Spinal cord
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What are Afferent nerves?
sensory
What are Efferent nerves
motor
What is a cluster of neuron cell bodies outside of the CNS?
ganglion
What is a cluster of neuron cell bodies inside the CNS?
nucleus
What is a particular cluster of axons called?
fasciculus
What is a general area of white matter called?
funiculus
What is grey matter made of?
neuron cell bodies
What is white matter made of?
axons
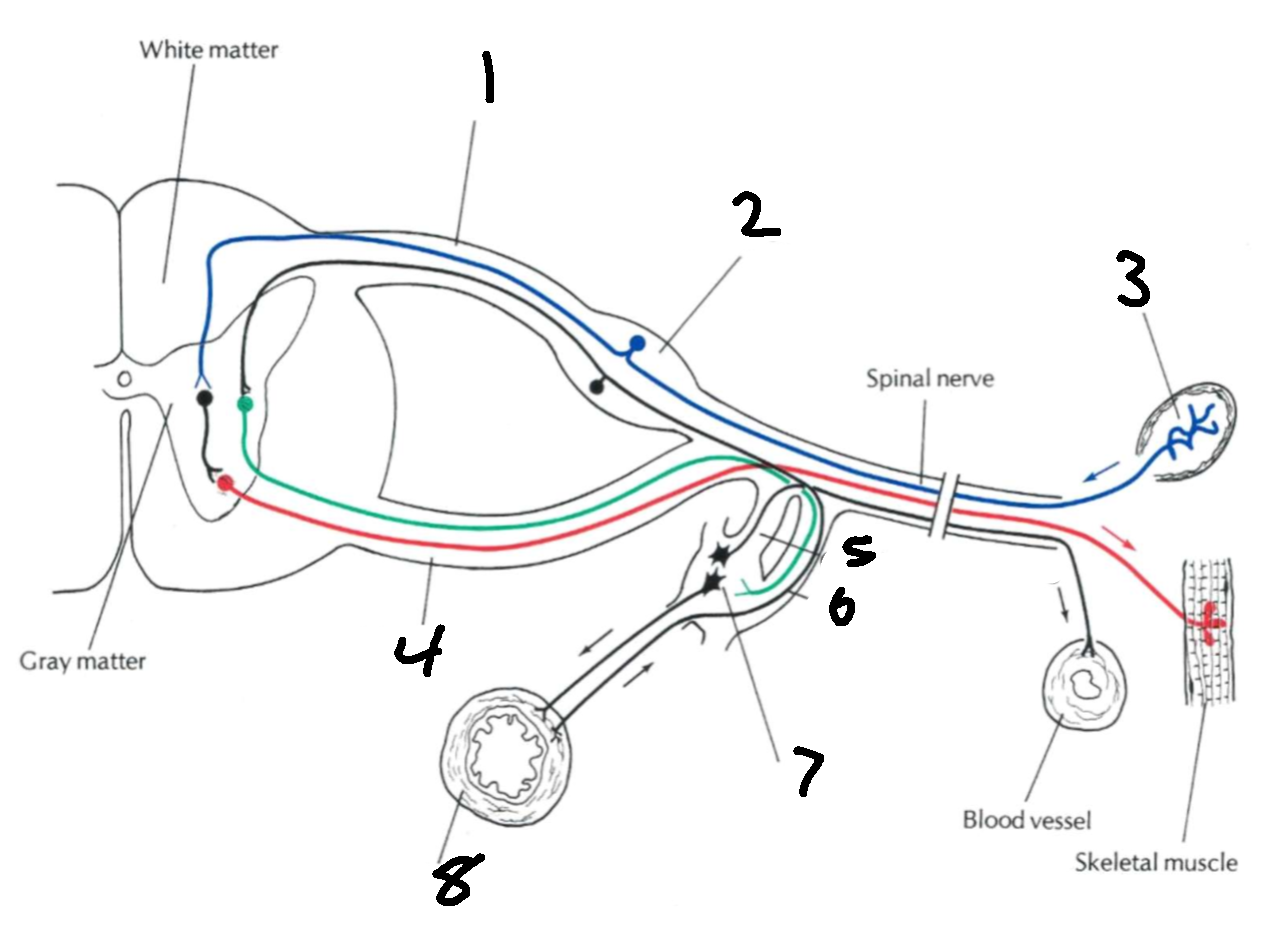
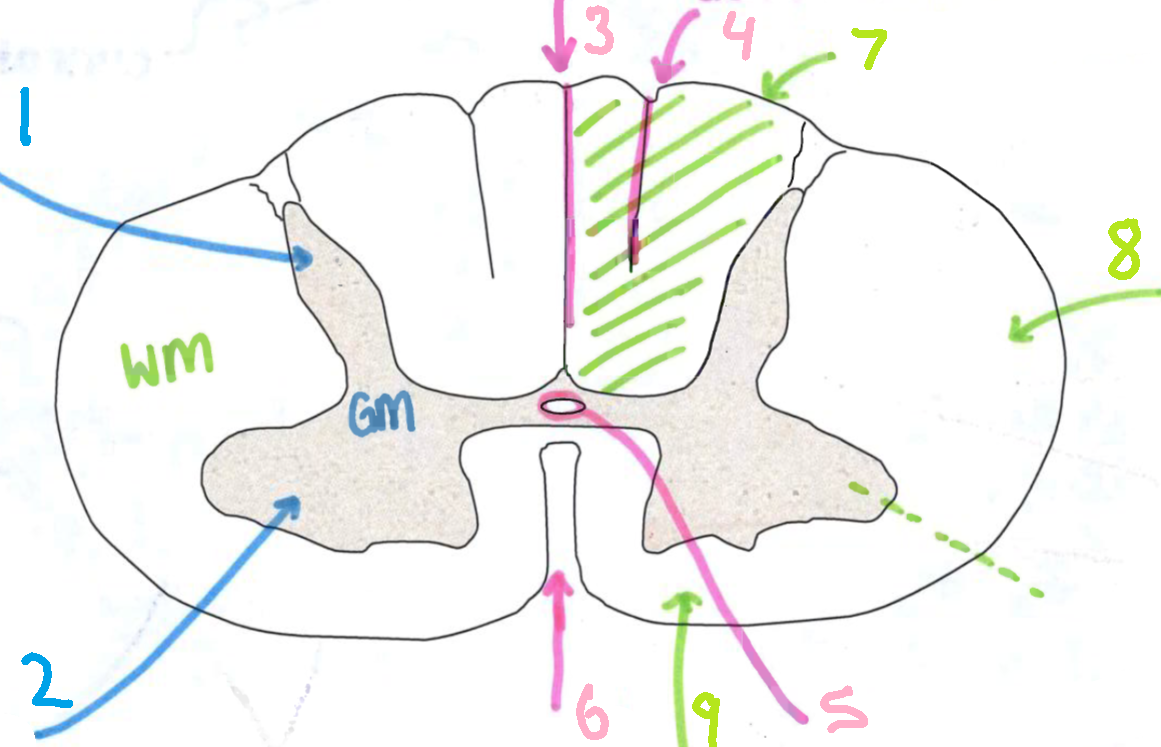
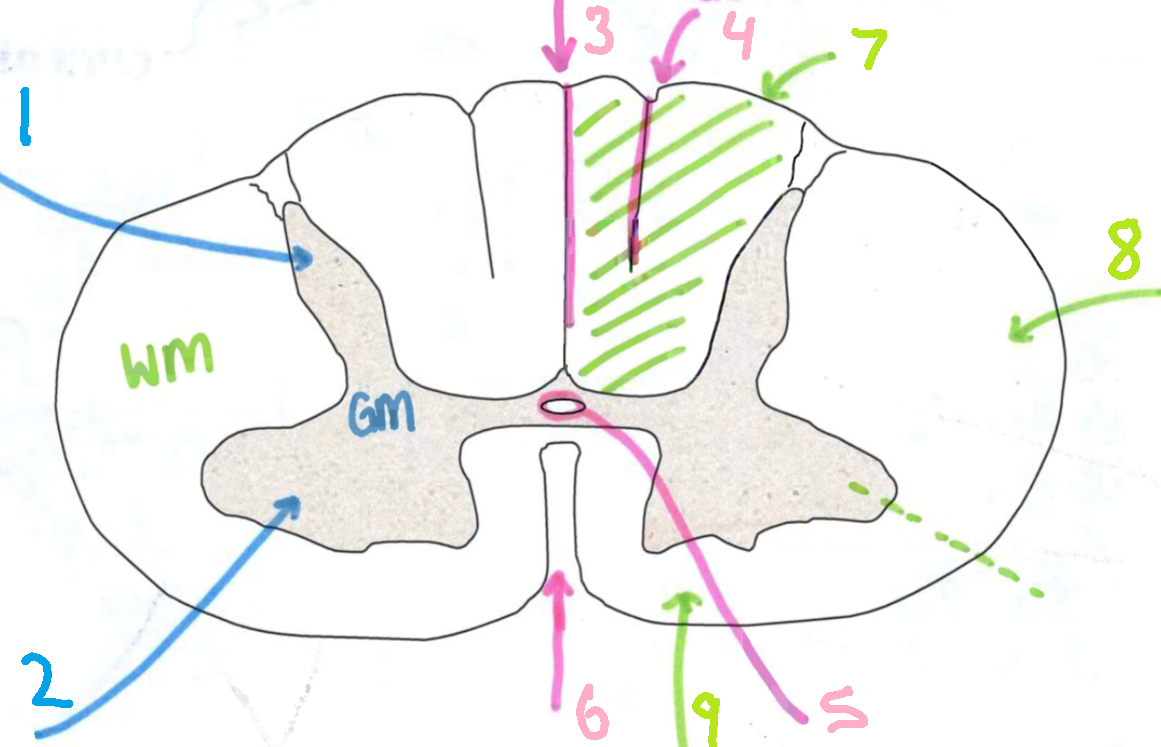
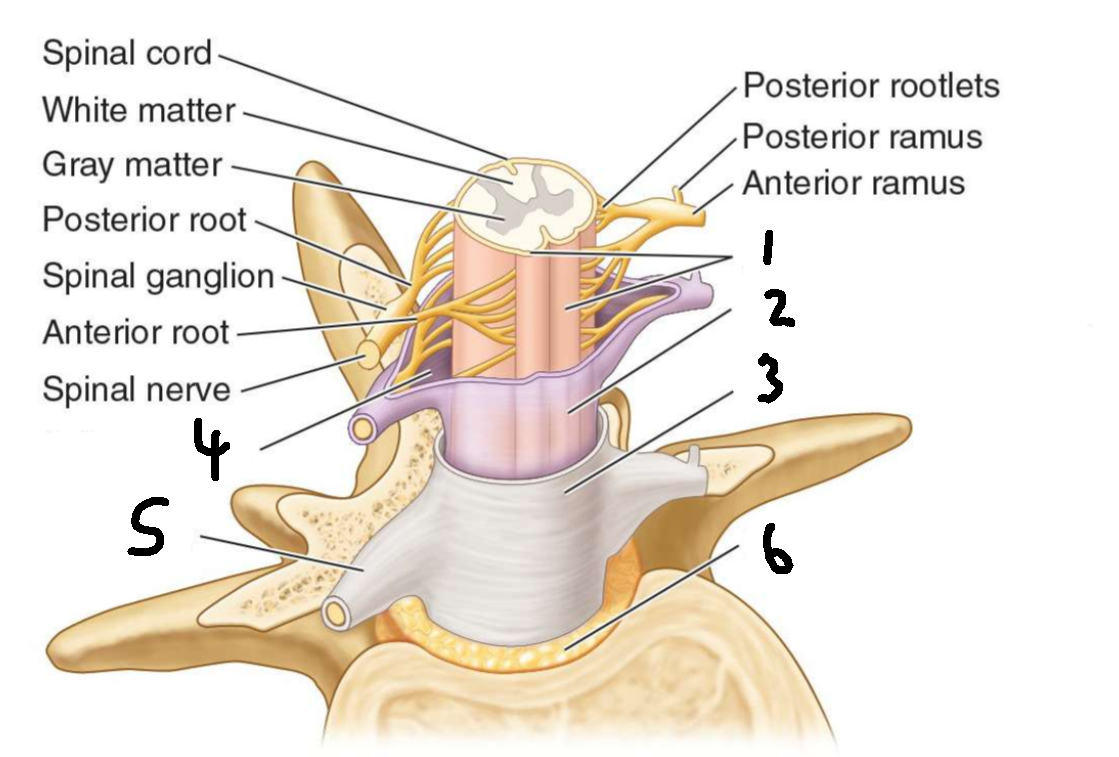
What is 1?
dorsal root
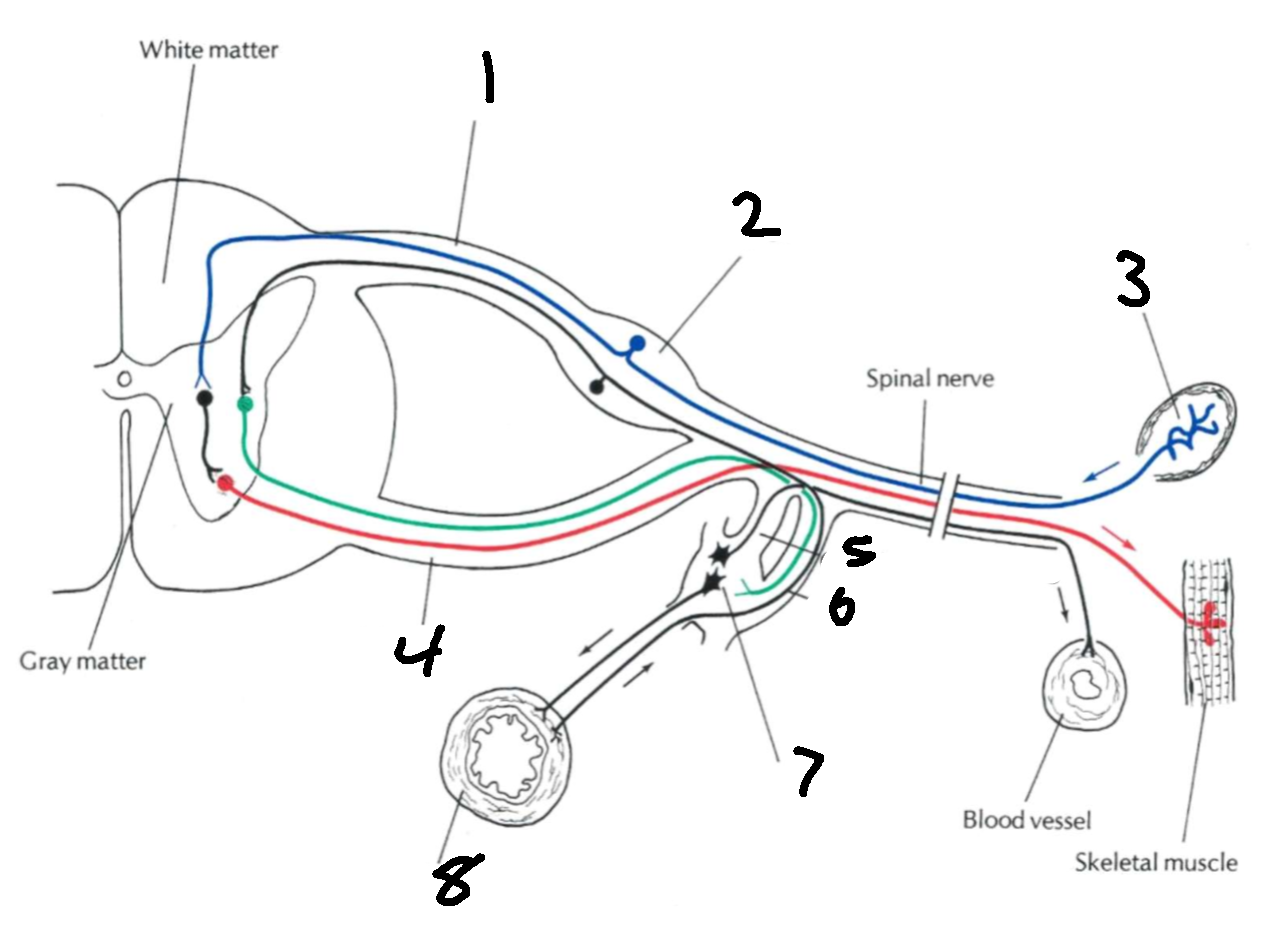
What is 2?
dorsal root ganglion
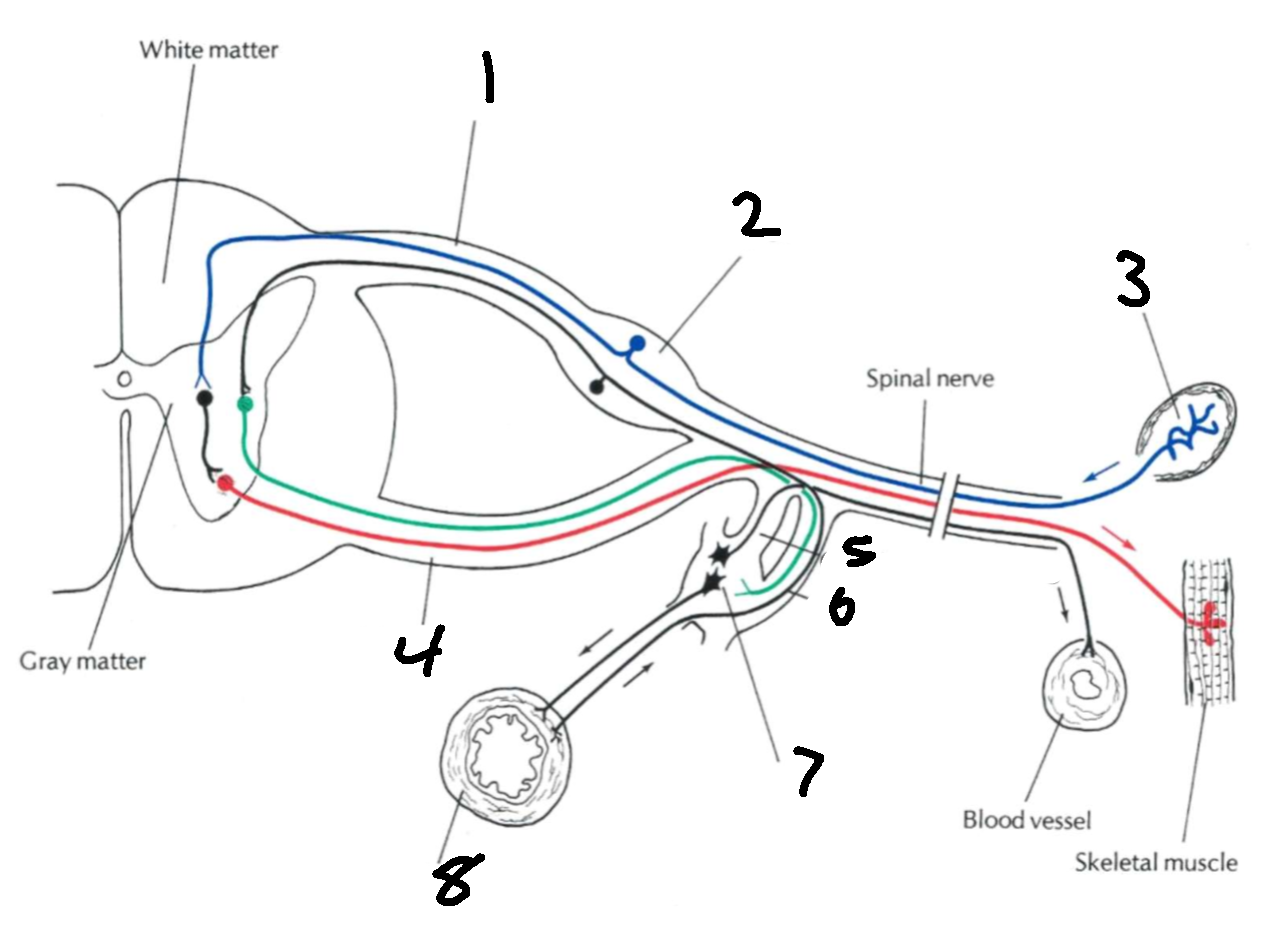
What is 3?
sensory ending
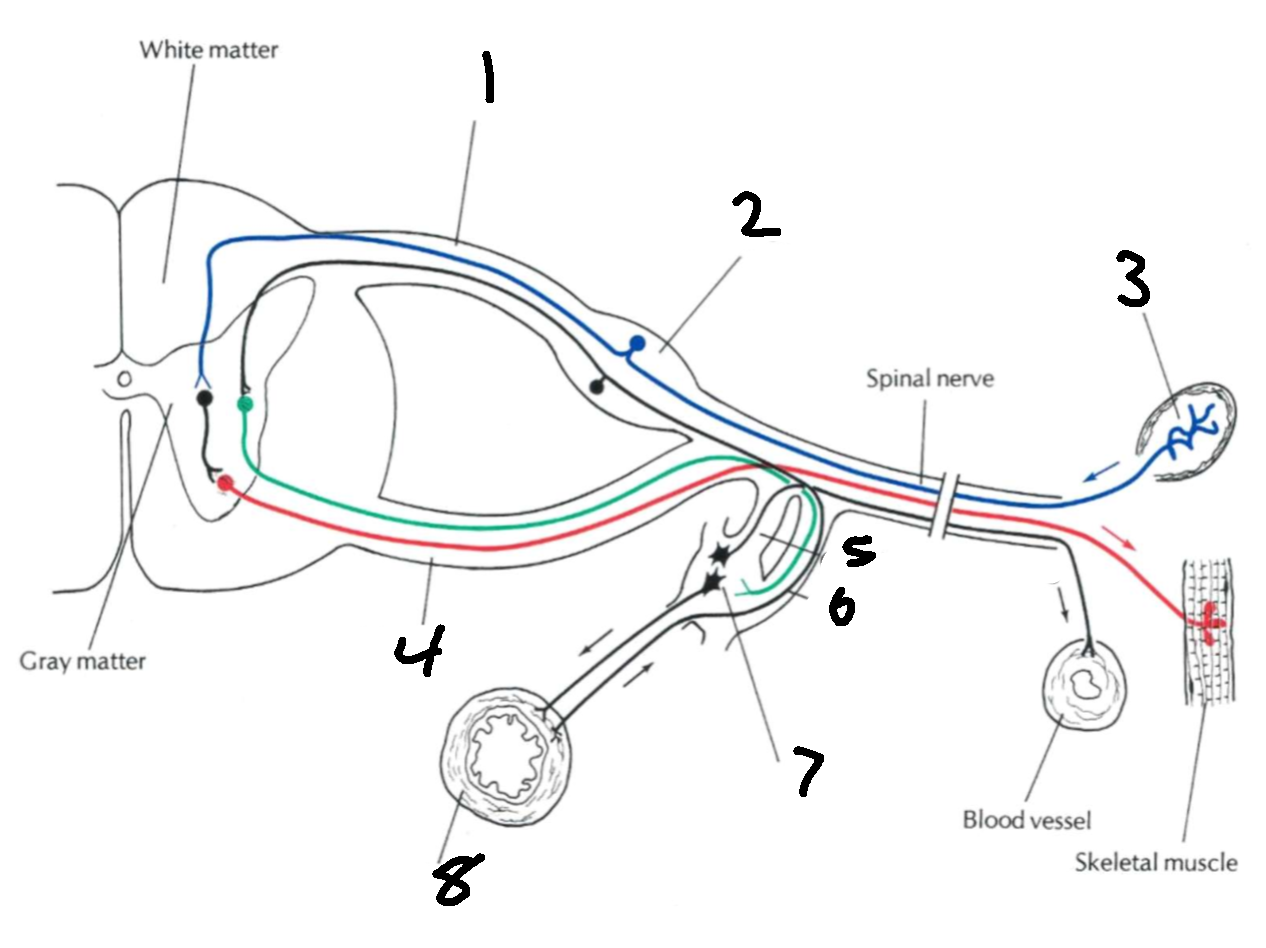
What is 4?
ventral root
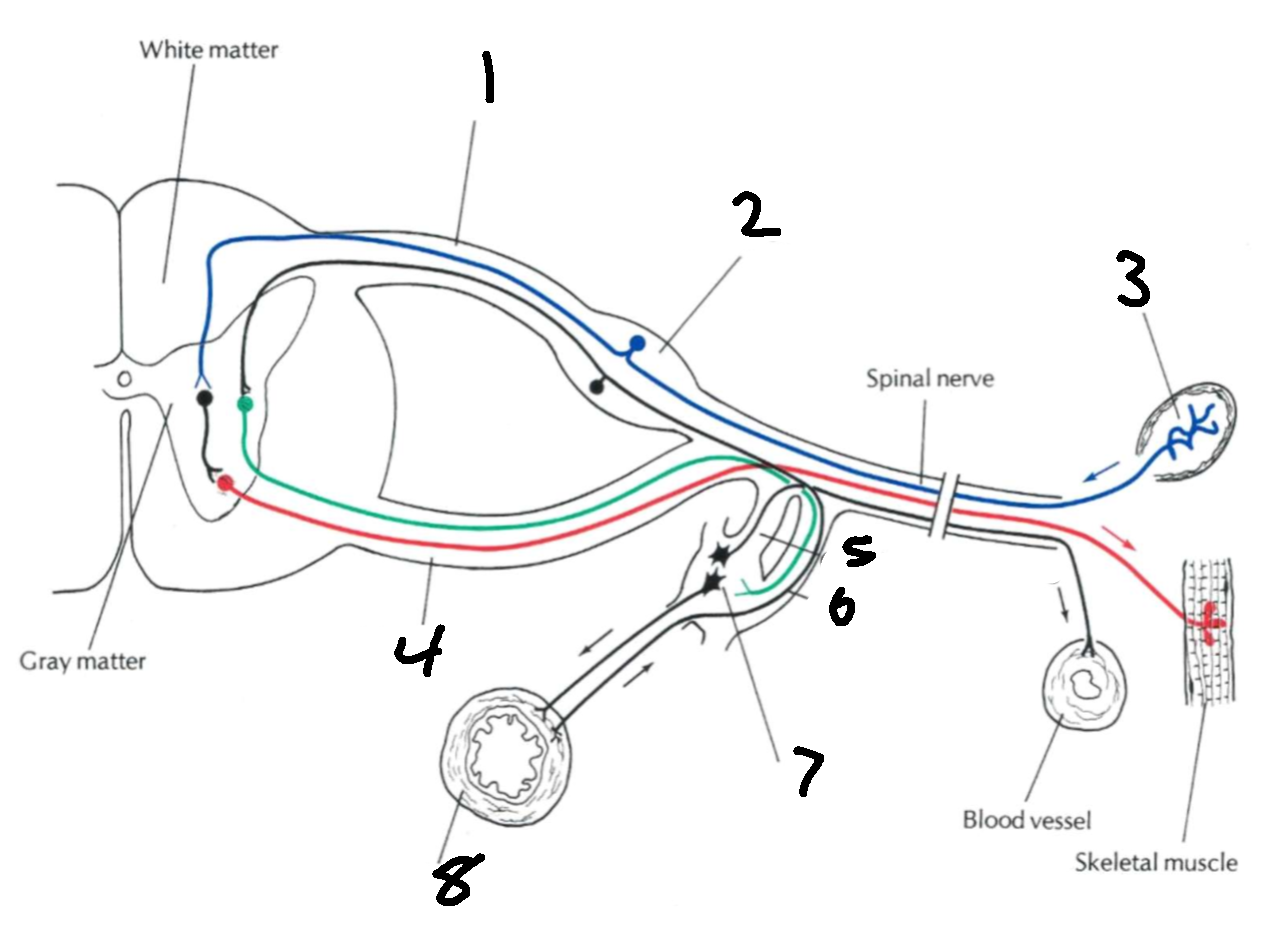
What is 5?
grey communicating rami
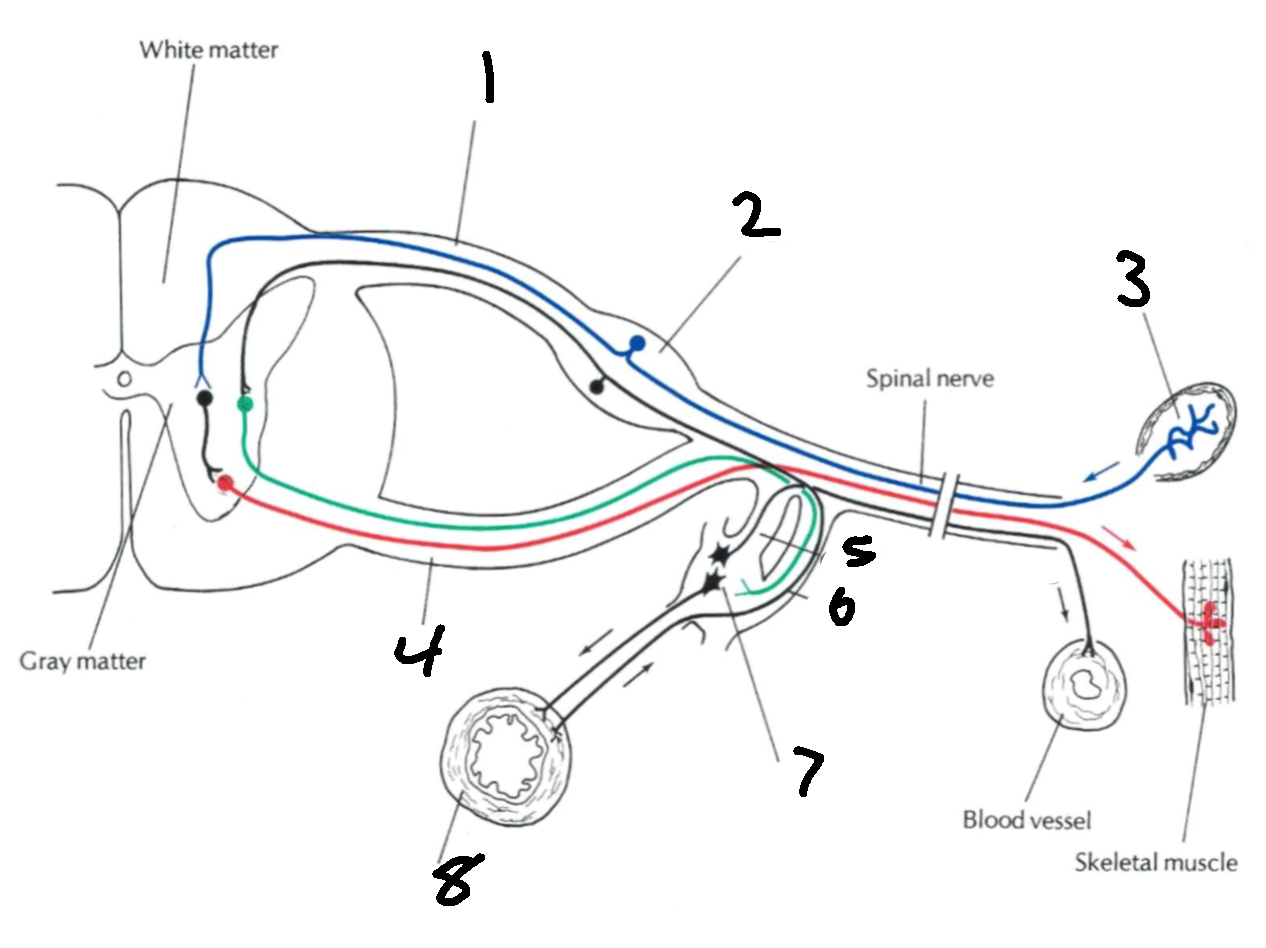
What is 6?
white communicating rami
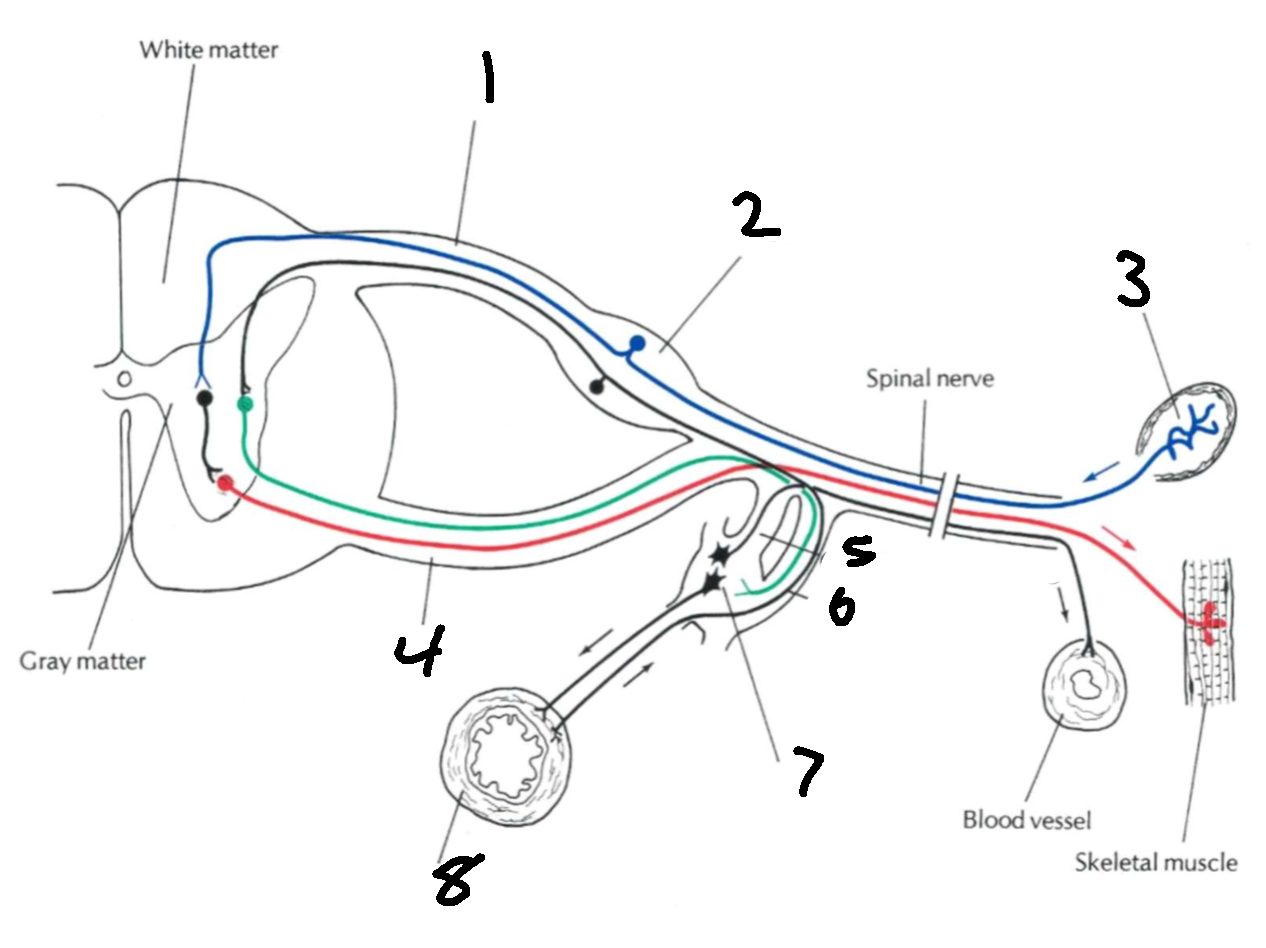
What is 7?
sympathetic ganglion
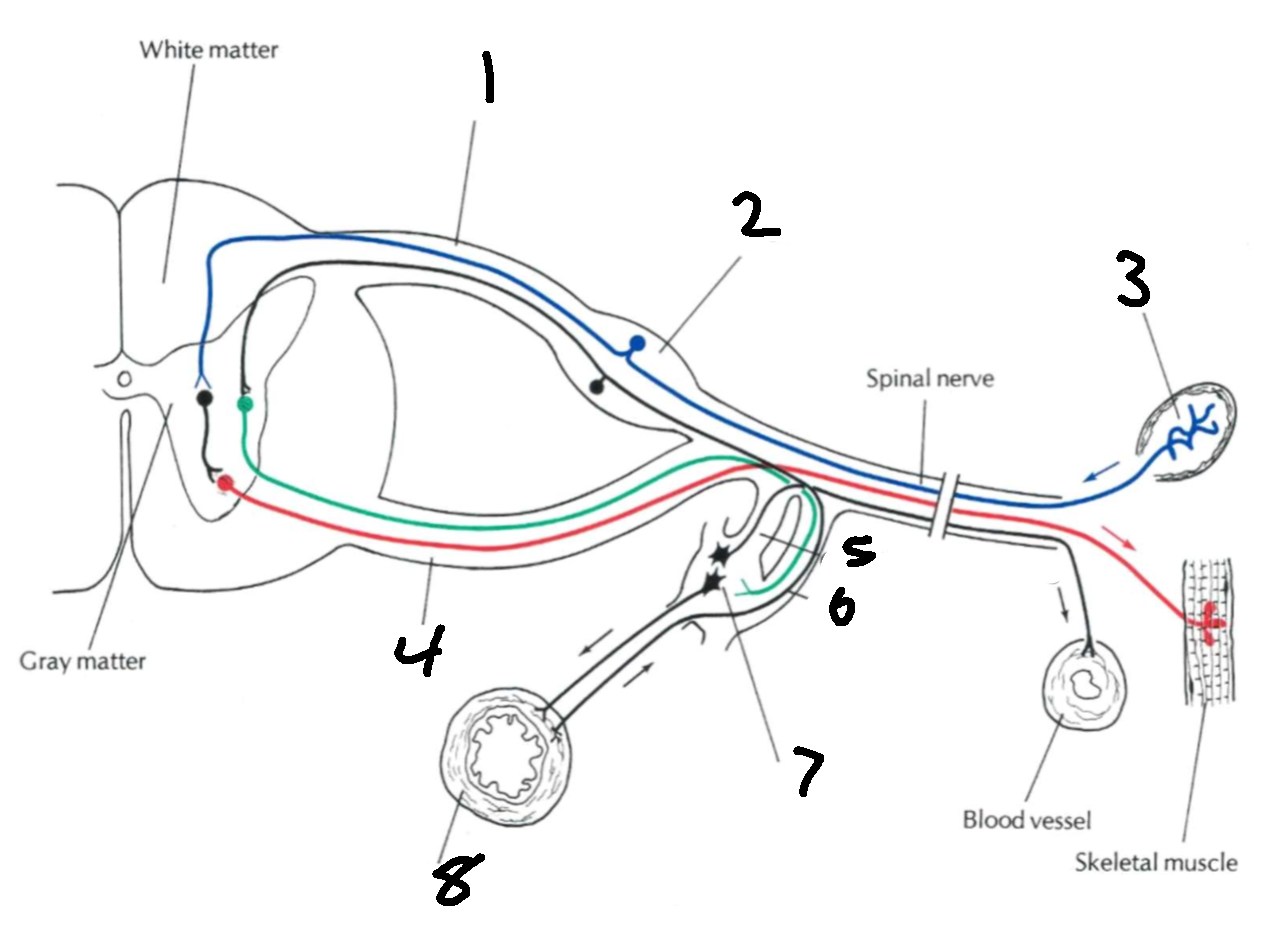
What is 8?
