growth hormone and parathyroid hormone - lecture 18
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
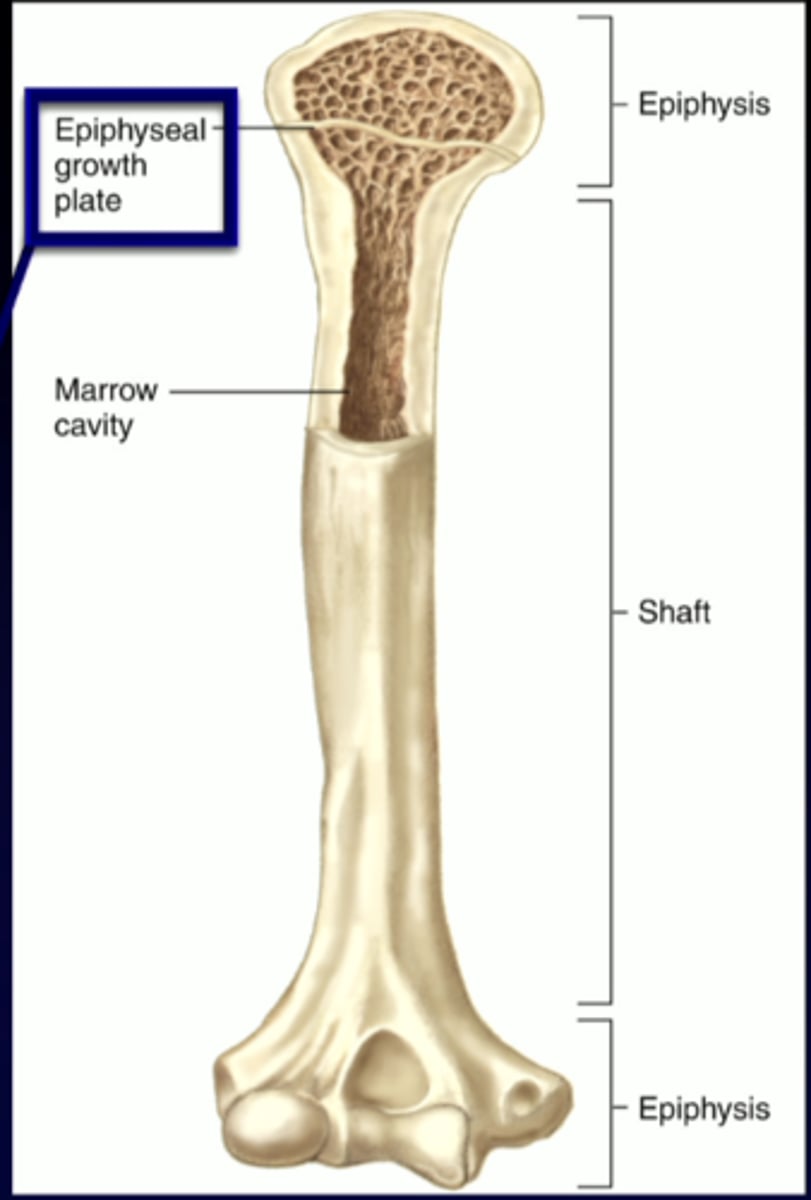
long bone
what type of bone is this
chondrocytes
facilitate active cartilage growth until puberty
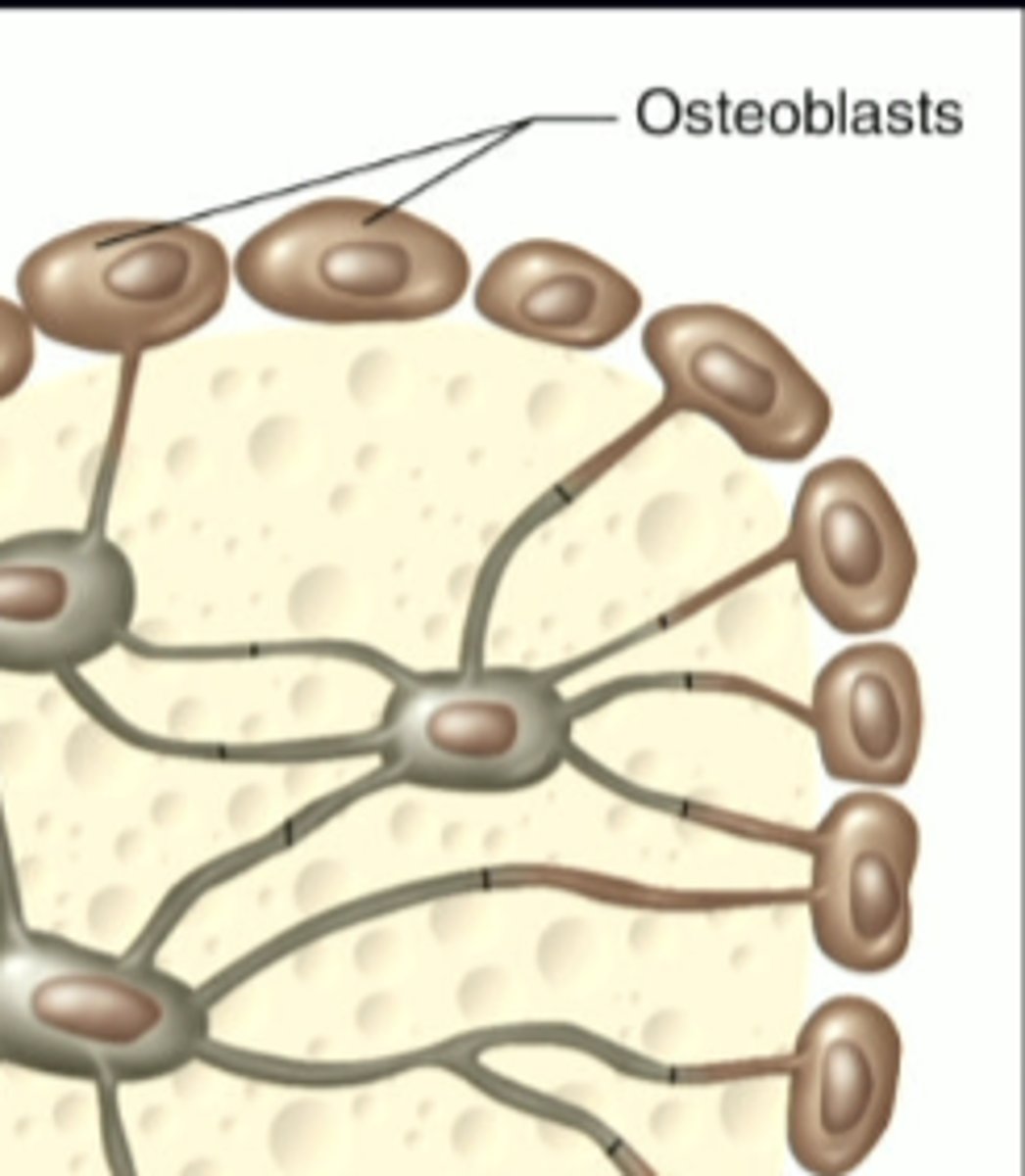
osteoblasts
mineralize the growth plate
hormonal regulation
