MCAT Gen. Chem. Review - Ch. 1 + 2: Atomic Structure; The Periodic Table
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Protons + Neutrons
Nucleus
Atomic mass unit (amu)
Atomic number (Z)
Mass number (A)
Isotopes
Atomic weight
Avogadro’s number, NA = 6.02 × 1023
Electrons
Electron shells
Valence electrons
Cation
Anion
Rutherford
Quanta
Energy
Planck equation (E = hf)
Planck’s constant = 6.626 × 10-34 J × s
Bohr Model
Angular momentum of electron (L = nh/2pi)
Energy of the electron (E = -RH/n2)
Rydberg unit of energy = 2.18 × 10-18 J/electron
Orbit
Ground state
Excited state
AHED
Atomic Emission + Absorption Spectra
Line spectrum
Atomic emission spectrum
Lyman/Balmer/Paschen series
Absorption spectrum
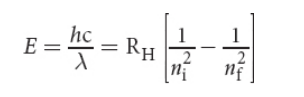
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atoms
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
Pauli exclusion principle
Principal quantum number n
Shell
Azimuthal Quantum Number
Azimuthal (angular momentum) quantum number I
Subshells
Spectroscopic notation
Magnetic + Spin Quantum Number
mI, Orbital
ms spin quantum number
Paired electrons vs. parallel spins
Electron configuration
Aufbau principle (building-up principle)
n + I rule
Hund’s Rule
Paramagnetic
Diamagnetic
Allotrope
The Periodic Table
Periodic law
Periods
Groups and families
Valence shell + electrons
A (representative) elements
B (nonrepresentative) elements (transition, lanthanide, actinide)
Metals
Lustrous
Ductile
Malleability
Electropositivity
Oxidation states
Conductors
Nonmetals + Metalloids
Semimetals
Periodic Properties of Elements
Effective nuclear charge (Zeff)
Noble/inert gases
Octet rule
Atomic radius
Ionic radii
Ionization Energy (IE)
Ionization potential
Endothermic process
First + second ionization energy
Active metals
Exothermic
Electron affinity
Electronegativity/Pauling electronegativity scale
Chemistry of Groups
Alkali metals
Alkaline earth metals
Chalcogens
Halogens
Noble gases
Transition metals (hydration complexes, subtraction frequencies, complementary color)