viscus
What types of nerves does the dorsal root carry?
afferent, sensory
What types of nerves does the ventral root carry?
efferent, motor
What is 1?
dorsal root
What is 2?
dorsal root ganglion
What is 3?
ventral root
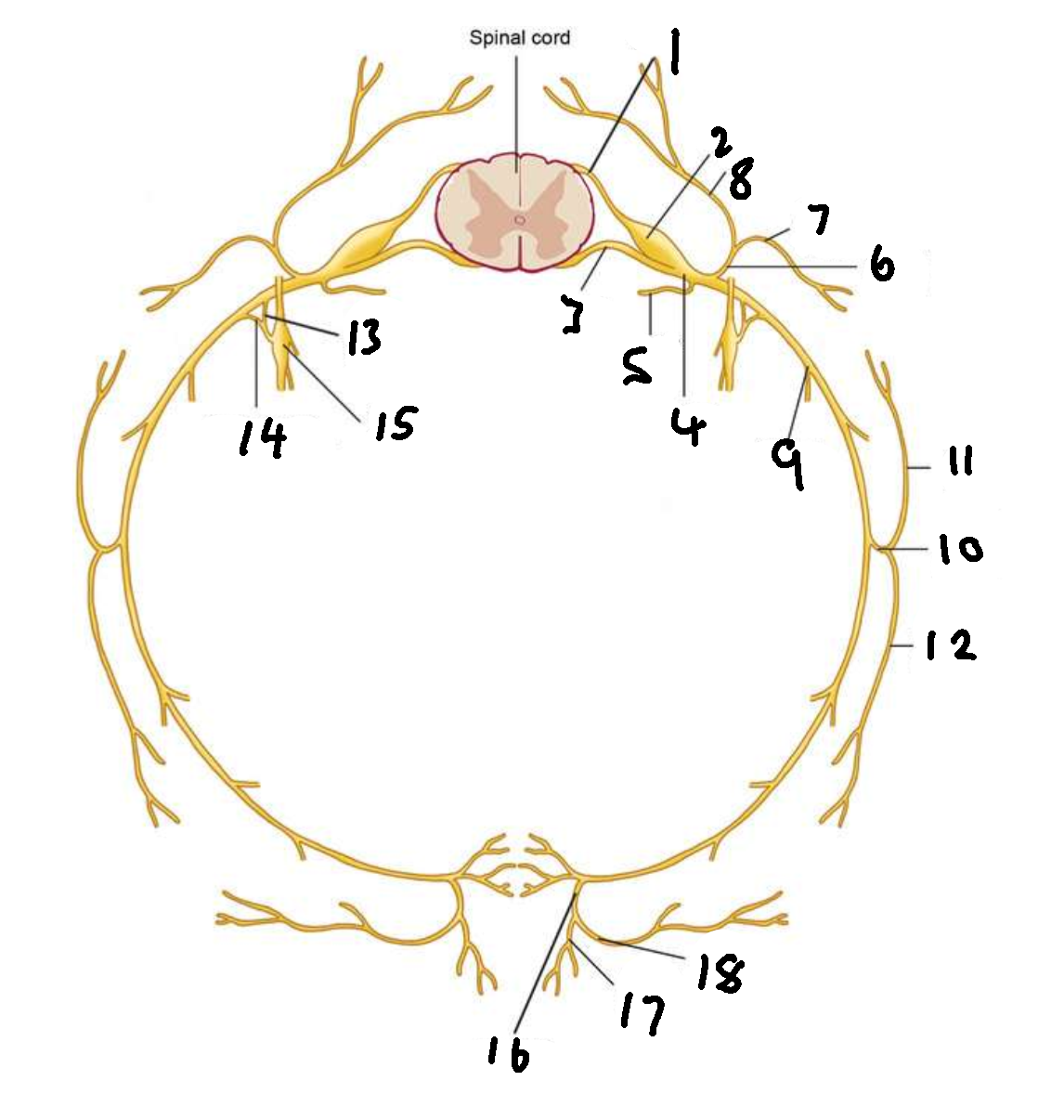
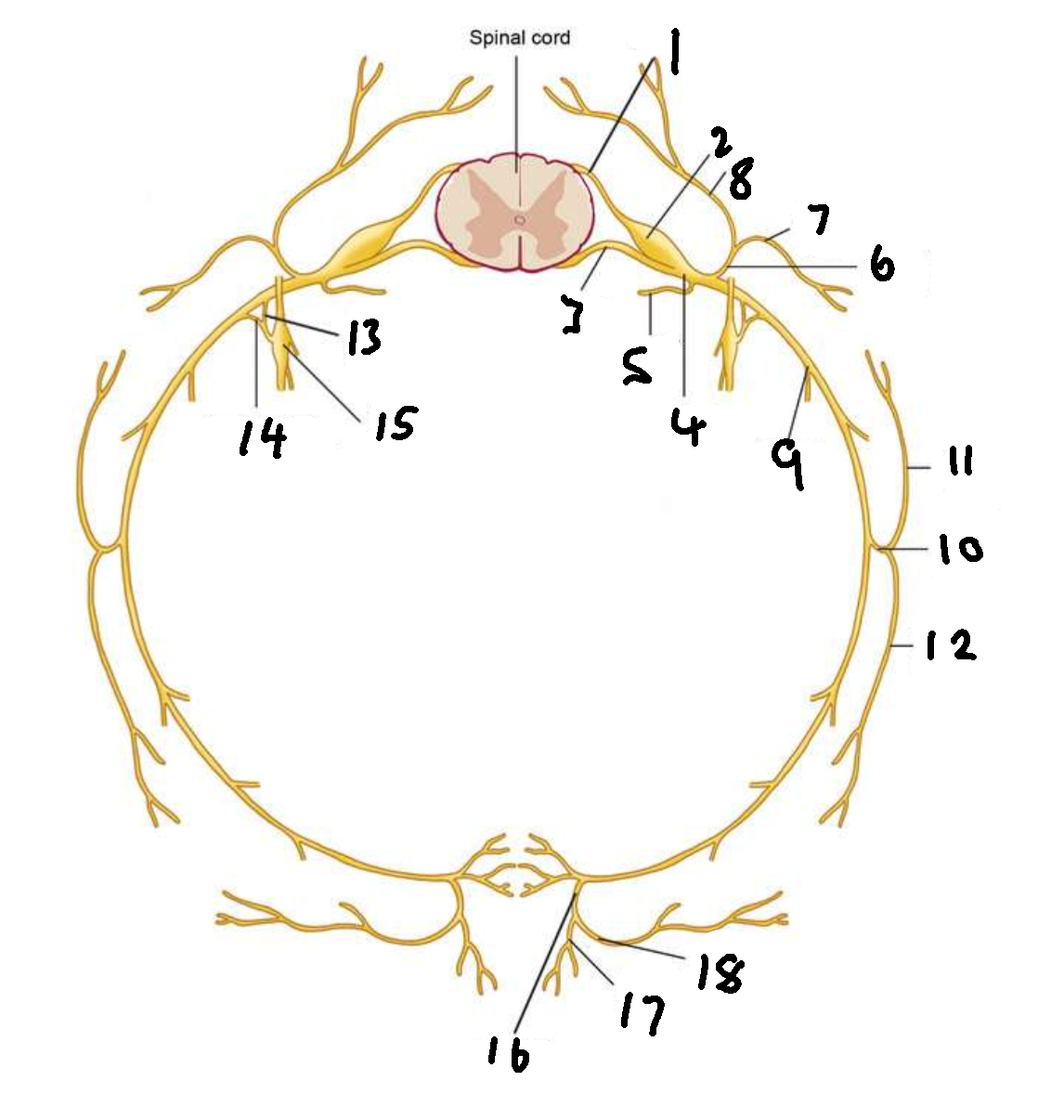
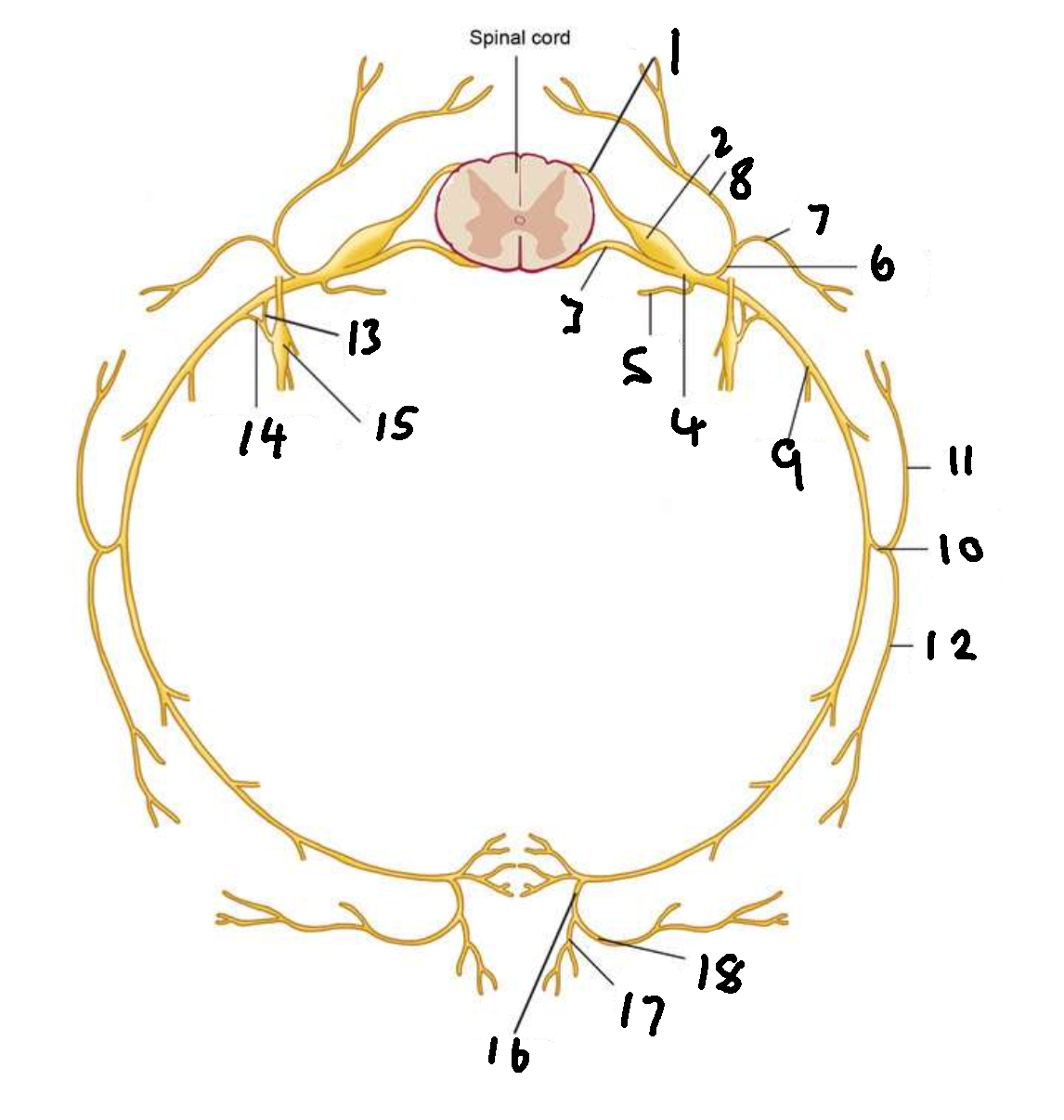
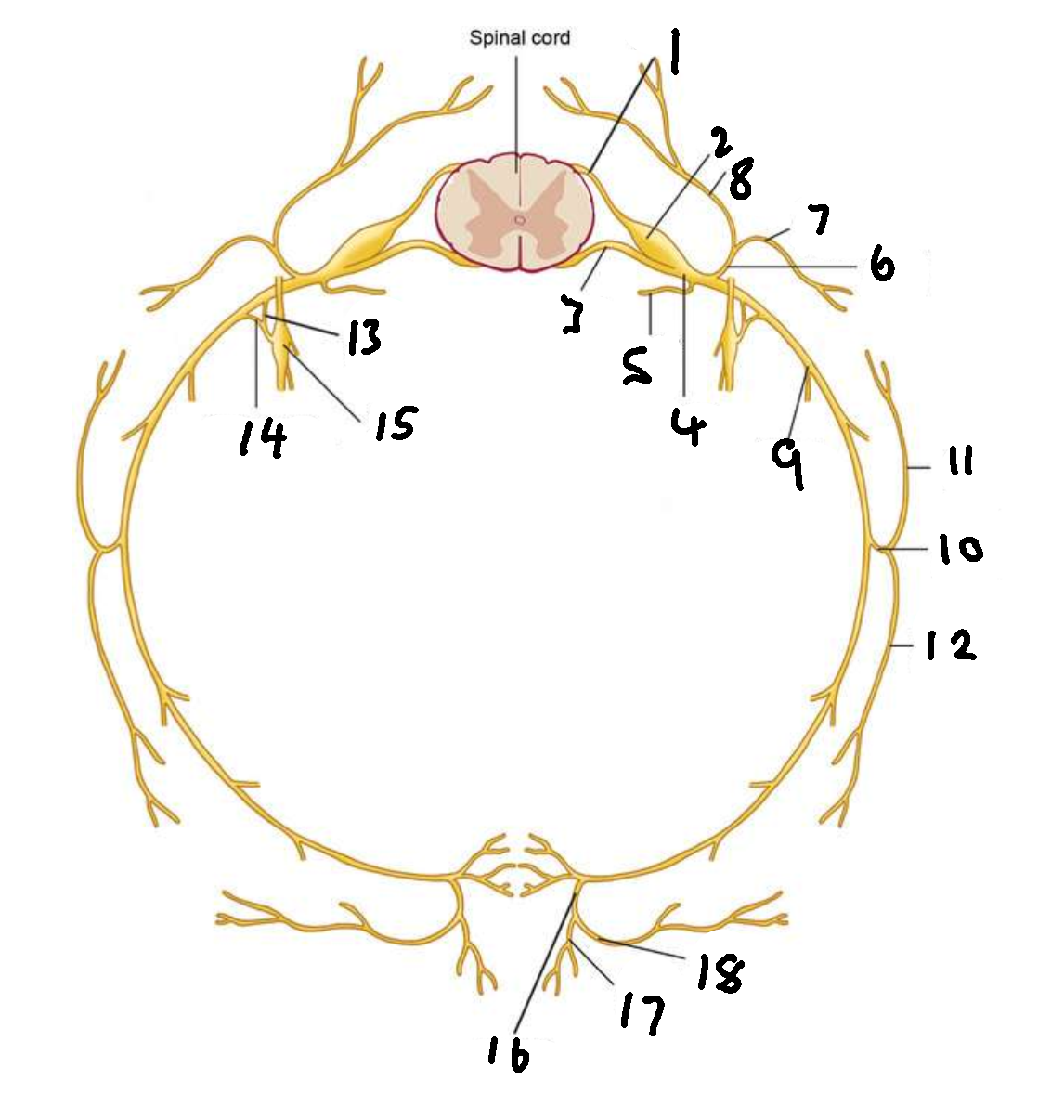
What is 4?
spinal nerve
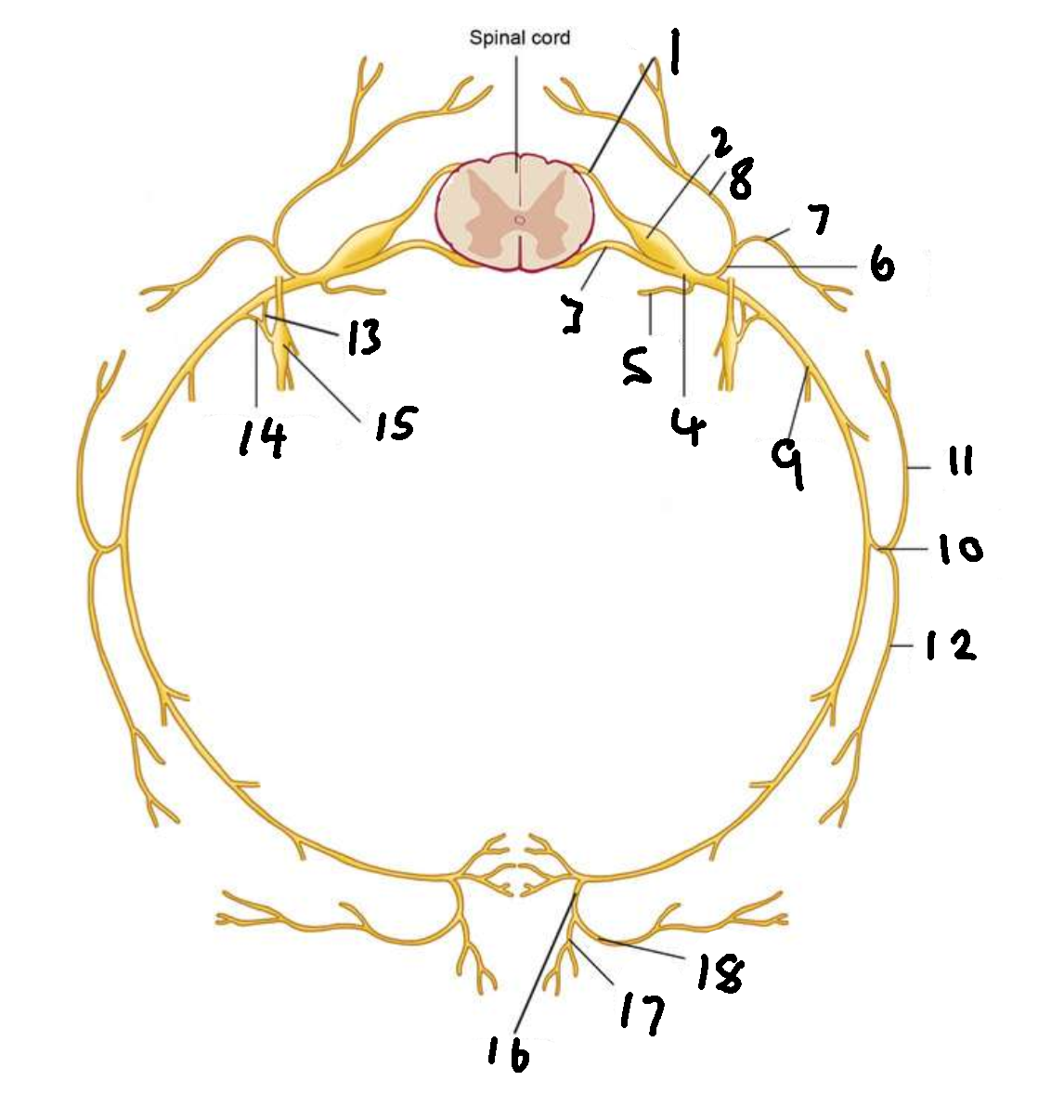
What is 5?
meningeal ramus
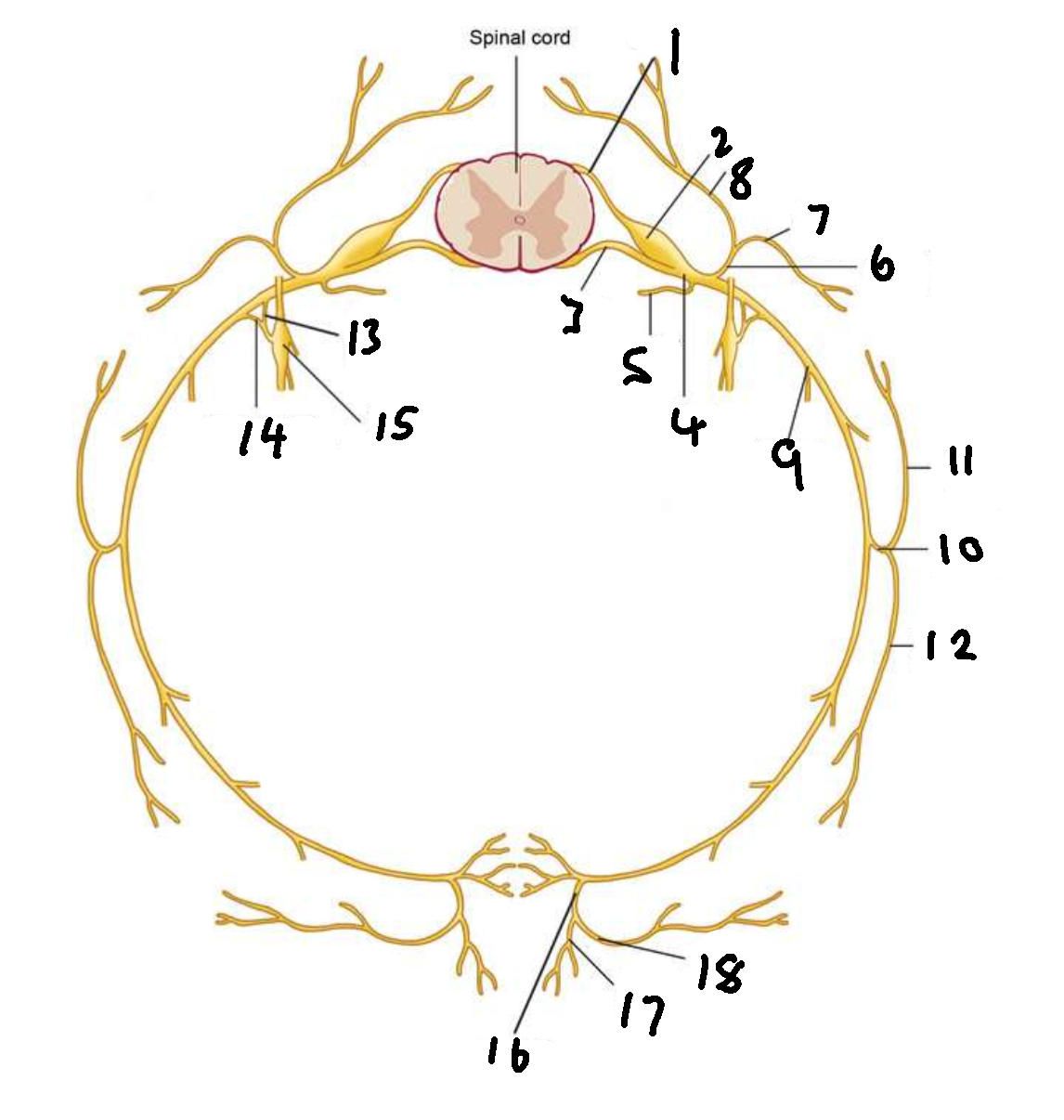
What is 6?
dorsal ramus
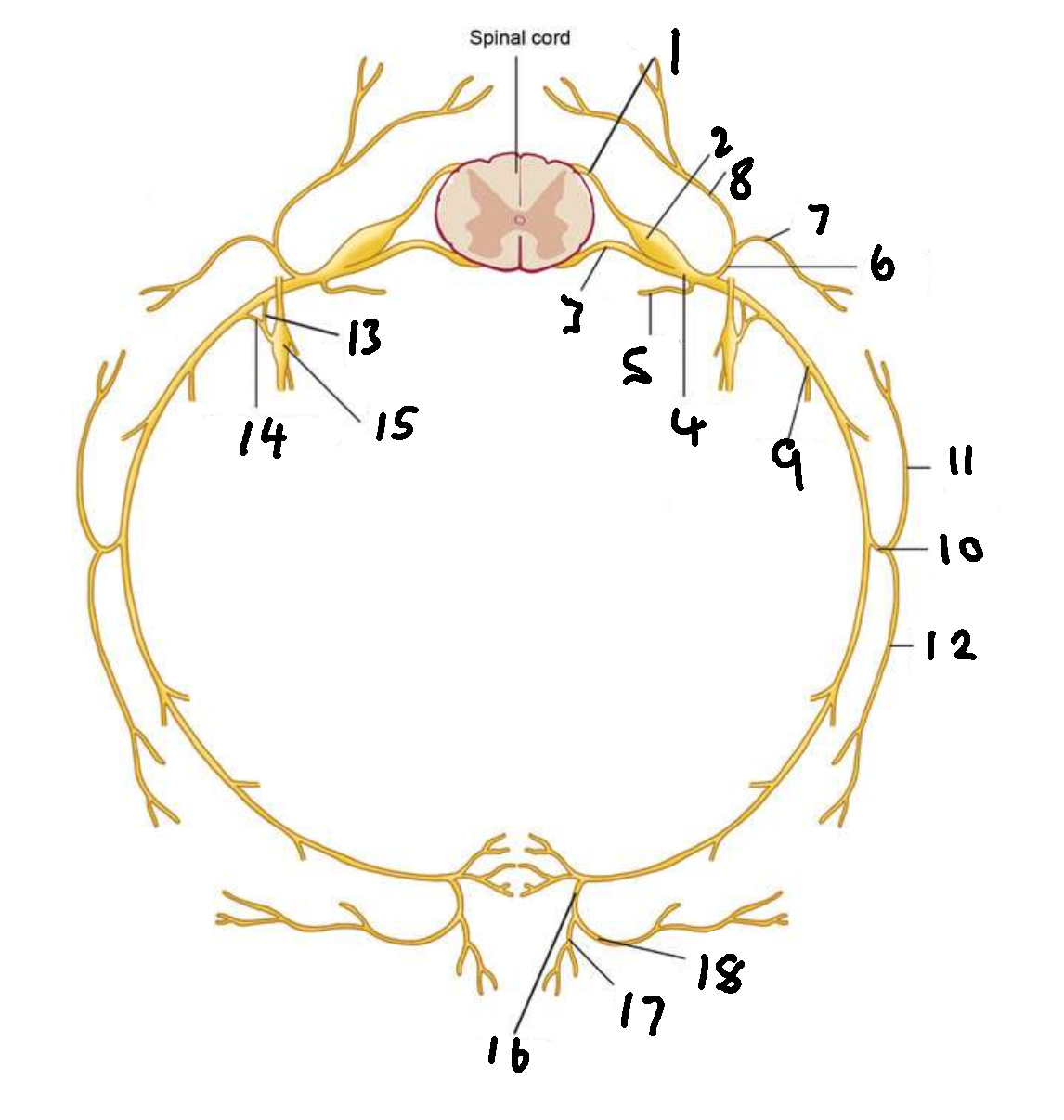
What is 7?
lateral branch
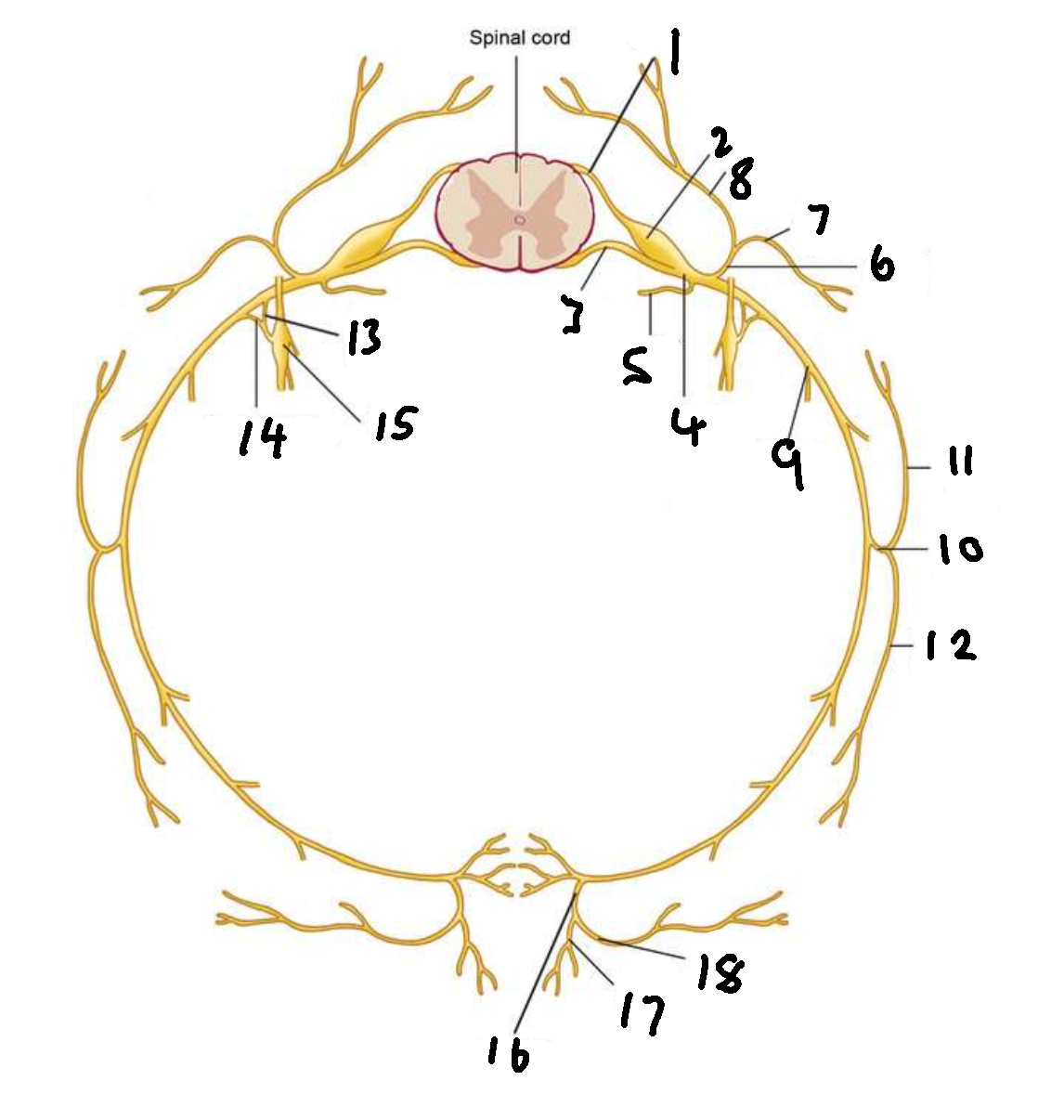
What is 8?
medial branch
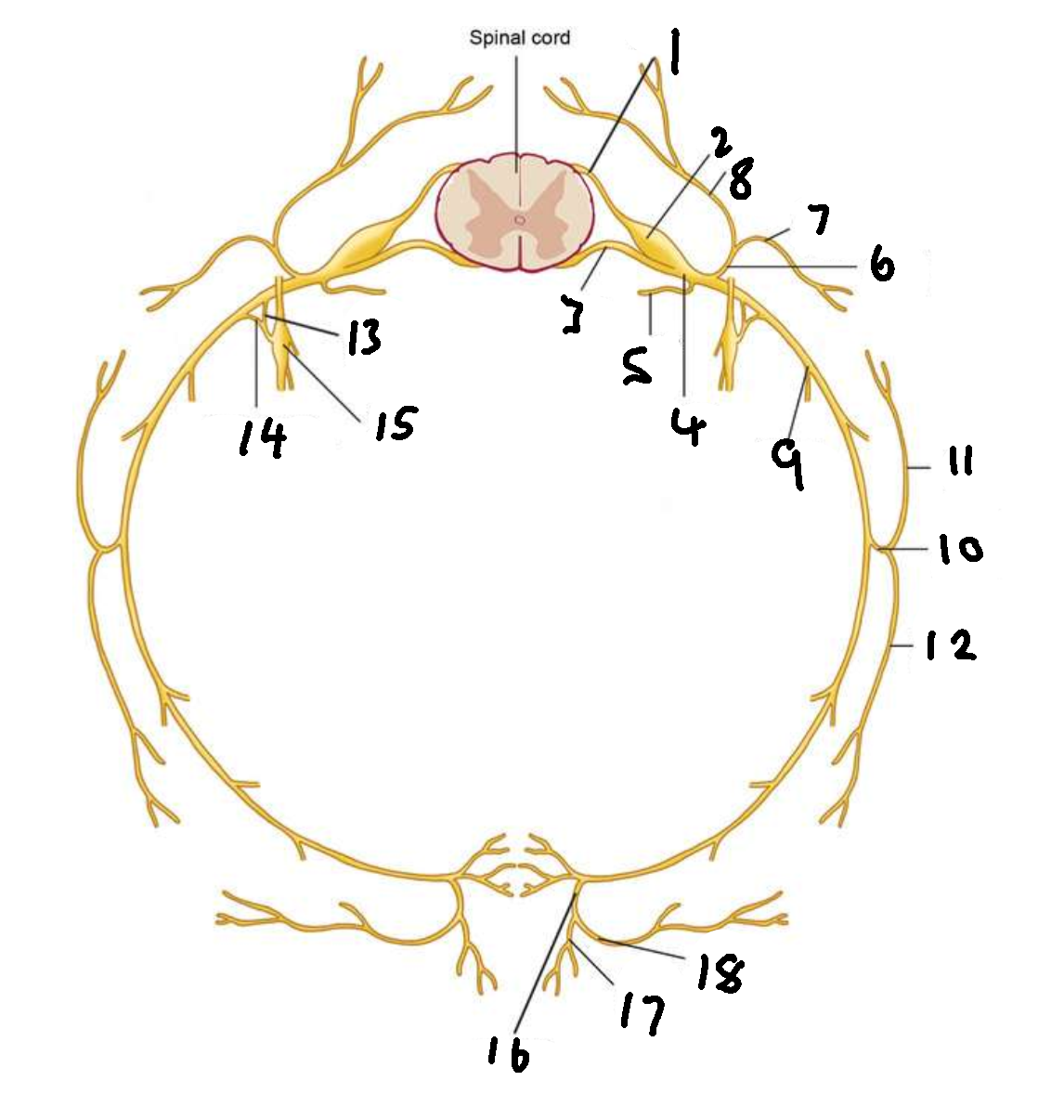
What is 9?
ventral ramus
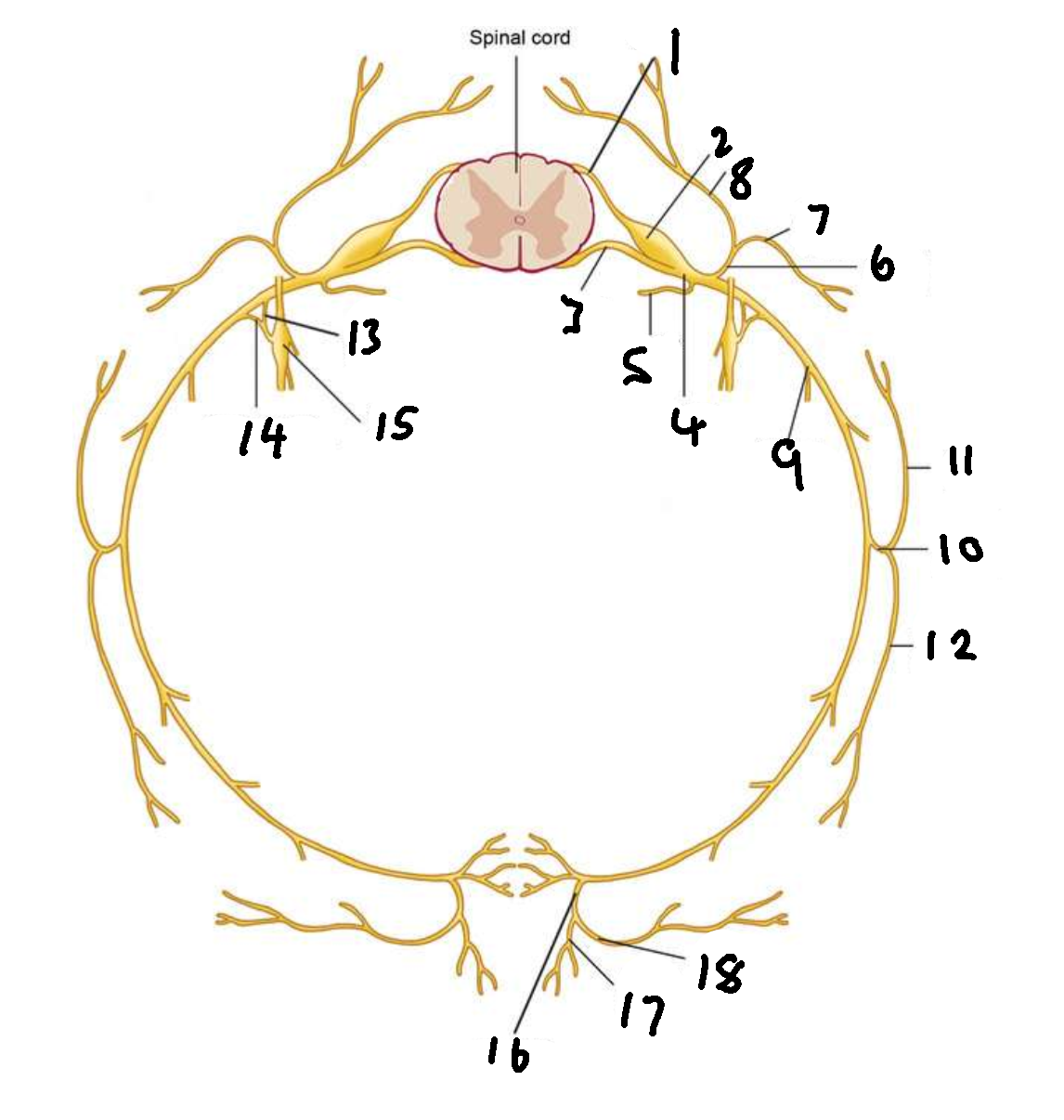
What is 10?
