Lecture 4 Caffeine
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
caffeine
most commonly used drug in the world
coffee, tea, soda, energy drink, otc cold medicine, chocolate
drug class
stimulant
buzz
low to moderate= increased alertness, concentration, euphoria
high=nervousness, agitation
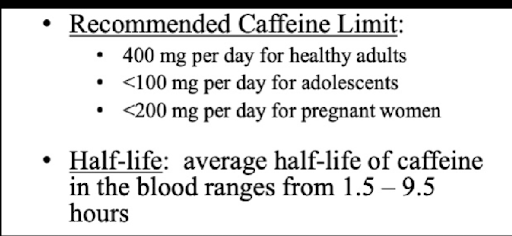
recommended caffeine limit
half life= 1.5-9.5 hours
xanthines
family of stimulant chemicals.
They all do basically the same thing, just stronger or weaker depending on which one it is.
Think of them like different strength versions of the same energy drink
3 types
caffeine
Found mostly in coffee
Strongest “wake-up” effect
Hits fast and hard
theophylline
tea
milder form of caffeine
theobromine
chocolate
very mild
lowest energy more like buzz
xanthine compounds actions
andenosine builds up in brain tells body to relax
xanthine blocks adenosine (major action)
sits on the receptors so they cannot do their job
like blocking brakes so telling caffeine to go
blocks receptors in blood vessels, fat cells, heart, kidneys, muscles
flips into fight or flight mode
increased blood pressure
hyperventillation to pull in more oxygen
muscles ready to move
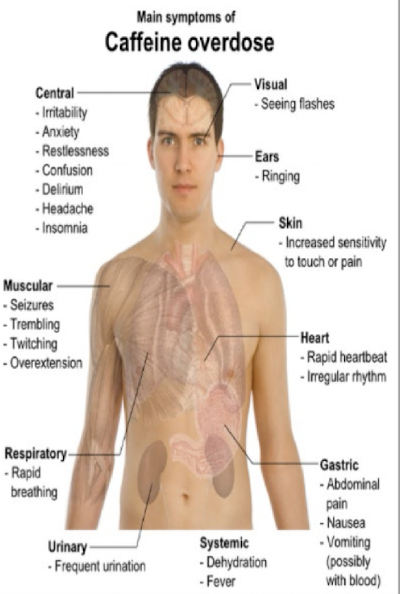
caffeine overdose
occurs when too much caffeine consumed
symptoms
fatal overdoses rare but exist
minor symptoms: dizziness, dhiarrhea, increased thirst, insomnia, headache, fever, irritability
major symptoms: trouble breathing, vomitting, hallucinations, confusions, chest pain, irregualr or fast heartbeat, uncontrollable muscle movments, convulsions, shock
caffeine sensitvity
some ppl experience greater sensitivity than someone who consumes caffeine daily
caffeine interactions
major
ephedrine - both stimulant
moderate
anitbiotics
adenosine
estrogens
minor
alcohol
birth control
etc.
