Factors affecting rate of photosynthesis
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Light Intensity
CO2 concentration
Temperature
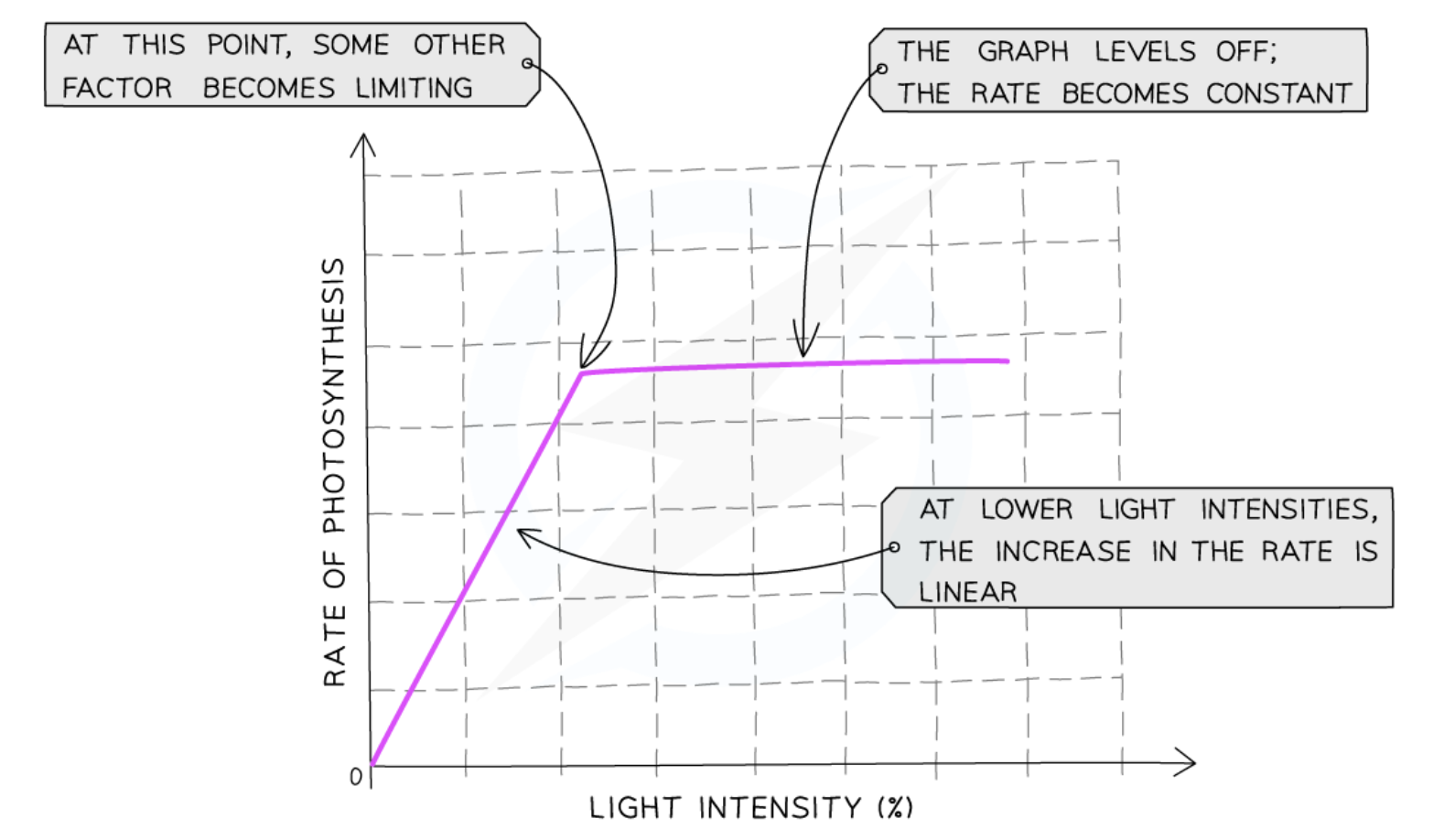
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis
Light needed as an energy source. As light intensity increases, ATP & red.NADP produced at higher rate (faster LDS occurs)
More ATP & red.NADP produced so Calvin Cycle occurs faster
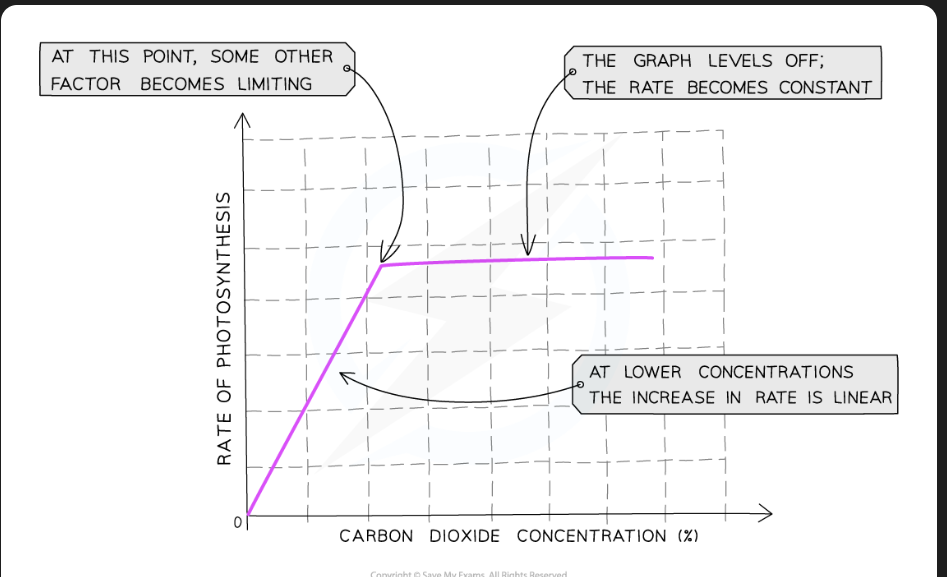
How does CO2 concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis
Increasing CO2 conc. increases rate of carbon fixation in Calvin Cycle, and rate of TP production
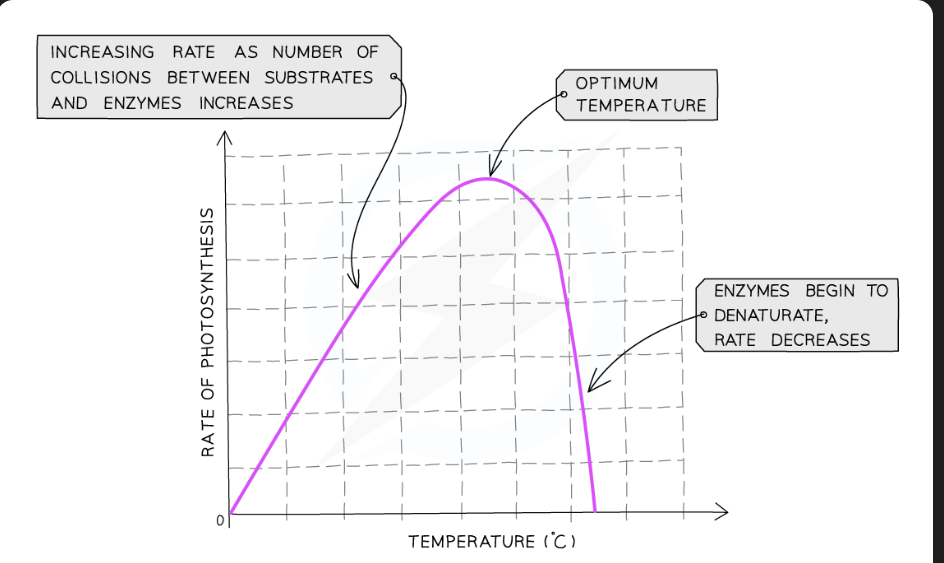
How does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis
As temp increases, rate of enzyme-controlled reactions in photosynthesis increases, until protein denatures, then decreases
E.g. carbon fixation (RuBisCo)
NOTE: Photorespiration increases above 25 degrees - higher photosynthetic rates may not be seen at higher temps even if enzymes still functioning
Implications of water stress on rate of photosynthesis
Stomata close to avoid water loss by transpiration during water stress e.g. during drought, when too hot
Stops CO2 diffusing in, reduces rate of LIR, eventually stops photosynthesis
LDS relies on H+ gradient forming across thylakoid membrane
Membrane permeability can change w. temperature
May lead to dissipation of H+ gradient, photosynthesis slows
Why is water not considered a limiting factor?