your bones are under
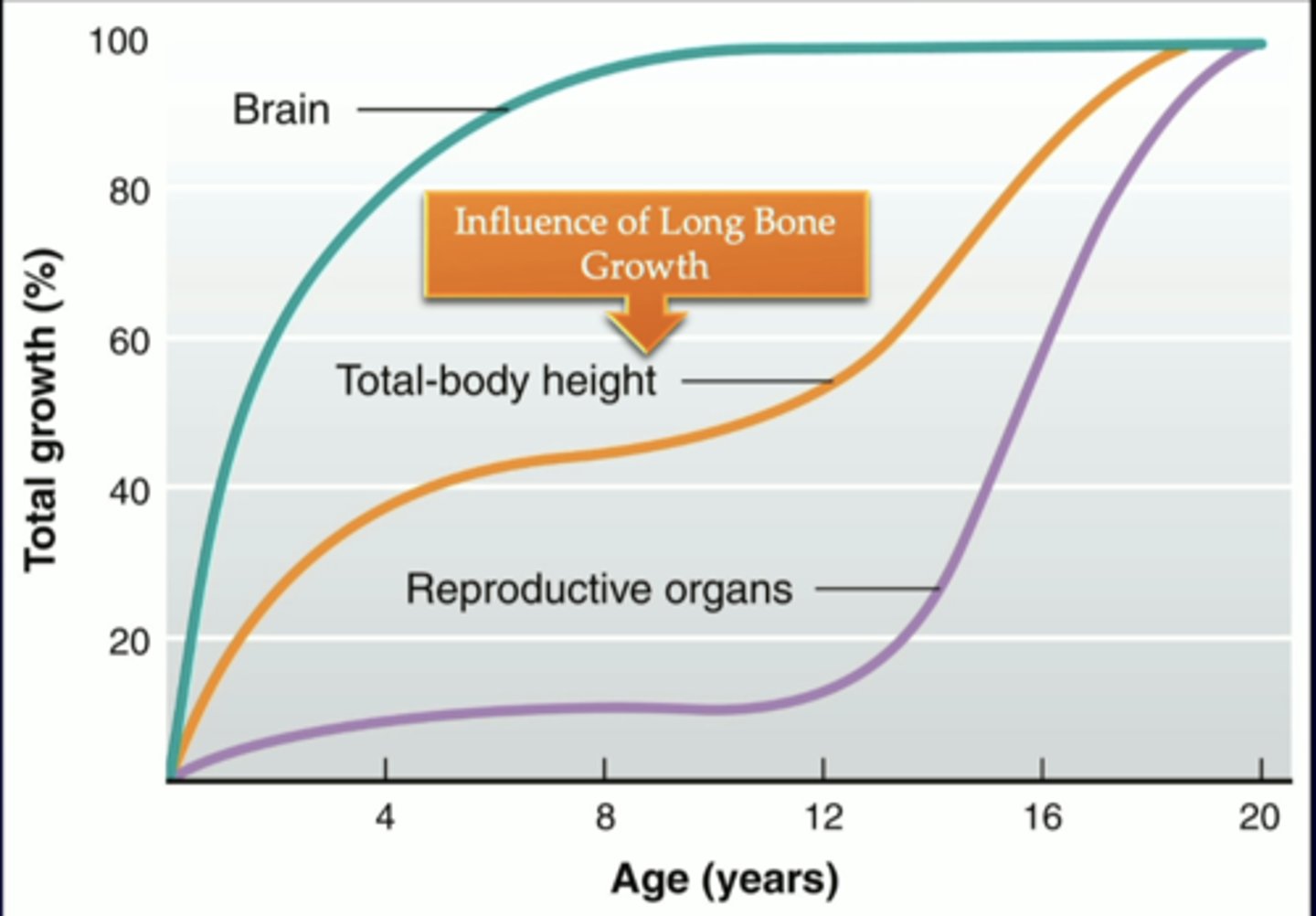
chart of how age is compared to total growth percentage
chart of how age is compared to total growth percentage
osteoblasts
-osteoBlast, Build Bone
build bone, mineralize cartilaginous bone, Ca 2+ and PO4 3- combine to form calcium phosphate crystals
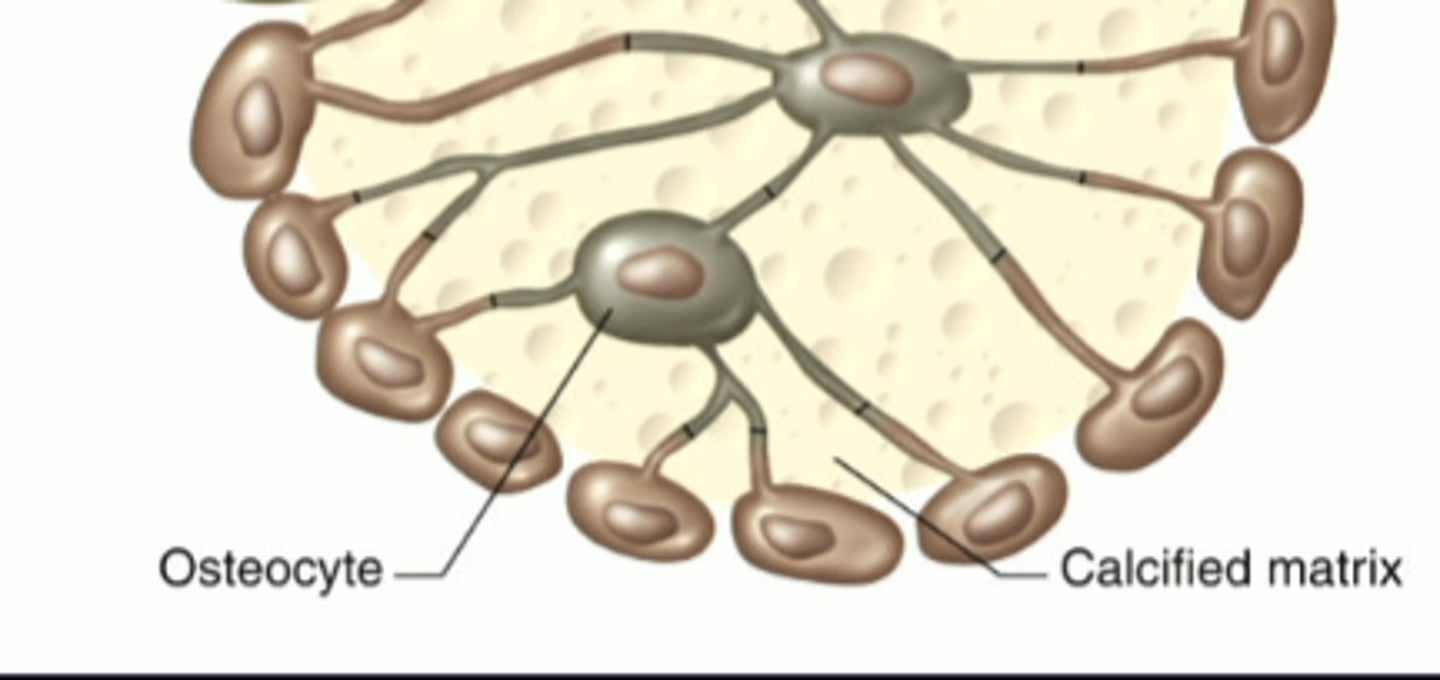