caffeine interacts with 83 drugs of which 11 are major
caffeine and health concerns
◦ preexisting conditions
‣ heart problem, glaucoma, high blood pressure, ibs, bleeding/anxiety
‣ less safe to mix caffeine with
◦ bipolar disorder
‣ caffeine= possible mania
◦ diabetes
‣ caffeine effects how body metabolizes sugar
‣ must monitor blood sugar levels in relation to caffeine intake
◦ osteoporosis
‣ increases urination, flushes calcium out of symptom
‣ worsens
caffeine and the body
◦ taken orally
‣ absorption into blood primarily thru stomach lining small/large intestine
‣ only slowly absorbed thru stomach, most absorption in small intestine
◦ caffeine evenly distributed thru body
‣ metabolized by liver and excreted thru kidneys
‣ slowly eliminated by body
‣ half life of single dose= 3 hours
◦ regular caffeine use
‣ maybe leads to lower risk of death due to heart disease, cancer, stroke, diabetes, and respiratory kidney disease
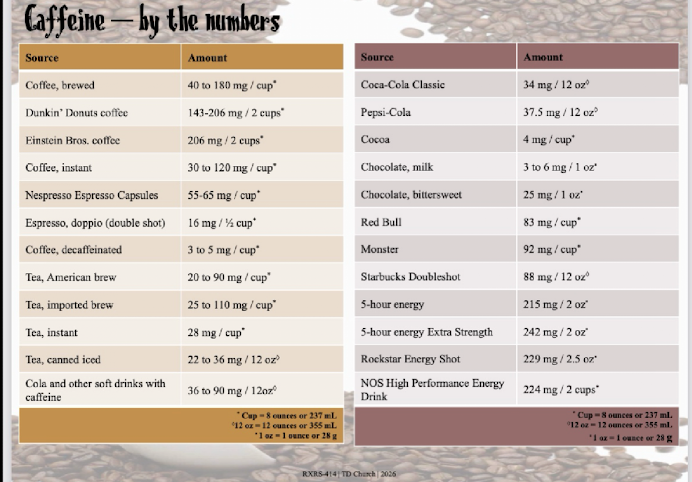
caffeine by numbers
caffeine heart effects
caffeine is a vasodillator
stimulates the heart to beat faster increasing blood flow, blood sugar, urine production and body temp
stimulates receptors within heart to beat faster by blocking enzyme phosphodiestrate
caffeines full cardiovascular profile varies
some genetically suceptible to caffeine while others are not
effects of caffeine depends on use- habitual or infrequent
individuals <18 may be more vulnerable to effects of caffeine
AMA supports ban on marketing of high caffeine beverages to anyone under 18
AAP says energy drinks never consumed by children or adolescents
benefits of caffeine on heart
◦ preemie lifesaver
‣ caffeine administered to neonates born preterm to coax their brain and lungs to keep breathing
‣ reduces apnea- pauses in preemie's breathing
‣ keeps intermitten drops in their blood oxygen levels from occuring
◦ performance enhancer
‣ caffeine= safer performance enhancer
‣ 1972 caffeine banned for athletes but removed in 2004
‣ improves cognitive function and focus
‣ significantly improves performance during cardiovascular endurance activities
caffeine kidney effects
◦ calcium oxalate stones
‣ most common type of kidney stone formed from combined crystals of calcium and oxalate
‣ typically leached from bone and caffeine increases that
‣ 2004: patients who had history of kidney stones- caffeine increased urinary calcium levels, modest increase in risk of developing kidney stones after caffeine consumption
‣ taurine also increases
◦ diuretic
‣ produce more urine
‣ output 3 cups for each 1 cup u drink
◦ fluid balance
‣ although large doses of caffeine taken in short periods of time can stimulate urine output
‣ people quickly develop tolerance to effects on caffeine
‣ diminishing diuretic effect among users
‣ have to make sure fluids balanced in body
‣ caffeine doses found in standard serving of caffeinated beverages not detrimental to fluid balance in the body
caffeine- mineral absorption and kidneys
heavy caffeine users have difficulty getting enough minerals in diet
prevents iron absoprtion in stomach
kidneys cannot retain
calcium, zinc, magnesium
minerals are vital for good health but from a digestive standpoint any interference with magnesium absorption is worrying
magneisum needed for bowel regularity
modern diets leave many of us deficient in magnesium
caffeine- digestive system effects
caffeine stimualtes stomach acid production
caffeine does not cause ulcers
but ppl with ulcers should avoid caffeine
ulcers: open sores that occasionally develop in stomach lining, esophagus, small intestine
GERD
caffeine alone does not lead to gerd but can worsen it
coffee post meal can aid in the digestive process and for adults is generally good for your overall digestion
caffeine is diuretic and stimulates muscles in digestive track making them contract
caution: bc coffee is diureti can lead to harder stool
constipation
caffeine- brain effects
◦ caffeine can invigorate some individuals
‣ in doses up to 2 oz- 0.5 shot glass studies suggest caffeine
• enhances attention
• improves reaction time and vigilance
‣ these studies concluded - individuals are able to stick with lengthy, boring or tedious tasks
‣ impact on problem solving and decision making not conclusive
◦ caffeine can help ease migraine and tension headaches by constricting swollen blood vessels in brain
‣ OTC excedrin migraine with caffeine boosts effectiveness of medication by 40%