lateral cutaneous branch
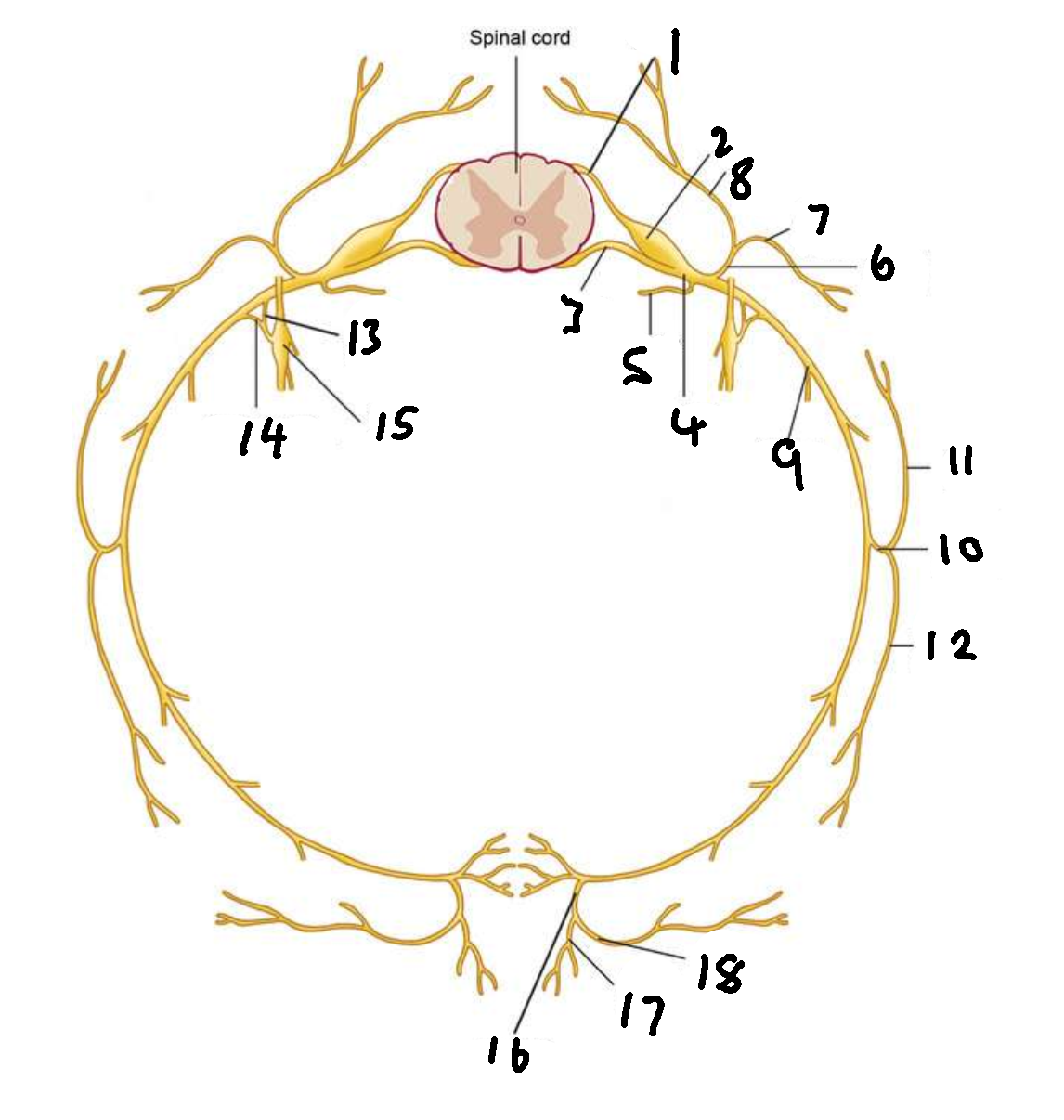
What is 11?
medial branch
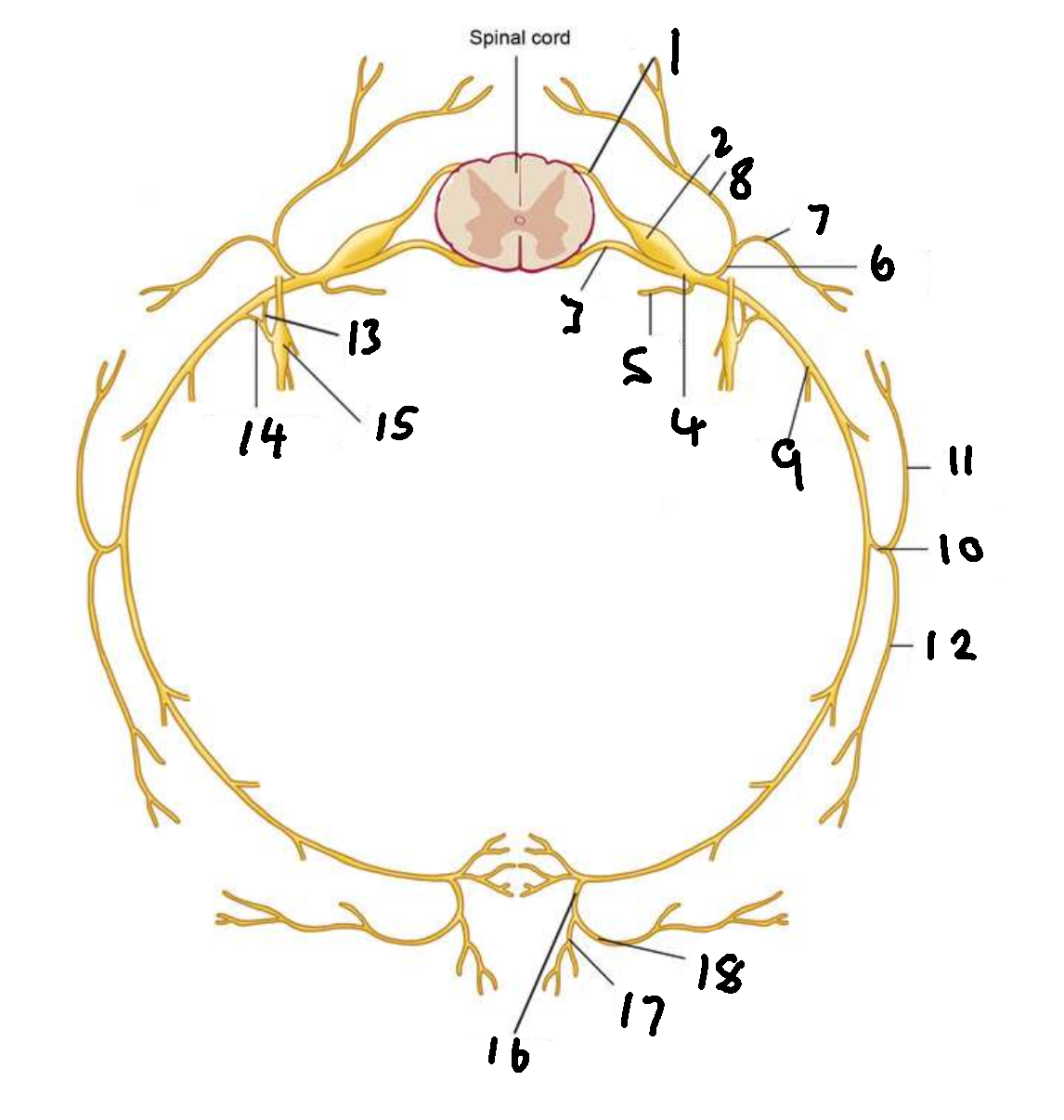
What is 12?
lateral branch
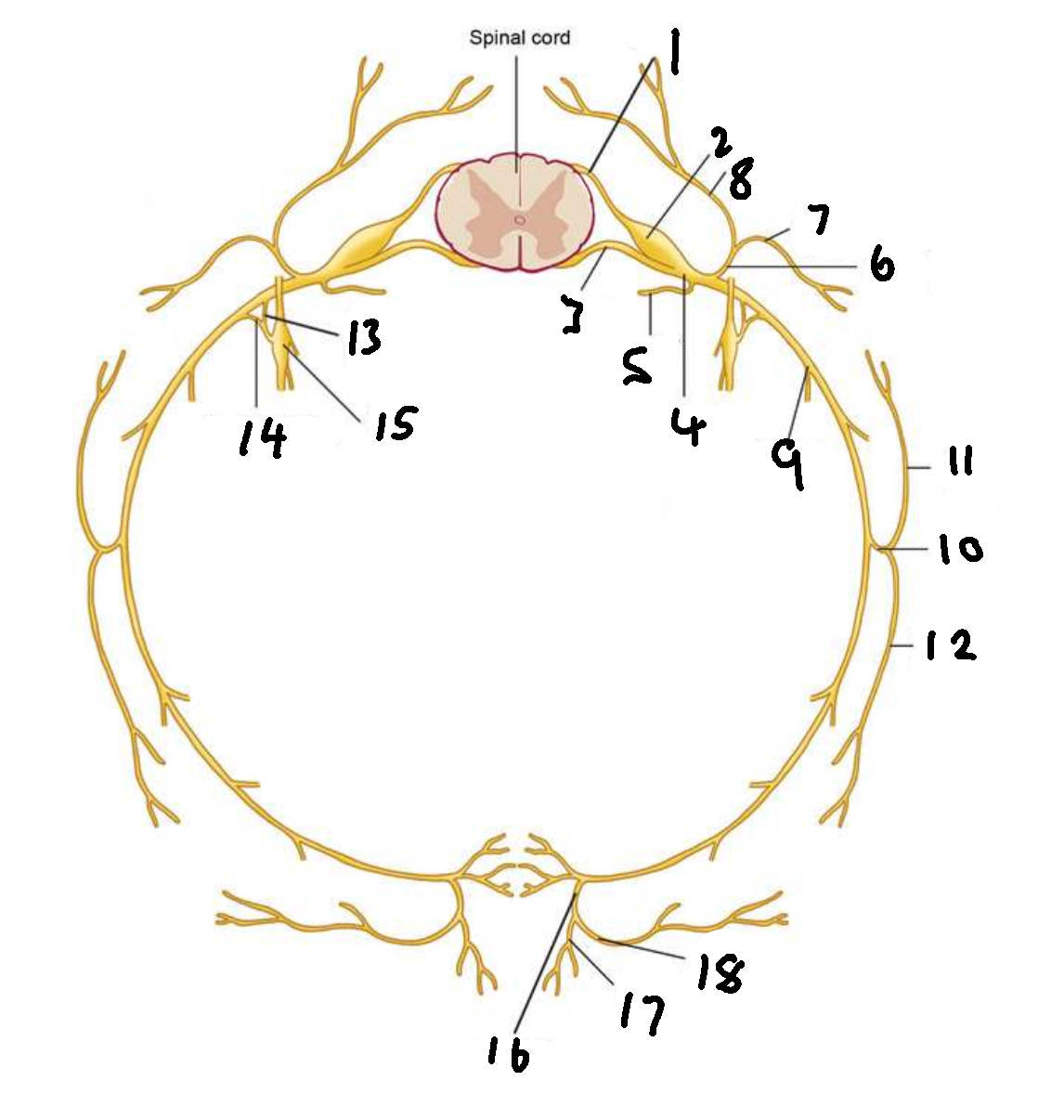
What is 13?
white ramus communicans
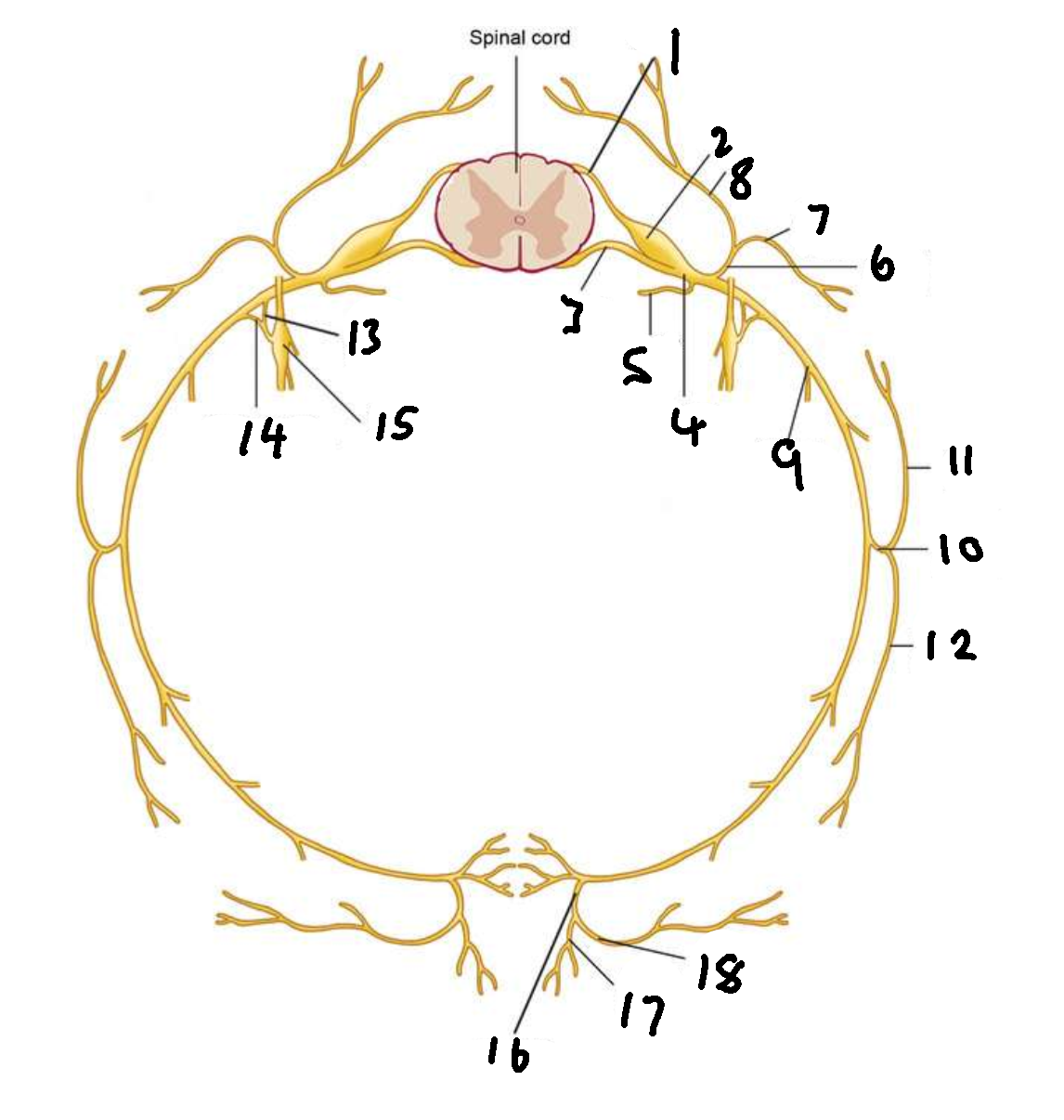
What is 14?
grey ramus communicans
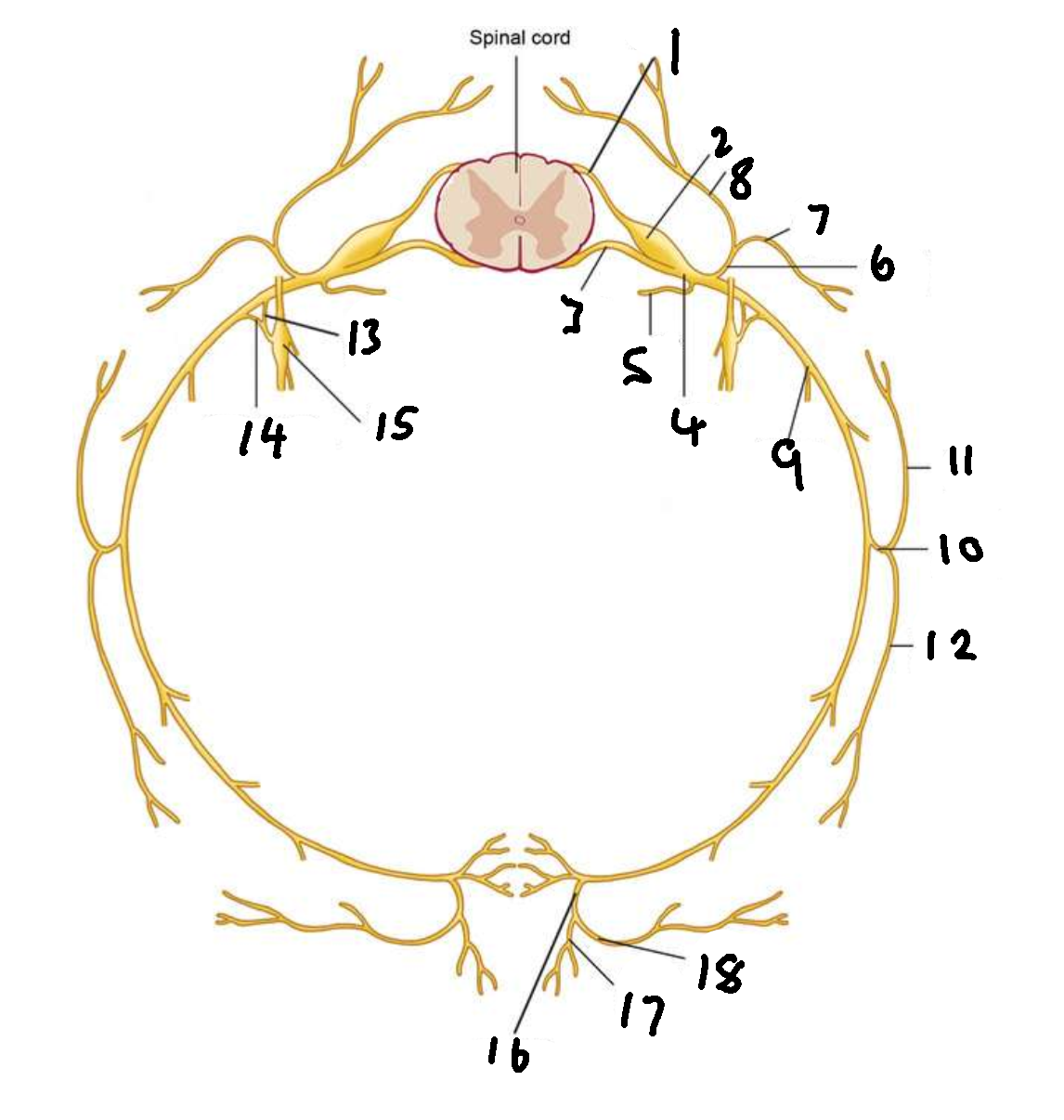
What is 15?
sympathetic ganglion
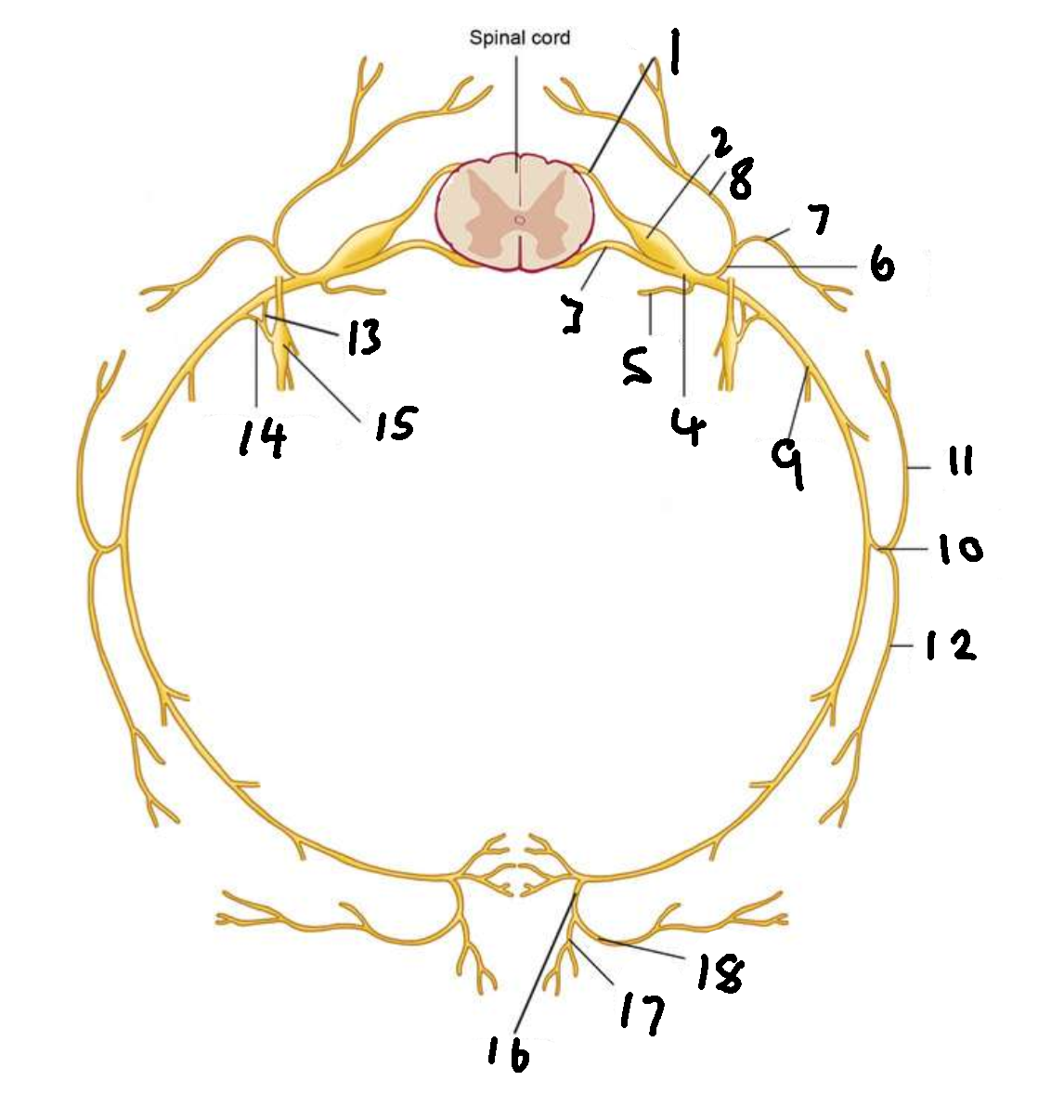
What is 16?
anterior cutaneous branch
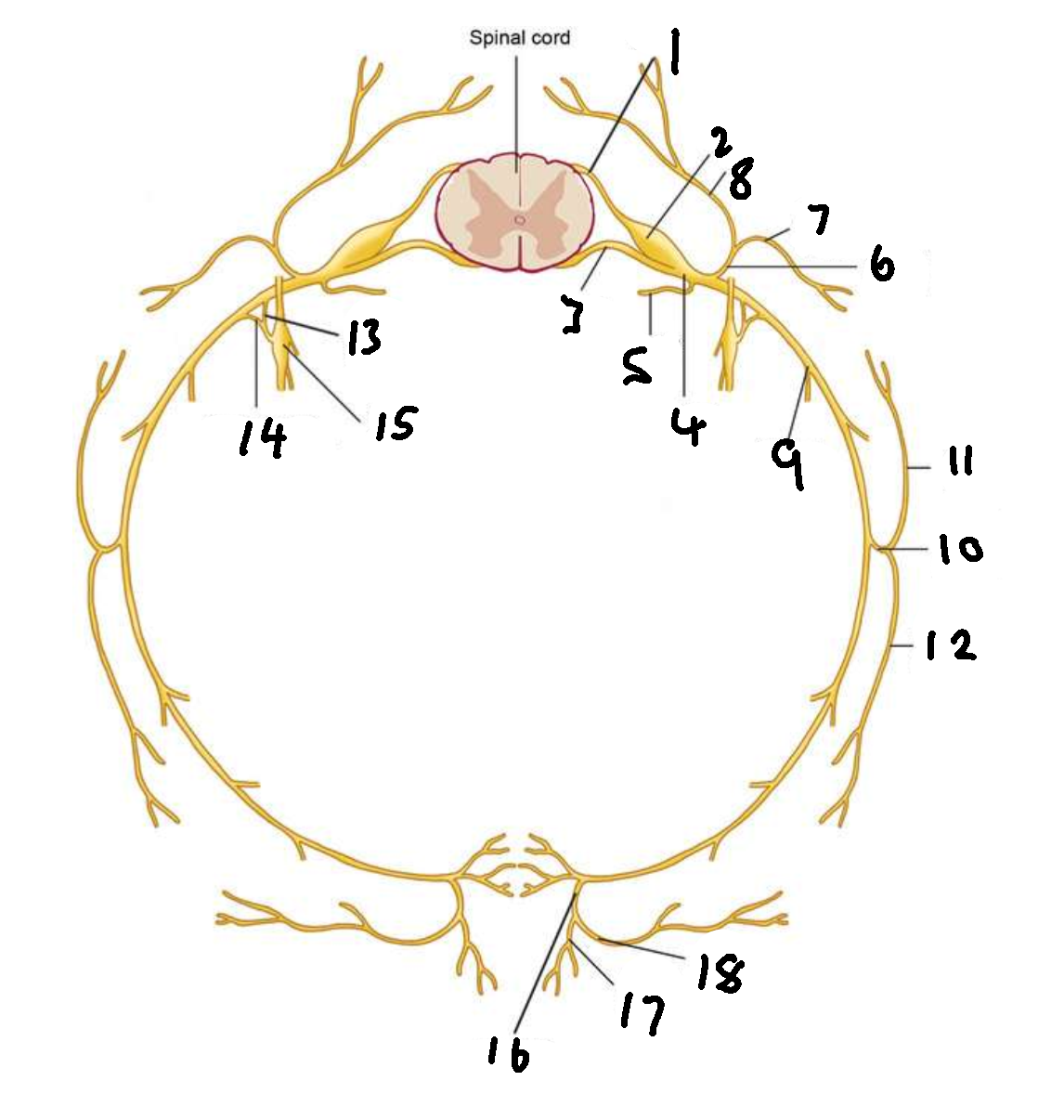
What is 17?
lateral branch
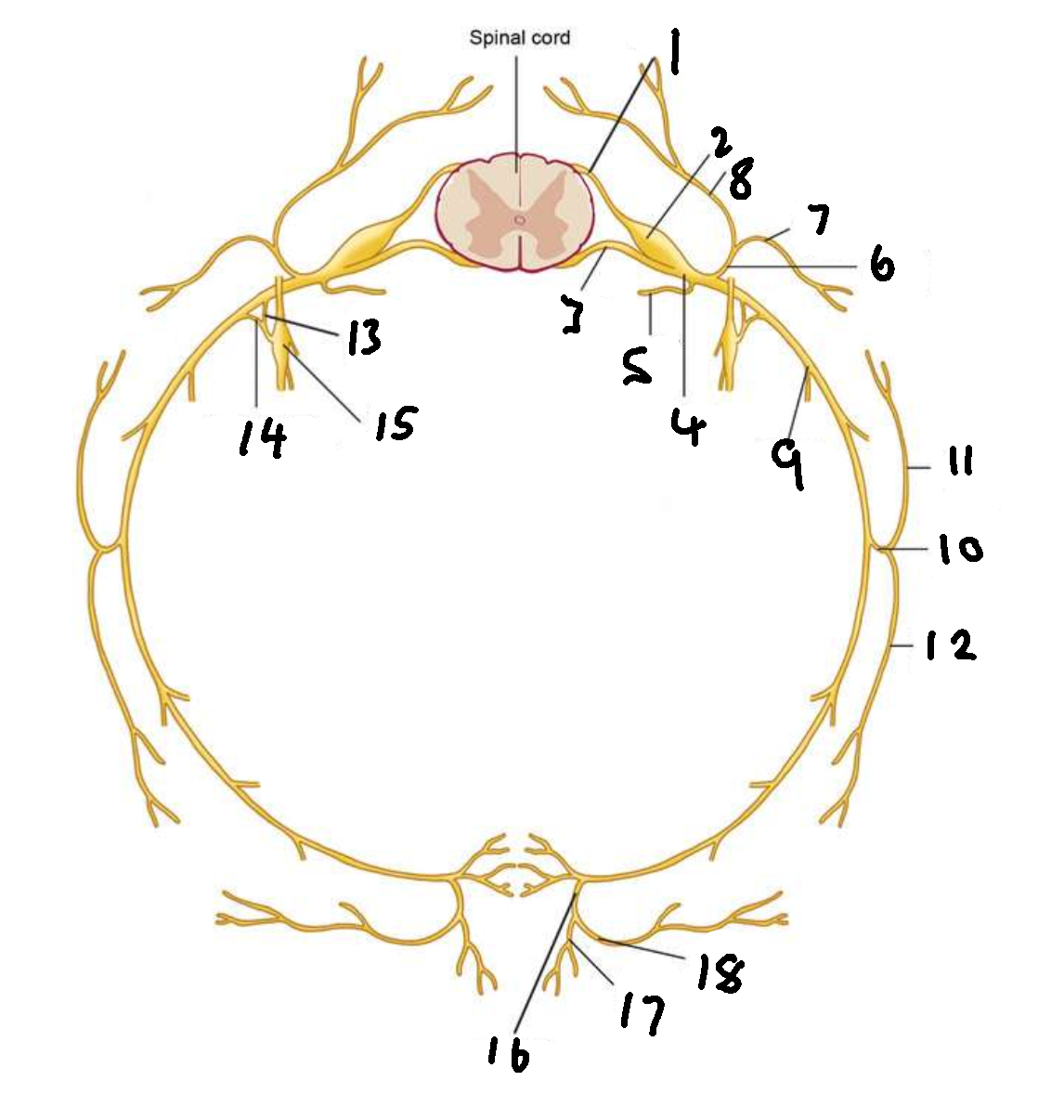
What is 18?
medial branch
What is 1?
dorsal horn
What is 2?
ventral horn
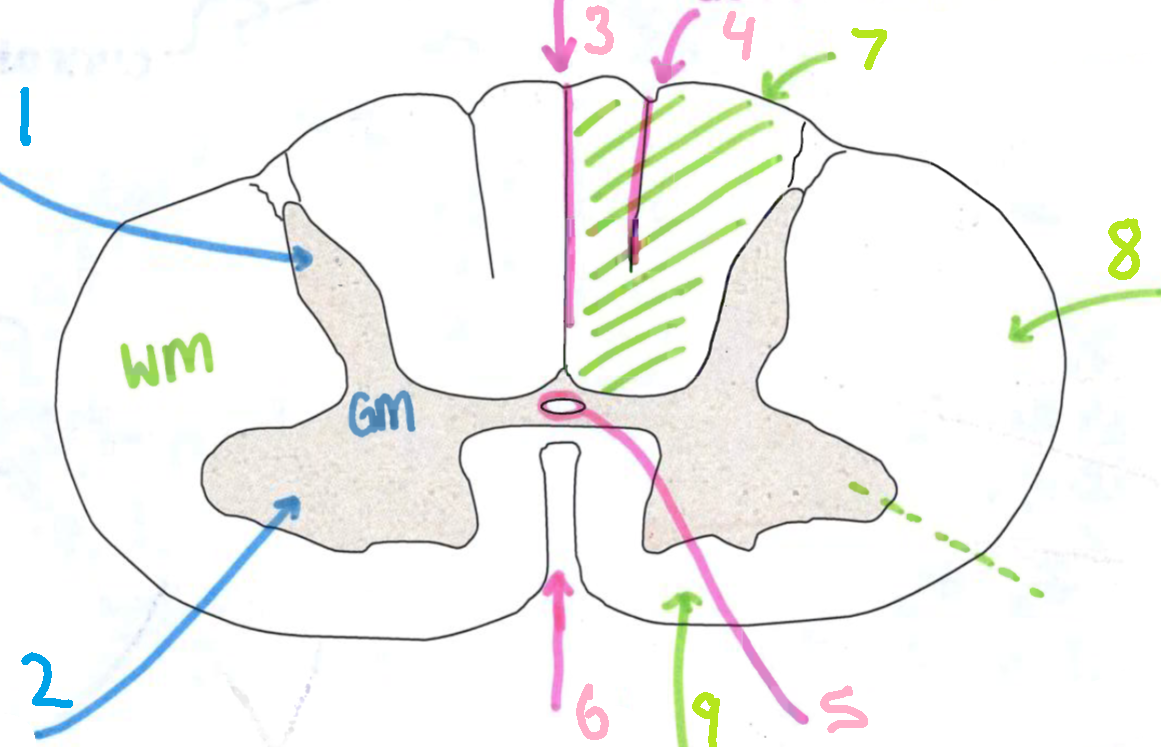
What is 3?
dorsal median sulcus
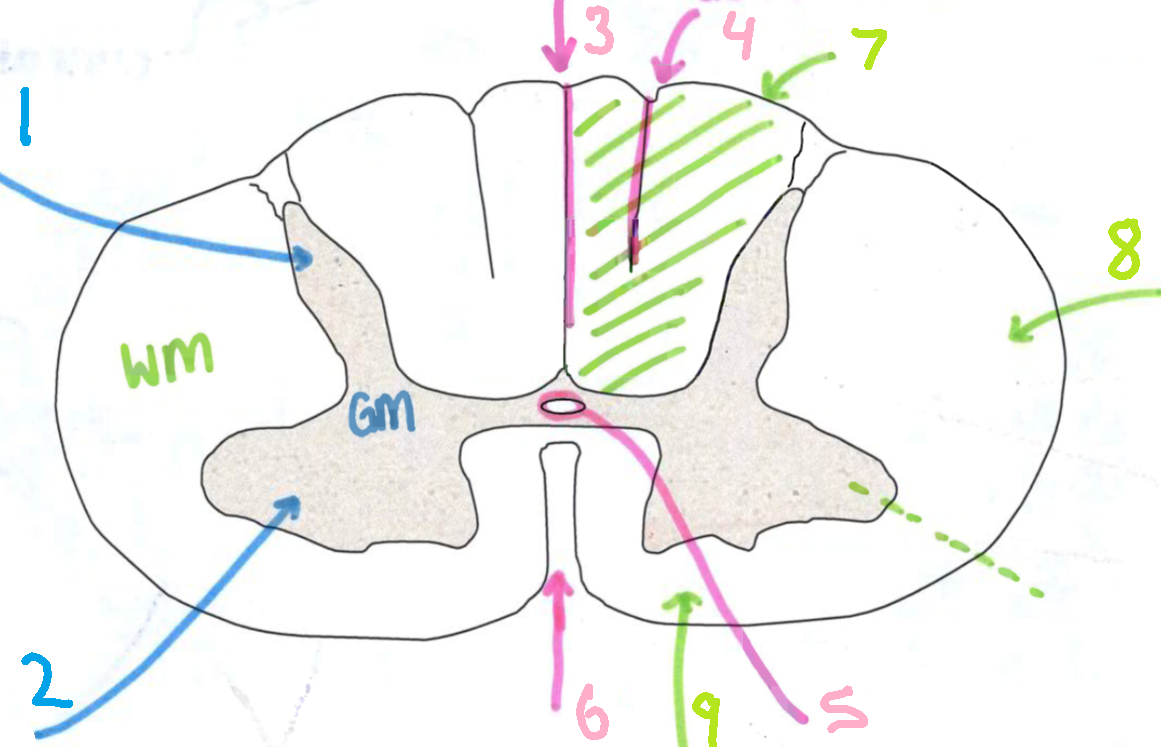
What is 4?