osteocytes
-osteoCytes, bone Cells
bone cells, sense "pressure" and remodel bone
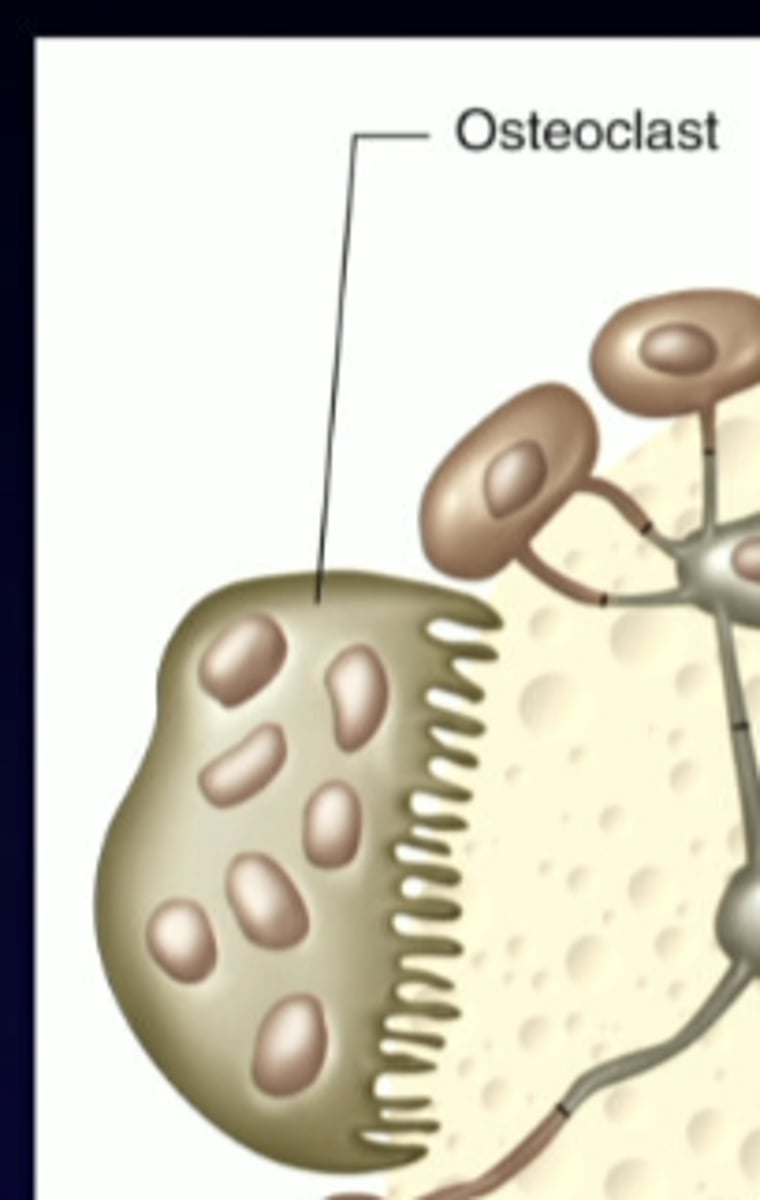
osteoclasts
-cl put together looks like a d, for break down
break down bone, resorb bone to increase Ca 2+
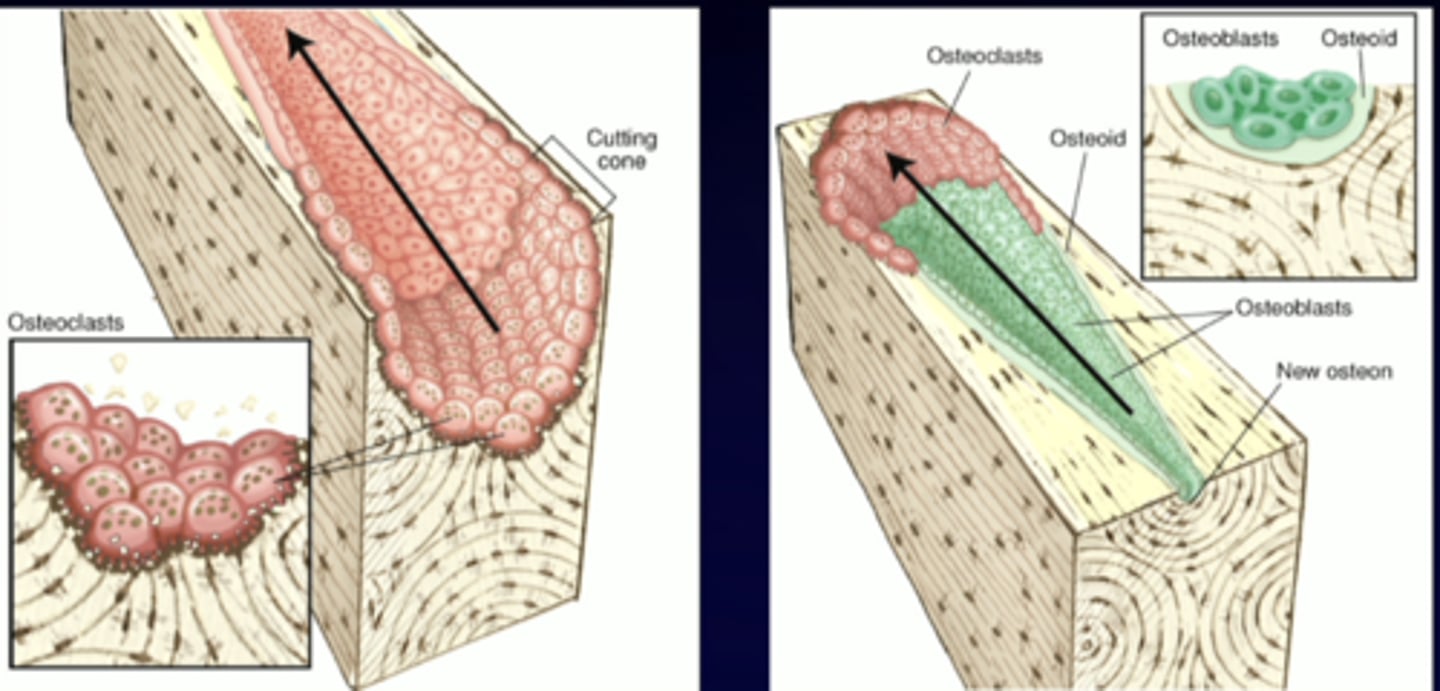
10 years
adult skeleton is replaced about every ...