‣ caffeinated painkillers get overused- individual can experience rebound headaches from stopping meds
‣ caution- if you have habitual caffeine habit, quitting cold turkey will lead to massive headaches due to caffeine withdrawal
caffeine- respiratory system effects
◦ increases heartbeat and quickens breathing rate delivering more blood and oxygen to the body
‣ increase in blood and oxygen that helps provide the feeling of a boost of energy
◦ acts as bronchodilator
‣ substance that dilates opens up- breathing passages by relaxing the bronchial smooth muscle
‣ 2 effects creates less resistance in airways, which in turn increase airflow to and fro lungs
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
general term for condition that causes difficulty breathing- asthma bronchitis
coffee increasing breathing rate, too much stress on heart and lungs for ppl who alr cannot breath properly
caffeine may negatively interact with medications being used to treat copd
caffeine- reproductive effects
◦ effects of caffeine on fertility have been ongoing debates
◦ excessive caffeine intake- associated with adverse effects on sperm
◦ no consistent evidence, linking moderate consumption of caffeine to reduced sperm quantity, quality, or motility
• women who drink more than 4 cups of coffee a day reduce their ability to conceive by about 26%
pregnant women should restrict or abstain from caffeine to avert withdrawal symptoms like headaches, irritability, restlessness and nausea
research conducted by kaiser permanente concluded that drinking more than 2 cups of coffee increases miscarraige by 5%
caffeine crosses placenta and disrupts fetal development
caffeine- eye effects
◦ caffeine causes blood vessels in eyes to constrict- become narrow
‣ decreasing flow of oxygen and nutrients to cells within the eyes
‣ decreasing the clearing of waste products from the eyes
◦ dry eye syndrome
‣ medical condition in which body does not make enough tears or have consistency to keep eyes moist- cry more?
caffeine- stress and panic attacks
◦ caffeine= catalyst for full blown panic attack
◦ typically occurs in people who have slight genetic variation in adenosine receptors
‣ can elevate cortisol levels in the body
• high amounts can lead to negative health effects associated with prolonged elevated levels of cortisol
‣ cortisol responsible for
• glucose metabolism, regulation blood pressure, insulin release for blood sugar, immune function, inflammatory response
caffeine- bone health
slightly reduces the body’s ability to absorb calcium
caffeine and phosphorus in colas (carbonated only) have been linked to bone loss
if healthy no evidence that says consuming up to 1.5 cups of caffeine will harm their bones
no studies have shown significant fracture or heightened risk of osteoporosis (decrease in density of bone) among health adults with adequate calcium intake
caffeine- toxicity
overall caffeine for healthy person is safe if consumed in moderation
main side effects- gastric upset, nervousness, jitteriness
as individuals age, they tend to have more problems related to sleep
pills containing caffeine
result in severe side effects for individuals who laod up on them to stay awake- procrastinating students and long distance drivers
individuals who have concomitant conditions (obesity, hypertension) are more vulnerable to heart related problems from caffeine
caffeine- human consumption
historically coffee, tea chocolate were caffeine
energy drinks, pain relievers, diet pills more recent
tea= 4th centure ce china
preferred beverage of europe in 16th century ce
coffee= 6th century ce yemen
strong relatioship with us in founding of nation
due to unfair taxation of tea via british stamp act 1765 ce and trade revenue act 1767 ce
boston tea party
chocolate= 4th century bce yucatan
before tea and coffee was available
was not popular until 18oos when dutch confectioners refined cacao into chocolate
how coffee came to be
ethiopian legend- 1671 ce
goat herder kaffa saw goats eating caffeinated red berries dancing
he tried and thought divine effects
went to wife and said to share heaven sent cherries w monks
monks said devils work and threw cherries on fire but roasting bean smell was good- berries scooped out of fire crushed covered in hot water, monks loved- used for spiritual practice
yemen legend 650ce