dorsal intermediate sulcus
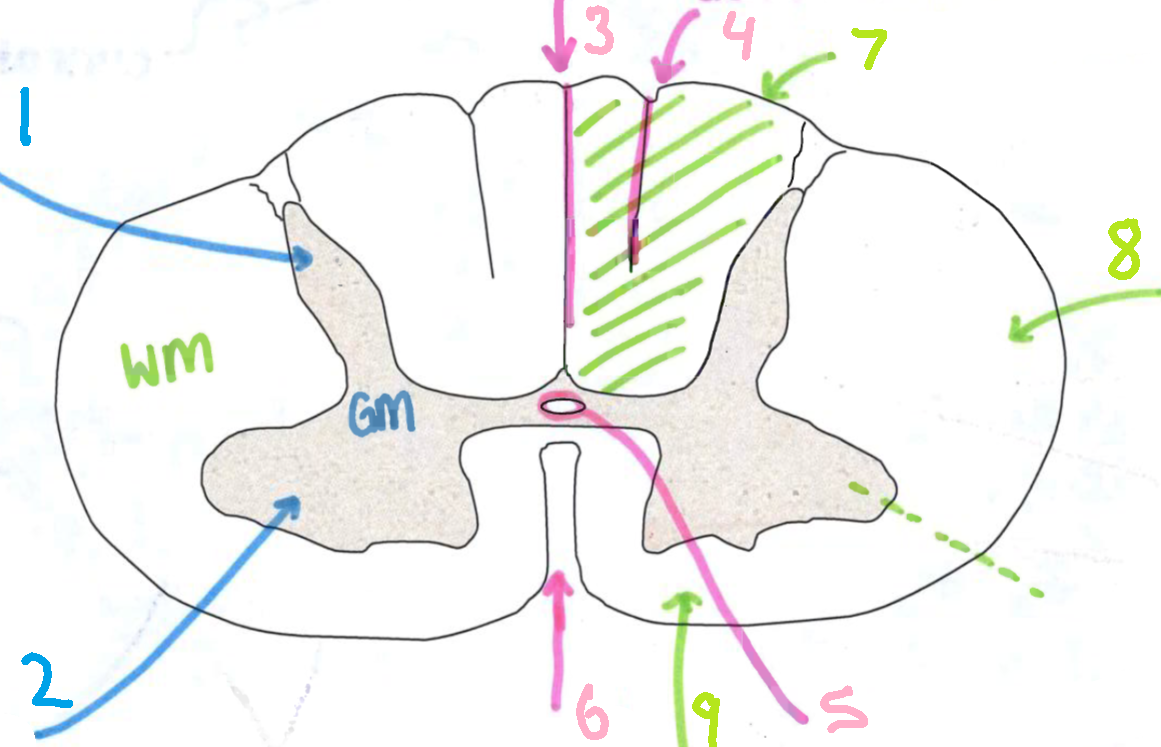
What is 5?
central canal
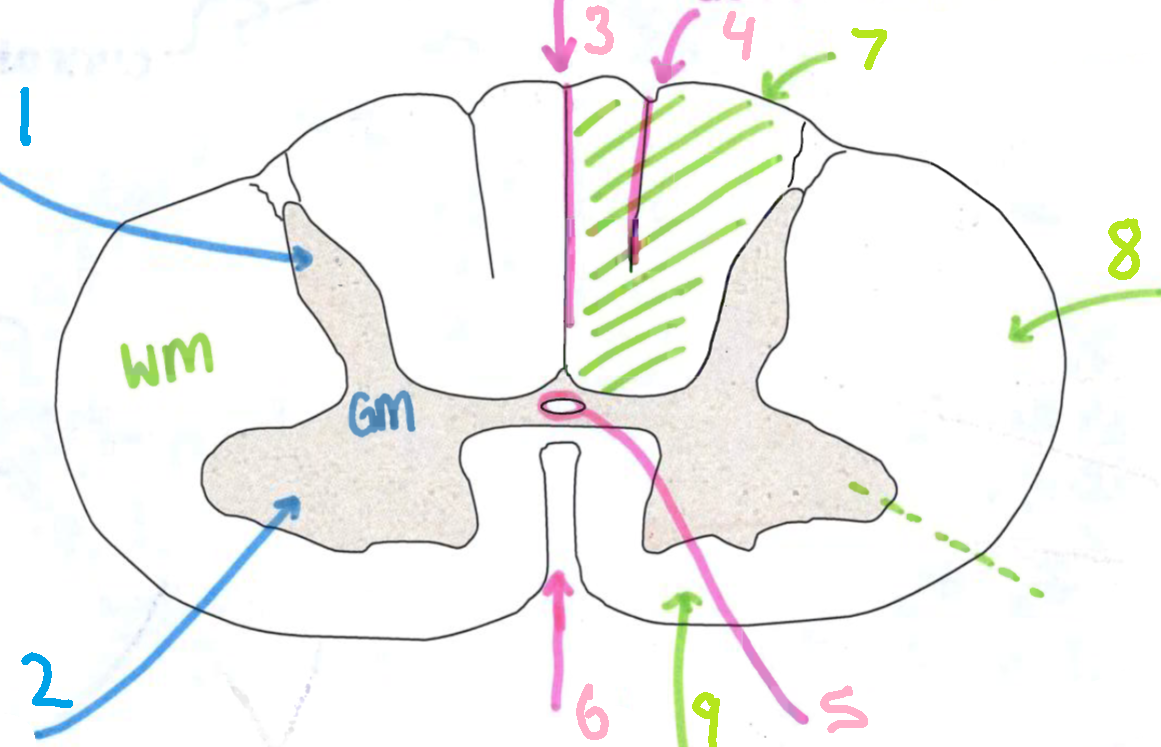
What is 6?
ventral median fissure
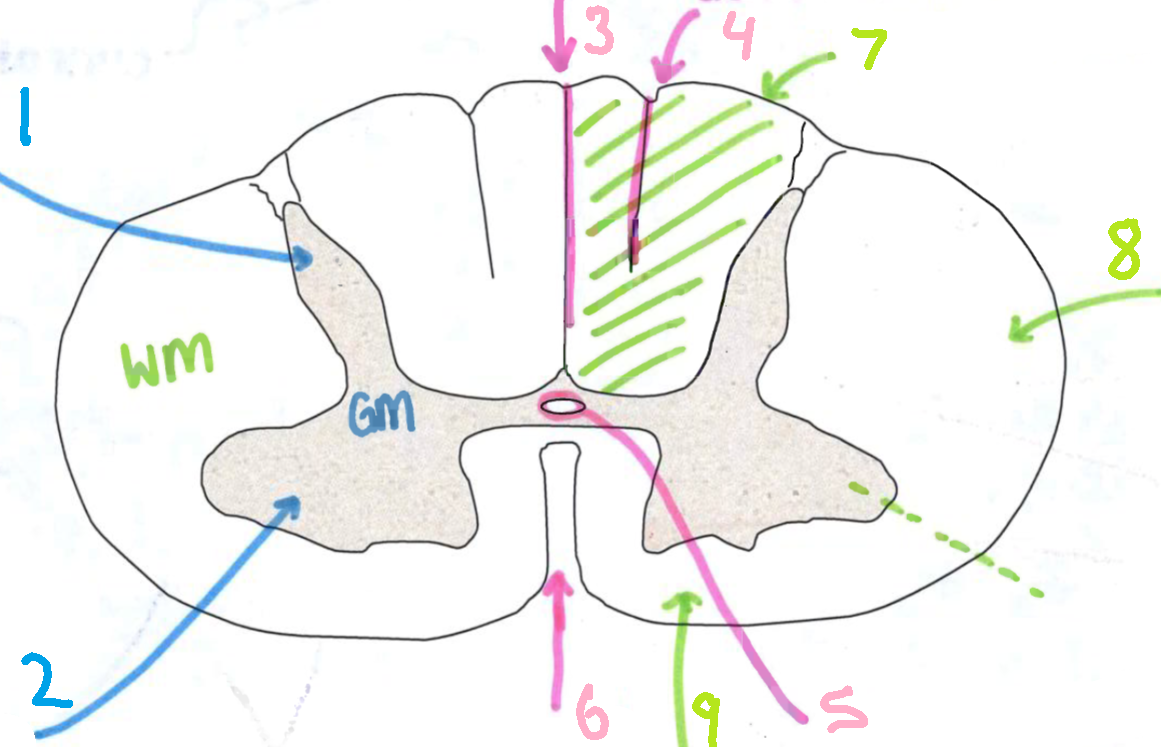
What is 7?
dorsal funiculus
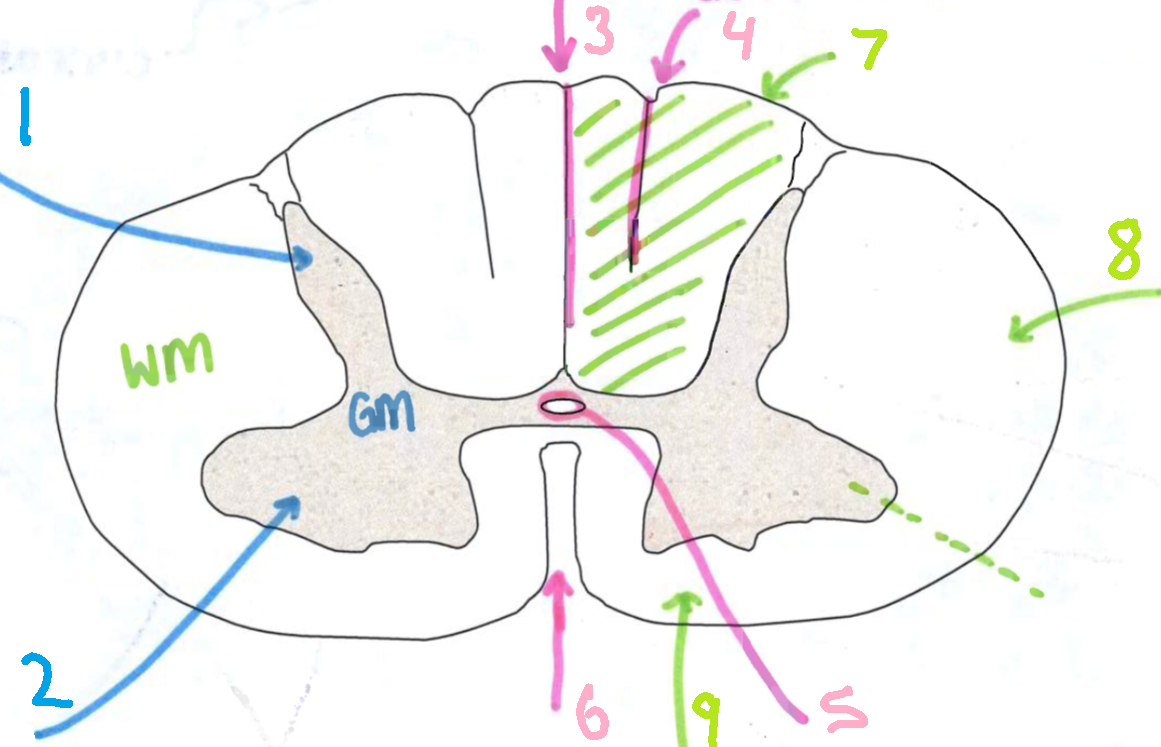
What is 8?
lateral funiculus
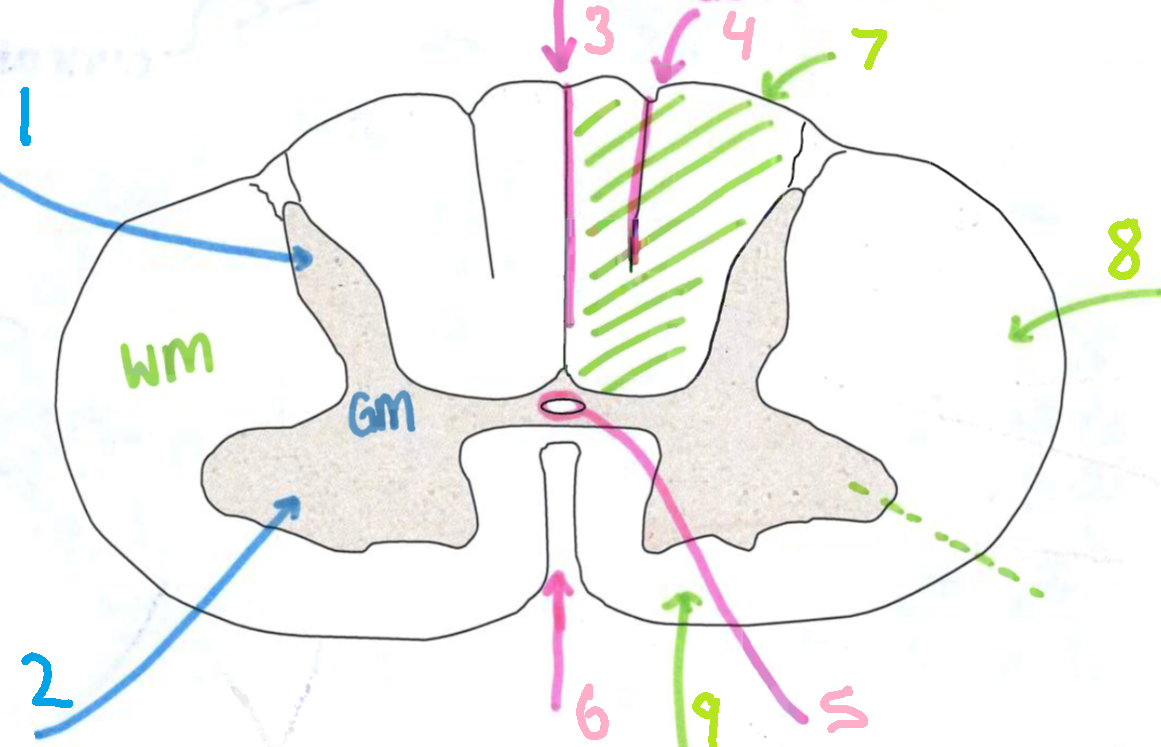
What is 9?
ventral funiculus
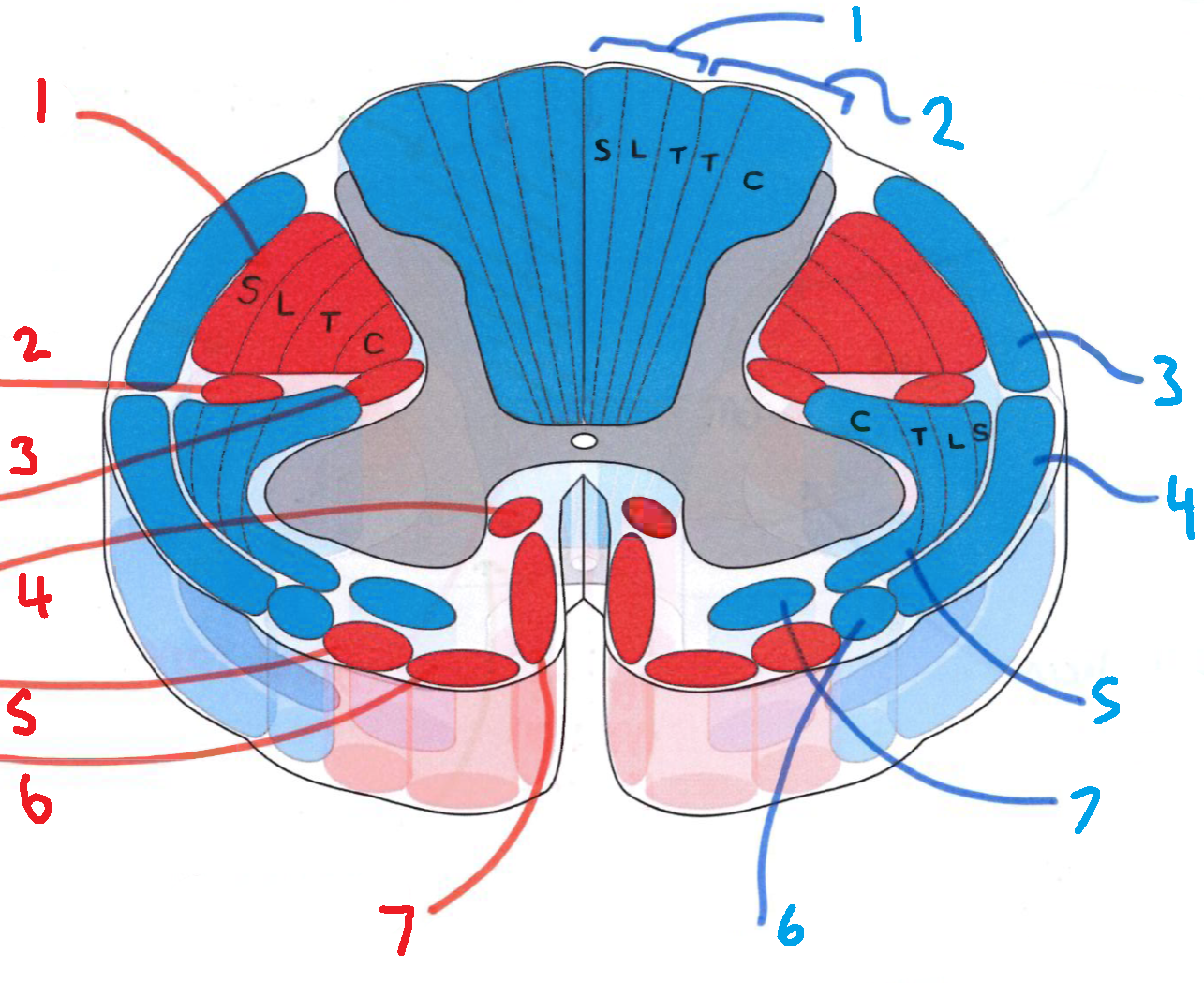
What does S stand for?
sacral
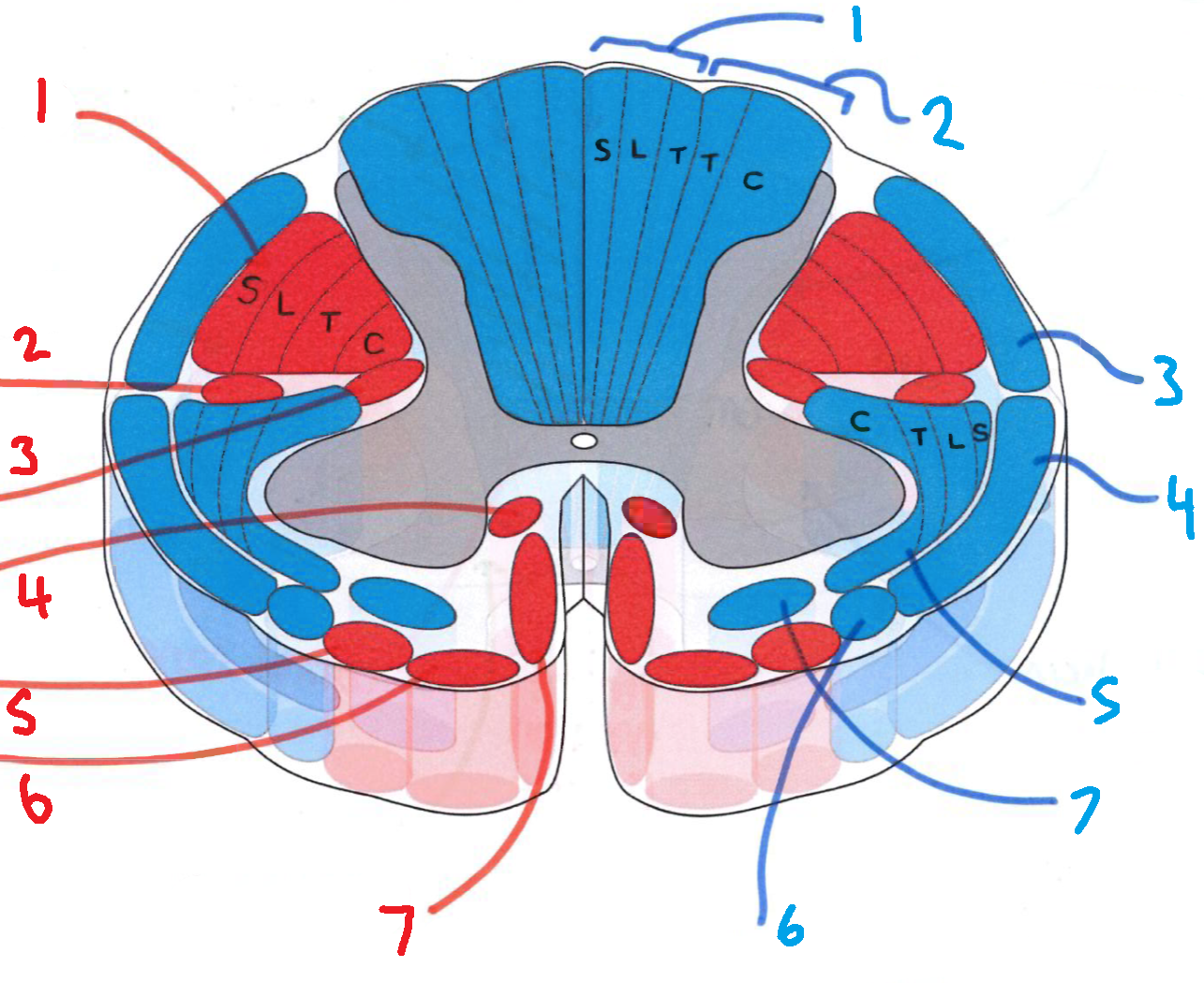
What does L stand for?
lumbar
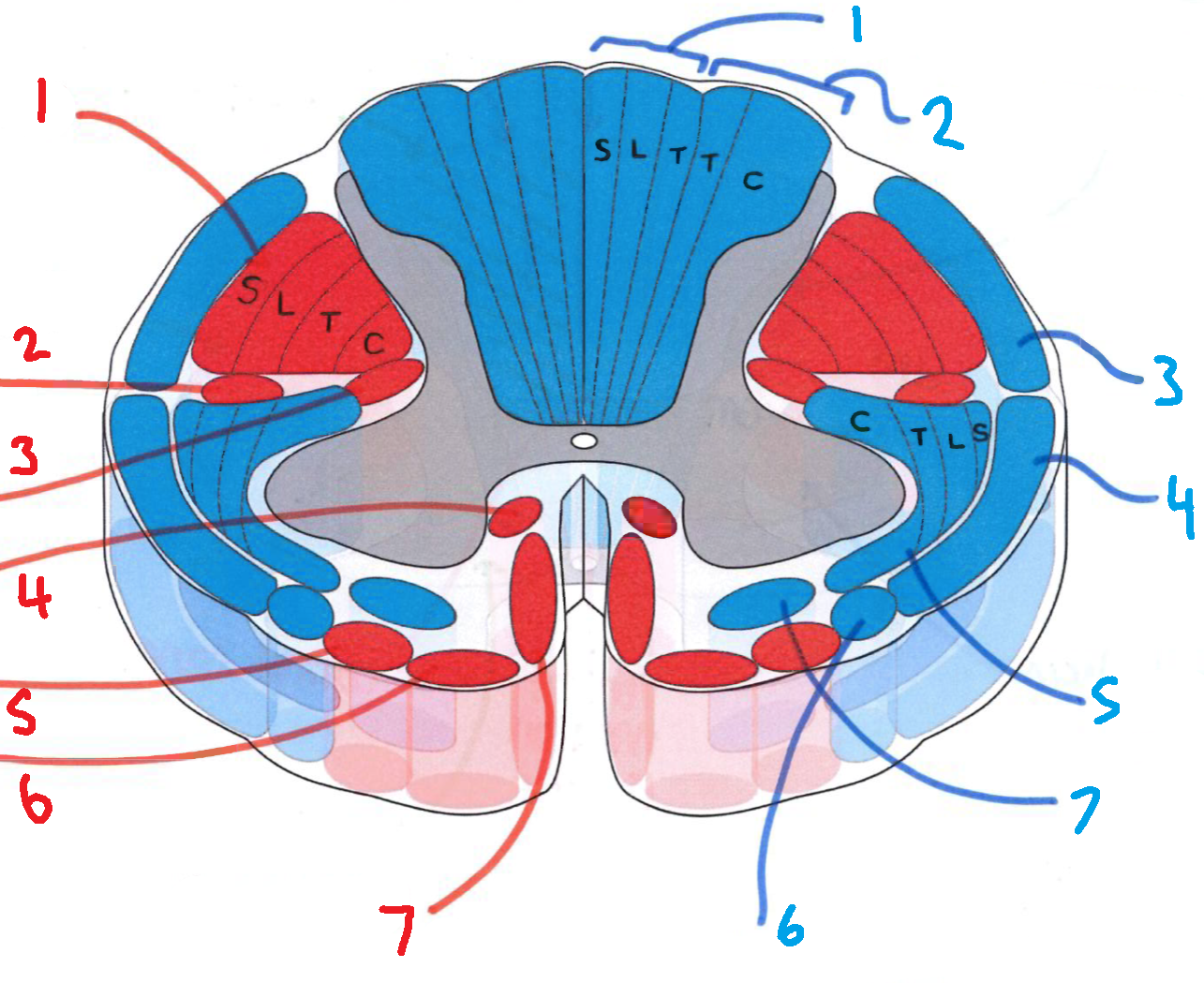
What does T stand for?
thoracic
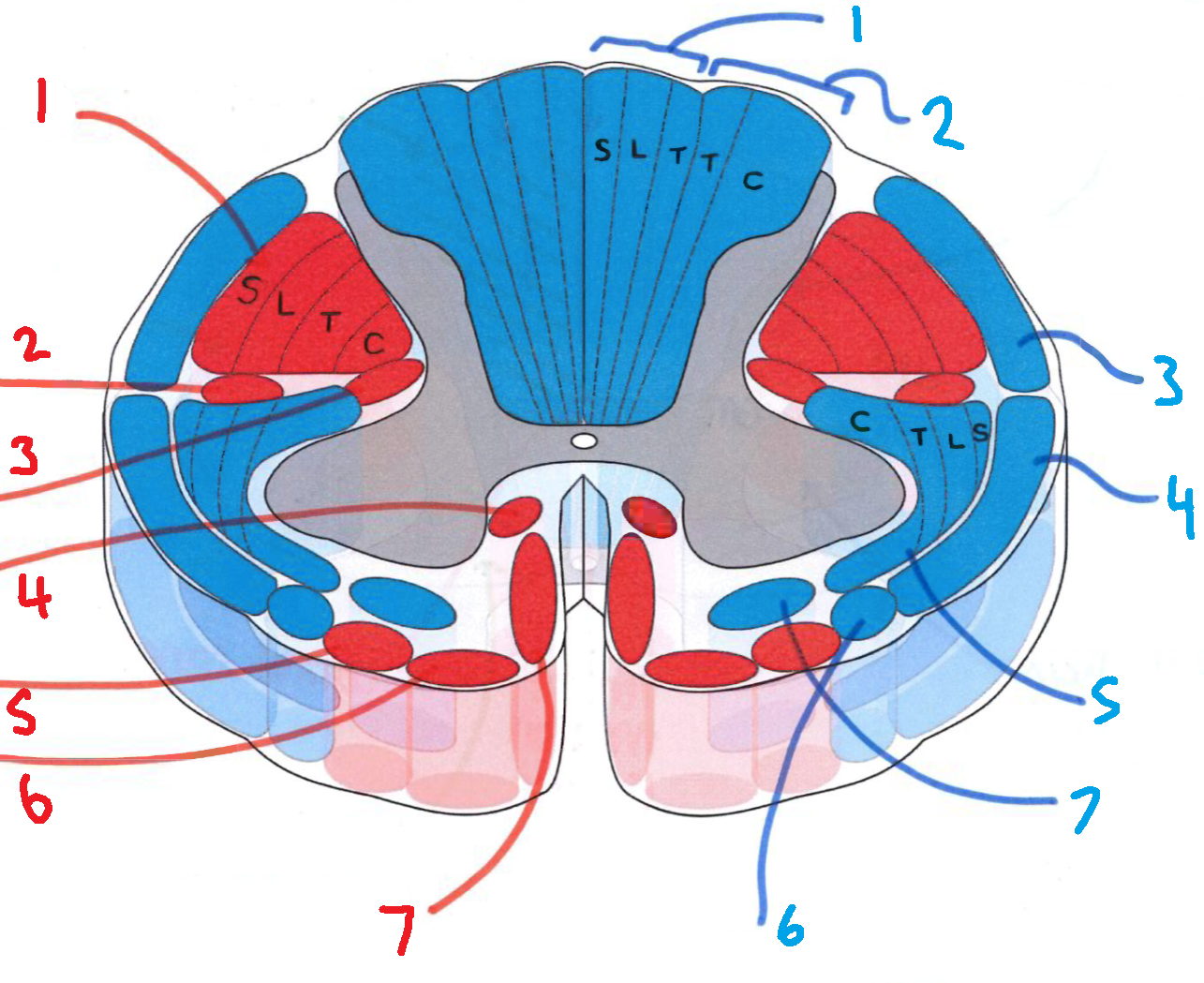
What does C stand for?
cervical
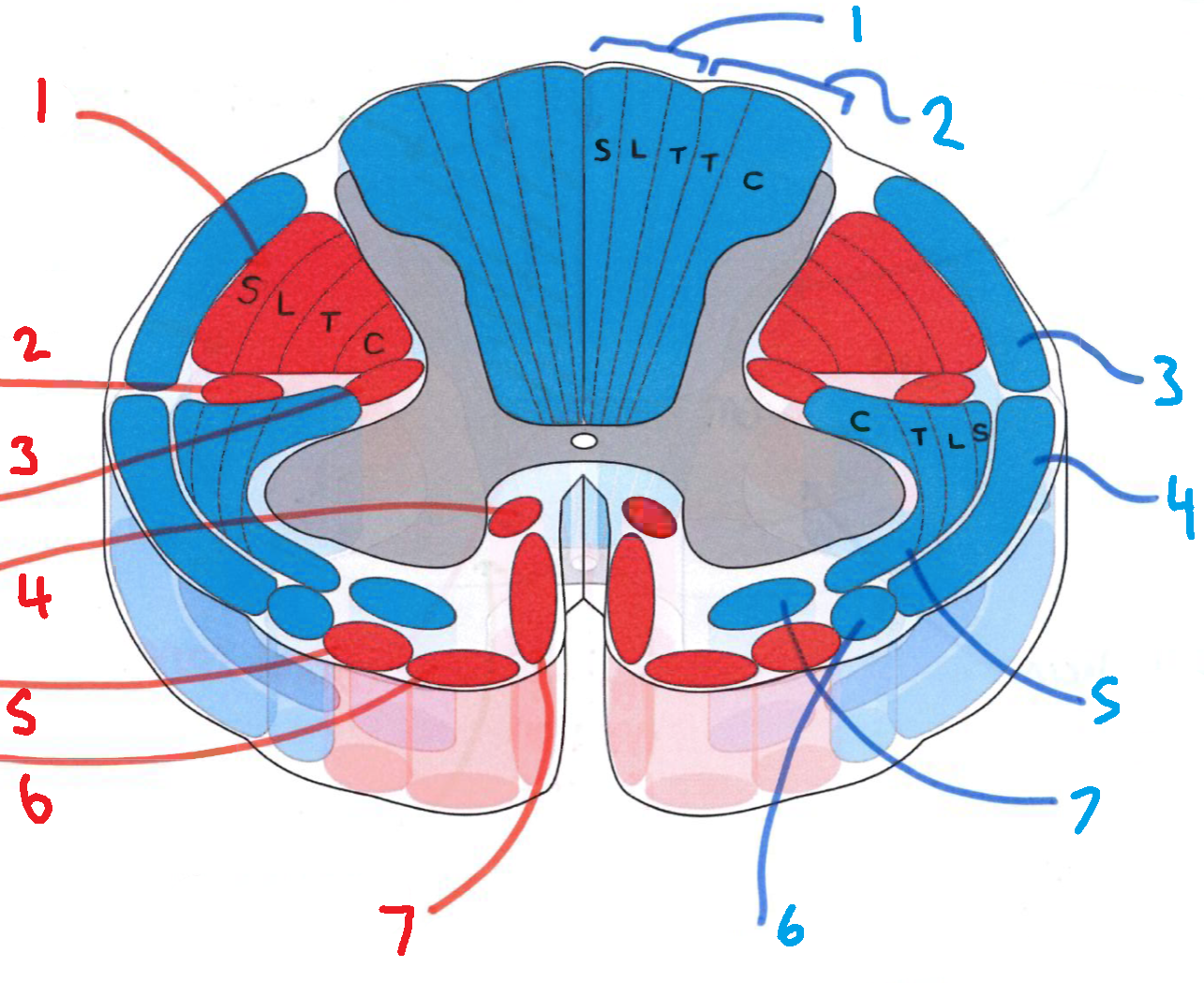
What is in red?
efferent descending pathways
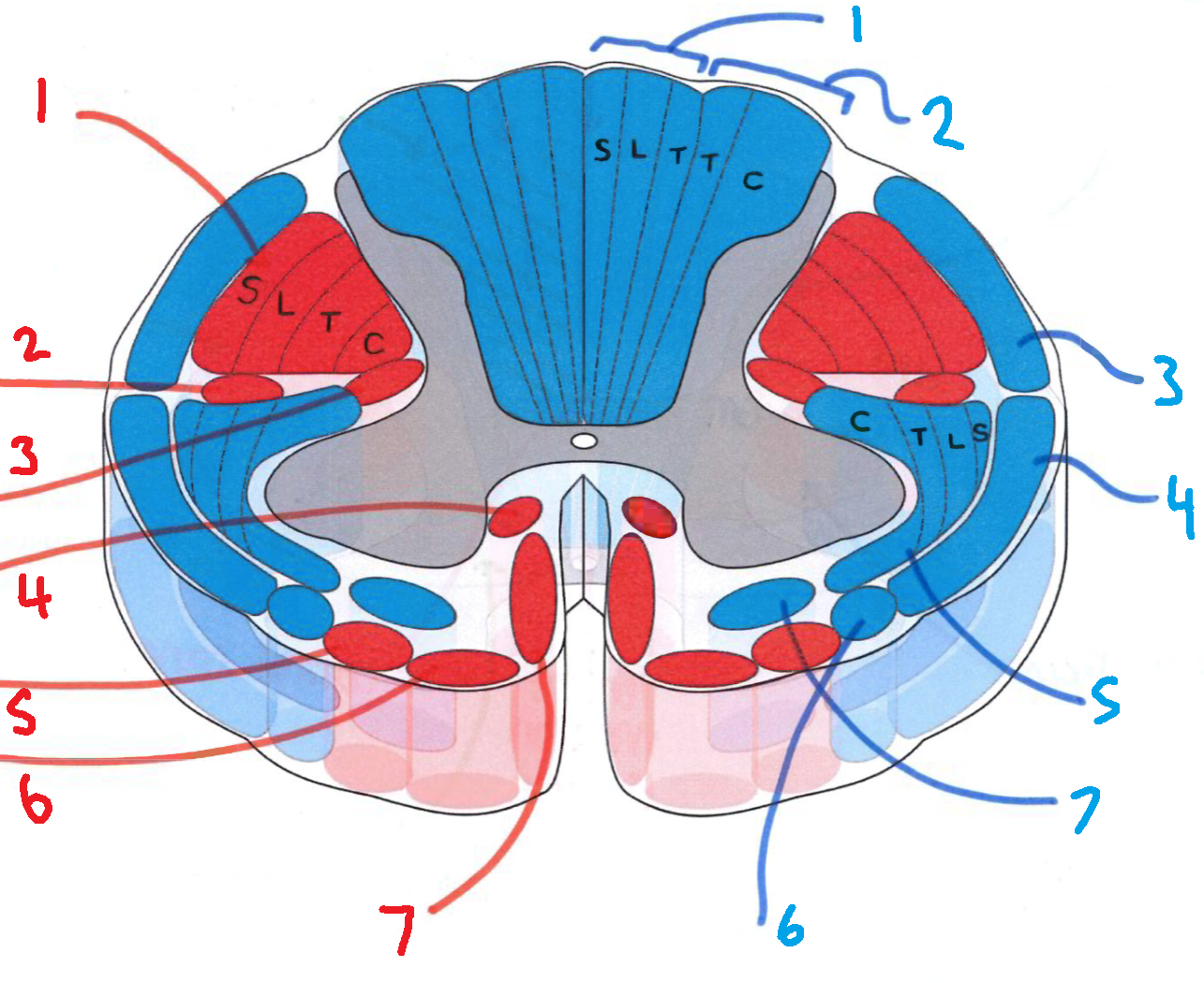
What is in blue?
afferent ascending pathways
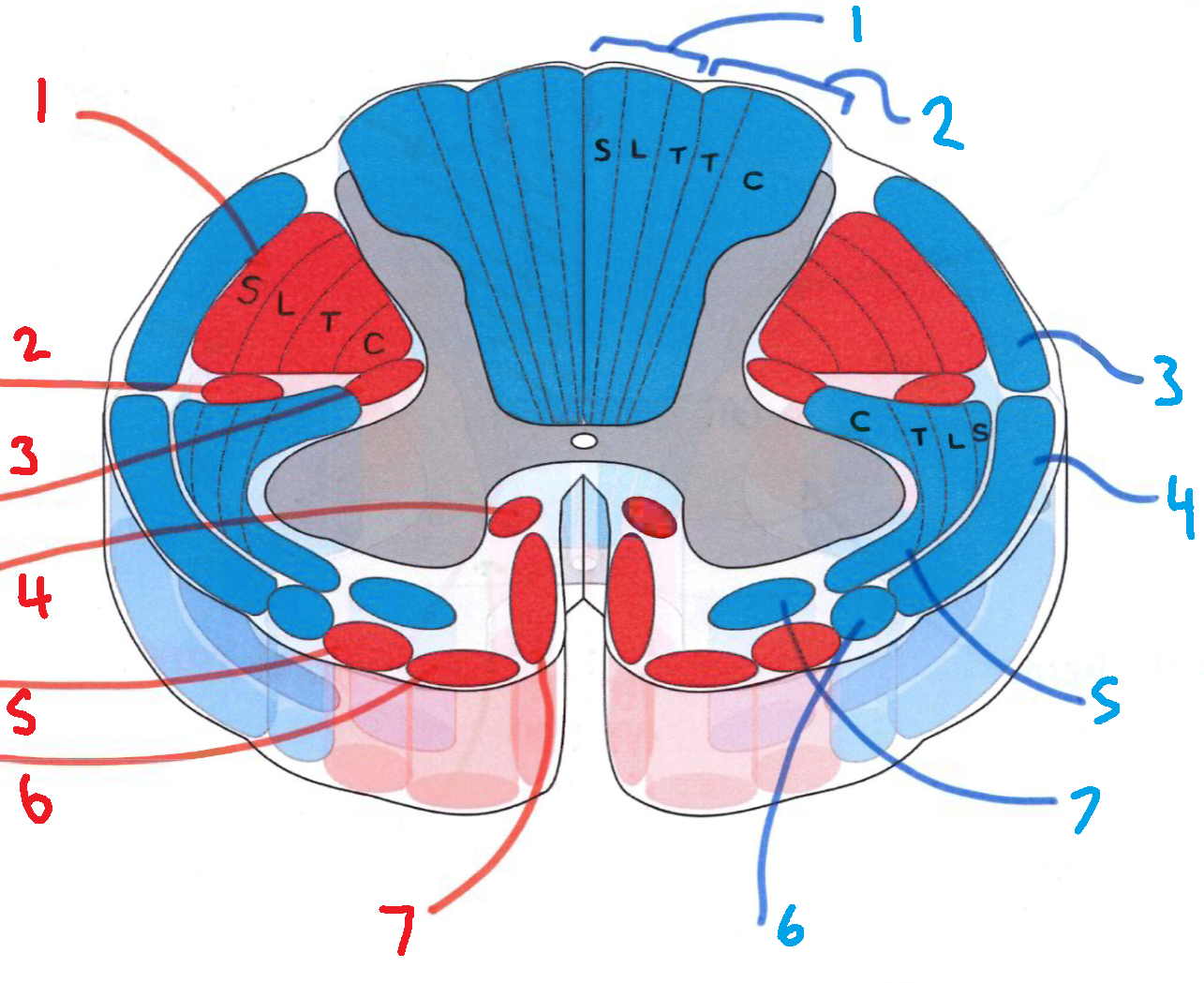
What is blue 1?