1. growth hormone (GH) and insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)
2. thyroid hormones (T3)
3. insulin
4. sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone)
5. cortisol (negative regulator)
what are the key players of hormonal influences on bone growth
hypothalamic-pituitary-somatic (HPS) axis
what axis are we looking at when talking about growth hormones
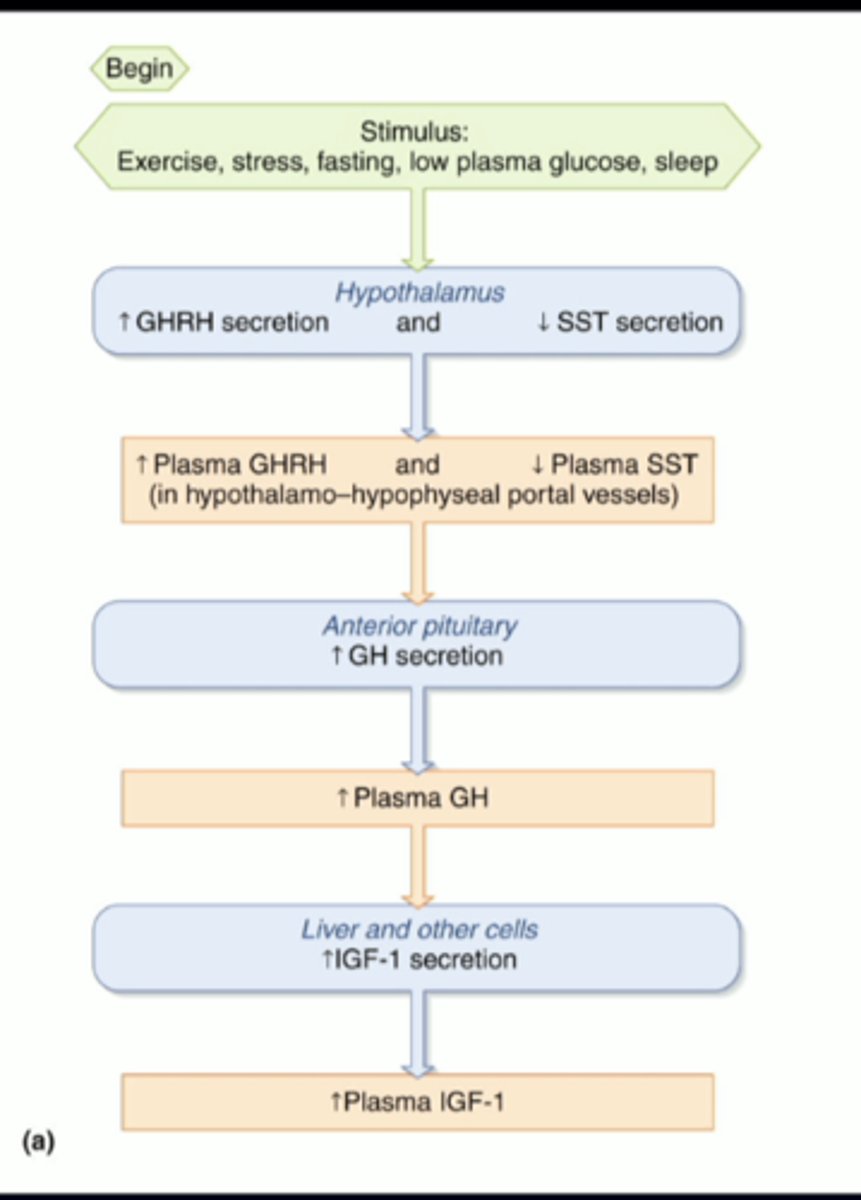
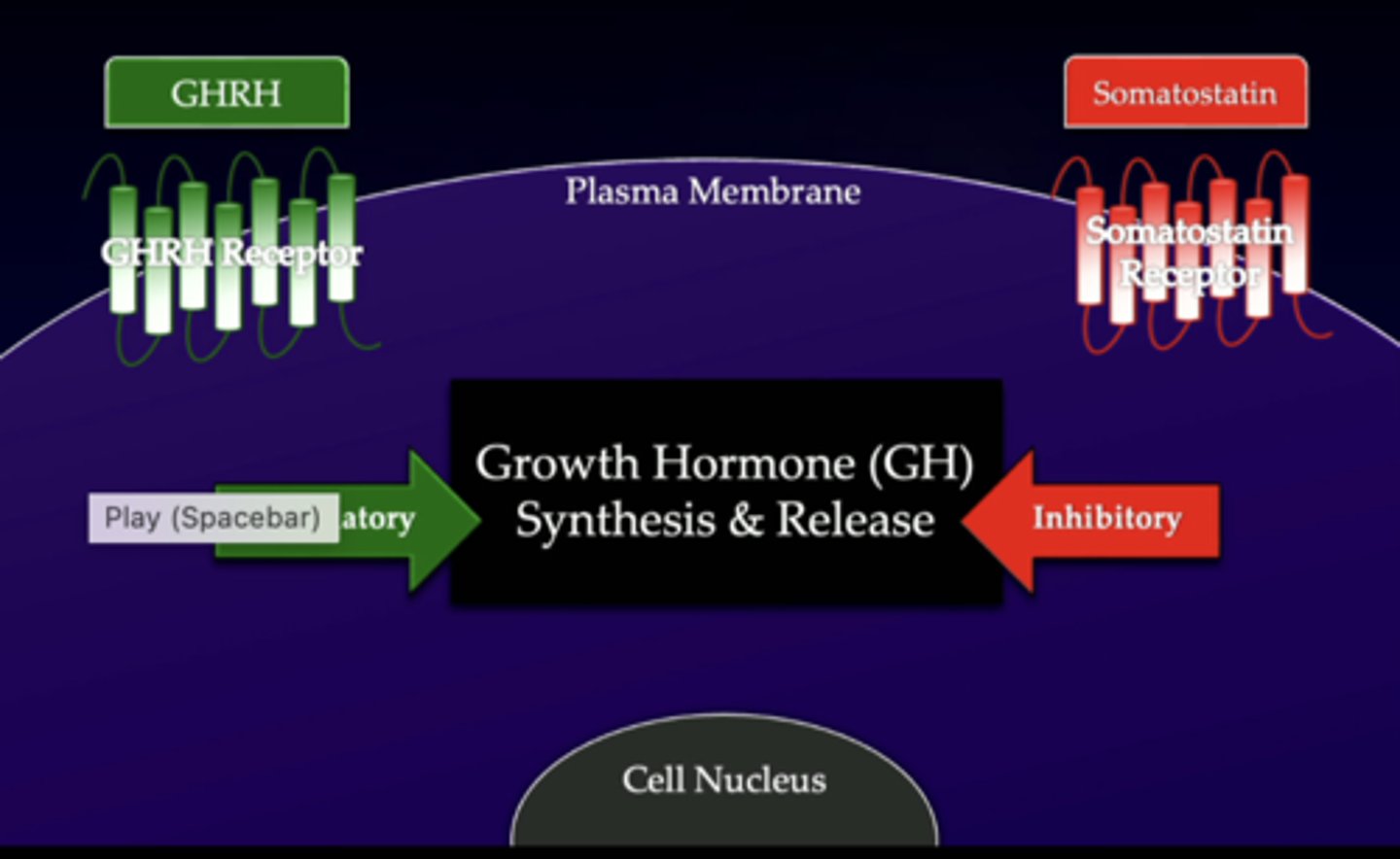
growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
the hypothalamus is going to release...
GHRH receptors
GHRH is going to travel to the anterior pituitary, binding to the...
growth hormone (GH)
the GHRH receptors activate the somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary, which then release....
GH receptor
growth hormone is going to travel around the body, but specifically to the target cells on the liver, where it is going to bind to the...
insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) into the body to target tissues and musculoskeletal system, as well as returning to the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus to make sure there is not a constant release of these hormones when it is not needed
the liver is then going to release ....