If water potential low enough to limit photosynthesis rate, plant will have closed stomata & stopped photosynthesis
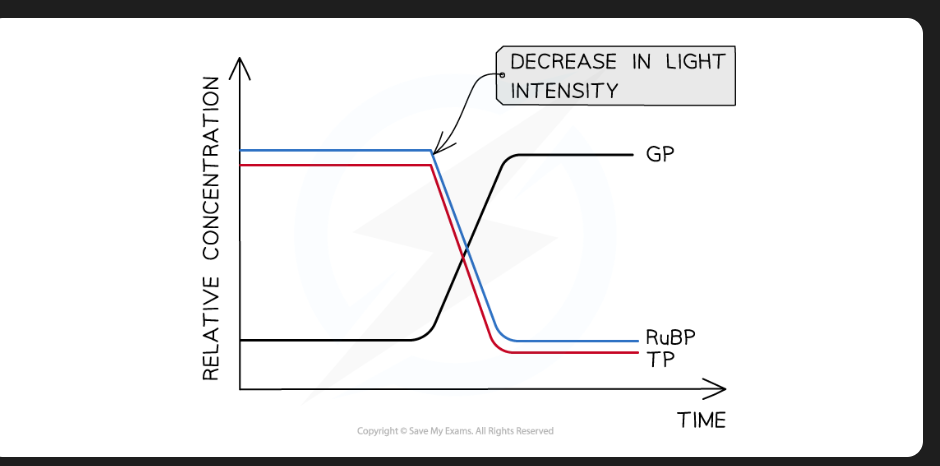
Effect of reduced light intensity on Calvin Cycle
Reduces rate of light-dependent stage
Reduced ATP & red.NADP quantity
Needed to convert GP to TP
Conc. of GP increases (slight), conc. of TP decrease
Less TP to regenerate RuBP = conc. of RuBP decreased
Over time, CO2 fix. stops, conc. of GP plateaus
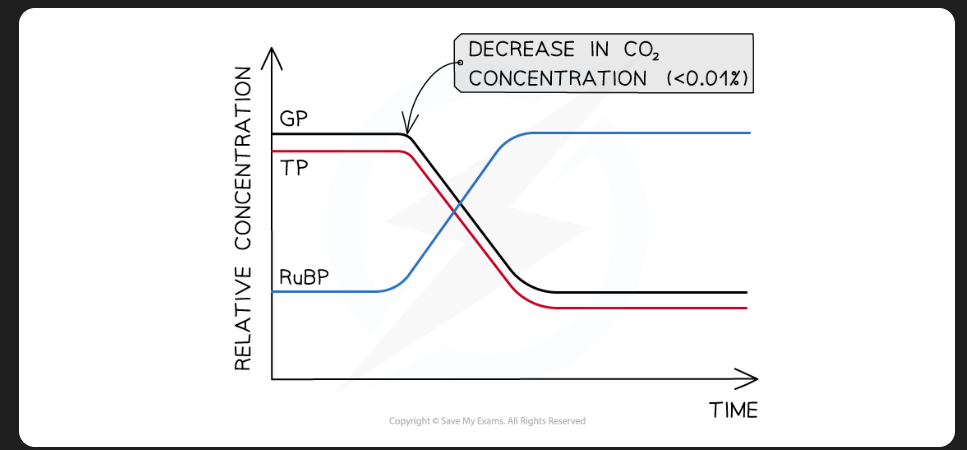
Effect of CO2 conc. on Calvin Cycle
Low conc. of CO2 = reduced GP conc. (less C to fix), & less TP
RuBP conc. increase as is still formed from TP but isn’t being used to fix CO2
RuBP unfixed & builds up
Effect of Temperature on Calvin Cycle
At low temps or too high temps, rate is reduced, as light independent reactions are enzyme-controlled (RuBisCo)
Enzyme & substrates have less KE
Fewer successful collisions, reduced rate of reaction
Lower conc. of GP, TP, & RuBP
NOTE: As long there’s enough light to produce ATP + red.NADP, increasing temp to optimum, increases rate of LIR & so photosynthesis rate