gracile fasciculus
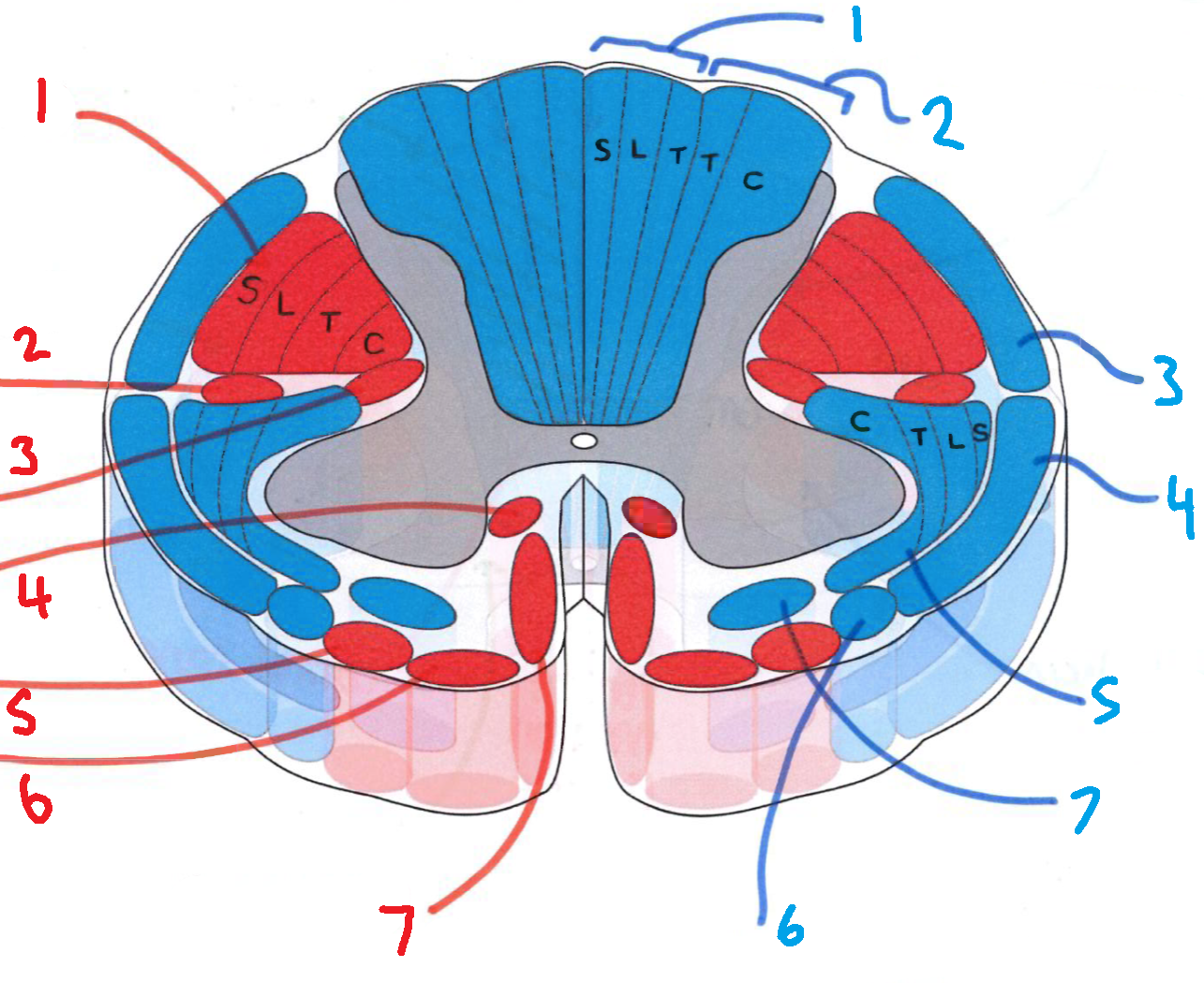
What is blue 2?
cuneate fasciculus
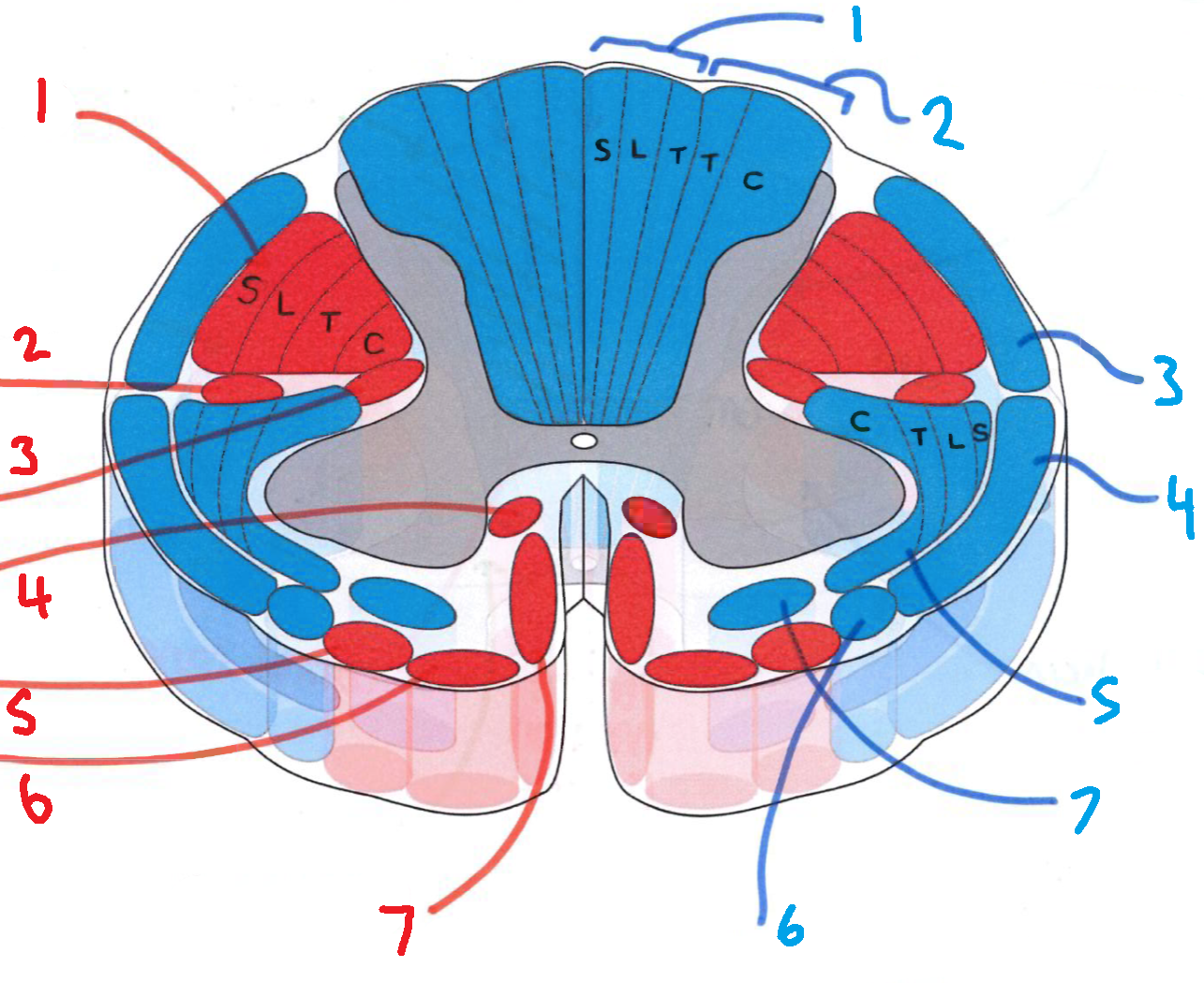
What is blue 3?
dorsal spinocerebellar tract
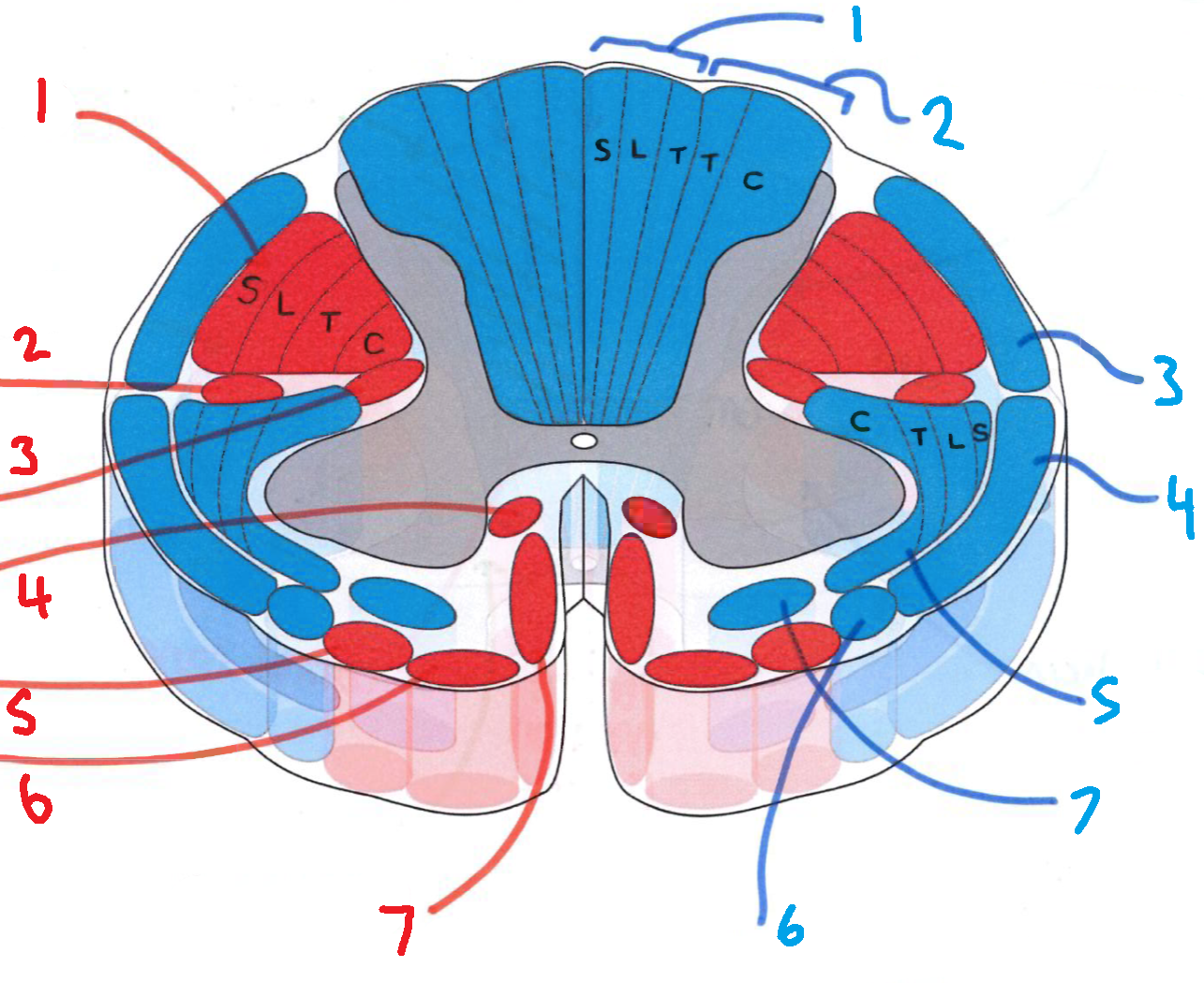
What is blue 4?
ventral spinocerebellar tract
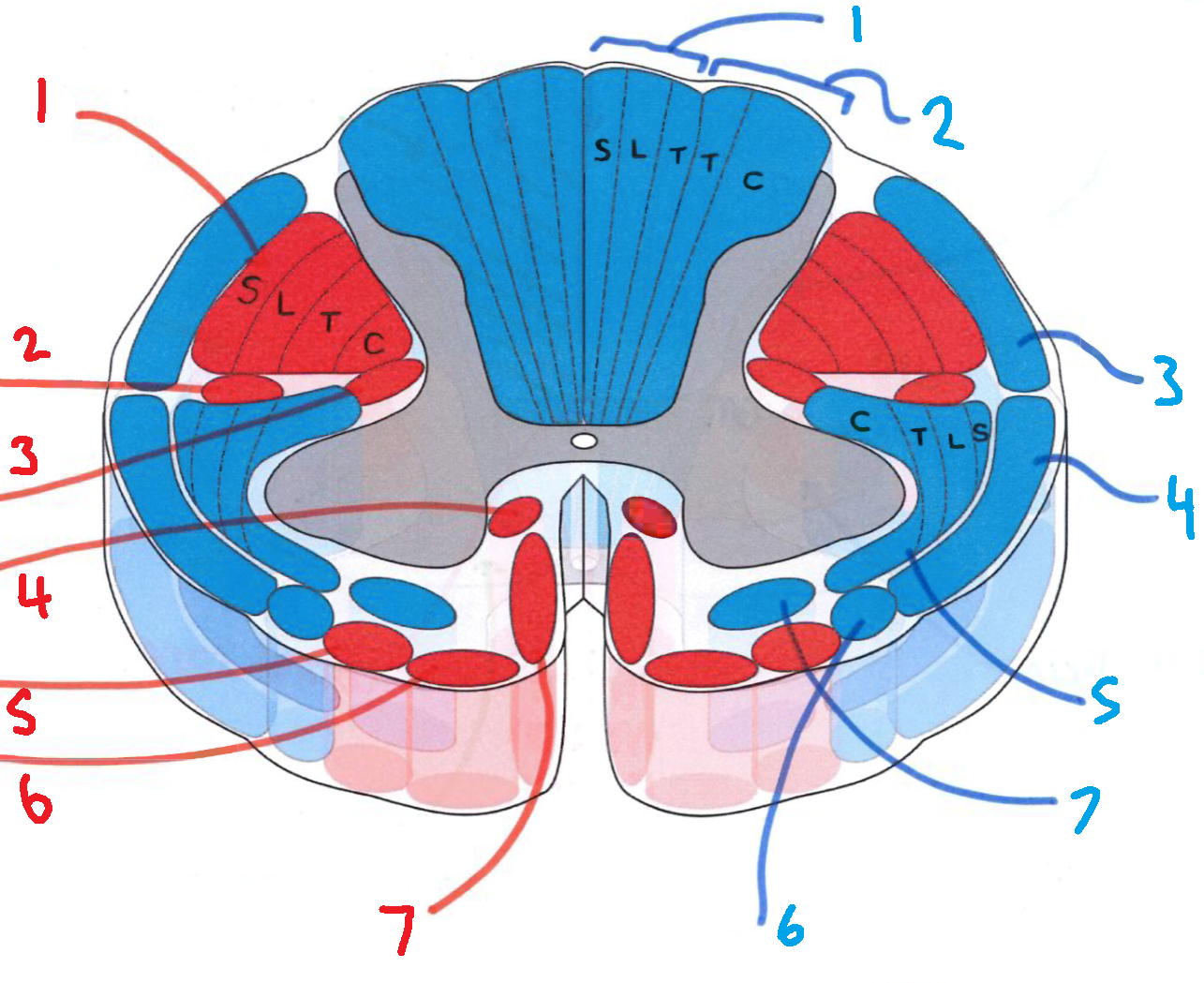
What is blue 5?
lateral spinothalamic tract
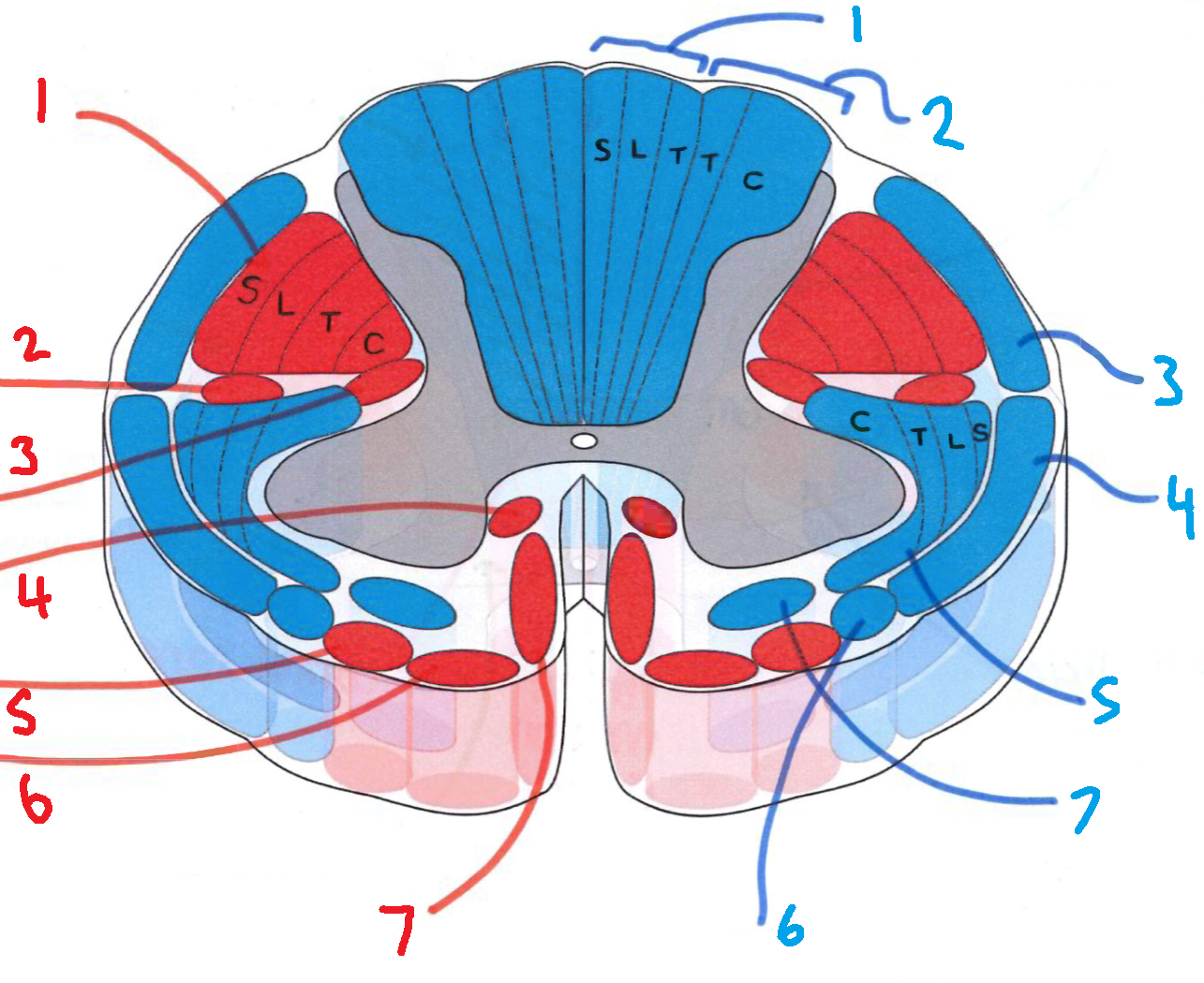
What is blue 6?
spino-olivary fibres
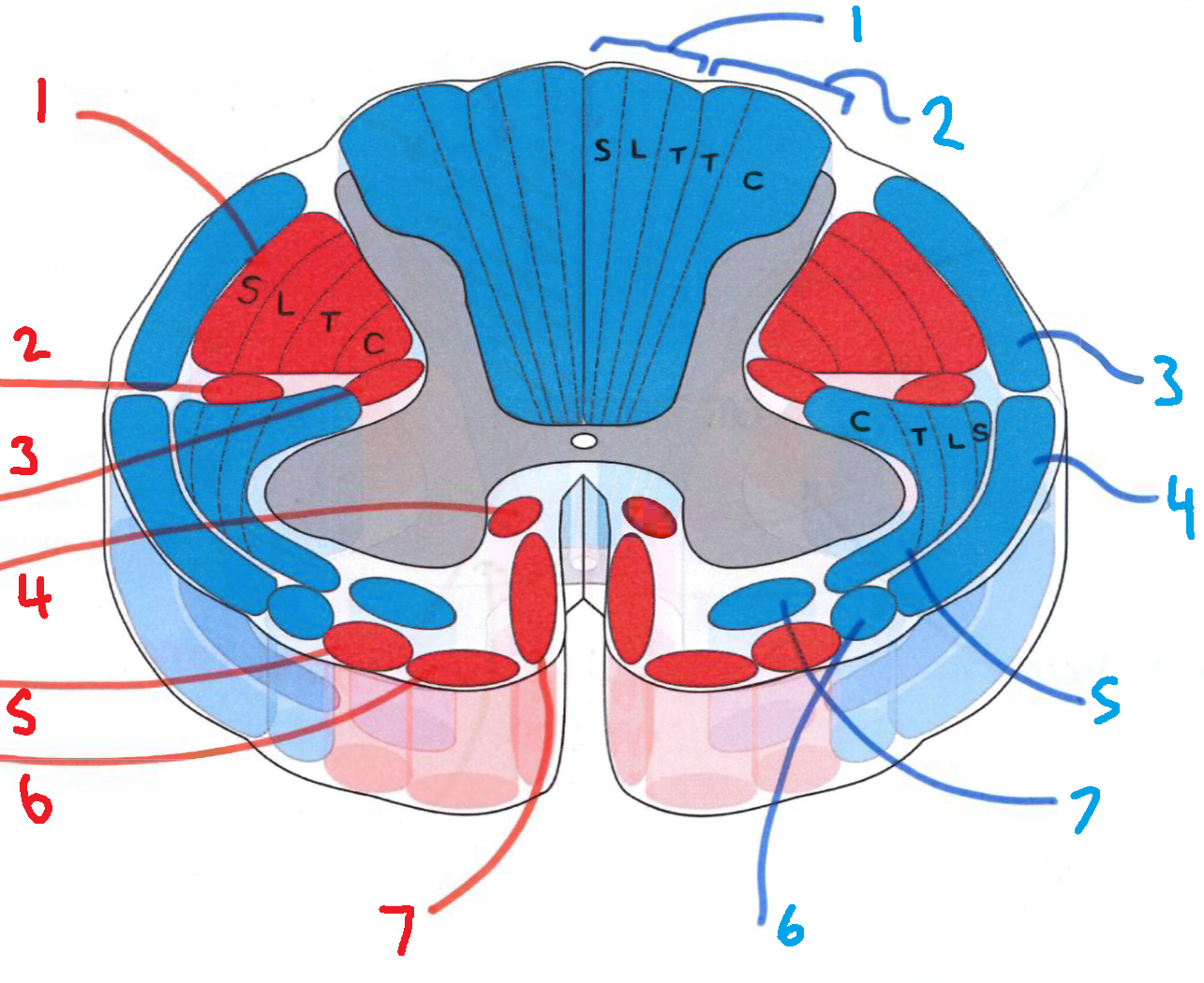
What is blue 7?
anterior spinothalamic tract
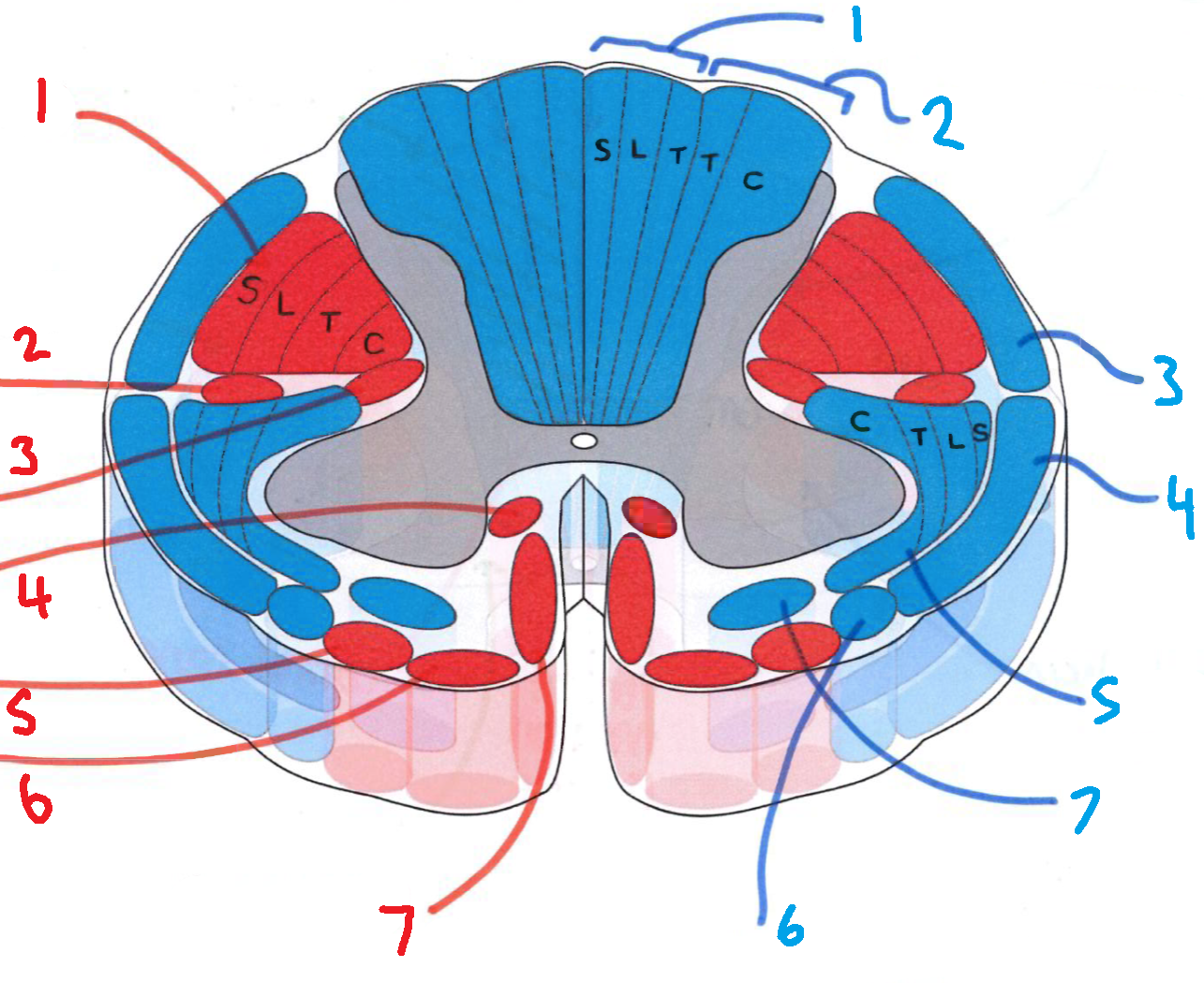
What is red 1?
lateral corticospinal tract
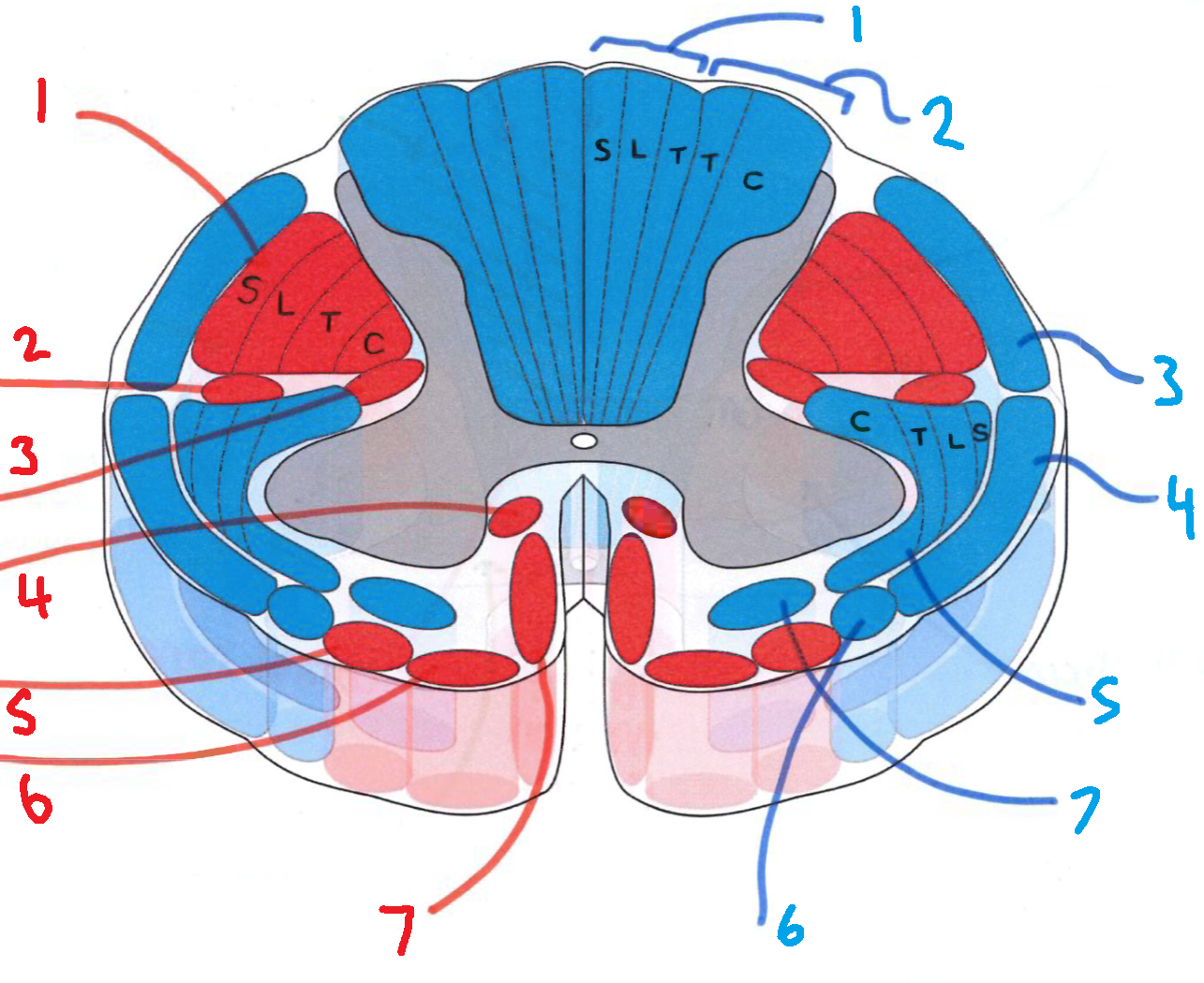
What is red 2?
rubrospinal tract
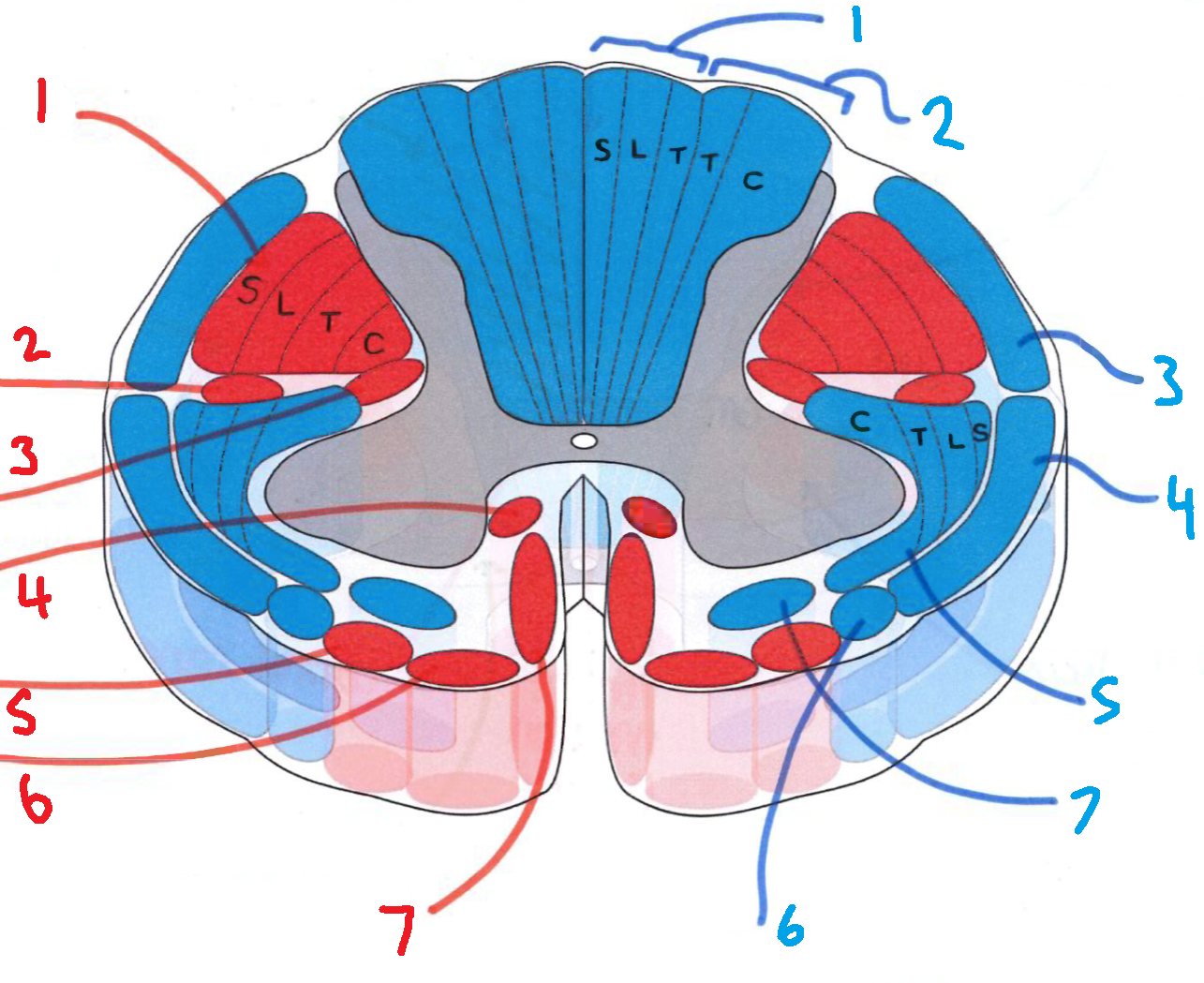
What is red 3?
lateral reticulospinal tract
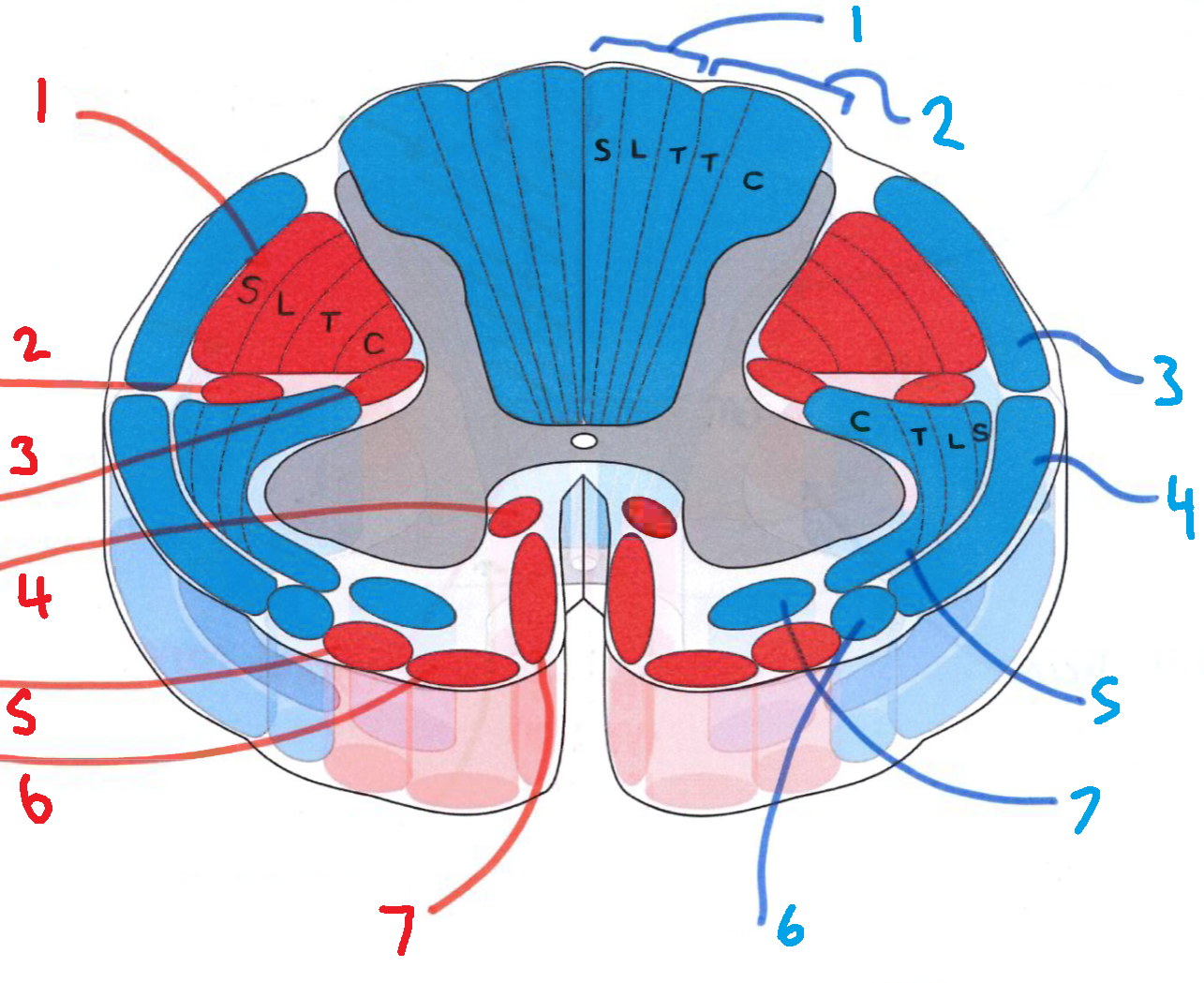
What is red 4?