GH/IGF-1 axis
GHRH - growth hormone releasing hormone
xxxxx SST - somatostatin xxxxx
---bc it is the opposite of growth hormone
GH/IGF-1 axis
GHRH - growth hormone releasing hormone
xxxxx SST - somatostatin xxxxx
---bc it is the opposite of growth hormone
somatostatin
hormone that inhibits release of growth hormone and insulin
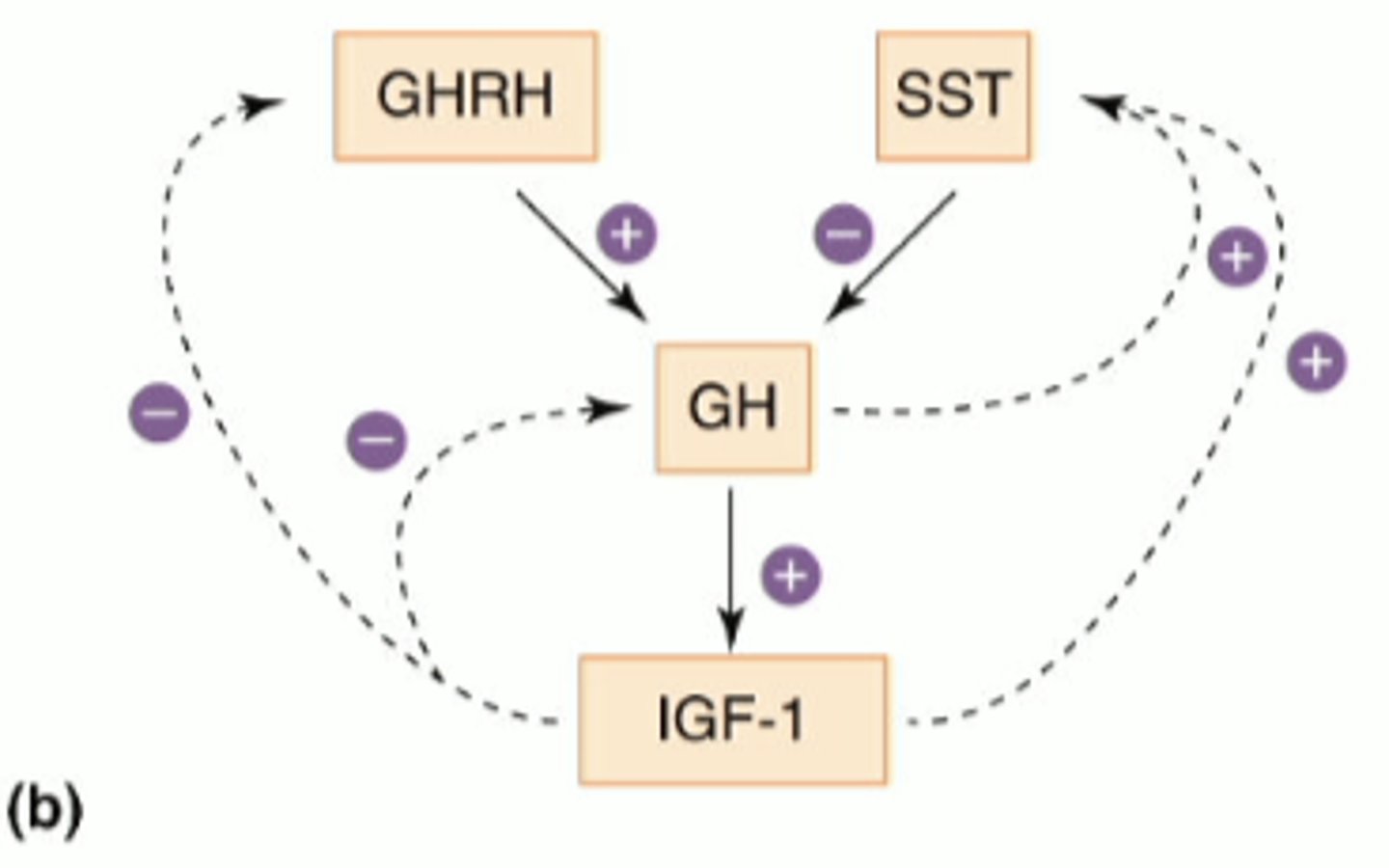
stimulatory (green) - GHRH is having a stimulatory effect
inhibitory (red) - somatostatin is having an inhibitory effect
peptide hormones have to interact with the cell surface plasma membrane receptors so...
effects of growth hormone
-promotes growth
---with insulin like growth factor (IGF-1)
-stimulates protein synthesis (x/ IGF-1)
-during fasting, it increases glucose and lipid availability but preserves muscles
-stimulates gluconeogenesis
---production of new glucose
-decrease glucose uptake
-increase lipolysis (breakdown of fat)
effects of estrogen
-stimulates growth at puberty through GH
-causes epiphyseal closure (cessation of long bone growth)