monk could not focus and read koran bc kept falling asleep
discovered cherries that gave him energy to finish
went to monastery and becae devoted monk and grew berries around religious center
used during prayers
history of coffee today
coffee slowly introduced in europe in 1600 by cofeehouses
salon style intellectual convo
england outlawed for 10-15 years then was back
environment of early coffeehouses turned to be one that gave rise to creative thinking and entrepreunial legal business realms
coffee in the us
coffee may be more expensive bc coffee species risk of extinction

tea
◦ aromatic beverage commonly prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over leaves, fruits, flowers
◦ most commonly cured leaves of camellia sinesis
◦ used for medicine
tea originated in 2737 bce
highly disliked emperor shen nung of china was deposed of power and exiled to an isolated corner of southern china
having no money shen nung sat under tree when gust of wine and wayward leaves into his cup of boiling water
blend was so relaxing he drank tea for next 7 years and would only drink tea
tea cultures
◦ tea ceremonies
‣ ritualized form of making practiced in asian cultures by chinese, korean, japanese, indian, vietanemse, taiwanesse
• chado
◦ japanese tea ceremony
◦ formalized
◦ way of tea
◦ ritualized process
• afternoon tea
◦ british
◦ light meal eaten between 3:30-5pm
◦ light and chill
• turkish tea
◦ conversation tea
◦ offered in small tulip shaped glass held by rim
◦ social gathering of men
• chai wallah
◦ person in india who makes/sells tea
• sweet tea
◦ southeastern us
◦ heavily sugared iced tea
• egyptian mint tea
◦ creating and maintaining connections with friends and fam then quality of tea
◦ alleviate pressure of heat
• us= more coffee but rest= more tea
cacao
◦ theobroma cacao
◦ source of original natural chocolate
◦ evergreen cacao tree us native to meso america
◦ from seeds of fruit of cacao tree
◦ for 4k years consumed as bitter bev
◦ used as food, medicine, currency as olmex, aztec, zapotec, maya civilization
◦ integral to mayan creation myth
‣ kukulcan gave to gods after ceating humans
‣ restricted to elites
xocoatl
◦ mayan word for chocolate
◦ soanish conquistadores and missionaries transcribed as chocolate- bitter water
◦ may have been bitter water but held in high esteem maya modify word to food of the gods
brief history of cacao


chocolatiers and the world of imagination
75 years major chocolate houses came into existence
1765 ce irish chocolatiers introduced chocolate to the us and by 1780 ce bakers chocolate factory opened
iin 1852 ce ghiradelli begins production in sf
1866 ce nestle was founded by 2 illinois brothers in cham switzerland
1884 hershey
1926 belgian- godiva
energy drinks
◦ consumption of caffeinated sodas has increased in the us
‣ concentration of caffeine per ounce in sodas much lower than coffee or tea
‣ serving size of soda is 12-24 oz which is double or quadruple that of coffee or tea
‣ diet drinks tend to contain the same or more amount of caffeine than their regular counterparts
‣ bit of misnomer
‣ beverages do not produce more energy but generate a feeling of alertness and very distinct buzz due to their caffeine content
‣ concentration is often 2 or 3 times as higher as other caffeinated drinks
‣ serving sizes are generally much smaller
north america is major consumer
target 18-35 year olds
blackout in a can
4 loko- alc and energy
stimulants and caffeine get you drunk faster but you do not feel it because the alcohol masks it
yerba mate
stimulant equivalent to caffeine in coffee
missionaries associated with idolatry - elixir of sorcerers
beverage of natives seen as offensive
mate became transformed into beneficial paraguay tea
620 ce consumption reached high levels even when prohibited
guarana
found in southern tributaries of the amazon
caffeine concentration twice as much as mate, coffee, or cola by volume
did not get much negative attention bc was deep in jungle
become important with energy drinks, weight loss, brazils top export
producing caffeine with high concentration is defensive toxin
koalnut
in nigeria beleived to be first tree on earth
caffeine rich nut that is native to tropical africa
symbol of hospitality and kindness
tasteless on own but synergic with caffeine
oldest forms used for natural remedy for chest colds and weightloss
increases bodys metabolic rate by 118% and can burn calories