anterior reticulospinal tract
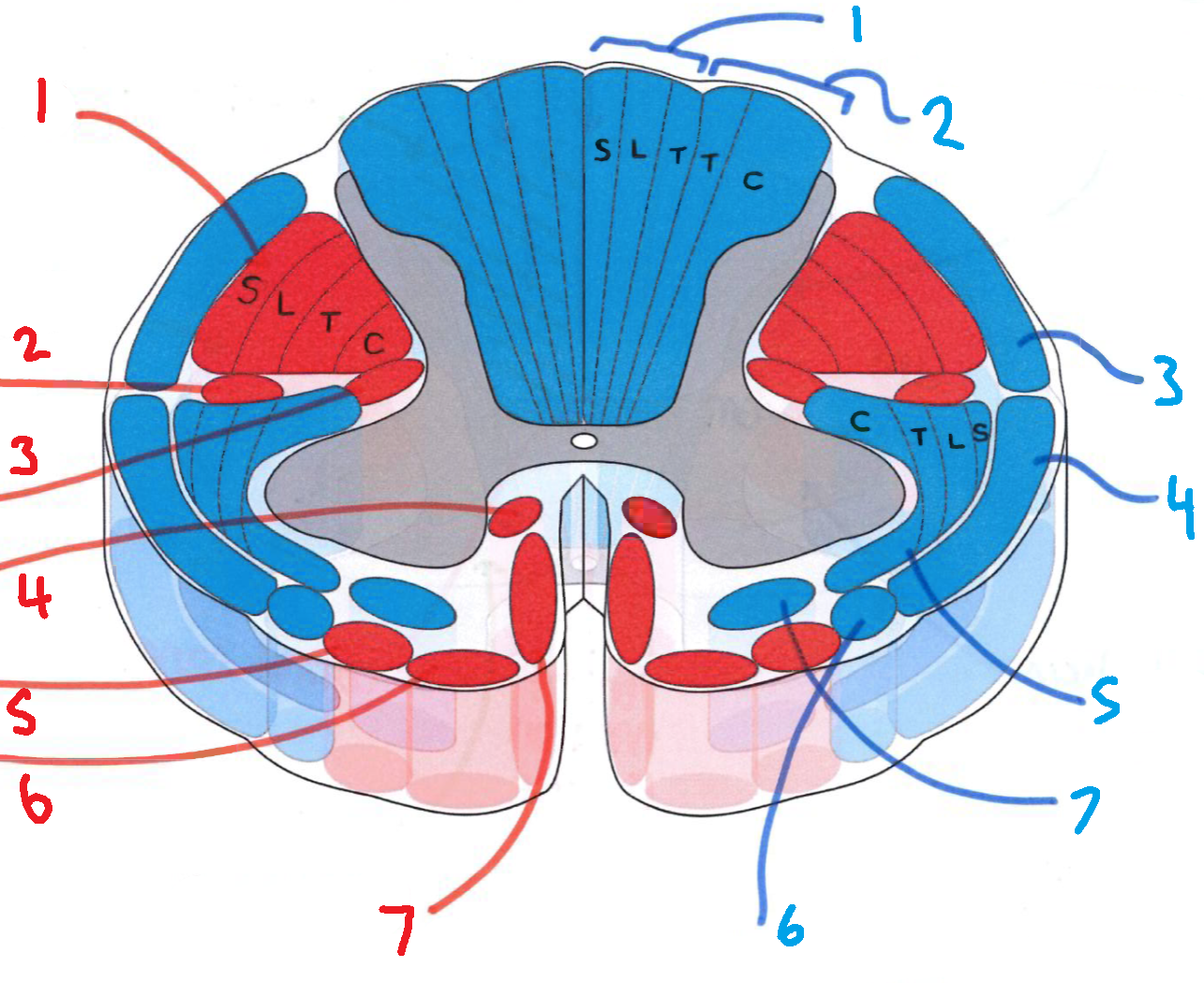
What is red 5?
olivospinal tract
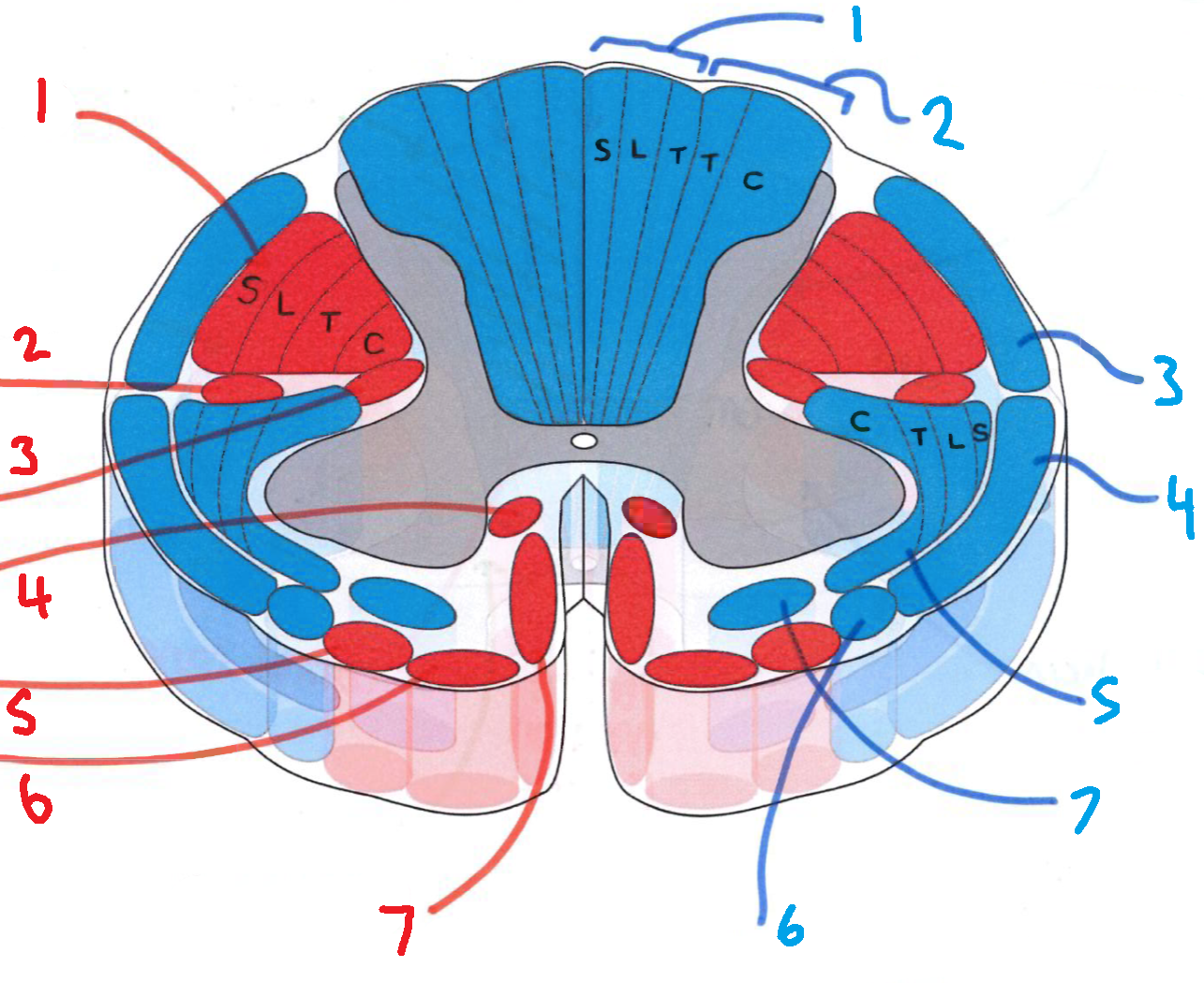
What is red 6?
vestibulospinal tract
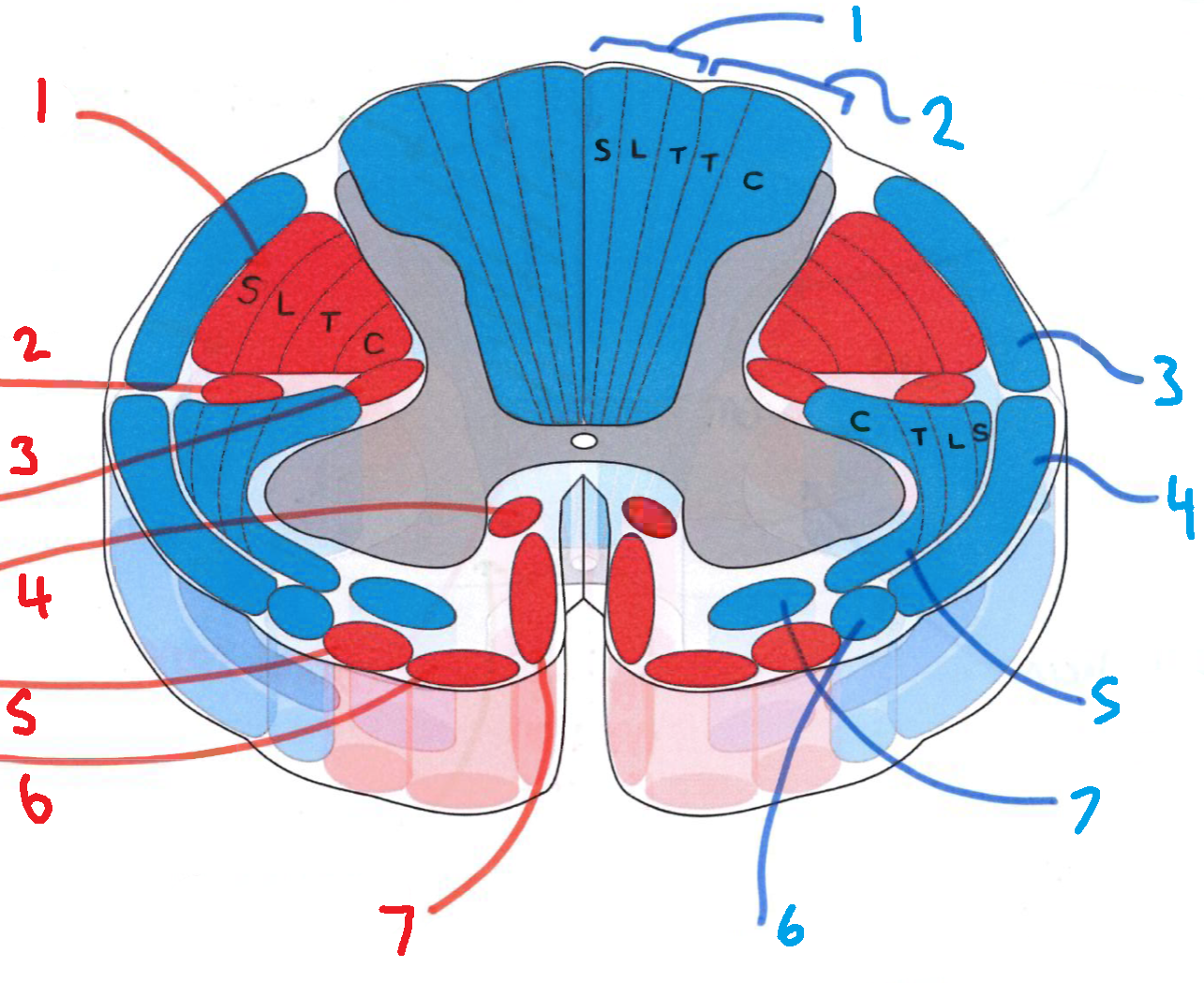
What is red 7?
anterior corticospinal tract
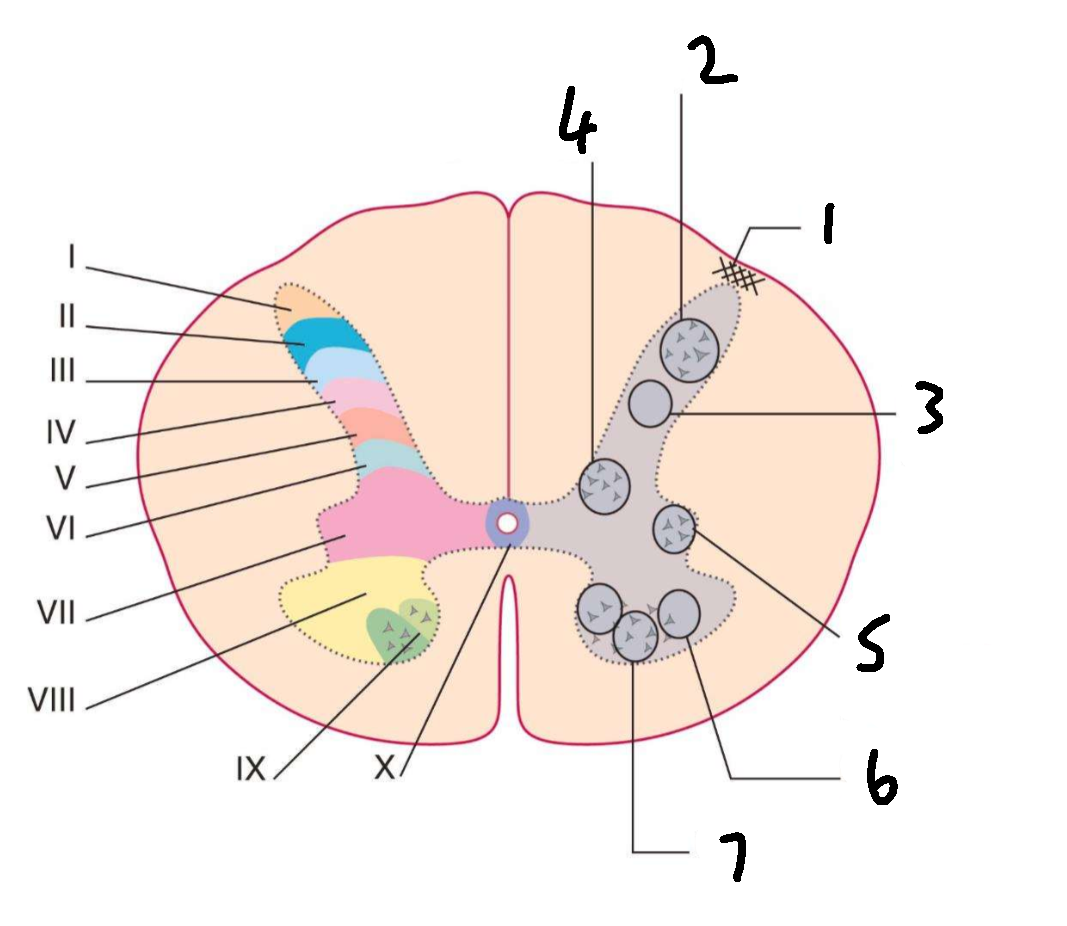
What is 1?
lissauers tract
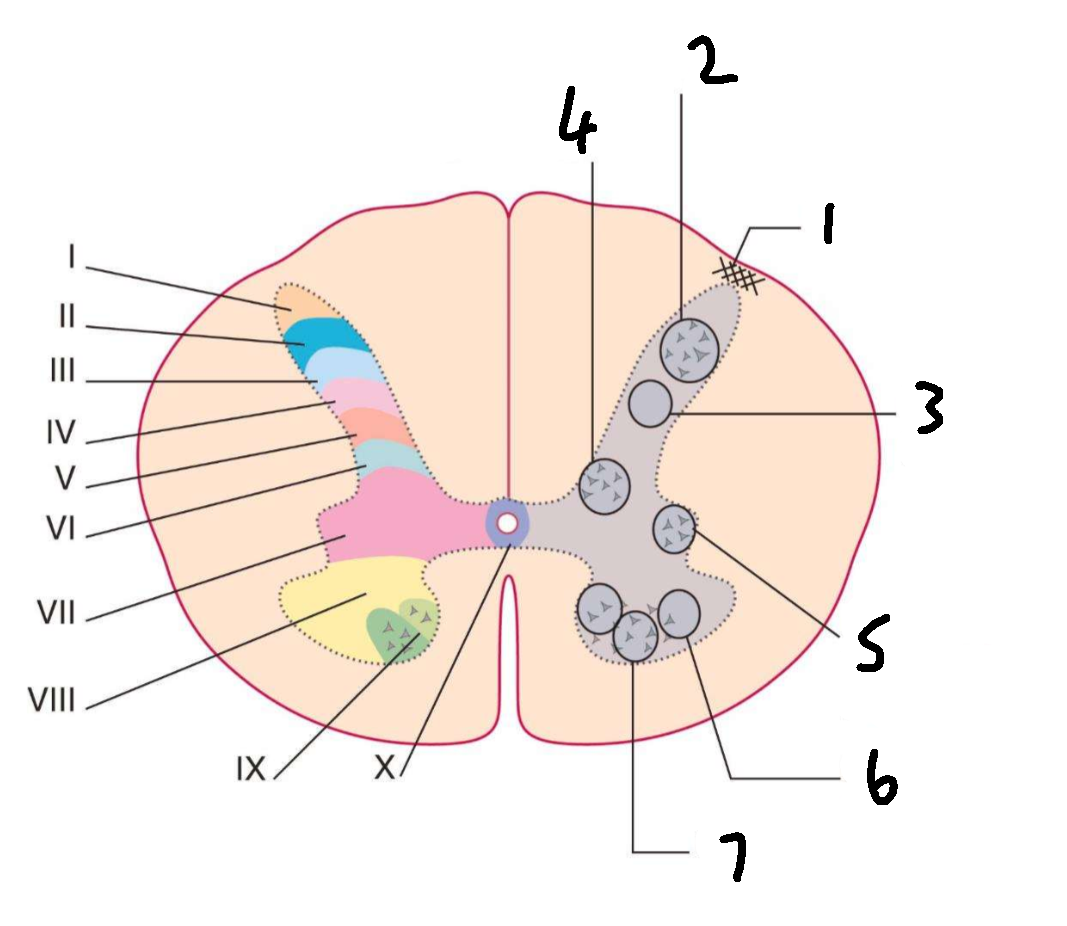
What is 2?
substantia gelatinosa
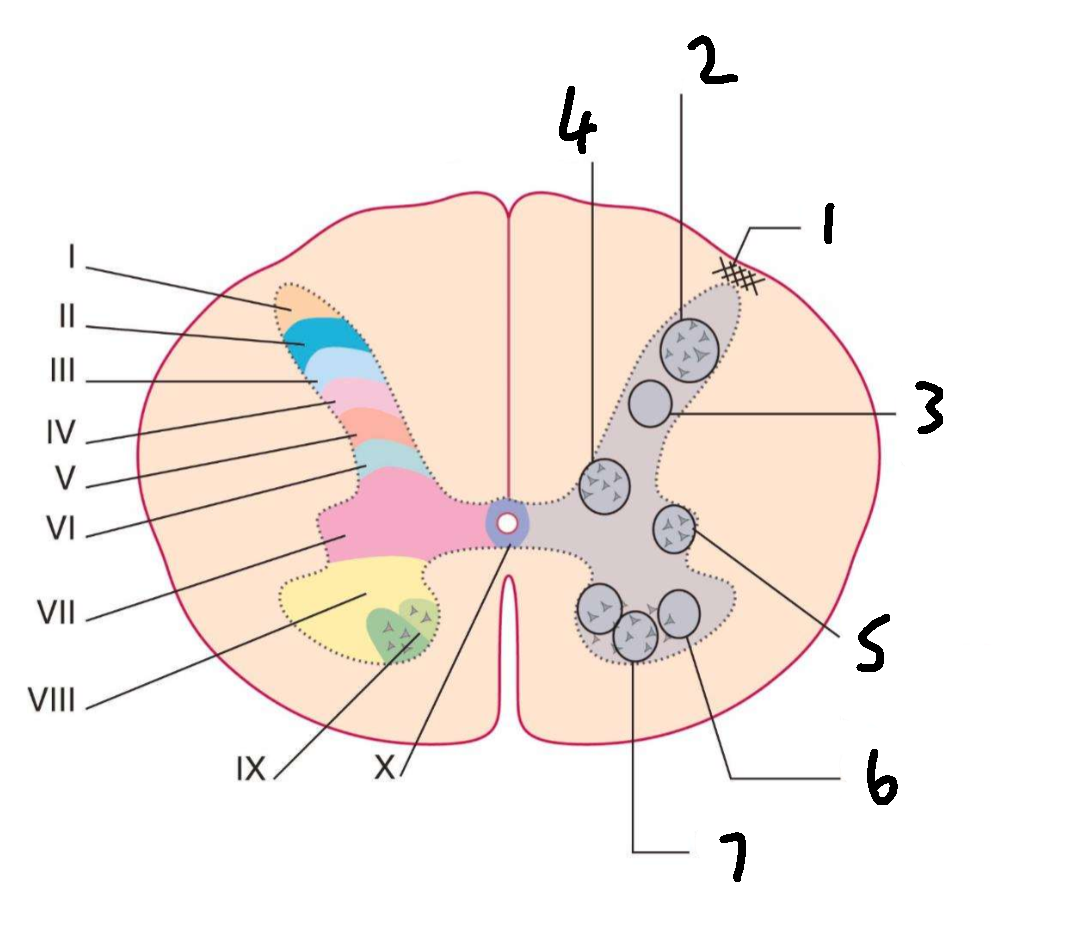
What is 3?
nucleus proprius
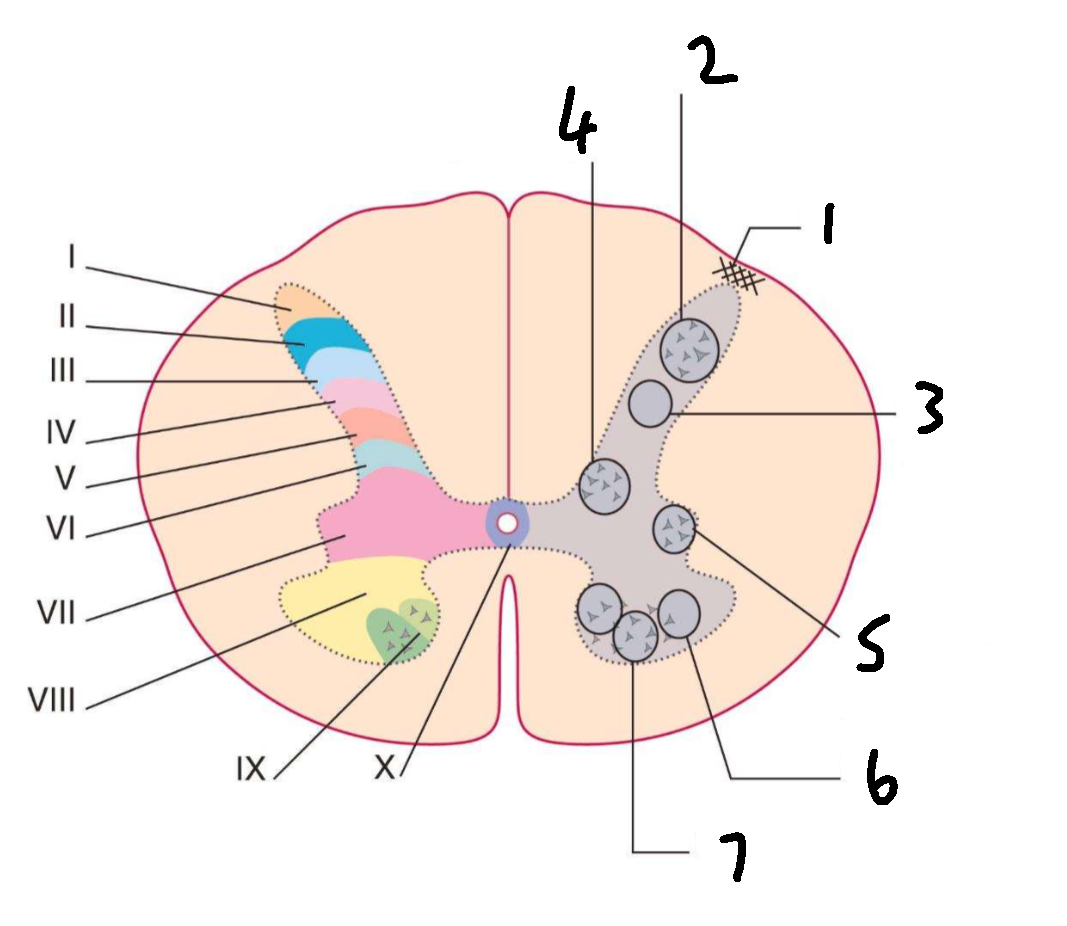
What is 4?
clarks column
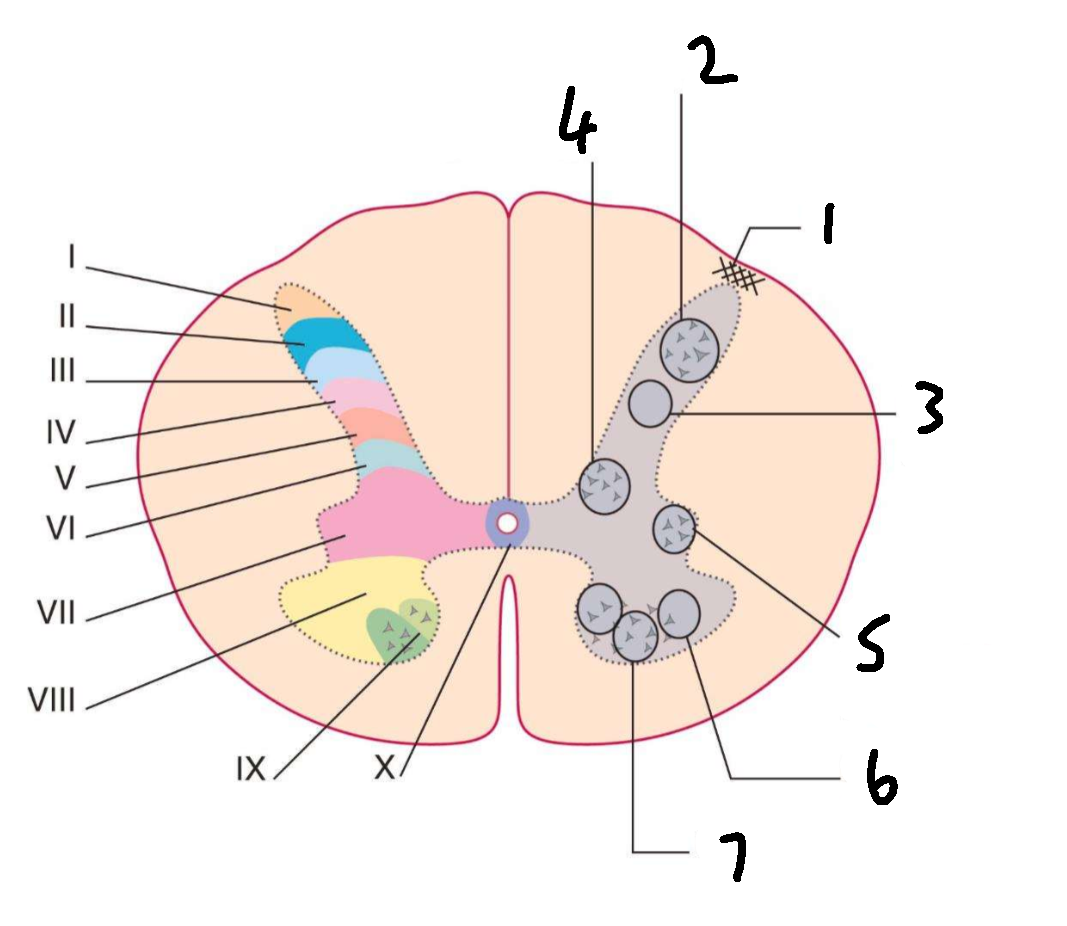
What is 5?
interomedial lateral nucleus
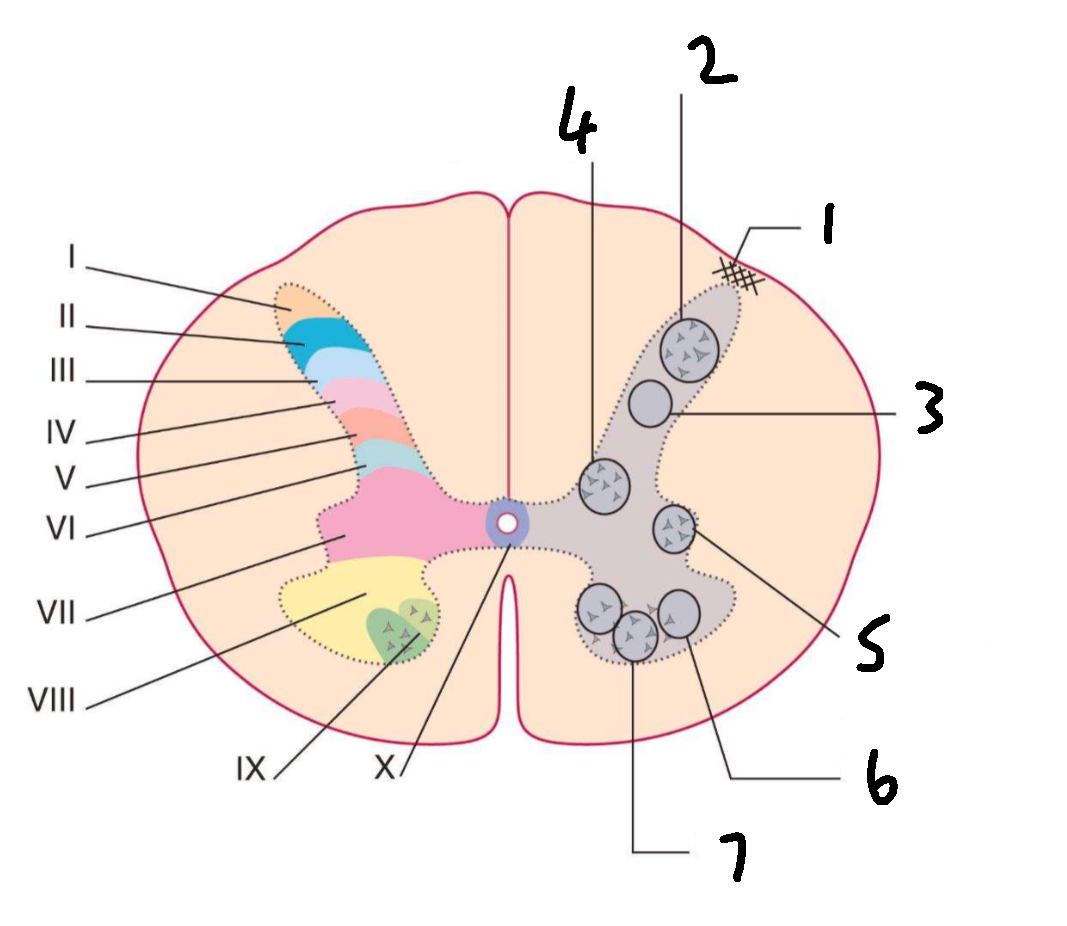
What is 6?
lateral motor nuclei
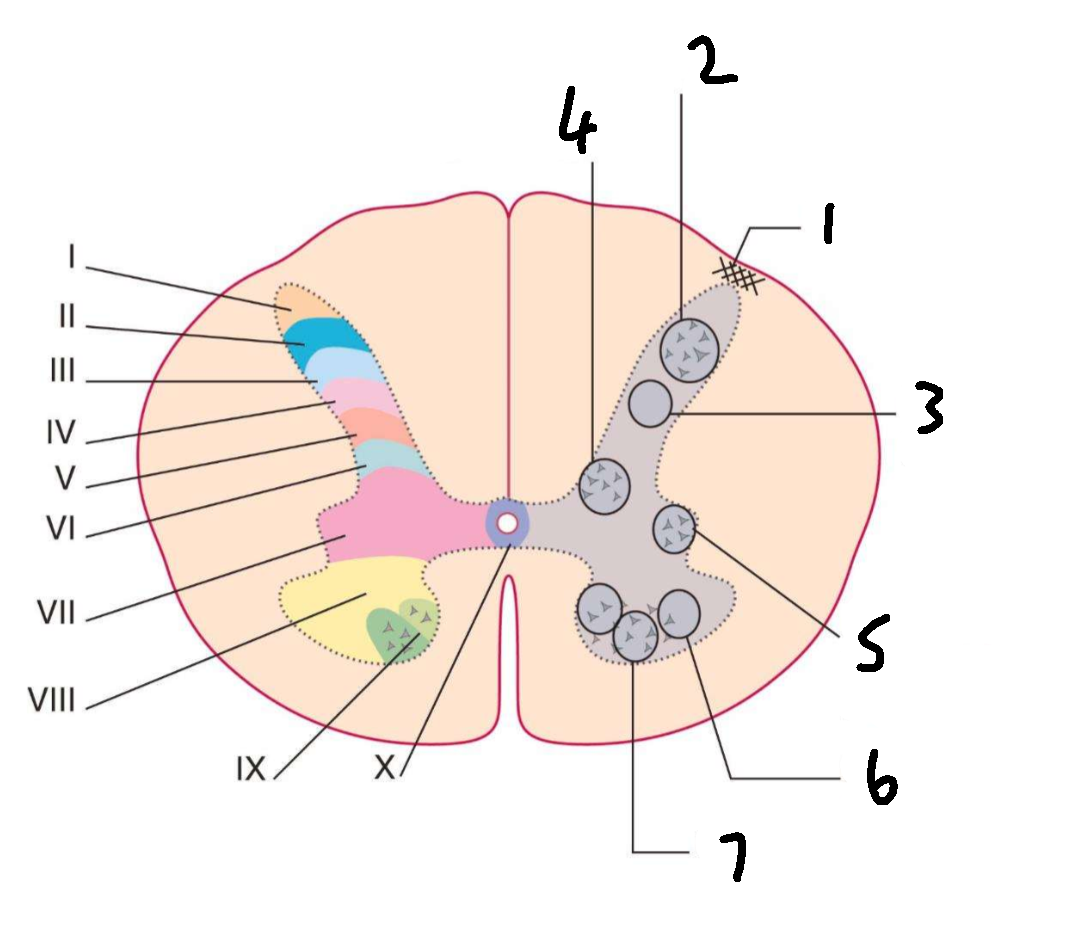
What is 7?
medial motor nuclei
What are the types of spinal reflexes?