effects of testosterone
-stimulates growth at puberty through GH
-causes epiphyseal closure (shutting down)
-stimulates protein synthesis in males
effects of cortisol
-major stress hormone
-inhibits bone growth
-stimulates protein catabolism
-inhibits GH secretion

calcium regulation and homeostasis
calcium regulation and homeostasis

Ca 2+ homeostasis throughout the body
critical and tightly regulated by specific hormones
act at effector sites within specific organs
bone
effector sites for ca2+ homeostasis:
storage vs release
GI tract
effector sites for ca2+ homeostasis:
absorption
kidney
effector sites for ca2+ homeostasis:
reabsorption
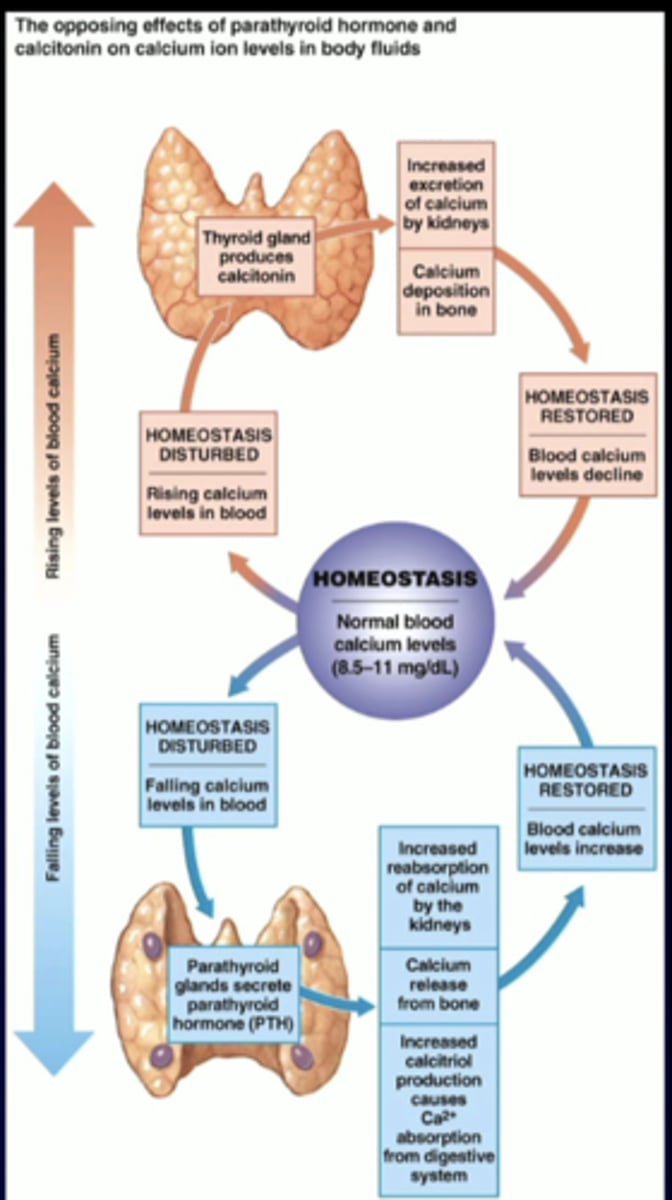
1. parathyroid hormone (PTH)
2. 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol)
---note: calcitonin plays a minor role
what are the two major hormones that regulate plasma ca 2+ levels
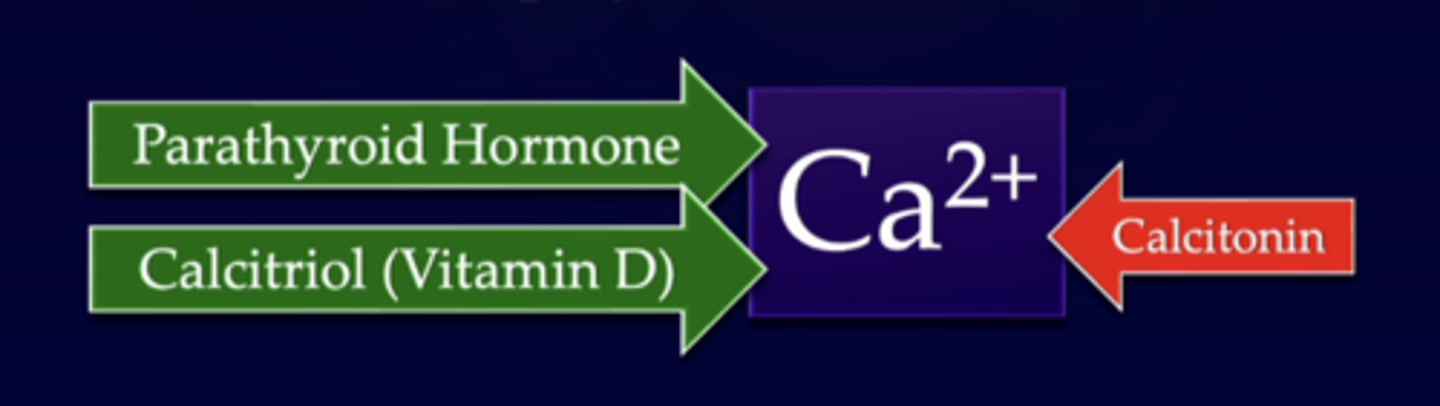
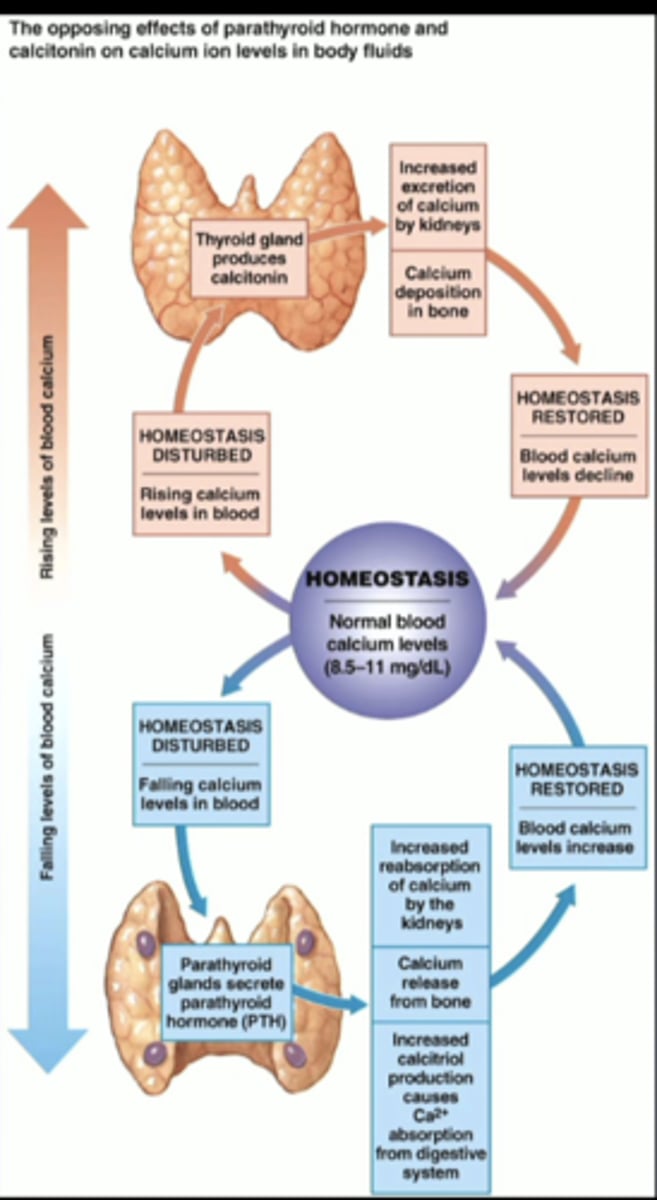
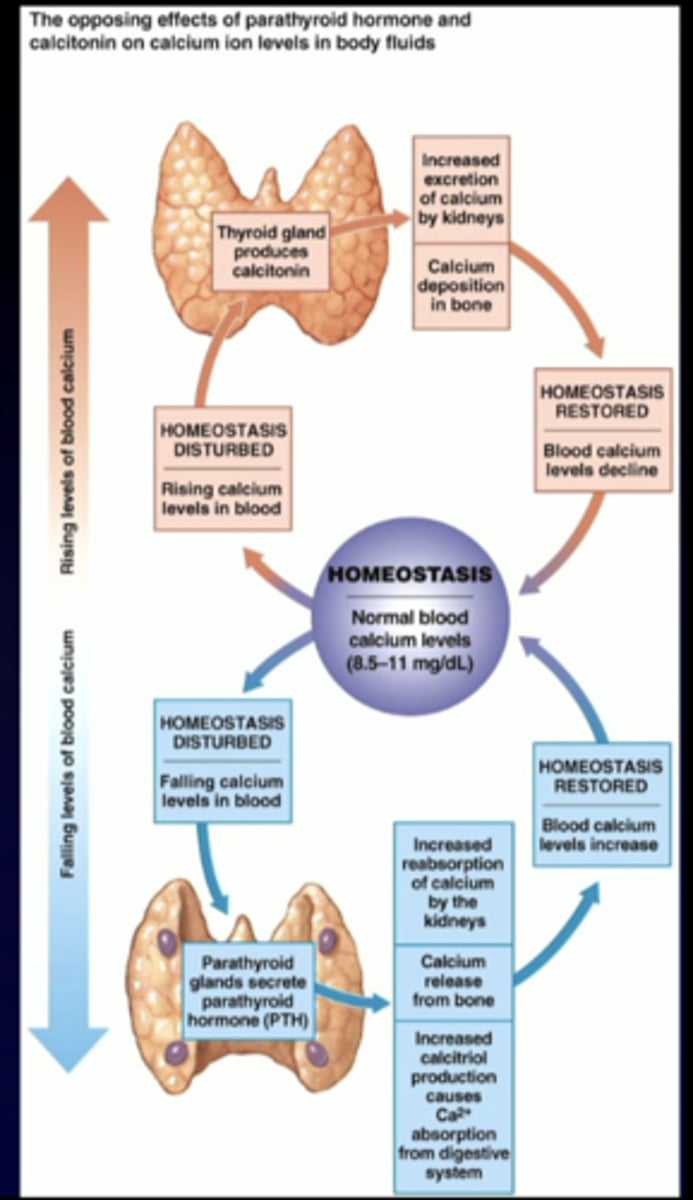
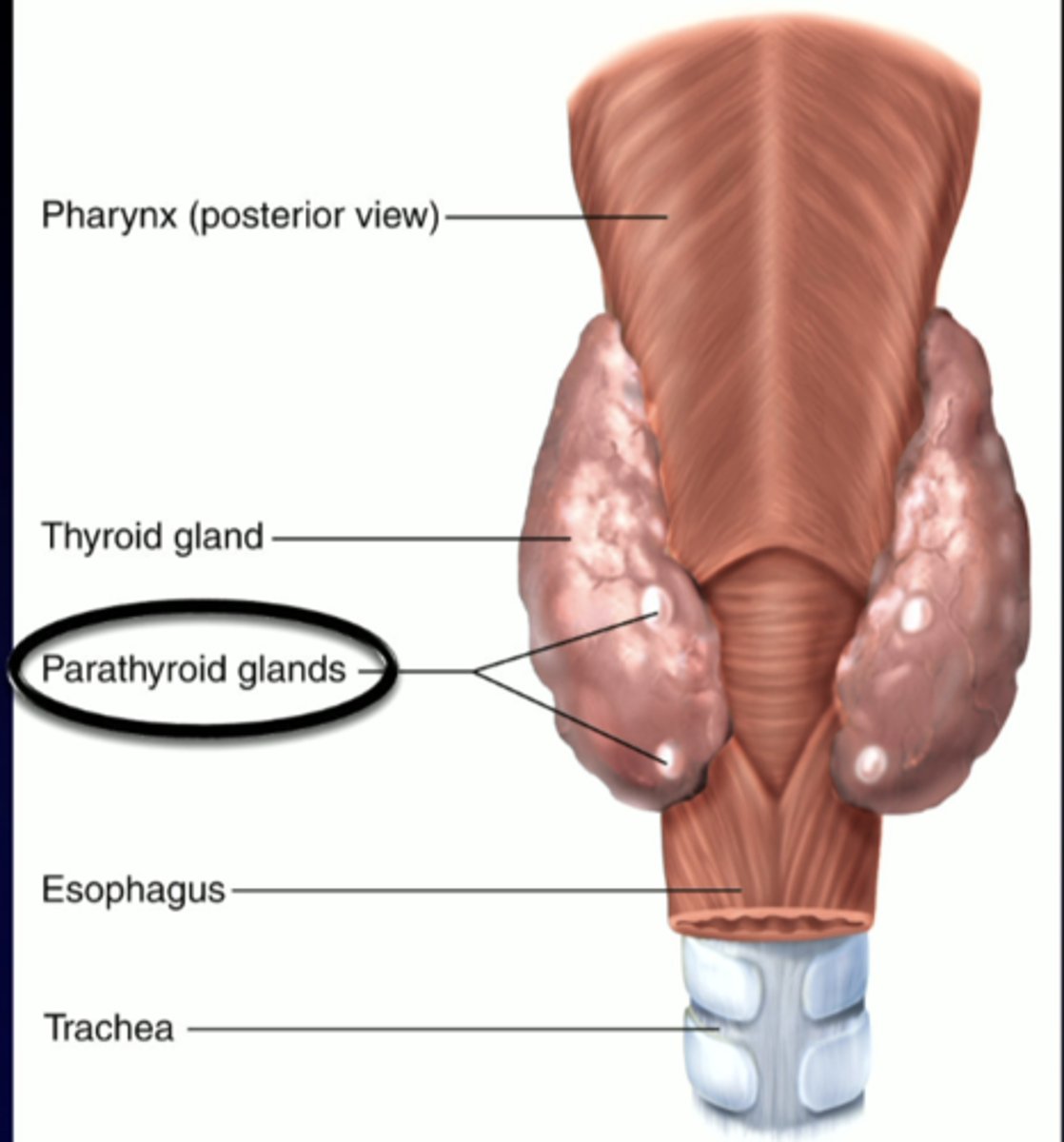
