
Examines the social meaning of deviant labels by looking at reactions rather than norm violations
not about the act, but how/what we label
Prime Deviance
Initial common deviant act where the individual violates norms without viewing themselves or being labeled as deviant
Can trigger labeling process
Secondary Deviance
When you begin to engage in deviant acts in order to take on the label of deviant and adjust your sense of self
Taking on deviant acts as a means of defense, attack, or adjustment to the problems created by reactions to them
self-fulfulling prophesy
Retrospective Labeling
Interpreting someone's past in light of present deviance
distorts a person’s biography

Projective Labeling
Using deviant identity to predict future actions
“If he’s this bad when he’s 10, how bad is he gon abe when he’s 18?”