monosynaptic/stretch and polysynaptic/flexor
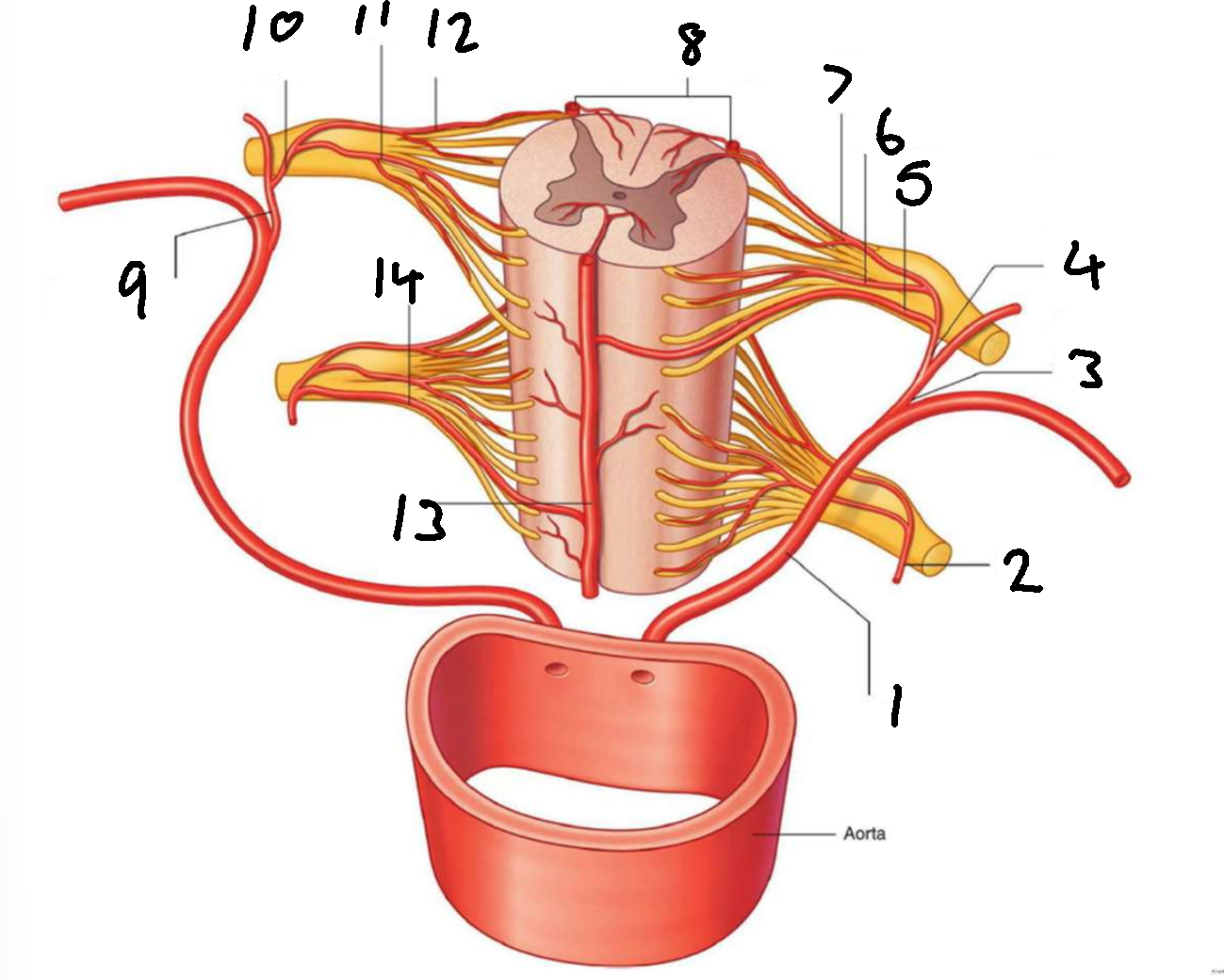
What is 1?
left posterior intercostal artery
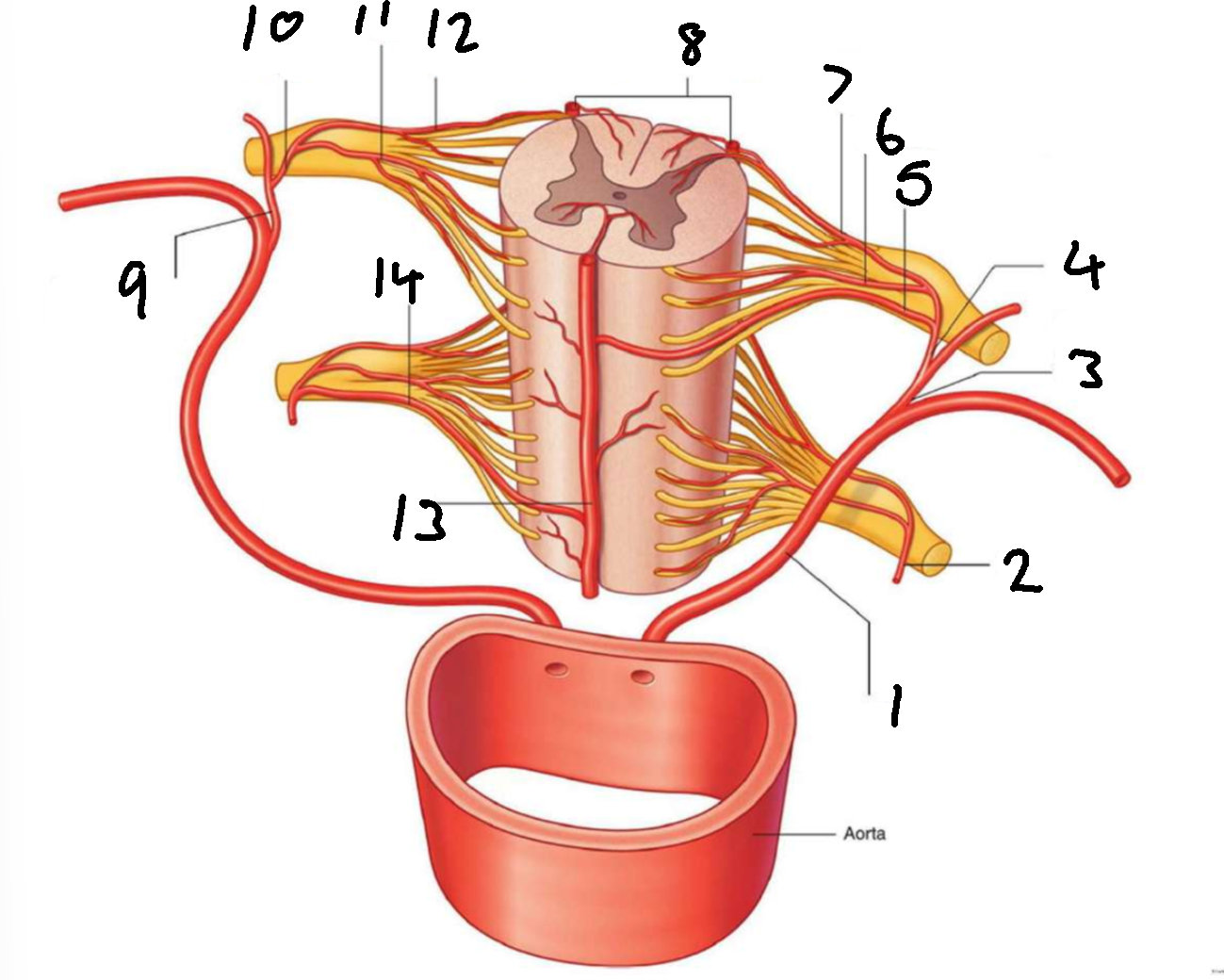
What is 2?
segmental spinal artery
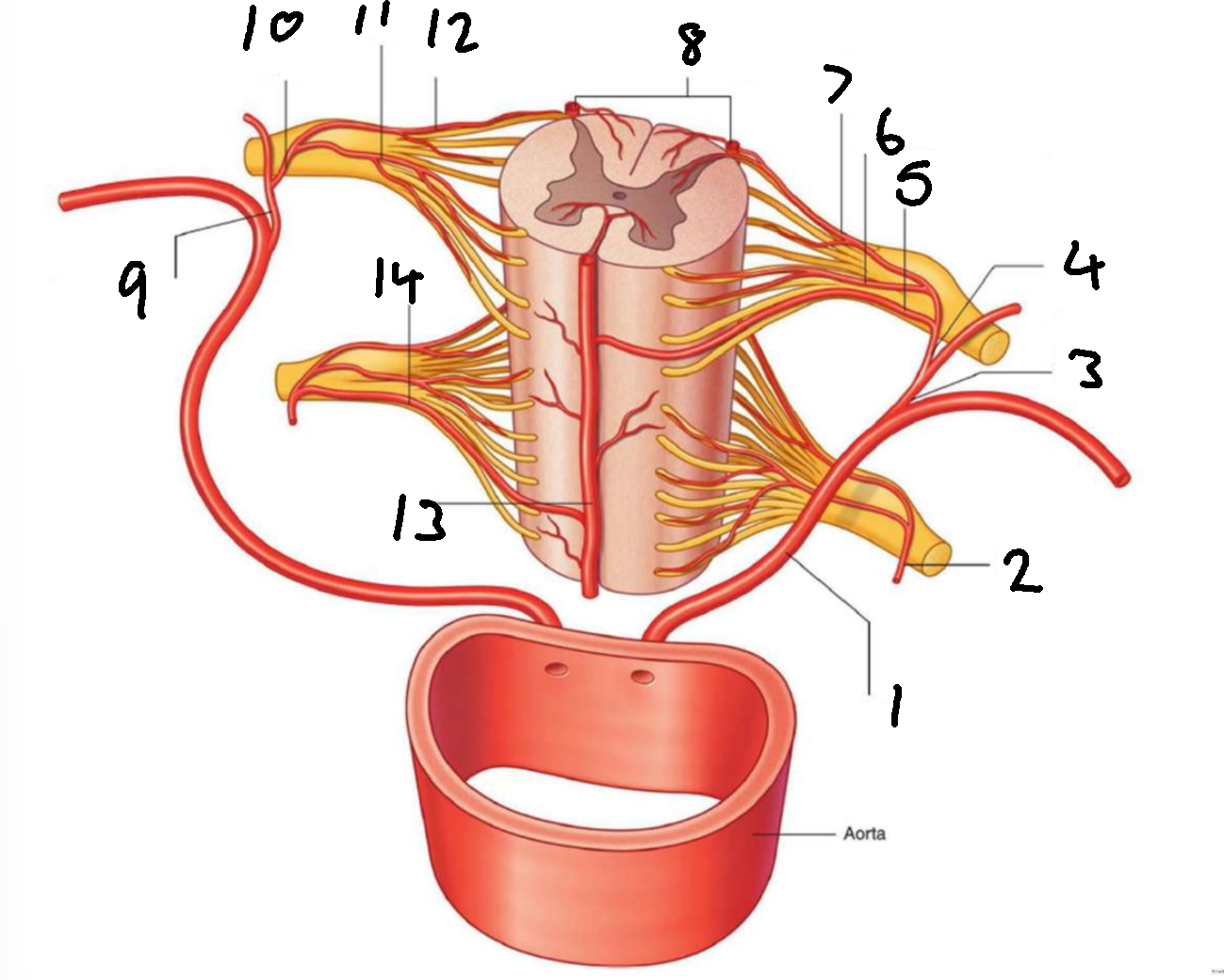
What is 3?
posterior branch of left posterior intercostal artery
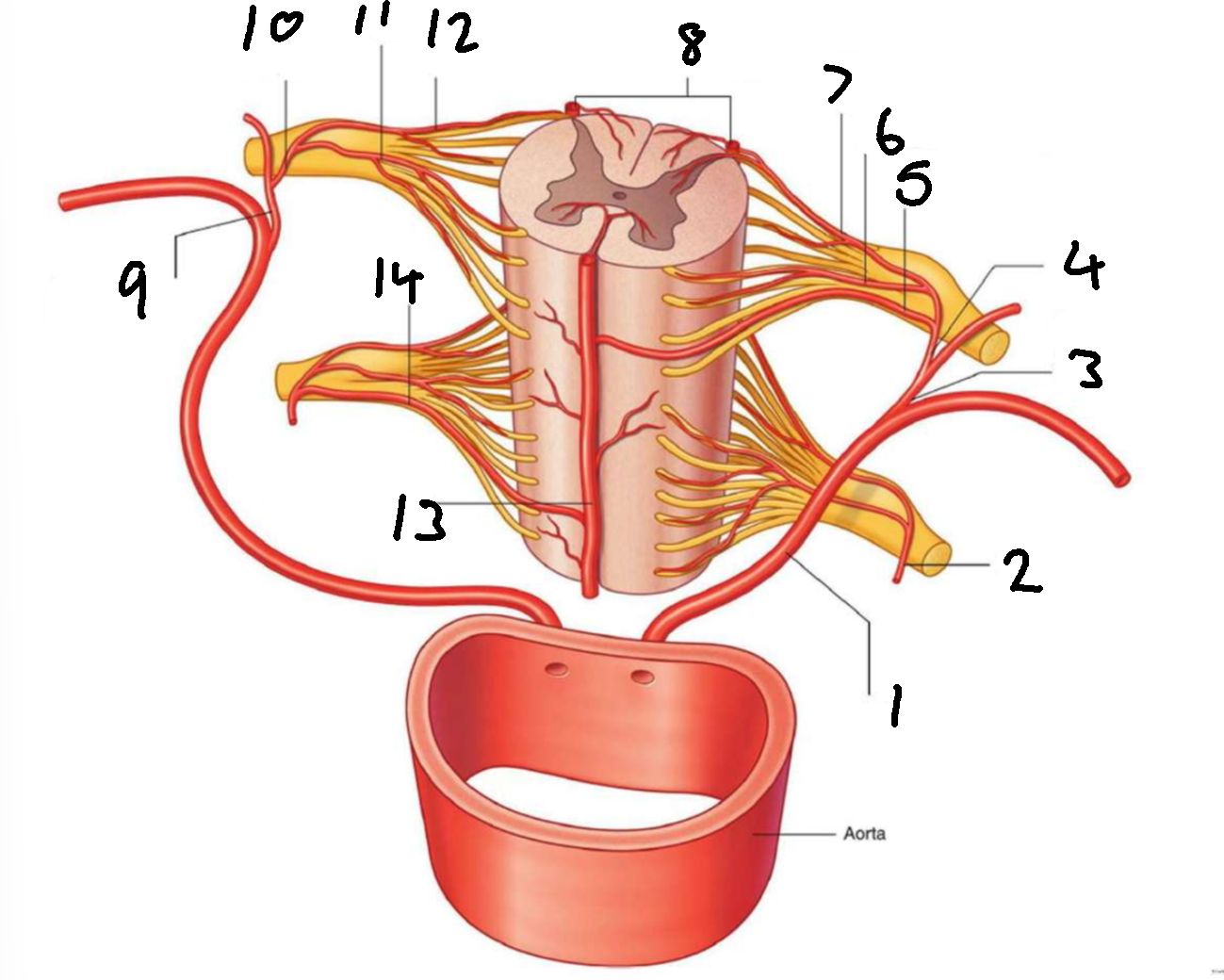
What is 4?
segmental spinal artery
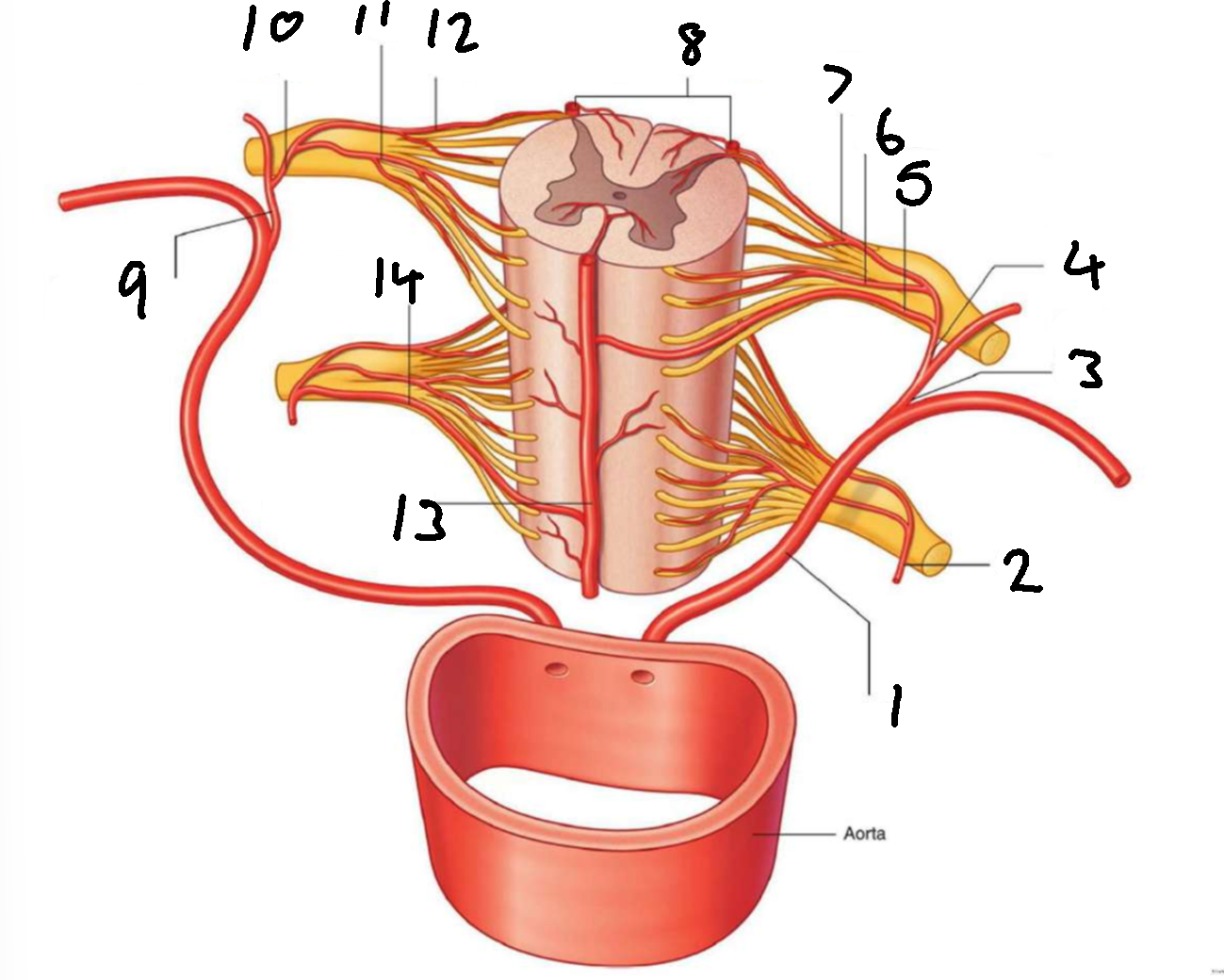
What is 5?
segmental medullary artery
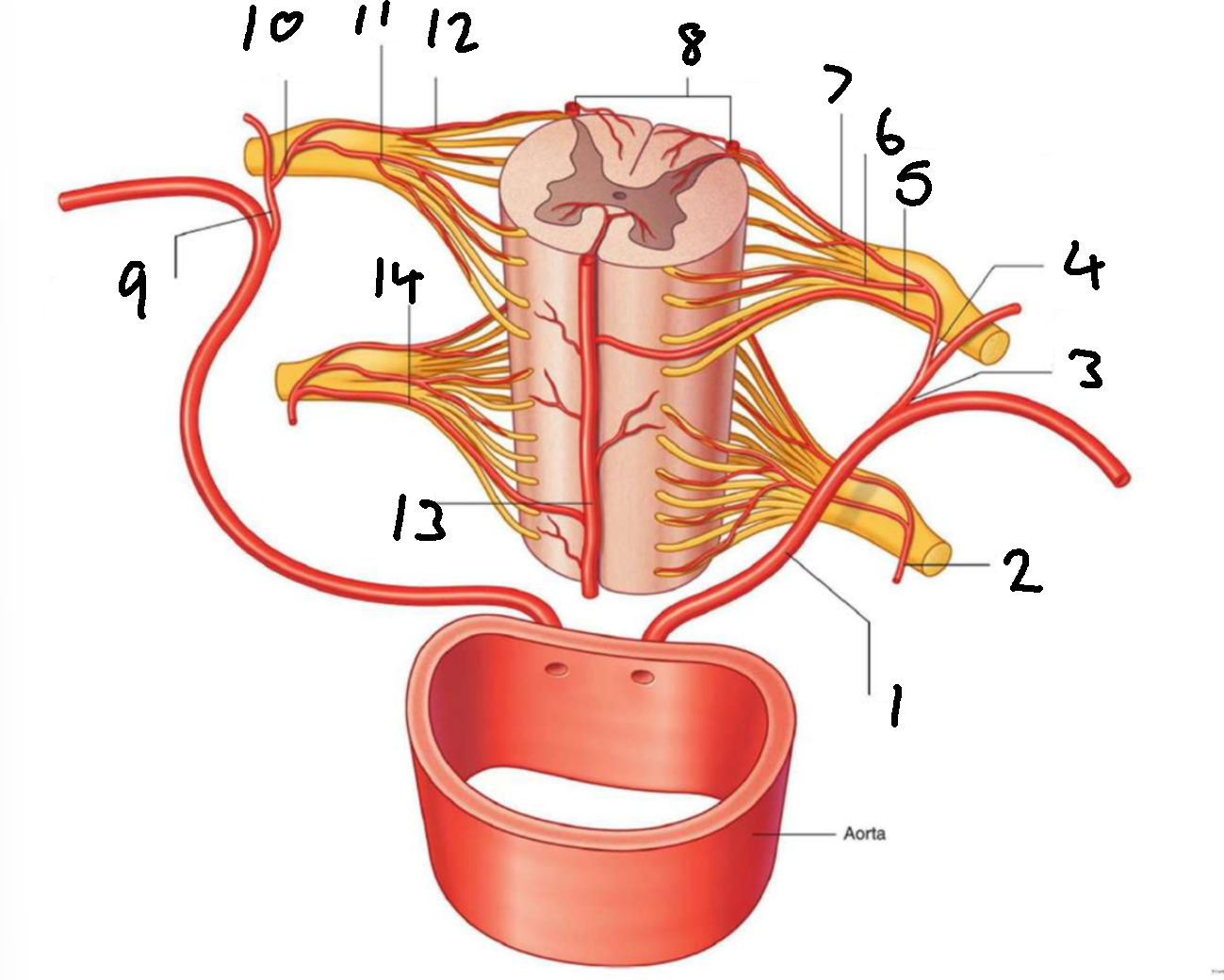
What is 6?
anterior radicular artery
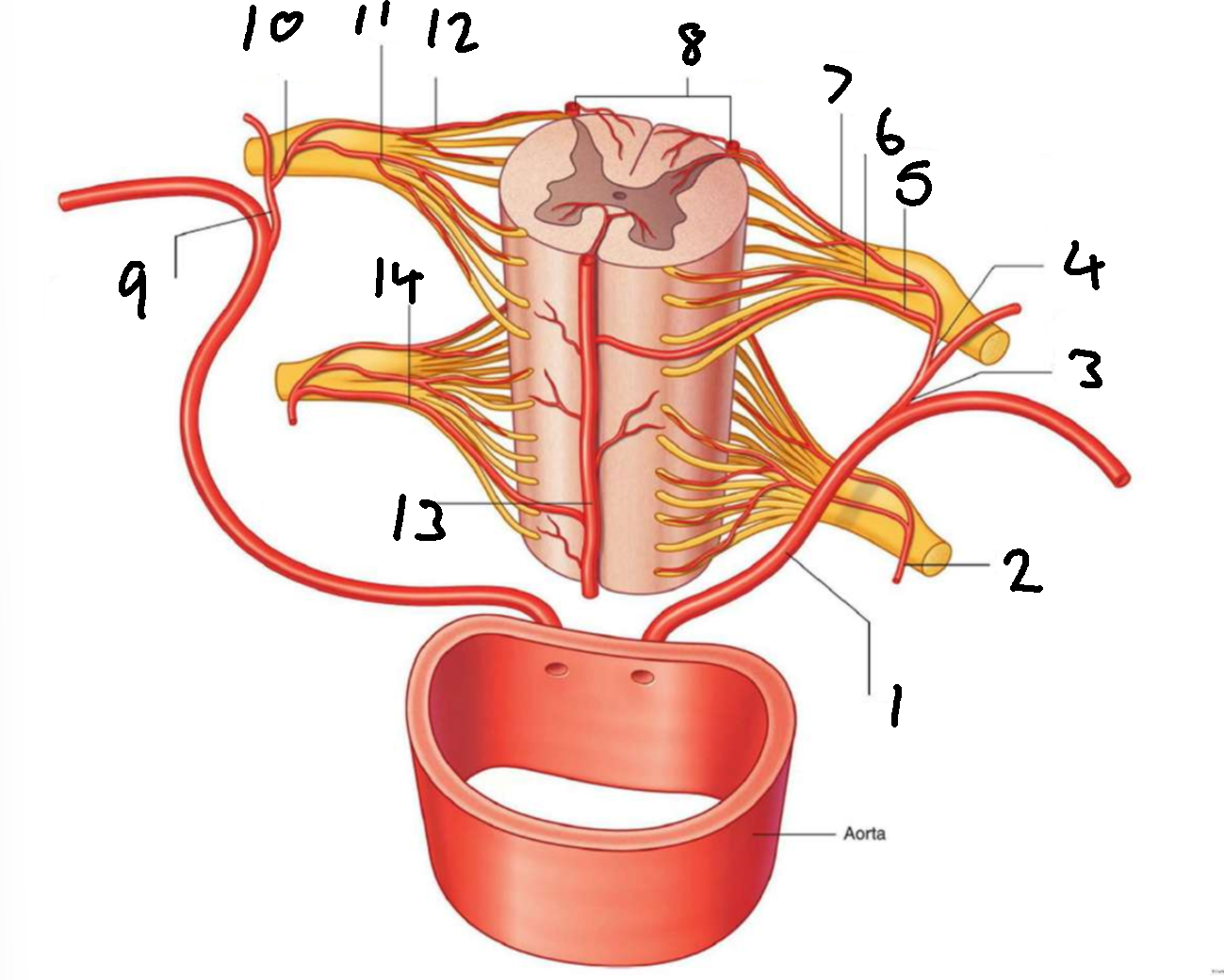
What is 7?
posterior radicular artery
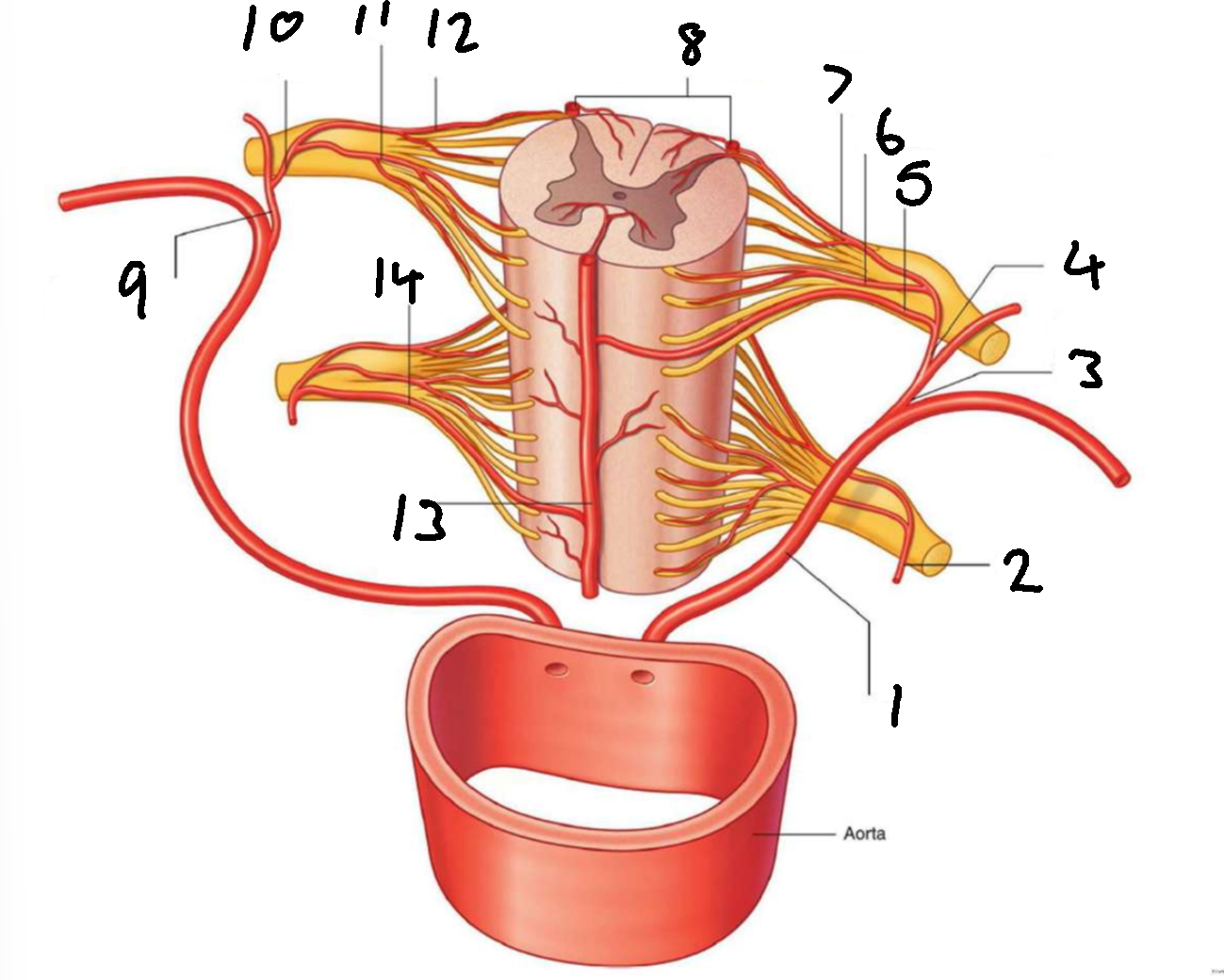
What is 8?
posterior spinal arteries
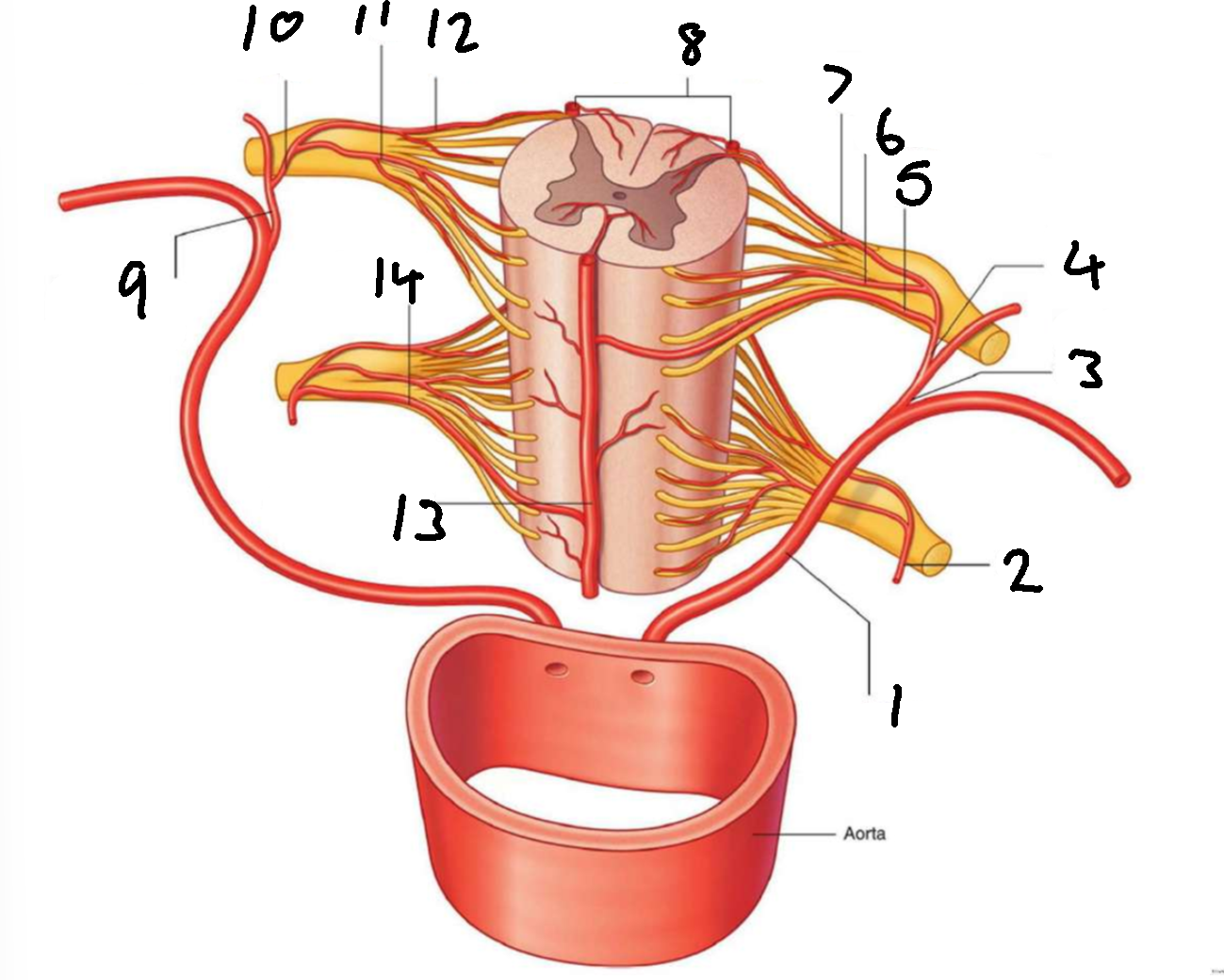
What is 9?
posterior branch of right posterior intercostal artery
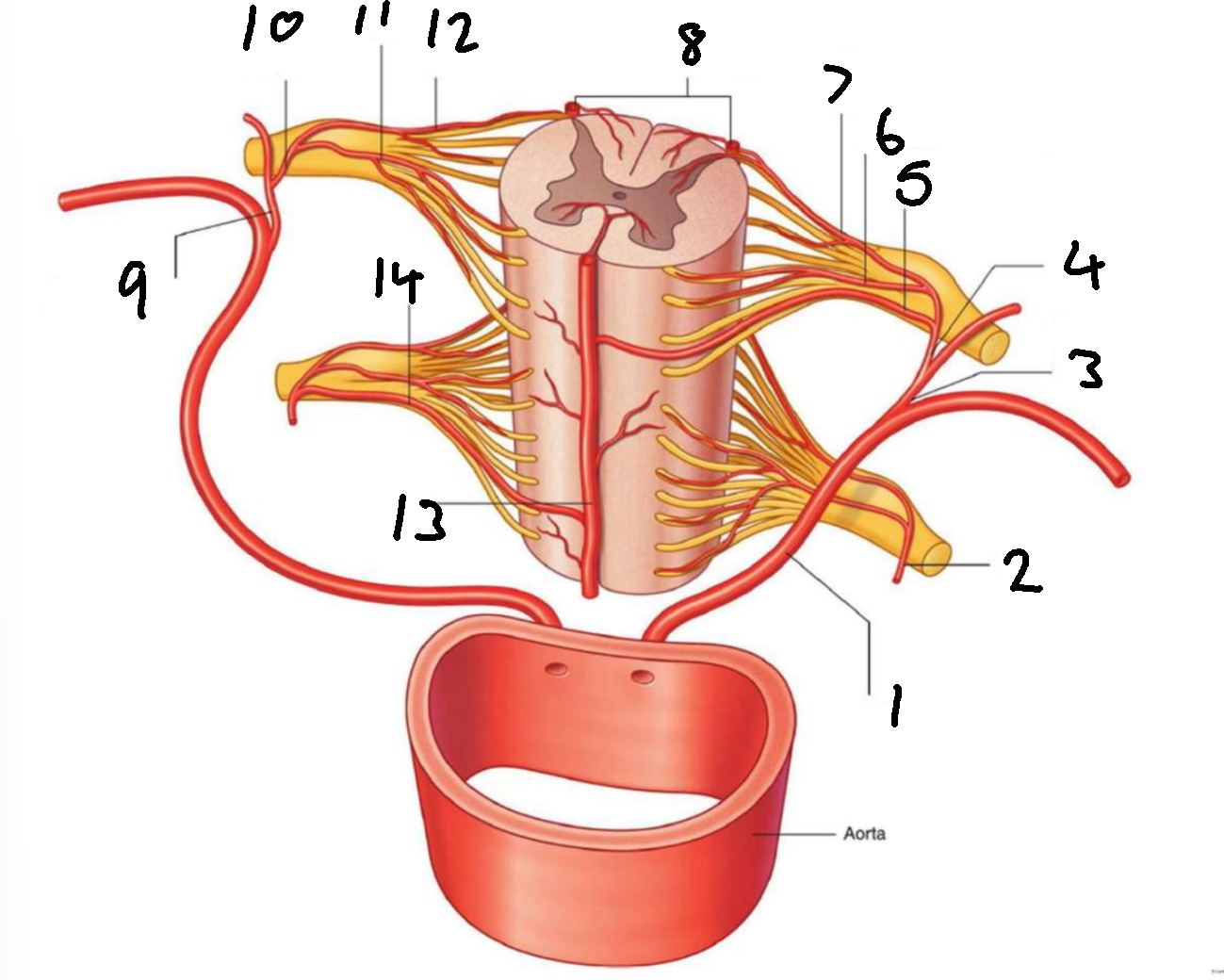
What is 10?