parathyroid hormone
-secreted by the parathyroid glands
-four small glands located in the neck on the (much larger) thyroid gland
-critically important for regulation of Ca 2+ levels
posterior view of neck: parathyroid glands
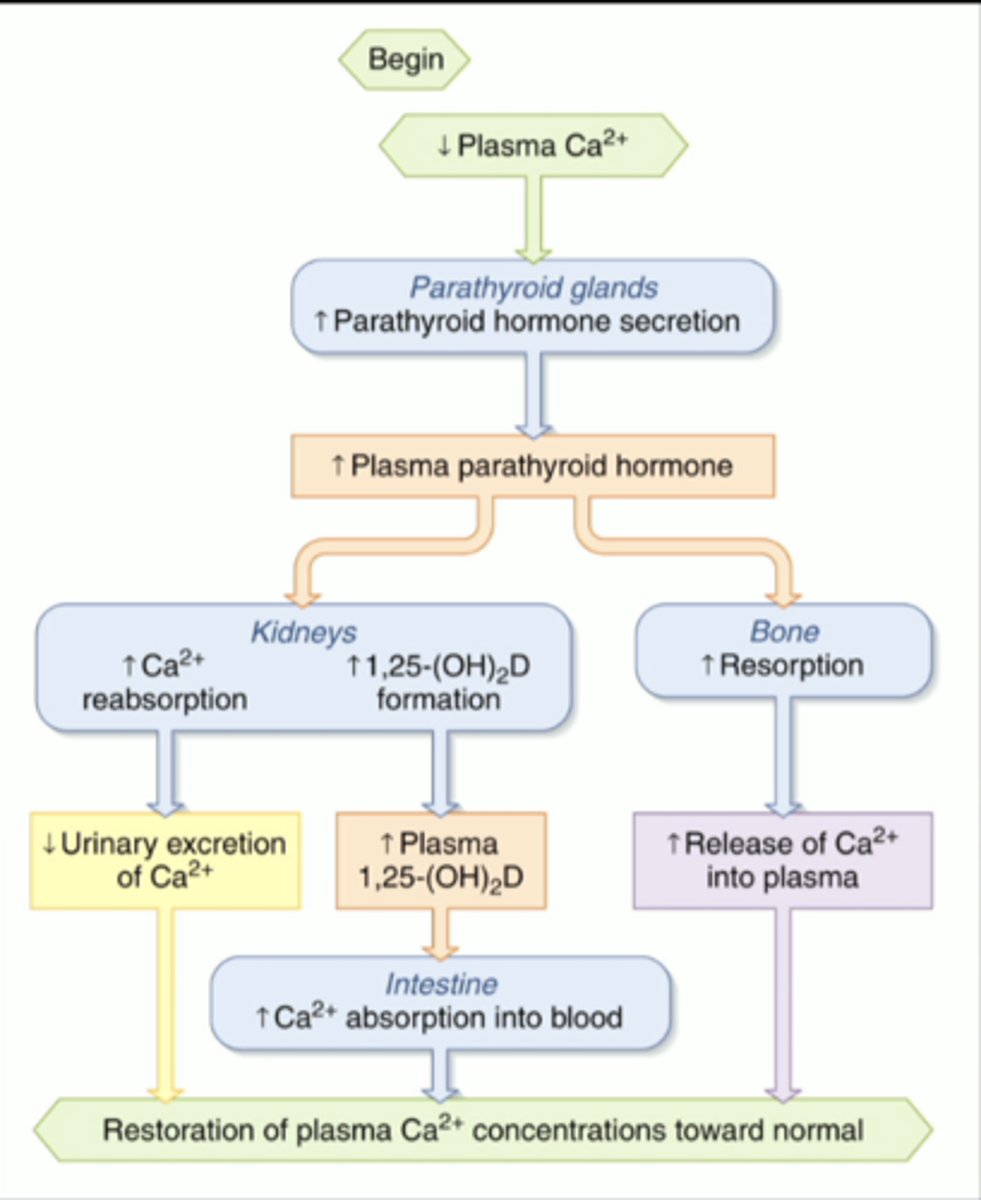
effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH)
-increases Ca 2+ availability to increase plasma levels
-increases ca 2+ reabsorption in kidneys
-increases osteoclast activity
-increases formation of vitamin D, which increases uptake of Ca2+ in GI tract
regulation of plasma calcium levels by PTH
regulation of plasma calcium levels by PTH
(1) 3:2
(2) optimal for bone formation
renal regulation of Ca2+ and phosphate:
(1) ___:___ ratio of Ca2+ : phosphate = (2)
--increases ca2+ but not phosphate, you cant reform bone
parathyroid hormone
sets the right balance
-increases Ca2+ reabsorption in the kidney
-decreases PO4 3- reabsorption in the kidney
vitamin D
active form produced in kidneys
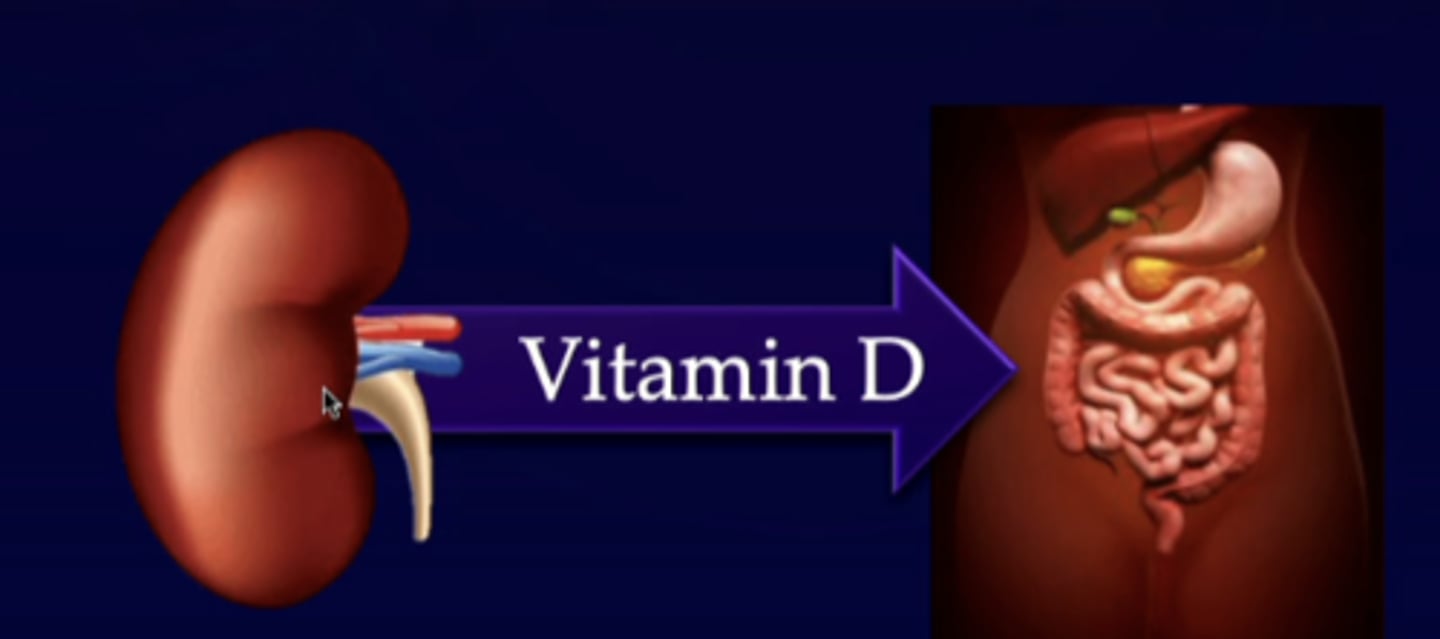