segmental spinal artery
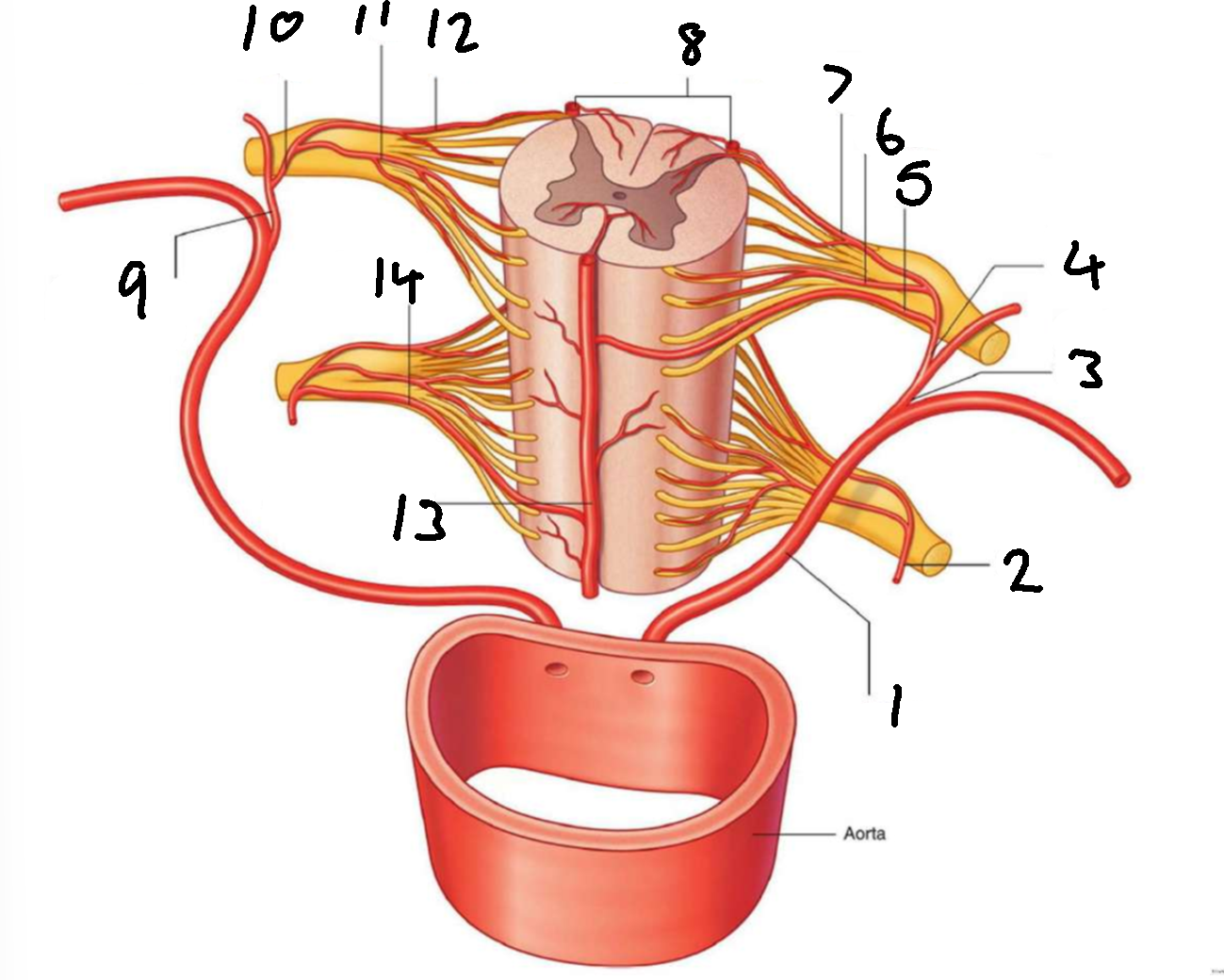
What is 11?
anterior radicular artery
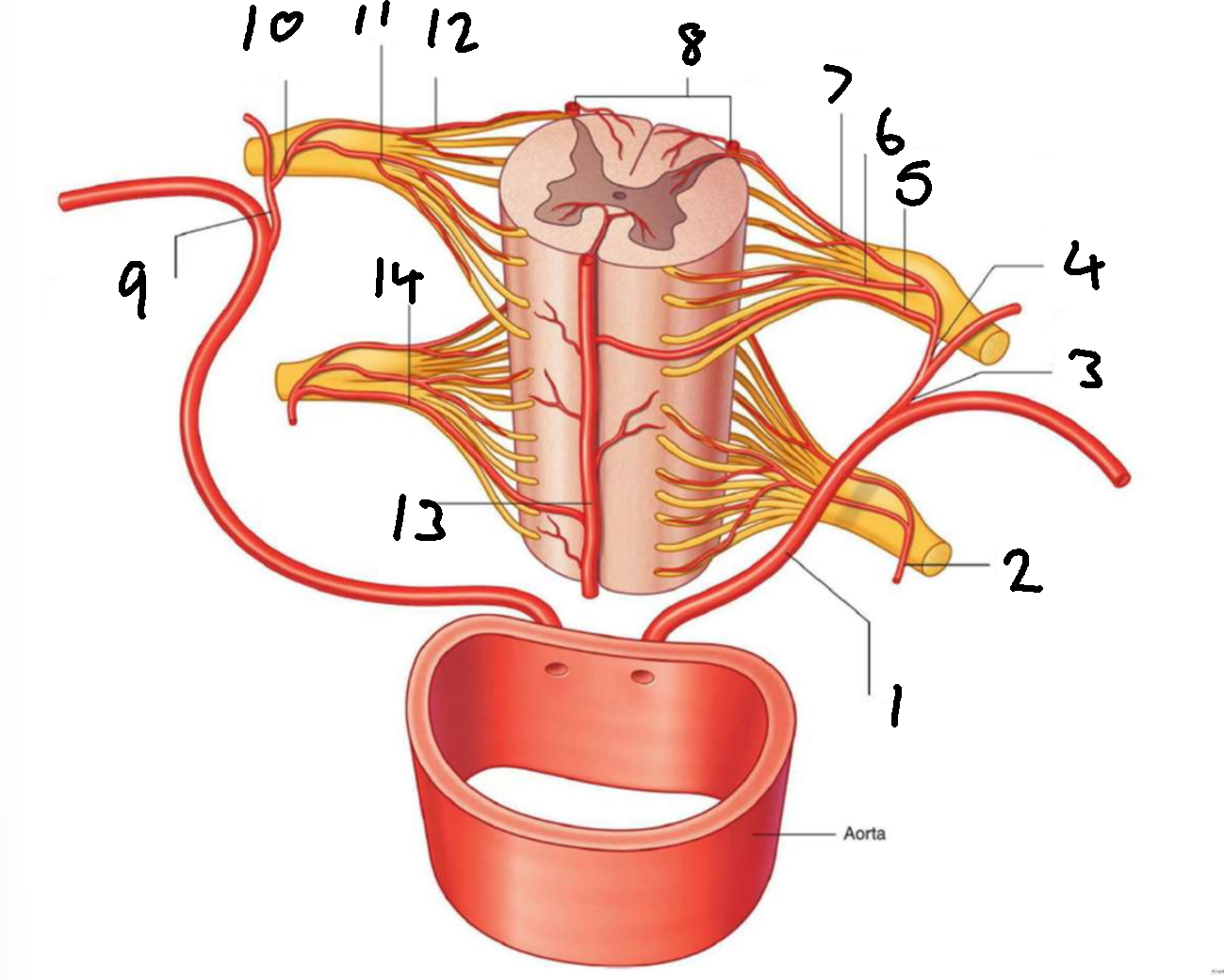
What is 12?
posterior radicular artery
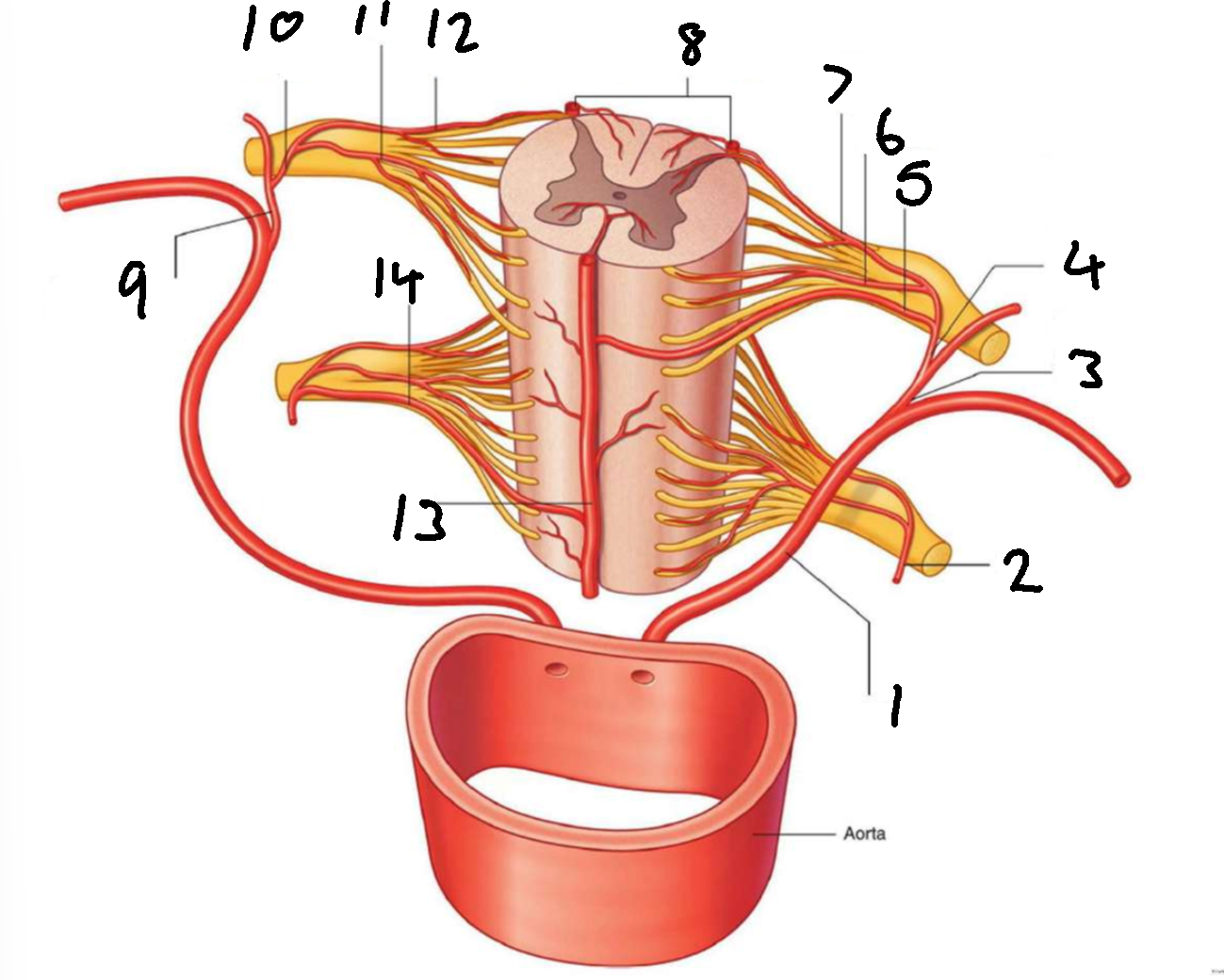
What is 13?
anterior spinal artery
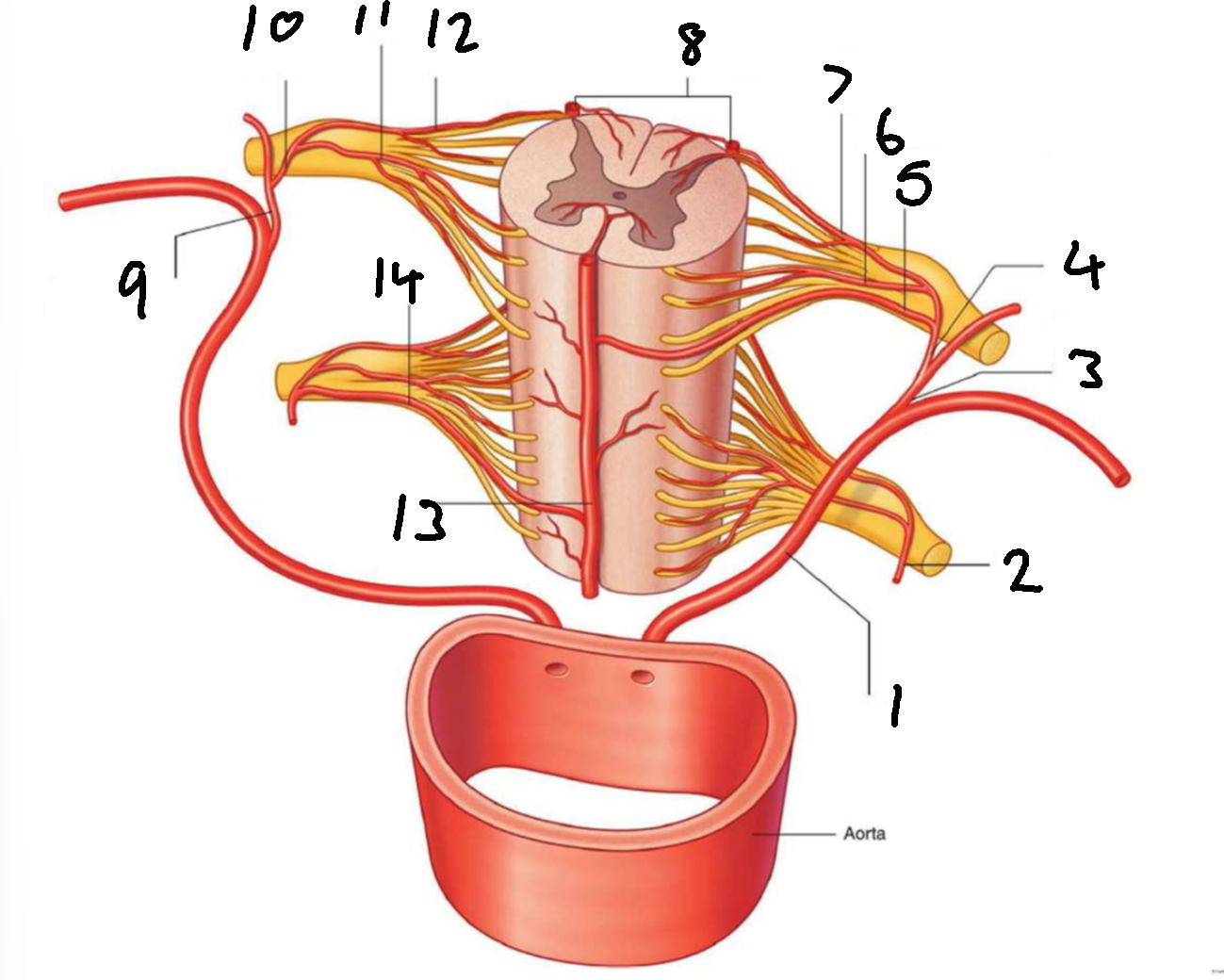
What is 14?
segmental medullary artery
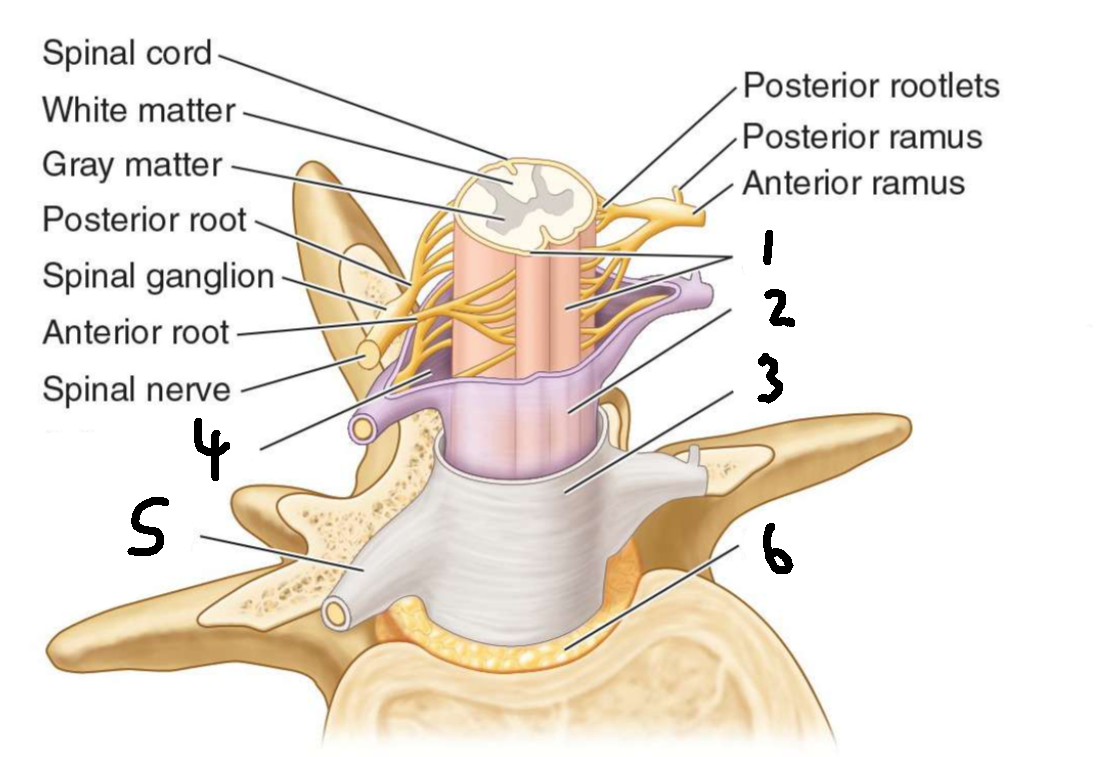
What is 1?
pia mater
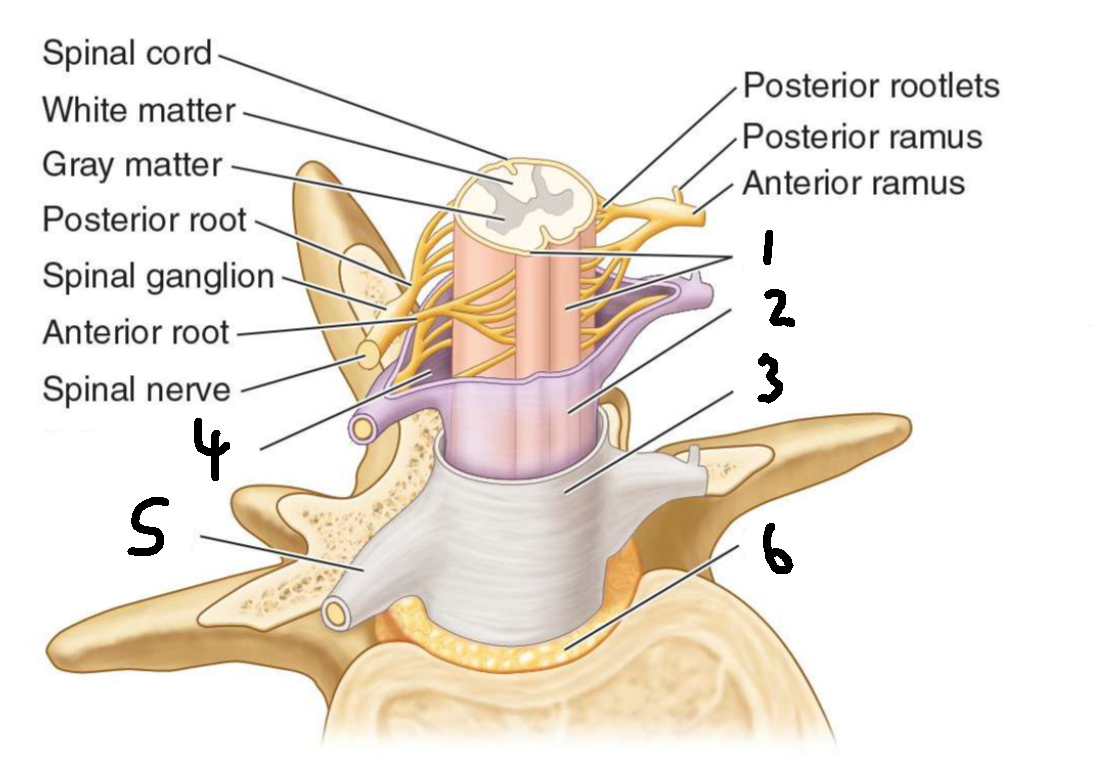
What is 2?
arachnoid mater
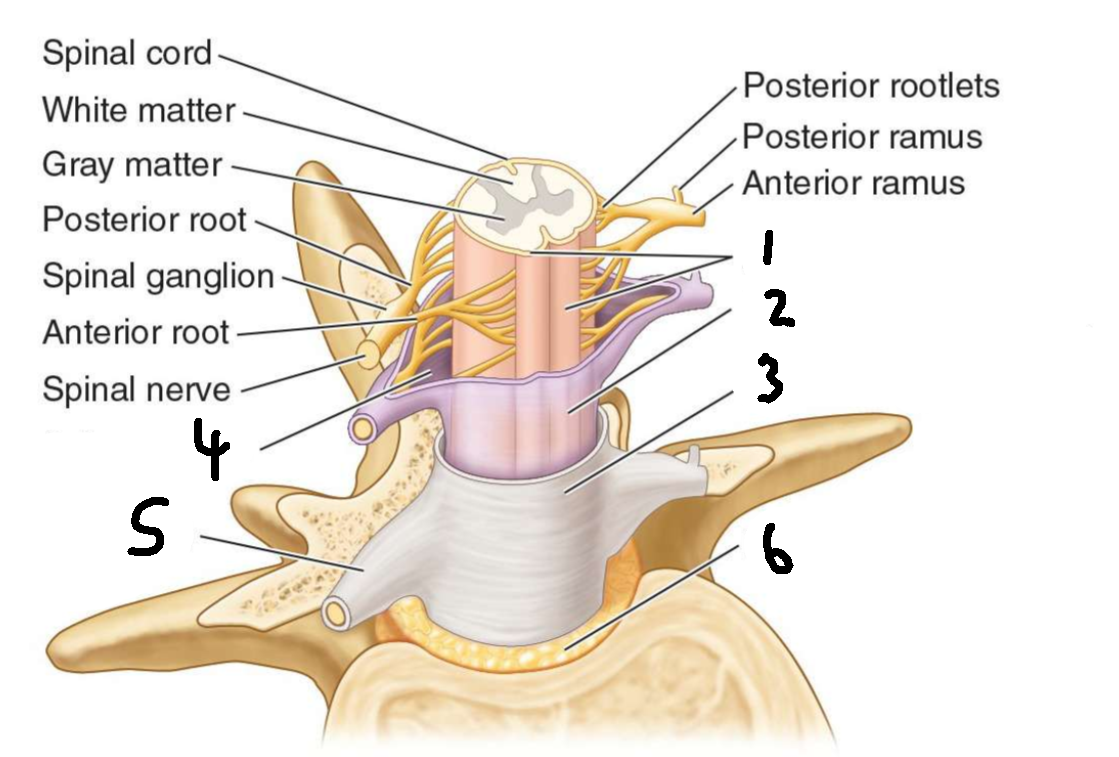
What is 3?
dura mater
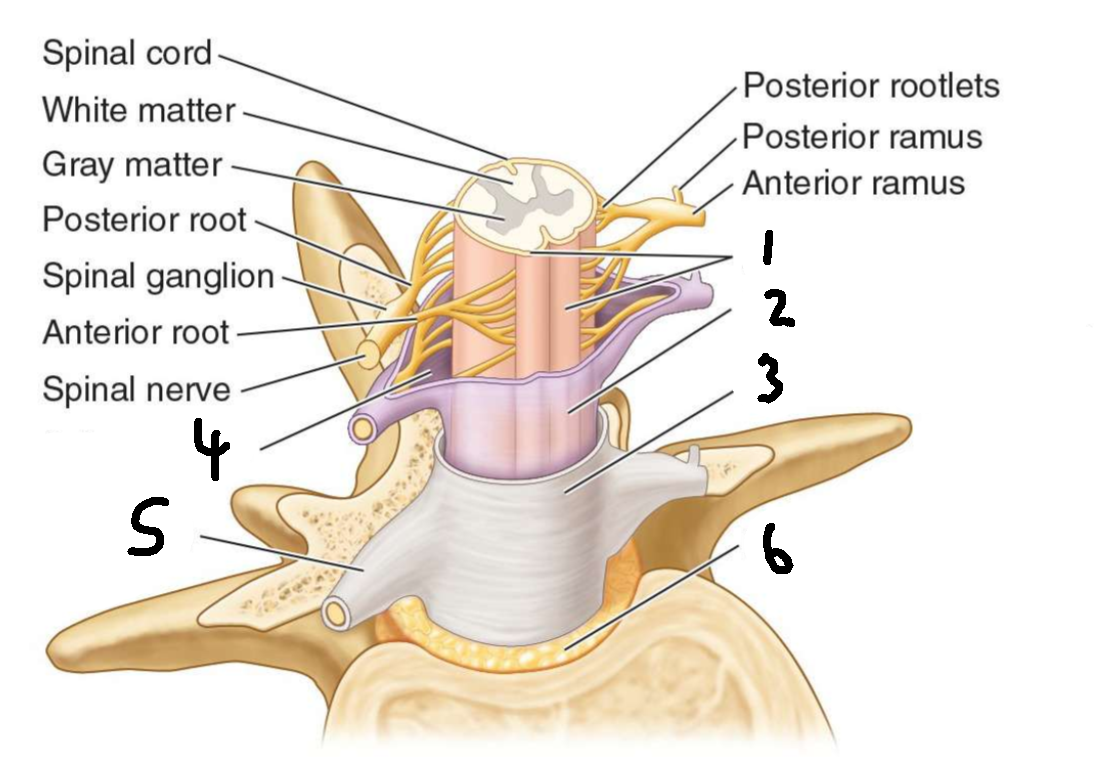
What is 4?
subarachnoid space
What is 5?
dural root sheath
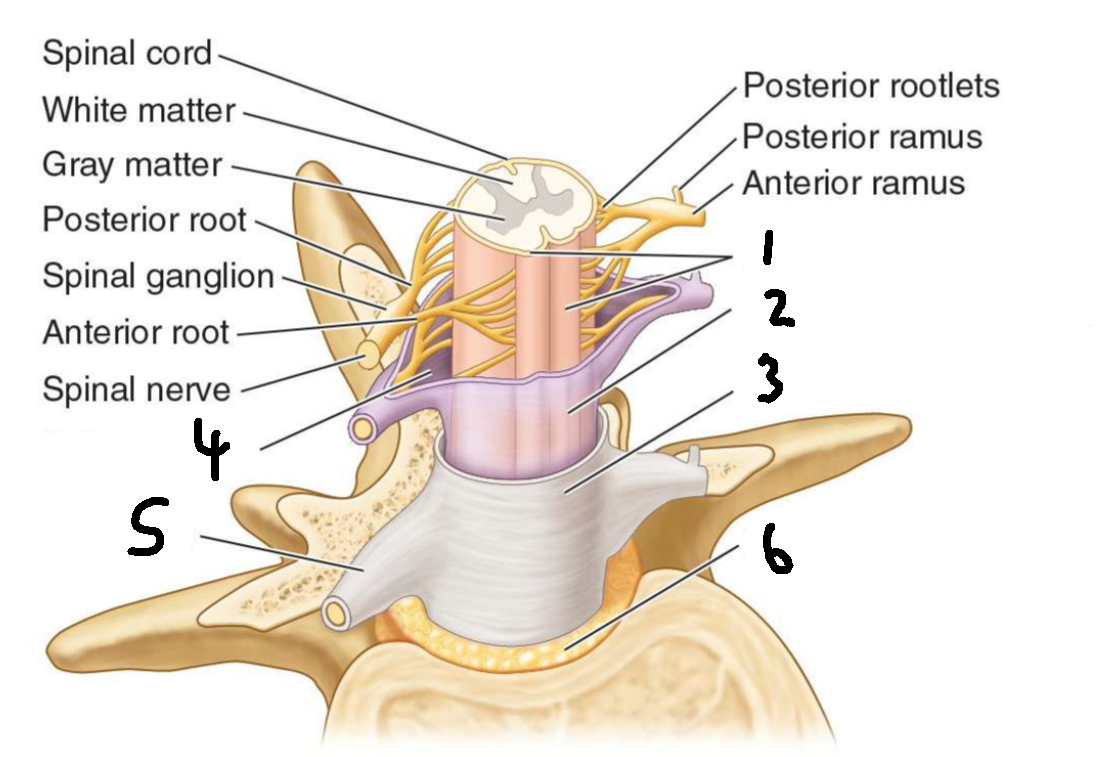
What is 6?
epidural fat
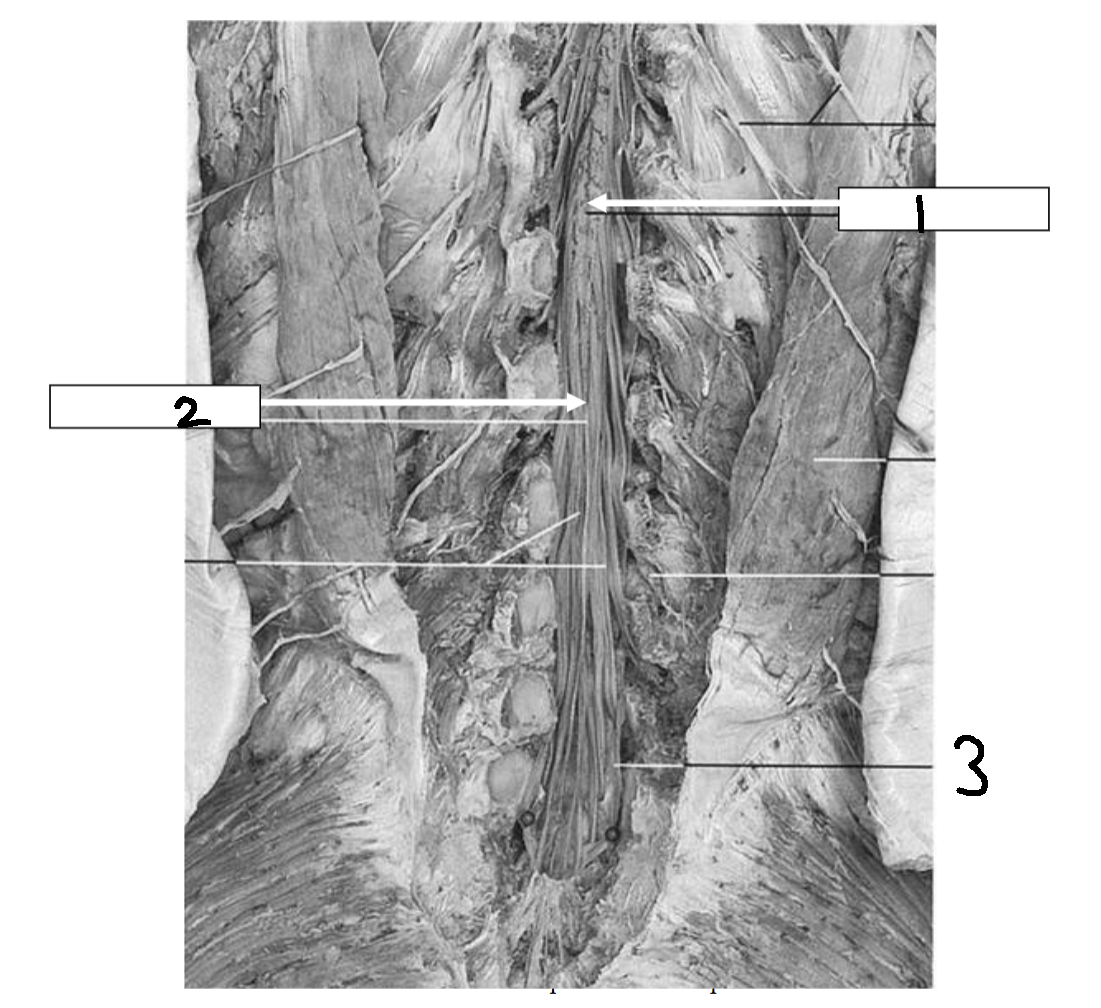
What is 1?
conus medullaris
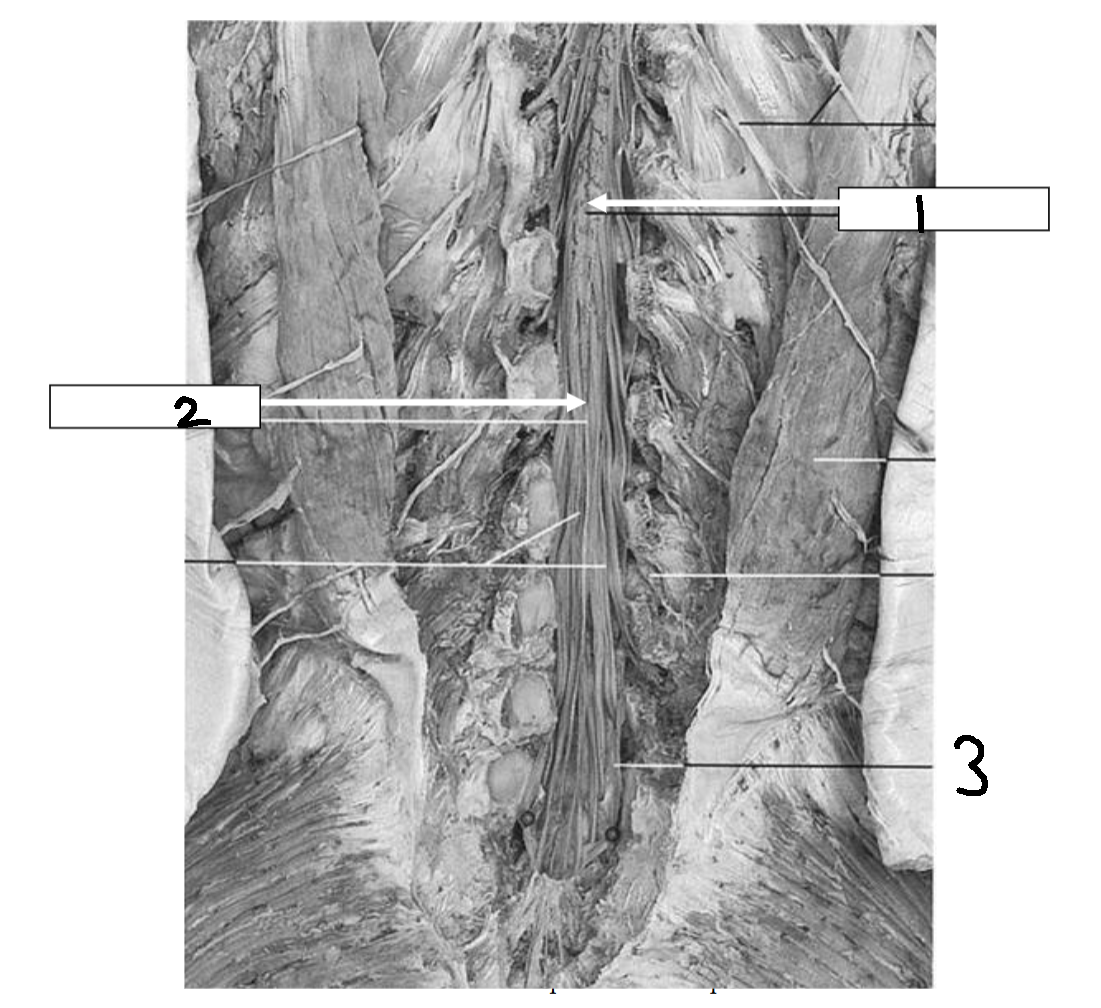
What is 2?
filum terminale
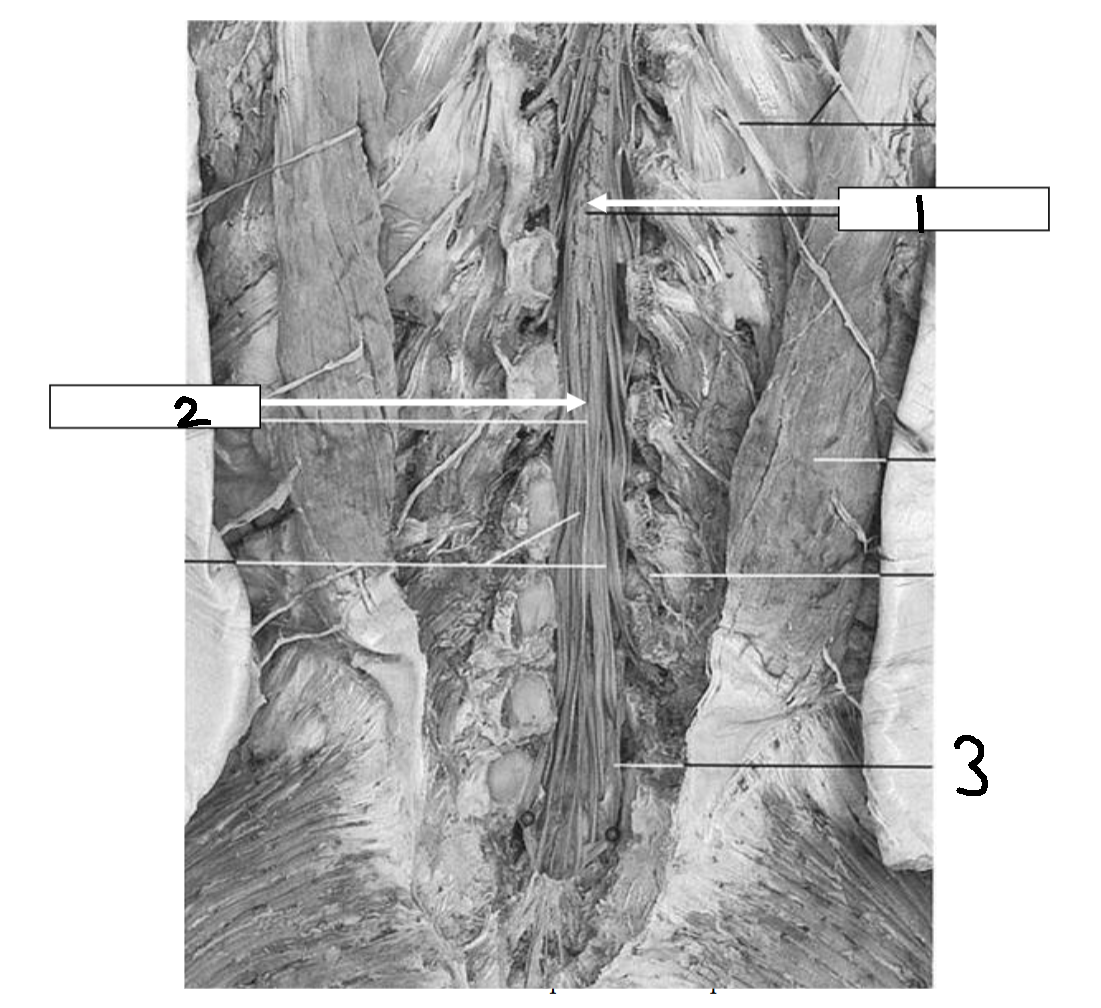
What is 3?
cauda equina