activated 1, 25 -(OH)2D (vitamin D), which increases gene expression of CA2+ and PO4 3- transporters in GI tract
if we have active vitamin D, we have....
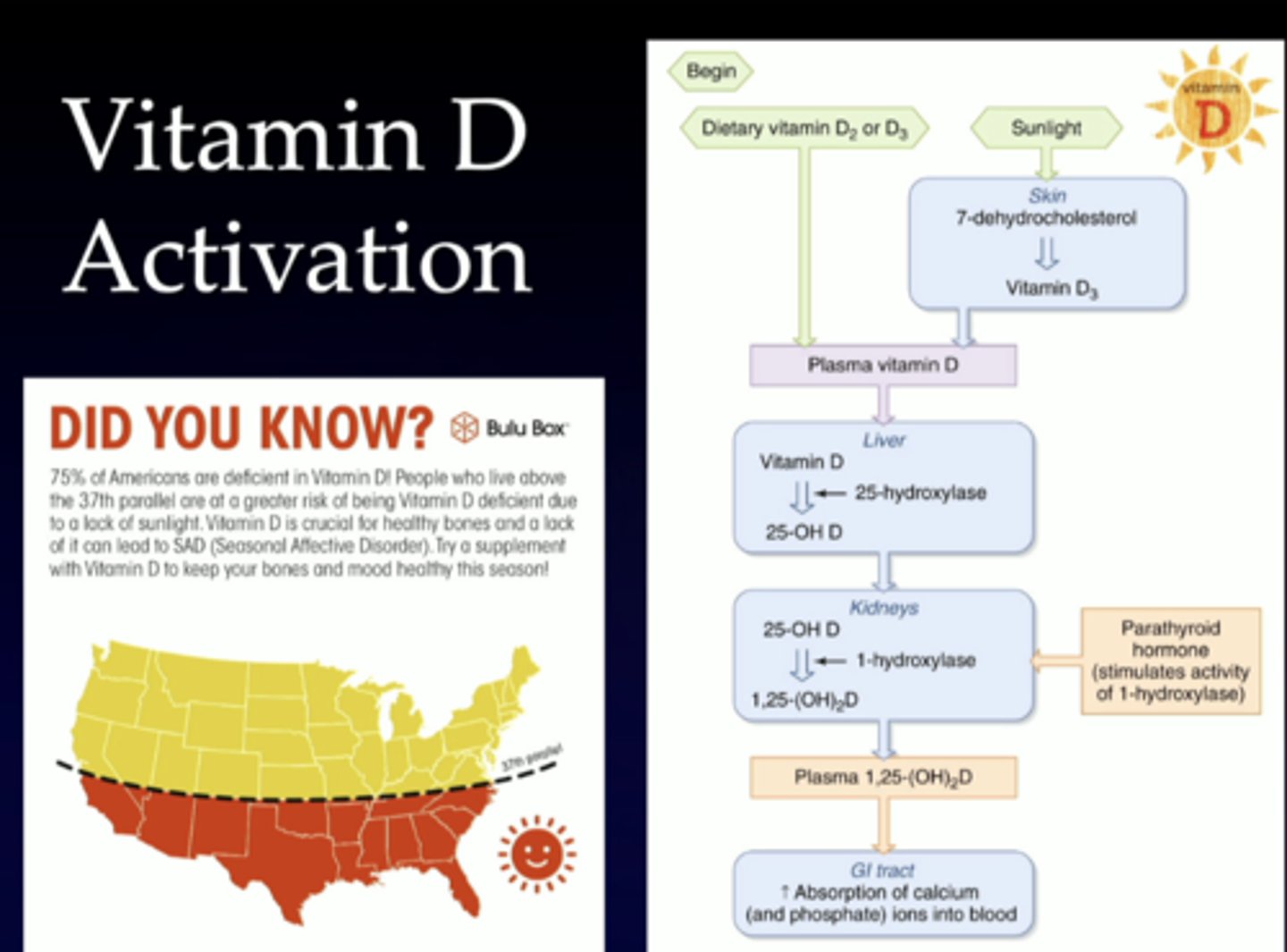
dont need to memorize this, just showing how important the sun is in vitamin D production
dont need to memorize this, just showing how important the sun is in vitamin D production
calcitonin (minor role)
-secreted by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland
-decreases plasma Ca2+ concentration by inhibiting osteoclasts
-secretion only stimulated by VERY HIGH plasma Ca2+ levels
c. break down bone to make calcium available to the body
osteoclasts:
a. are mature bone cells that sense pressure
b. build new bone as a natural part of bone turnover
c. break down bone to make calcium available to the body
b. increases calcium reabsorption in the kidney
parathyroid hormone:
a. decreases calcium reabsorption in the kidney
b. increases calcium reabsorption in the kidney
c. is released by the thyroid gland and inhibits osteoclast activity
d. a and c
e. b and c